Analysis on split-head cracking of Y1Cr13 stainless rolled bar
-
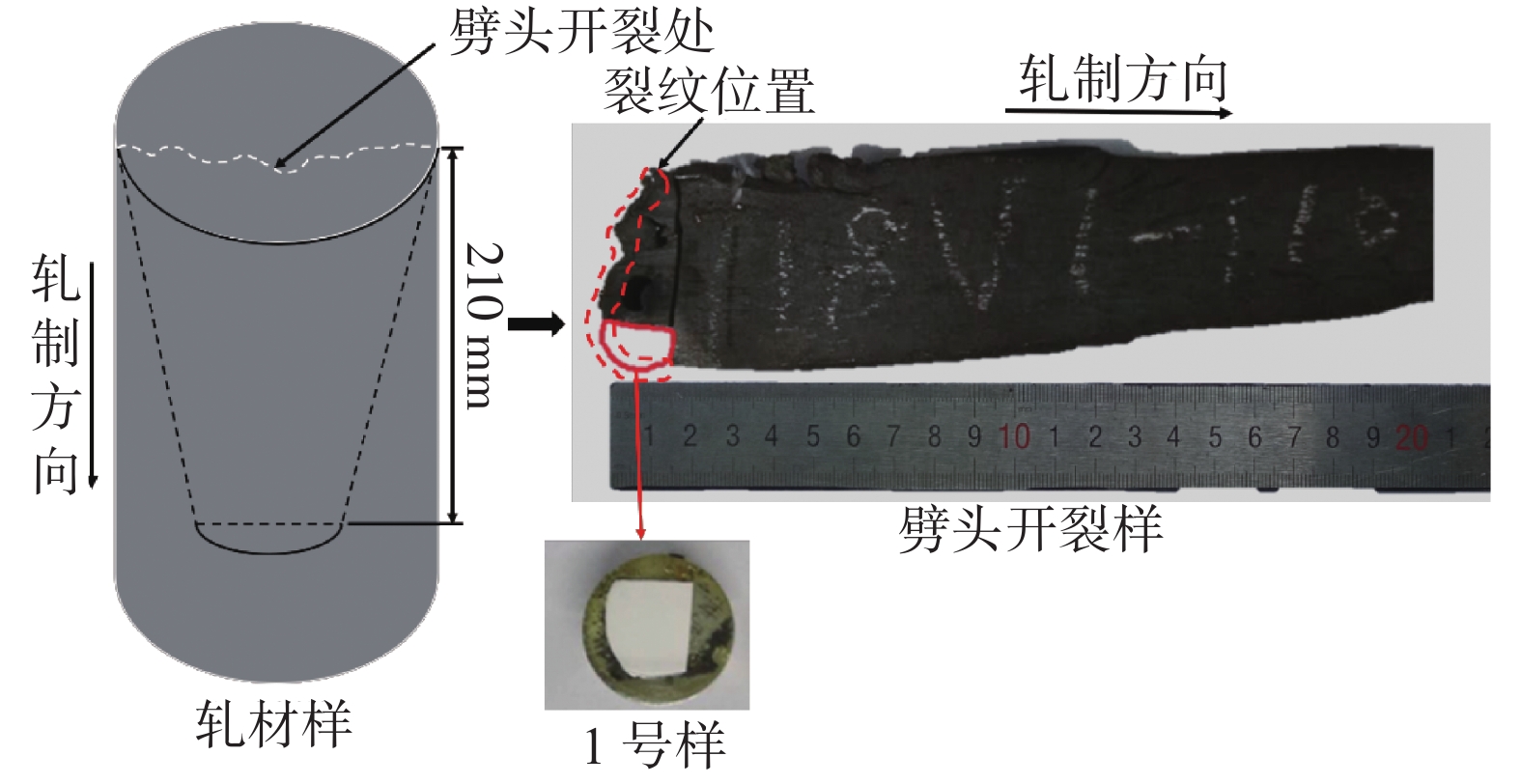
摘要: 针对某厂生产的Y1Cr13不锈钢在轧制过程产生劈头开裂的问题,采用金相显微镜、扫描电子显微镜、小样电解等分析检测方法,从夹杂物微观形貌角度对钢劈头开裂样中硫化物的微观形貌特征进行了表征分析,并探究了Y1Cr13不锈钢轧制时劈头开裂形成的原因。结果表明:该不锈钢轧材存在大量长条状硫化物,硫化物长宽比较大,长宽比分布在3以内的夹杂物占比为65.4%,长宽比大于3的夹杂物占比为34.6%,硫化物的国标评级为:粗系4.5级,细系5.5级,德标评级为3-3级;钢中过多的热脆细长条状硫化锰和锰铁硫化物是劈头开裂的主要原因。采用镁、碲等新工艺可对硫化物形态进行改质,将其控制为球形或纺锤形,并提高硫化物硬度,轧制时不易变形;通过适当减少钢中的[S]含量以及提高钢中Mn/S等措施可减少钢中的(Mn,Fe)硫化物。Abstract: In order to find out the causes of split-head cracking of Y1Cr13 stainless steel in the rolling process, the splitting samples of steel were analyzed and characterized from the view of inclusions microstructure with a metallographic microscope, a scanning electron microscope and the method of electrolytic etching. Also, the causes of split-head crackingof Y1Cr13 stainless steel during the rolling process were explored. The results show that there exist a lot of long strip sulfides in rolled steel, and the ratio of length/width of sulfides is large. The proportion of the inclusions with length/width ratio below 3 is 65.4%. The proportion of the inclusions with length/width ratio above 3 is 34.6%. The standard ratings of sulfides are 4.5 for coarse series, 5.5 for fine series, and 3-3 for German standard. A large number of long strip hot shortness manganese sulfides and ferromanganese sulfides are the main causes of split-head cracking of Y1Cr13 rolled bar. Such as magnesium and tellurium can be used to modify the form of sulfide into a spherical or spindle shape, and increase the hardness of the sulfide, making it difficult to deform during rolling. The (Mn, Fe) sulfide in steel can be reduced by properly reducing [S] content and increasing Mn/S in steel.
-
Key words:
- Y1Cr13 stainless steel /
- split-head /
- cracking /
- manganesesulfide /
- ferromanganesesulfide
-
表 1 试验钢的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of experimental steels
% 厂家 C Si Mn P S Cr Mo Ni A 0.13 0.54 1.15 0.027 0.31 12.89 0.04 B 0.122 0.229 0.957 0.026 0.350 12.300 0.105 C 0.120 0.430 1.160 0.018 0.270 12.790 0.260 表 2 三个厂硫化物评级对比
Table 2. Comparison of inclusions rating of samples provided by three plants
厂家 国标评级(GBT 10516—2005) 德标评级 A 粗系4.5级,细系5.5级 3-3级 B 粗系3.0级,细系5.5级 2-3级 C 粗系1.5级,细系5.5级 2-2级 -
[1] Zhang Yu. Analysis on the causes of rolling cracking of Y1Cr13[J]. Special Steel Technology, 2013,(3):17−19. (张宇. Y1Cr13轧制开裂原因浅析[J]. 特钢技术, 2013,(3):17−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0971.2013.03.005 [2] Fan Zhijin, Cheng Xiufeng. Crack analysis and process optimization of high sulfur stainless steel SUSY1Cr13 in hot working[J]. Special Steel, 1996,(5):42−44. (范植金, 程秀峰. 高硫不锈钢SUSY1Cr13热加工裂纹分析及其工艺优化[J]. 特殊钢, 1996,(5):42−44. [3] Ma Baoguo, Xu Songqian, Zhao Suwu, et al. Research on splitting head of BT303CuS free-cutting stainless steel rolling stock[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2010,31(3):381−384. (马宝国, 徐松乾, 赵肃武, 等. BT303CuS易切削不锈钢轧件劈头的研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2010,31(3):381−384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2010.03.020 [4] Wang Weining. Analysis of cracking causes of Y1Cr13 steel[J]. Special Steel Technology, 2010,16(4):23−26. (王维宁. Y1Cr13钢开裂原因浅析[J]. 特钢技术, 2010,16(4):23−26. [5] Hao Shifeng, You Xiaodong, He Ning. Analysis and process improvement of M7 steel rolling split[J]. Hebei Metallurgy, 2015,(8):61−63. (郝世风, 尤晓东, 何宁. M7钢轧制劈头分析及工艺改进[J]. 河北冶金, 2015,(8):61−63. [6] Zhang D, Shen P, Xie J B, et al. A method for observing tridimensional morphology of sulfides by non-aqueous solution electrolytic etching[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2019,26(3):275−284. doi: 10.1007/s42243-018-0142-z [7] Deng Xiangyang, Li Jian, Xie Jianbo, et al. Comparative analysis of steel quality for C70S6 expanding connecting rod at home and abroad[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018,39(1):148−154. (邓向阳, 李健, 谢剑波, 等. 国内外C70S6胀断连杆用钢质量对比分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2018,39(1):148−154. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2018.01.026 [8] Chen Yu, Liu Hongliang, Zheng Zhong, et al. Development of QStE series automotive structural steel products of bengang[J]. Science and Technology and Enterprise, 2014,10:299. (陈宇, 刘宏亮, 郑中, 等. 本钢QStE系列汽车结构用钢产品的开发[J]. 科技与企业, 2014,10:299. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9207.2014.17.277 [9] Yang Wen, Yang Xiaogang, Zhang Lifeng, et al. Review of MnS inclusion control in steel[J]. Steelmaking, 2013,29(6):71−78. (杨文, 杨小刚, 张立峰, 等. 钢中MnS夹杂物控制综述[J]. 炼钢, 2013,29(6):71−78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1043.2013.06.017 [10] Zou Changfei, Yang Jieming, Wei Xianyi, et al. Microstructure characteristics of point segregation zone in 25CrMo ingot Steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2017,52(3):21−26. (邹长飞, 杨接明, 韦贤毅, 等. 25CrMo钢锭点状偏析区微观组织特点[J]. 钢铁, 2017,52(3):21−26. [11] Ma Yue, Pan Tao, Jiang Bo, et al. Study on the effect of S content on fracture toughness of high speed wheel steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2011,47(8):978−983. (马跃, 潘涛, 江波, 等. S含量对高速车轮钢断裂韧性影响的研究[J]. 金属学报, 2011,47(8):978−983. [12] Liu Yangbo, Tong Qian, Sun Qisong, et al. Effect of notch, short crack and inclusion on fatigue strength of high strength steel[J]. Shanghai Metal, 2017,39(4):69−74. (柳洋波, 佟倩, 孙齐松, 等. 缺口、短裂纹以及夹杂物对高强钢疲劳强度的影响[J]. 上海金属, 2017,39(4):69−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2017.04.014 [13] Li Hongsheng, Gao Hui. The form of manganese sulfide in steel and its effect on steel properties[J]. Yizhong Technology, 2004,(4):26−28. (李洪生, 高辉. 钢中硫化锰的形态及对钢性能的影响[J]. 一重技术, 2004,(4):26−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3355.2004.04.011 [14] Koseki T. Inclusion assisted microstructure control in C-Mn and low alloy steel welds[J]. Metals Science Technology, 2005,21(8):867−879. doi: 10.1179/174328405X51703 [15] Liu Z. Nucleation of acicular ferrite on sulfide inclusion during rapid solidification of low carbon steel[J]. CAMP-ISIJ, 2006,19(4):743. [16] Ai Kenan, Xie Jianbo, Zeng Zhiqi, et al. Effect of magnesium on microstructure and sulfide in non-quenched and tempered steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2019,31(4):361−367. (艾克南, 谢剑波, 曾志崎, 等. 镁对非调质钢中组织及硫化物的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2019,31(4):361−367. [17] Shen P, Yang QK, Zhang D, et al. The effect of tellurium on the formation of MnTe-MnS composite inclusions in non-quenched and tempered steel[J]. Metals, 2018,8(8):639−652. doi: 10.3390/met8080639 -





 下载:
下载: