Evolution of mineral facies in magnetic field enhanced reduction of Bayan Obo ore
-
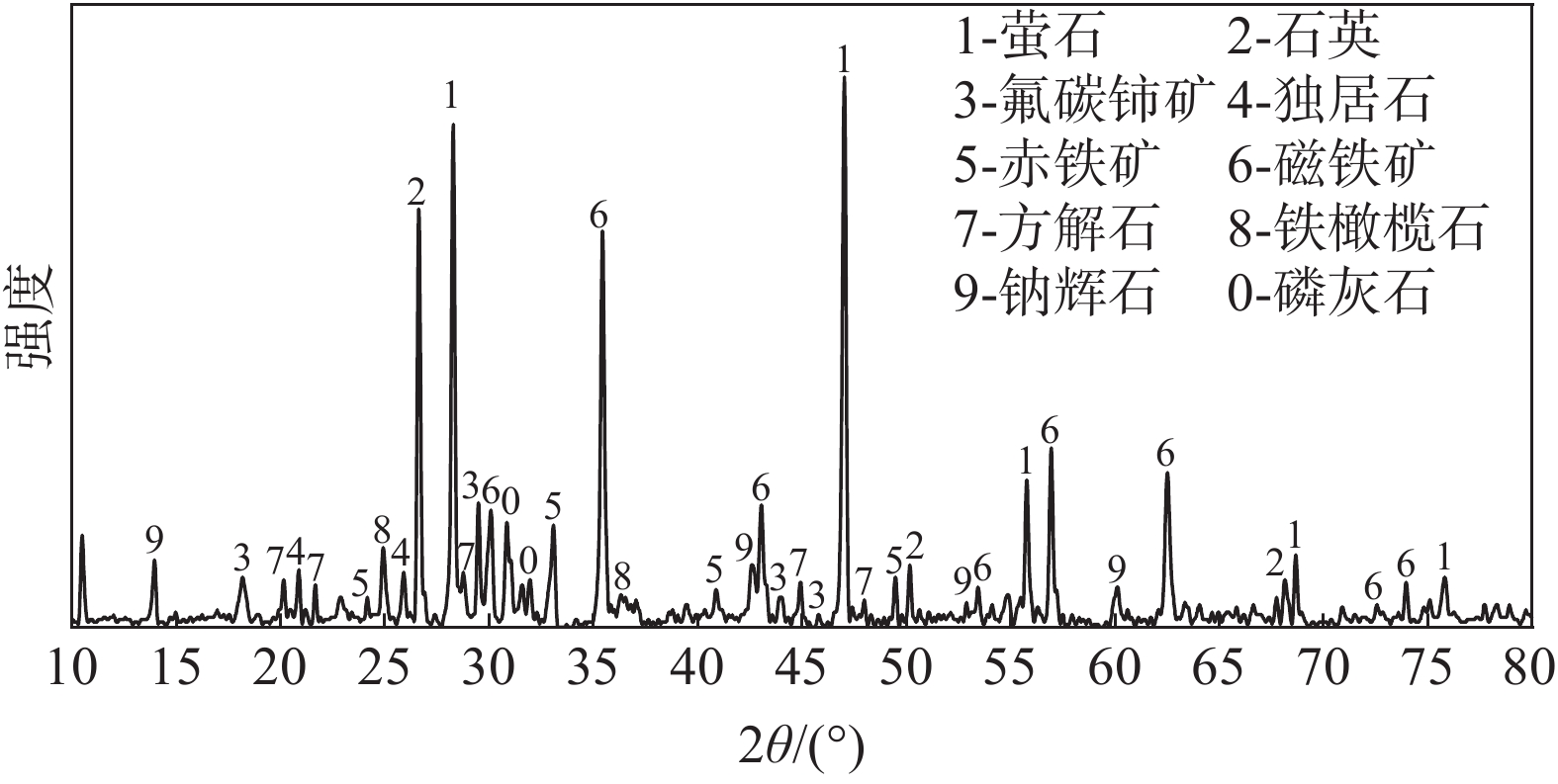
摘要: 以低温直接还原工艺为基础,在1 223 K,B=1.02 T条件下,对白云鄂博含碳球团进行磁场强化还原试验,通过考察铁矿物的还原效率和稀土矿物的矿相演变规律,来研究磁场对白云鄂博矿中铁氧化物还原以及稀土相转变的作用。结果表明:磁场可以促进铁氧化物的还原,还原进行到60 min时,试样金属化率可以达到90.23%,与无磁条件相比,金属化率增加了52.82个百分点;磁场加快了氟碳铈矿以及独居石的分解,同时可以促进CaO·2RE2O3·3SiO2和RE2O3·2SiO2的生成。Abstract: Based on the low-temperature direct reduction process, the magnetic field enhanced reduction experiment of Bayan Obo carbon bearing pellets was carried out at 1 223 K, B = 1.02 T. The effect of magnetic field on iron oxide reduction and rare earth phase transformation of Bayan Obo ore was studied by investigating the reduction efficiency of iron minerals and the ore phase evolution of rare earth minerals. The results show that the magnetic field can promote the reduction of iron oxide, and the metallization rate of the sample can reach 90.23% after 60 min reduction, increased by 52.82% compared with that under the non-magnetic condition. The magnetic field can accelerate the decomposition of bastnaesite and monazite, and promote the formation of CaO·2RE2O3·3SiO2 and RE2O3·2SiO2 (RE = rare earth elements).
-
表 1 白云鄂博原矿主要化学成分
Table 1. Main composition of raw ore in Bayan Obo
% TFe FeO SiO2 P2O5 S F 37.17 12.17 16.30 1.48 0.86 8.42 Na2O CaO Al2O3 TiO2 BaO Fe2O3 0.35 14.22 0.28 1.02 2.90 39.58 Nb2O5 ThO2 RE2O3 MgO 0.31 0.038 5.84 0.94 表 2 焦炭粉成分
Table 2. Composition of coke powder
% 固定碳 灰分 挥发分 硫 80.32 8.92 10.5 0.26 表 3 还原后物料的铁相组成
Table 3. Iron phase composition of reduced materials
时间/ min 磁场条件 常规条件 主相 副相 主相 副相 0 Fe2O3、Fe3O4 Fe2O3、Fe3O4 5 Fe2O3、Fe3O4 FeO Fe2O3、Fe3O4 20 FeO Fe FeO Fe3O4 45 Fe FeO Fe 60 Fe FeO Fe 表 4 扫描电镜图片中各点能谱分析结果
Table 4. Energy spectrum analysis results of dots in the scanning electron microscope images
% 序号 Fe C O Ca Si F 1 56.60 6.04 33.57 0.17 0.24 0 2 86.48 6.02 2.89 0.46 0.30 0 3 0 0 0 37.47 0 62.53 4 3.34 81.79 10.58 0.53 0 0 5 61.31 0 36.85 0 0 0 6 14.39 30.70 29.10 8.15 11.80 0 7 0 0 0 38.83 0 60.59 8 0 83.12 12.15 3.14 0 0 表 5 不同还原时间内产物中稀土相的组成
Table 5. Composition of rare earth phase in the product with different reduction time
时间/min 常规条件 磁场条件 0 RECO3F、REPO4、CaF2、SiO2、CaCO3 RECO3F、REPO4、CaF2、SiO2、CaCO3 5 RECO3F、REPO4、REOF 、CaO·2RE2O3·3SiO2、CaF2、SiO2、Ca3(PO4)2、Ca2SiO4 RECO3F、REPO4、REOF 、CaO·2RE2O3·3SiO2、CaF2、SiO2、Ca3(PO4)2、Ca2SiO4 20 RECO3F、REPO4、REOF 、CaO·2RE2O3·3SiO2、CaF2、SiO2、Ca3(PO4)2、Ca2SiO4 CaO·2RE2O3·3SiO2、CaF2、Ca3(PO4)2、Ca2SiO4 45 RECO3F、CaO·2RE2O3·3SiO2 、CaF2 、Ca2SiO4、Ca3(PO4)2 CaO·2RE2O3·3SiO2 、RE2O3·2SiO2、CaF2 、Ca2SiO4、Ca3(PO4)2 60 CaO·2RE2O3·3SiO2 、RE2O3·2SiO2、CaF2 、Ca2SiO4、Ca3(PO4)2 CaO·2RE2O3·3SiO2 、RE2O3·2SiO2、CaF2 、Ca2SiO4、Ca3(PO4)2 -
[1] Cheng Jianzhong, Che Liping. Current situation and development trend of rare earth resources exploitation in China[J]. Rare Earth, 2010,31(2):65−69,85. (程建忠, 车丽萍. 中国稀土资源开采现状及发展趋势[J]. 稀土, 2010,31(2):65−69,85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2010.02.015 [2] Yu Yongfu. Research on comprehensive utilization of rare earth and niobium resources in Baiyunebo mine is of great significance[J]. Rare Earth Information, 2007,(8):8−9. (余永富. 白云鄂博矿稀土、铌资源综合利用研究意义重大[J]. 稀土信息, 2007,(8):8−9. [3] Yang Xueming, Zheng Yongfei, Yang Xiaoyong, et al. A geochemical study of an ree-rich carbonatite dyke at bayan obo, inner mongolia, northern China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 2000,74(3):605−612. [4] Yasuo Kanazawa, Masaharu Kamitani. Rare earth minerals and resources in the world[J]. J Alloys Compd, 2005,408:1339−1343. [5] Yang He, Rong Yi, Xue Xiangxin, et al. Study on direct reduction of iron recovered from Baotou rare earth tailings[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Earth, 2012,30(4):470−475. (杨合, 荣宜, 薛向欣, 等. 包头稀土尾矿回收铁的直接还原研究[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2012,30(4):470−475. [6] Li Xiangdong, Lei Shutao, Li Shusheng, et al. Study on roasting process of mixed sulfuric acid of Sichuan ore and Baotou ore[J]. Rare Earth, 2015,36(5):119−122. (李向东, 雷树涛, 李树胜, 等. 四川矿和包头矿混合硫酸焙烧工艺研究[J]. 稀土, 2015,36(5):119−122. [7] World Steel Assoeiation. Steel statistieal yearbook 2009[M]. Brussels: World Committee on Economic Studies, 2010. [8] Boscolo, Padoano, Tommasi. Identification of possible dioxin emission reduction strategies in pre-existing iron ore sinter plants[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2008,35(2):146−152. [9] (陈津, 林万明, 赵 晶, 等. 非焦煤冶金技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007.)Chen Jin, Lin Wanming, Zhao Jing, et al. Metallurgical technology of non coking coal[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2007. [10] Ma Wei, Ma Rongjun, Shen Dianbang. Application and mechanism of magnetic field in metallurgy[J]. Physics, 1996,25(7):430−432,444. (马伟, 马荣骏, 申殿邦. 磁场在冶金中的应用和机理探讨[J]. 物理, 1996,25(7):430−432,444. [11] (张清泉. 磁场对CO气氛下Fe3O4还原为浮氏体的化学反应影响[D]. 包头: 内蒙古科技大学, 2016.)Zhang Qingquan. Effect of magnetic field on the chemical reaction of Fe3O4 reduction to faustite in CO atmosphere[D]. Baotou: Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology, 2016. [12] (陈林. 磁场对CO气氛下Fe2O3还原为Fe3O4的影响研究[D]. 包头: 内蒙古科技大学, 2015.)Chen Lin. Effect of magnetic field on reduction of Fe2O3 to Fe3O4 in CO atmosphere[D]. Baotou: Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology, 2015. [13] (金永丽. 含铁矿物低温还原的磁场强化机制[D]. 上海: 上海大学, 2019.)Jin Yongli. Magnetic field strengthening mechanism of low temperature reduction of iron bearing minerals[D]. Shanghai : Shanghai University, 2019. [14] Jin Yongli, Han Futie, Yu Hai, et al. Effect of magnetic field on reduction of iron oxides containing SiO2 and CaO[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018,39(6):103−109. (金永丽, 韩福铁, 于海, 等. 磁场对含SiO2和CaO的铁氧化物还原的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2018,39(6):103−109. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2018.06.017 [15] Jin Yongli, Yu Hai, Zhang Jieyu, et al. Effect of magnetic field on reduction of iron oxide containing CaO[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2019,55(3):410−416. (金永丽, 于海, 张捷宇, 等. 磁场对含CaO铁氧化物还原的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2019,55(3):410−416. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2018.00492 -





 下载:
下载: