Annealing process and stacking method for reducing hardness of as rolled/forged high quality special steel
-
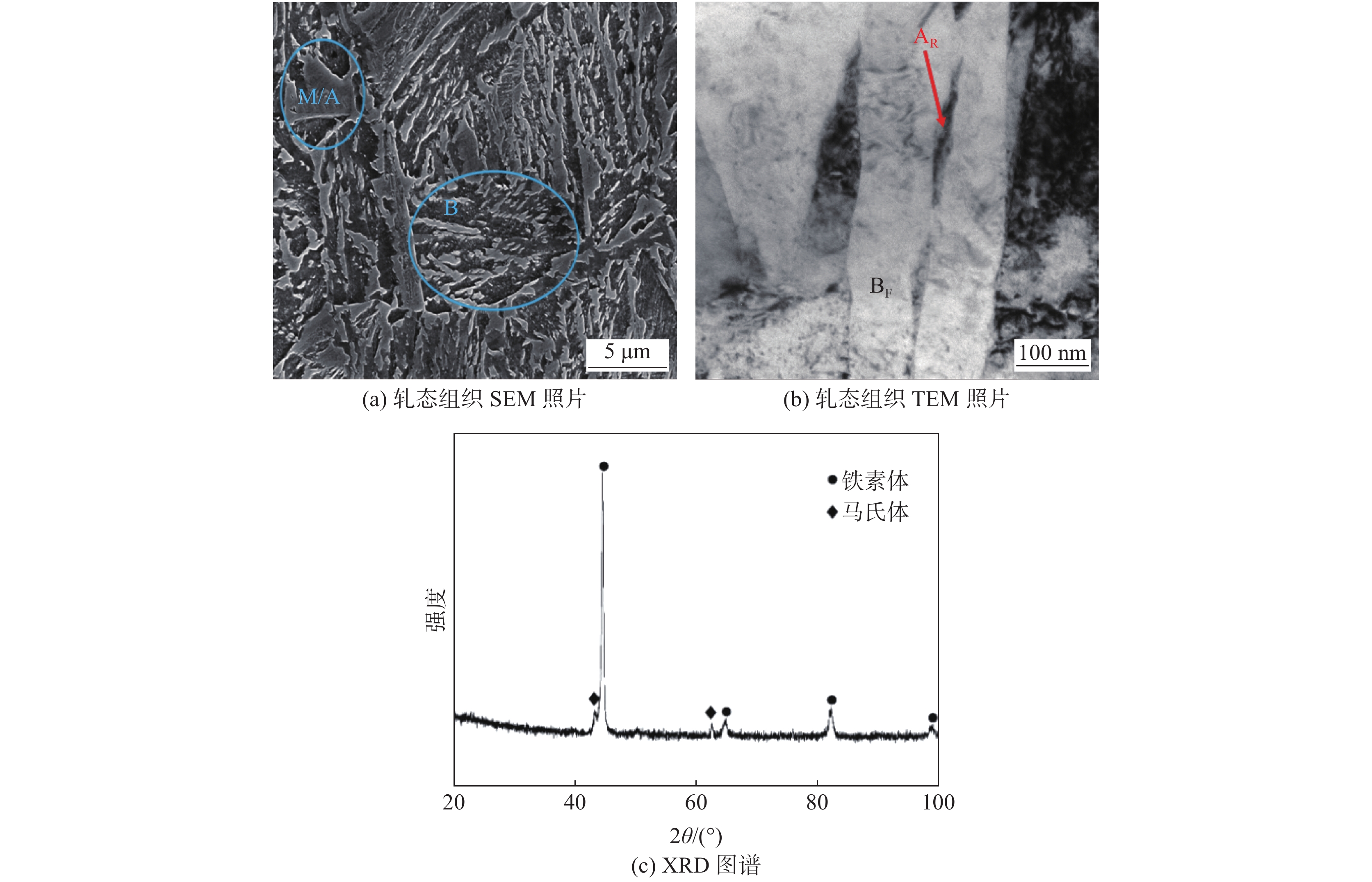
摘要: 针对高品质特殊钢(如CTHQ25、1Cr11Ni2W2MoV、30CrNi4Mo等)现有轧/锻棒料工艺退火后硬度(HB)超标(>270)、同炉硬度不均匀(270~290),退火周期长(不同直径棒料退火40~60 h不等)等难题,开展短周期退火软化工艺及设备工装设计应用研究。以轧/锻态CTHQ25钎具钢为例,基于热力学计算和试验研究,揭示了退火软化机理,设计出一步退火工艺、两步退火工艺,阐明了原始组织、退火温度、退火时间对退火组织和硬度的影响规律。结果表明,采用“低温-高温”两步退火工艺后硬度(HB)由原工艺的276降至240。同时,基于温度场-流场耦合模拟计算,设计工装垫块,将原堆垛式布料优化为平铺式布料,提高了炉温均匀性,保证了同炉产品硬度的均一性(241±4),退火工艺周期缩短20%以上。Abstract: The technical issues such as machinability, hardness uniformity and longer annealing time present for a wrought and hot-rolled special steels (e.g. CTHQ25, 1Cr11Ni2W2MoV, 30CrNi4Mo) manufactured by Pangang Jiangyou Changcheng Special Steel Co., Ltd. In order to address those issues, a a hot-rolled CTHQ25 drill steel had been used, a single-step heat-treating route was designed to soften the steel to less than HB 260 based on thermodynamic calculations of phase stability and experimental study on kinetics of phase evolution. To accelerate the annealing process, a double-step annealing, where the first step annealed at a lower temperature to promote the decomposition of retained austenite and the second step annealed at a higher temperature to accelerate microstructure coarsening, was designed and carried out to achieve a hardness of HB 240. In the meantime, special consideration was given to workpiece layout in the furnace to ensure hardness uniformity. With the coupled numerical simulation of temperature-fluid field of the furnace, the workpiece layout in the furnace was optimized with fixture topologically re-designed to achieve the maximum fuel efficiency and temperature uniformity in contrast to originally random stacks of workpieces.
-
表 1 CTHQ25钢主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of CTHQ25 steel
% C Si Mn Cr Ni Mo V Cu P S 0.23~0.26 1.30~1.50 1.30~1.50 0.35~0.55 1.75~2.00 0.50~0.65 0.15~0.25 ≤0.20 ≤0.010 ≤0.008 表 2 轧态CTHQ25钢偏析带和基体的合金元素含量
Table 2. Alloying element content in segregation area and matrix in rolled CTHQ25 steel
% 合金元素 Mn Cr Mo Si V Ni 带状偏析 1.992 0.604 0.977 1.799 0.263 2.228 基体 1.426 0.462 0.505 1.327 0.185 1.772 偏析系数 1.397 1.307 1.936 1.356 1.426 1.257 表 3 500 ℃/5 h-680 ℃/30 h退火试样带状组织和基体的合金元素含量
Table 3. Alloy element contents of the sample annealed at 500 ℃/5 h-680 ℃/30 h in segregation and matrix
% Mn Cr Mo Si V Ni 带状区域 1.563 0.623 0.507 1.570 0.243 1.970 基体 1.45 0.59 0.483 1.423 0.270 1.863 M带/M基 1.078 1.056 1.048 1.103 0.901 1.057 -
[1] Dong Xinye, Hu Ming. Brazing steel and brazing tools at home and abroad[J]. Rock Drilling Machinery & Pneumatic Tools, 2007,(1):1−5. (董鑫业, 胡铭. 国内外钎钢与钎具[J]. 凿岩机械气动工具, 2007,(1):1−5. [2] Cheng Juqiang, Liu Zhixue, Wang Yuanhui. Influence of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of new bainite drill steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2008,(5):77−79. (程巨强, 刘志学, 王元辉. 热处理工艺对新型贝氏体钎具钢组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2008,(5):77−79. [3] Yan T, Yu E, Zhao Y. Constitutive modeling for flow stress of 55SiMnMo bainite steel at hot working conditions[J]. Materials & Design, 2013,50:574−580. [4] Sun M Y, Wang X L, Wang Z Q, et al. The critical impact of intercritical deformation on variant pairing of bainite/martensite in dual-phase steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2019,771:138668. [5] Huda N, Midawi A R H, Gianetto J, et al. Influence of martensite-austenite (MA) on impact toughness of X80 line pipe steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2016,662(26):481−491. [6] LePera F S. Improved etching technique to emphasize martensite and bainite in high-strength dual-phase steel[J]. JOM, 1980,32:38−39. -





 下载:
下载: