Simulation on rolling process of vanadium-bearing spring steel 55SiCrV
-
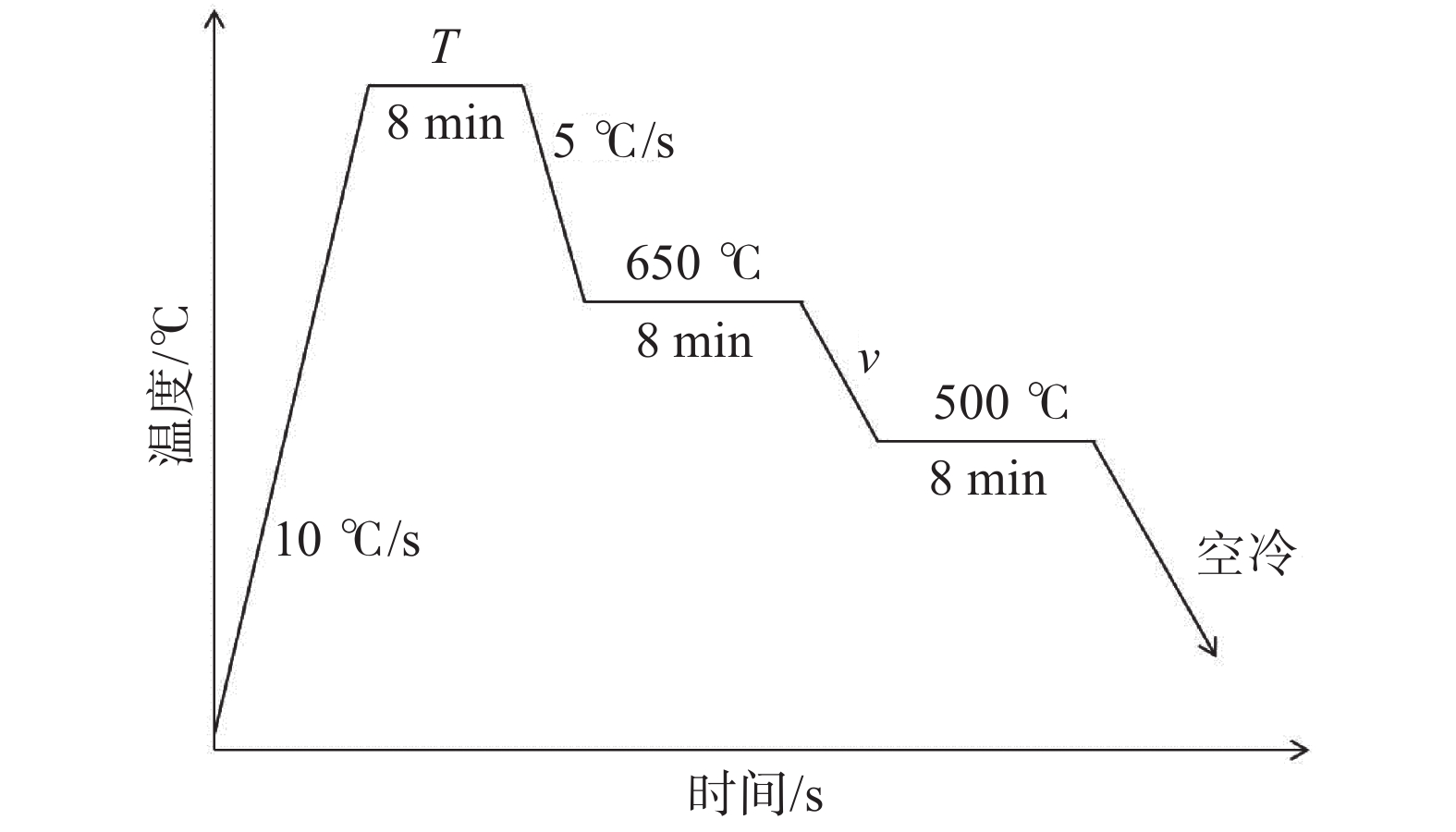
摘要: 以一种实验室冶炼的含钒弹簧钢55SiCrV为原材料,借助CCT曲线绘制、热模拟试验和金相组织观察等手段研究了55SiCrV轧制变形温度和冷却速度对其力学性能和金相组织的影响,分析确定了其合理的轧制及冷却工艺参数范围。结果表明:55SiCrV 的CCT曲线显示其马氏体生成临界冷速约3 ℃/s,马氏体生成温度Ms点约245 ℃;55SiCrV实际轧制过程中的轧制变形温度应控制低于900 ℃且冷却速度不高于5 ℃/s,这样可以避免显微组织中生成马氏体而显著恶化其疲劳性能的同时保证其获得最佳的强度和韧性匹配。Abstract: A new spring steel 55SiCrV smelted in the laboratory was used as the raw material i n this paper to investigate the effects of rolling deformation temperature and cooling speed on the mechanical properties and microstructure of 55SiCrV by means of CCT curve drawing, thermal simulation test and metallographic structure observation, and the reasonable parameters of rolling and cooling process were determined. The CCT curve of 55SiCrV shows that the critical cooling rate of martensite formation is about 3 ℃/s, and the temperature of martensite formation is about 245 ℃. The rolling deformation temperature of 55SiCrV should not be higher than 900 ℃ and the cooling rate should be lower than 5 ℃/s in the actual rolling process, which can avoid the formation of martensite in the microstructure and significantly deteriorate the fatigue performance, while ensuring the best combination of strength and toughness.
-
Key words:
- spring steel /
- 55SiCrV /
- rolling /
- deformation temperature /
- cooling rate /
- martensite
-
表 1 试样主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical conpositions of used samples
% C Si Mn P S Cr V 0.57 1.23 0.74 0.008 0.005 0.65 0.20 表 2 试验钢力学性能
Table 2. Mechanical Properties of test steel
Rp0.2/MPa Rm/MPa Z/% 616 1057 34.5 表 3 不同冷却速度的金相组织
Table 3. Microstructures of samples after cooling at different cooling rate
冷速/(℃·s−1) 金相组织 冷速/(℃·s−1) 金相组织 40 马氏体 2 珠光体+铁素体 20 马氏体 1 珠光体+铁素体 10 马氏体 0.5 珠光体+铁素体 5 马氏体+珠光体 0.2 珠光体+铁素体 表 4 控冷工艺对组织的影响
Table 4. Effect of controlled cooling process on structure
-
[1] (董瀚, 惠卫军, 时捷, 等. 汽车用合金结构钢进展[C]// 中国汽车工程学会汽车材料分会材料年会. 2004.)Dong Han, Hui Weijun, Shi Jie, et al. Progress of alloy structural steel for automobile [C]// Annual Meeting of Automotive Materials Branch of Chinese Society of Automotive Engineering. 2004. [2] Xu Dexiang, Yin Zhongda. Development status and trend of high strength spring steel[J]. Iron & Steel, 2004,(1):69−73. (徐德祥, 尹钟大. 高强度弹簧钢的发展现状和趋势[J]. 钢铁, 2004,(1):69−73. [3] (张弛, 张忠铧, 蔡海燕. 宝钢弹簧钢盘条现状与展望[C]// 线材制品国际技术研讨会. 2006.)Zhang Chi, Zhang Zhonghua, Cai Haiyan. Current situation and prospect of Baosteel spring steel wire rod [C]// International Technical Seminar on Wire Rod Products. 2006. [4] Xiao Jun. Suspension spring for vehicle and its market[J]. Metal Products, 2008,34(5):39−41. (肖军. 车用悬架弹簧及其市场[J]. 金属制品, 2008,34(5):39−41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4226.2008.05.013 [5] Hong Guohua, Yang Shunhu, Xiao Bo, et al. Production status and development prospect of spring steel at home and abroad[J]. Modern Metallurgy, 2009,37(1):1−5. (洪国华, 杨顺虎, 肖波, 等. 国内外弹簧钢的生产现状和发展前景[J]. 现代冶金, 2009,37(1):1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6068.2009.01.001 [6] Wang Chaoming, Lu Wenwei. Main factors affecting the quality of spring steel wire rod and control measures[J]. Hot Working Process, 2012,3:19−20. (王朝明, 卢文伟. 影响弹簧钢盘条质量的主要因素及控制措施[J]. 热加工工艺, 2012,3:19−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3814.2012.14.006 [7] Hui Weijun, Dong Han, Weng Yuqing, et al. Development trend of steel for automobile spiral suspension spring[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2001,13(2):67−72. (惠卫军, 董翰, 翁宇庆, 等. 汽车螺旋悬挂弹簧用钢的发展动向[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2001,13(2):67−72. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0963.2001.02.015 [8] (王桢. 悬架弹簧用SAE9259钢的组织和弹性减退特性的研究[D]. 上海: 上海大学, 2004.)Wang Zhen. Study on the microstructure and elastic degradation of SAE9259 steel for suspension spring [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University, 2004. [9] Lu Jun, Zeng Yu, Zhang Chi, et al. Research progress of steel for automotive engine valve spring[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2008,(11):5−9, 18. (卢俊, 曾渝, 张弛, 等. 汽车发动机气门弹簧用钢研究进展[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2008,(11):5−9, 18. [10] (张云祥. 高强度线材热加工的组织演变和性能预报系统研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2010.)Zhang Yunxiang. Study on the microstructure evolution and performance prediction system of high strength wire hot working [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2010. [11] (张绍菊. 热处理工艺对弹簧钢性能的影响[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2010.)Zhang Shaoju. Effect of heat treatment process on properties of spring steel [D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2010. [12] (付书红. 2 000 MPa级中碳高强度弹簧钢的疲劳破坏行为[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2005.)Fu Shuhong. Fatigue failure behavior of 2 000 MPa medium carbon high strength spring steel [D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Technology, 2005. -





 下载:
下载: