Preparation and properties of a new vanadium based anode alloy for automotive batteries
-
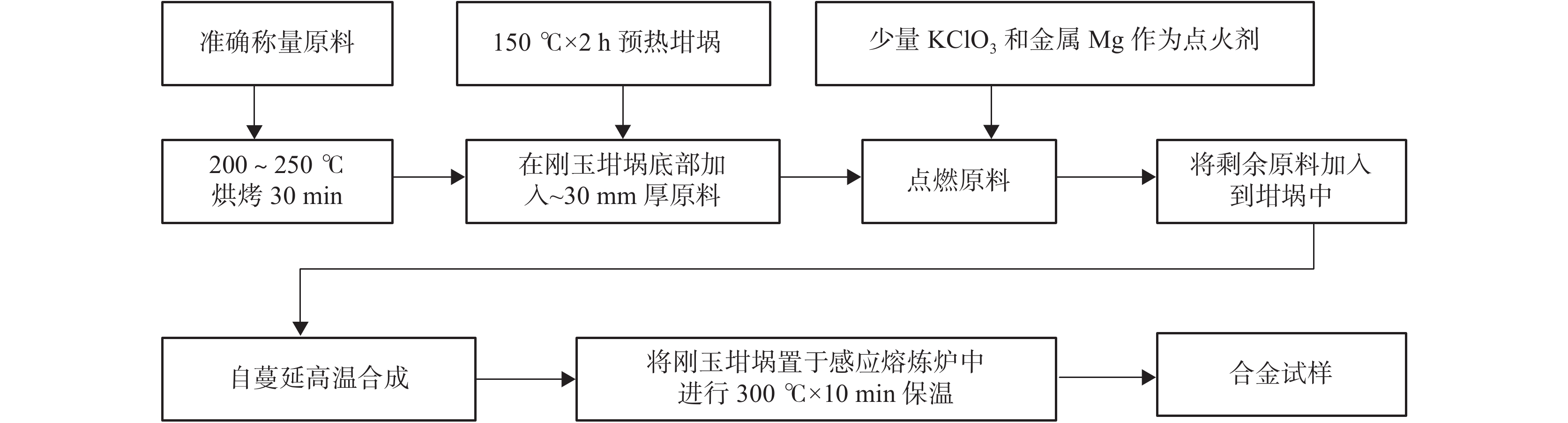
摘要: 采用自蔓延高温合成法制备了添加不同含量合金元素Al或Cr的新型钒基新能源汽车电池负极合金V65Ti20Ni15,并进行了显微组织、电化学循环稳定性和耐腐蚀性能的测试与分析。结果表明,合金元素Al或Cr,有助于改善合金内部组织,提高合金的电化学循环稳定性和耐腐蚀性能;复合添加合金元素Cr和Al的V59Ti20Ni15Al3Cr3合金的电化学循环稳定性和耐腐蚀性能最佳。与不添加合金元素的V65Ti20Ni15合金相比,复合添加合金元素Cr和Al的V59Ti20Ni15Al3Cr3合金的充放电循环50次后放电容量衰减率从85%减小到23%、腐蚀电位正移692 mV,合金的电化学循环稳定性和耐腐蚀性能得到显著提高。
-
关键词:
- 钒基汽车电池负极合金 /
- V59Ti20Ni15Al3Cr3 /
- 自蔓延高温合成 /
- 电化学循环稳定性 /
- 耐腐蚀性能
Abstract: A new vanadium based negative electrode alloy V65Ti20Ni15 for automotive batteries was prepared by self propagating high temperature synthesis (SHS) with different contents of Al or Cr. The microstructure, electrochemical cycle stability and corrosion resistance of the alloy were tested and analyzed. The results show that Al or Cr is helpful to improve the internal structure, electrochemical cycle stability and corrosion resistance of the alloy. The best electrochemical cycle stability and corrosion resistance can be obtained for V59Ti20Ni15Al3Cr3 alloy with Cr and Al added. Compared with the V65Ti20Ni15 alloy without alloying elements, the discharge capacity decay rate of V59Ti20Ni15Al3Cr3 alloy with alloying elements Cr and Al is reduced from 85% to 23% after 50 charge-discharge cycles, with the corrosion potential shifted forward by 692 mV. The electrochemical cycle stability and corrosion resistance of the alloy are significantly improved. -
表 1 合金试样化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of the alloy samples
% 合金试样 V Ti Ni Al Cr V65Ti20Ni15 65 20 15 0 0 V62Ti20Ni15Al3 62 20 15 3 0 V62Ti20Ni15Cr3 62 20 15 0 3 V59Ti20Ni15Al3Cr3 59 20 15 3 3 -
[1] Wang Haihua, Wang Xia. Effect of Ti content on electrochemical properties of MgNi hydrogen storage alloy[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018,39(4):70−73. (王海华, 王侠. 钛含量对MgNi储氢合金电化学性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2018,39(4):70−73. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2018.04.012 [2] Guo Ziyang, Shi Yong, Guo Haotian, et al. Discussion on hydrogen storage alloy[J]. Shanxi Science and Technology, 2019,34(1):129−132. (郭子杨, 石勇, 郭昊天, 等. 浅谈储氢合金[J]. 山西科技, 2019,34(1):129−132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6429.2019.01.034 [3] Zhao Xin, Xiong Wei, Wang Li, et al. Application and research progress of rare earth hydrogen storage alloys[J]. Rare Earth Information, 2016,(10):42−44. (赵鑫, 熊玮, 王利, 等. 稀土系储氢合金的应用及研究进展[J]. 稀土信息, 2016,(10):42−44. [4] Wang Li, Yan Huizhong, Wu Jianmin, et al. Research and development status of rare earth hydrogen storage alloys[J]. Rare Earth Information, 2018,(3):8−11. (王利, 闫慧忠, 吴建民, 等. 稀土储氢合金研究及发展现状[J]. 稀土信息, 2018,(3):8−11. [5] Wu Ling. Effects of solidification mode on electrochemical and hydrogen storage properties of vanadium-based alloy[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(3):67−70. (吴玲. 凝固方式对钒基储氢合金性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(3):67−70. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.03.012 [6] Wang Yanli. Effect of preparation method on the electrochemical performances of vanadium-titanium hydrogen storage alloy[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(5):60−63. (王艳丽. 制备工艺对钒钛储氢合金电化学性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(5):60−63. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.05.011 [7] Mo Junlin, Fang Lin, Cheng Chen, et al. Influence of heat treatment on the properties of vanadium-based solid solution hydrogen storage alloys[J]. Marine Electric & Electronic Technology, 2019,39(6):53−56. (莫俊林, 方林, 程臣, 等. 热处理对钒基固溶体储氢合金的性能影响[J]. 船电技术, 2019,39(6):53−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4862.2019.06.016 [8] Dai Xu, Wu Chaoling, Wang Qian, et al. Relationships between micro-strains and hydrogen storage characteristics of V60Ti25Cr3Fe12 alloy refined by ball milling[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2018,49(8):8155−8160. (代旭, 吴朝玲, 王倩, 等. 球磨法超细化的V60Ti25Cr3Fe12合金微观应变与吸放氢性能的关系[J]. 功能材料, 2018,49(8):8155−8160. [9] He Chunshan. Preparation of new vanadium based solid solution hydrogen storage material by ultrasonic stirring assisted casting[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014,35(5):21−24. (贺春山. 超声搅拌辅助铸造法制备新型钒基固溶体贮氢材料[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2014,35(5):21−24. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2014.05.005 -





 下载:
下载: