High-temperature tribological properties of AlFeCrCoNiTi high-entropy alloy coatings laser cladded with different parameters
-
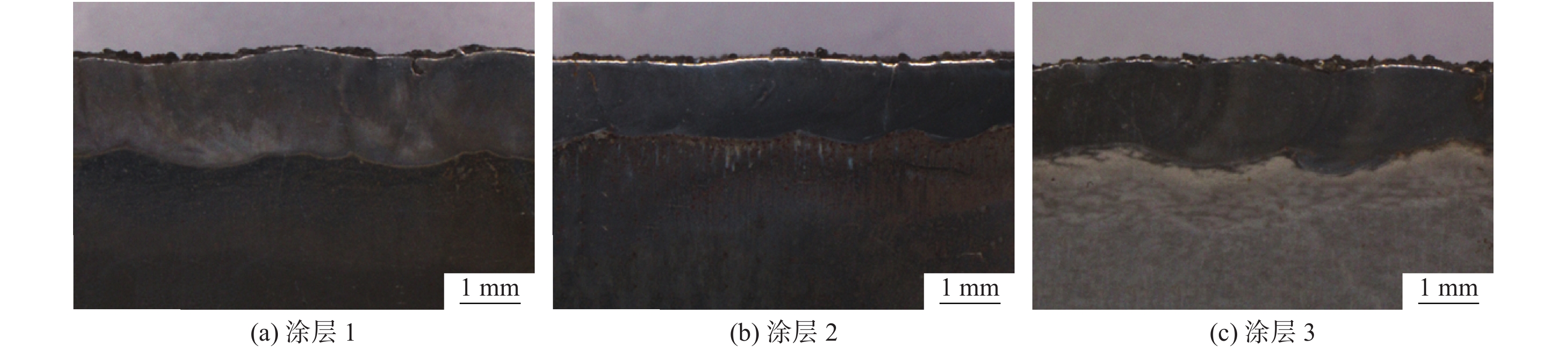
摘要: 选取H13钢进行激光熔覆,获得激光熔覆涂层,并进行了微观组织和硬度分析。采用销—盘式高温磨损试验机研究了H13钢及各个涂层的高温磨损行为。采用SEM、EDS以及XRD等微观分析手段对各个涂层上的磨面进行形貌、成分及物相分析,并探讨磨损机理。结果表明:不论温度的高低与载荷的大小,激光熔覆涂层的磨损量都比H13钢的磨损量低一个数量级。400 ℃下,涂层的磨损失重速度高于涂层的氧化增重速度,因此,涂层整体呈现失重的趋势;600 ℃下,涂层的磨损失重速度低于涂层的氧化增重速度,因此,涂层整体呈现增重的趋势。涂层1具有最好的抗高温软化能力,不论在400 ℃还是600 ℃下摩擦层表面都可以保持完整。涂层2的抗高温软化能力最弱。在400 ℃下,在载荷仅为50 N时就出现摩擦层表面大面积剥落;在600 ℃下,其挤出程度较其他两个摩擦层更为严重。涂层3的抗高温软化能力弱于涂层1的但高于涂层2。在400 ℃,下低载时,摩擦层保持完整,高载时,摩擦层发生大面积剥落;在600 ℃下,其挤出程度较为严重但轻于涂层2。Abstract: Some coatings were laser cladded on H13 steel and the micro-structure and hardness of the coatings were analyzed. The high-temperature tribological performance of H13 steel and each coating was studied by a pin-plate high-temperature wear testing machine. The analysis of the micro-morphology, composition and phase of the friction layer on each coating was conducted by SEM, EDS and XRD, which provided the evidence for the wear mechanism. The results show that the wear volume of laser cladding coatings is always an order of magnitude lower than that of H13 steel, regardless of the temperature or the normal load. When the temperature is 400 ℃, for all the coatings the velocity of weight loss caused by wear is higher than the velocity of weight gain caused by oxidation. As a result, the overall weight change tendency is decreasing. When the temperature is 600 ℃, in contrast, the velocity of the weight loss is lower than that of the weight gain. Thus, the overall weight change tendency is tincreasing. Coating 1 has the highest resistance to high-temperature softening. The surface of the friction layer on this coating always remains intact, regardless of the temperature or the normal load. Coating 2 has the lowest resistance to high-temperature softening. When the temperature is 400 ℃, mass peeling occurs on the surface of the friction layer even when the normal load is only 50 N. When the temperature is 600 ℃, the extrusion degree of the friction layer on this coating is more serious than those of other coatings. The resistance to high-temperature softening of coating 3 is lower than that of coating 1 but is higher than coating 2. When the temperature is 400 ℃, the surface of the friction layer remains intact with low normal loads. But mass peeling occurs on it with high normal loads. When the temperature is 600 ℃, the extrusion degree of the friction layer on this coating is less serious than that on coating 2 but still kind of harsh.
-
Key words:
- H13 steel /
- laser cladding /
- wear mechanism /
- resistance to high temperature softening
-
表 1 H13钢的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of H13 steel
% C Si Cr Mn V Mo S P Fe 0.42 1.04 5.15 0.43 0.90 1.45 ≤0.030 ≤0.030 余量 表 2 合金粉末的化学成分
Table 2. Chemical compositions of coating powders
% Al Fe Cr Co Ni Ti 9.0 18.6 17.3 19.6 19.6 15.9 表 3 激光熔覆工艺参数
Table 3. Laser cladding process parameters
参数编号 激光功率/W 扫描速度/(mm·s−1) 光斑直径/mm 送粉速度/(g·min−1) 搭接率/% 气流量/(L·min−1) 1 1600 5 4 8.57 50 10 2 1600 5 4 5.72 30 10 3 1600 5 4 5.72 50 10 表 4 磨损试验参数
Table 4. Tribological experiment parameters
温度/˚C 载荷/N 力矩/(N·m) 转速/(r·min−1) 时间/min 400、600 50、100、150 5 50 120 表 5 涂层及基体硬度
Table 5. Hardness of coating and substrate
涂层 硬度 (HRC) 退火前熔覆层 退火后熔覆层 基体 1 51.7 49.3 24.3 2 48.1 46.3 23.9 3 46.5 46.1 22.5 -
[1] (李志刚. 热铸模具钢H13表面改性研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2008: 1−15.)Li Zhigang. Investigation on surface modification of die-casting mould steel H13[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2008: 1−15. [2] Shahram K, Ahmad N. Effect of niobium on microstructure of cast AISI H13 hot work tool steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2008,15(4):61−66. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(08)60145-4 [3] Liu J, Guan Y, Xia X, et al. Laser cladding of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNiSi high entropy alloy coating without and with yttria addition on H13 steel[J]. Crystals, 2020,10(4):320. [4] Liu Lijun, Liu Dayu, Wang Xiaolu, et al. Parameter optimization of laser cladding ceramic repair layer of H13 steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020,41(7):65−70. (刘立君, 刘大宇, 王晓陆, 等. H13钢激光熔覆陶瓷修复层的参数优化[J]. 焊接学报, 2020,41(7):65−70. [5] Patra Karmakar D, Muvvala G, Nath A K. Effect of scan strategy and heat input on the shear strength of laser cladded Stellite 21 layers on AISI H13 tool steel in as-deposited and heat treated conditions[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2019:384. [6] Siddiqui A A, Dubey A K. Recent trends in laser cladding and surface alloying[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021,134:106619. [7] Liu H, Li X, Liu J, et al. Microstructural evolution and properties of dual-layer CoCrFeMnTi0.2 high-entropy alloy coating fabricated by laser cladding[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021,134:106646. [8] Li Y, Dong S, Liu X, et al. Interface phase evolution during laser cladding of Ni-Cu alloy on nodular cast iron by powder pre-placed method[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021,135(3):106684. [9] A. Khalili, M. Mojtahedi, A. Qaderi, et al Effect of pulse laser parameters on the microstructure of the in-situ Fe-TiC hard layer: Simulation and experiment[J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2021,135:106693. [10] J. -M. Wu, S. -J. Lin, J. -W. Yeh, et al Adhesive wear behavior of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloys as a function of aluminum content[J]. Wear, 2006,261(5−6):513−519. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2005.12.008 [11] M. -R. Chen, S. -J. Lin, J. -W. Yeh, et al Microstructure and properties of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNiTix (x = 0-2.0) high-entropy alloys[J]. Materials Transactions, 2006,47(5):1395−1401. doi: 10.2320/matertrans.47.1395 [12] (金冰倩. AlCoCrFeNiSi高熵合金制备与力学性能研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2019.)Jin Bingqian, Study on Preparation and Mechanical Properties of AlCoCrFeNiSi High Entropy Alloy[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2019. [13] (陈明. Al_(0.6)CoCrFeNi高熵合金在不同条件下的摩擦磨损性能[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2019.)Chen Ming, Friction and wear properties of Al_(0.6)CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy under different conditions[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2019. -





 下载:
下载: