Study on the carbide refining technology of semi high speed steel for cold roller
-
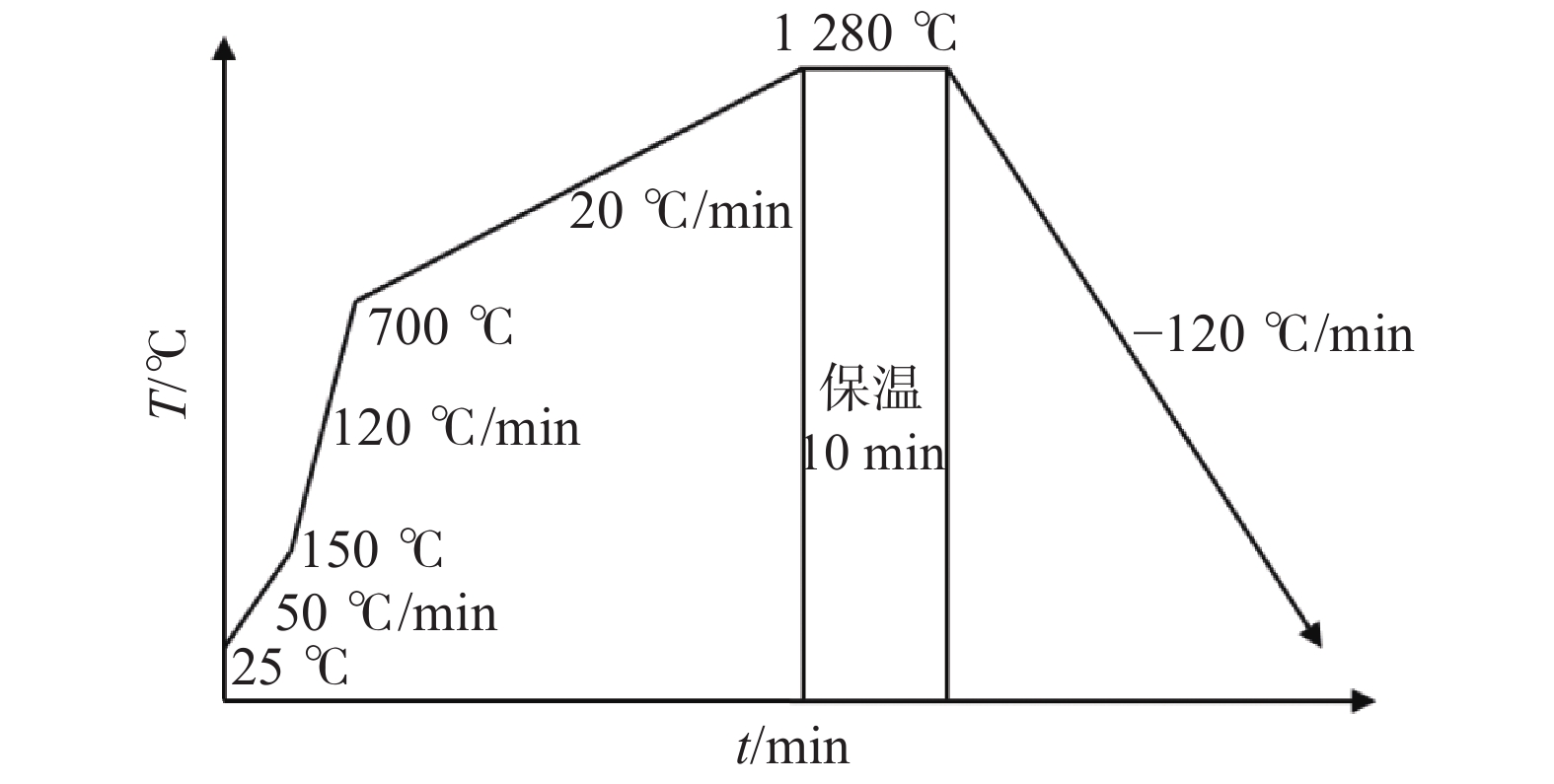
摘要: 基于Thermo-Calc热力学软件计算及原位观察结果,开展冷轧辊半高速钢95Cr5MoV碳化物细化技术研究。95Cr5MoV半高速钢平衡凝固碳化物类型主要有MC、M7C3和M23C6,其中M23C6型碳化物在785 ℃左右完全溶入基体,M7C3型碳化物在1100 ℃时完全溶入基体,MC型碳化物在1170 ℃左右完全溶入基体;采用高温共聚焦显微镜试验观察发现,大块状MC型碳化物在960 ℃时开始溶解,当温度升高到1170 ℃左右时,溶解加速,但一直到1217 ℃碳化物周围的基体开始局部熔化时仍然部分存在,表明非平衡态的溶解温度高于平衡态。为细化碳化物,实验室采用“1100 ℃高温固溶+880 ℃三次循环+740 ℃退火”的新热处理工艺后,大块液析碳化物尺寸明显减小,且组织均匀性好,并在工业化生产中验证了该工艺的可靠性。Abstract: Based on the results of thermos-Calc calculation and in-situ observation, the carbide refinement technology of 95Cr5mMoV cold roll semi high speed steel was studied. The equilibrium solidification carbides of 95Cr5MoV semi high speed steel mainly include MC, M7C3 and M23C6. Among them, M23C6 carbides completely dissolve into the matrix at about 785 ℃, M7C3 carbides completely dissolve into the matrix at 1100 ℃ and MC carbides completely dissolve into the matrix at about 1170 ℃. It is observed by high temperature confocal microscope that the massive MC carbides begins to dissolve at 960 ℃, and when the temperature rises to 1170 ℃, the dissolution accelerates, but it still exists until 1217 ℃, which indicates that the dissolution temperature of non-equilibrium state is higher than that of equilibrium state. In order to refine carbides, the heat treatment process of “1100 ℃ high temperature solid solution + 880 ℃ three times circulation + 740 ℃ annealing” was adopted in the laboratory. The size of large liquidus carbides decreased obviously, and the microstructure is uniform. The reliability of the process was verified in industrial production.
-
Key words:
- cold roller /
- semi high speed steel /
- carbide /
- in situ observation /
- superfine treatment
-
表 1 95Cr5MoV主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of 95Cr5MoV
% C Mn Si P S Cr Mo Ni V Al 0.95 0.44 0.50 0.008 0.005 4.5 1.22 0.35 0.85 0.045 表 2 试验方案及晶粒度检测结果
Table 2. Test scheme and grain size
序号 加热温度 /
℃保温时间 /
min平均晶粒度/
级冷却方式 a 1050 60 6.5 油冷 b 1100 60 4.0 c 1150 60 0.5 -
[1] Jia Jianping. Technology status and development trend of roller manufacturing industry in China (2)[J]. Technology Forum, 2008,(10):27−29. (贾建平. 中国轧辊制造业技术现状与发展趋势(下)[J]. 技术论坛, 2008,(10):27−29. [2] Zhang Dajian. Current situation and development trend of cold roll material[J]. Jiangsu Metallurgy, 2007,35(3):14−16. (章大健. 冷轧辊材质的现状与发展趋势浅谈[J]. 江苏冶金, 2007,35(3):14−16. [3] Wang Tianyi, Cao Jianfang, Rao Jianhua. Present situation and trend of roll materials and heat treatment technology[J]. Nanfang Metal, 2005,(1):4−10. (王天义, 曹建芳, 饶建华. 轧辊材料及其热处理工艺发展的现状与趋势[J]. 南方金属, 2005,(1):4−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9700.2005.01.002 [4] (王东冉. Cr8 钢锻造工作辊淬火过程的数值模拟及实验研究[D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2013.)Wang Dongran. Numerical simulation and experimental study on quenching process of Cr8 steel forging work roll[D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2013. [5] Liu Defu, Yin Zhongda. High speed steel and semi high speed steel roll[J]. Iron and Steel, 2004,39(4):69−73. (刘德富, 尹钟大. 高速钢及半高速钢轧辊[J]. 钢铁, 2004,39(4):69−73. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2004.04.019 [6] (陈馄. 控制钢冷轧辊坯质量的锻造变形工艺研究[D]. 上海: 上海大学, 2012.)Chen Hun. Research on forging deformation technology for controlling the quality of steel cold roll blank[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University, 2012. [7] (刘玉金, 陈伟, 曹静, 等. 新型钢工作辊在酸连乳机的研究与应用[C]//第九届中国金属学会青年学术年会论文集. 马鞍山: 中国金属学会, 2018: 331−332.)Liu Yujin, Chen Wei, Cao Jing, et al. Research and application of new type steel work roll in continuous acid milk machine[C]//Proceedings of the 9th Annual Youth Academic Conference of China Metal Society. Ma’anshan: China Metal Society, 2018: 331−332. [8] (徐咏梅. 锻造及热处理工艺对MC5冷轧辊坯缺陷与组织性能的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014.)Xu Yongmei. Effect of forging and heat treatment process on defects, microstructure and properties of MC5 cold roll blank[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014. [9] Zhou Li, Sun Dale, Liu Changsheng, et al. Oxidation behavior of carbides in roll materials of new type steel for hot rolling roughing[J]. Iron and Steel, 2007,42(8):69−73. (周利, 孙大乐, 刘常升, 等. 热轧粗轧用新型钢轧辊材料中碳化物的氧化行为[J]. 钢铁, 2007,42(8):69−73. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749x.2007.08.017 [10] Liu Defu, Yin Zhongda, Xu Dexiang, et al. Dissolution and precipitation of carbides in semi high speed steel for cold rolling work roll[J]. Iron and Steel, 2005,40(4):69−71, 82. (刘德富, 尹钟大, 徐德祥, 等. 冷轧工作辊用半高速钢中碳化物的溶解和析出[J]. 钢铁, 2005,40(4):69−71, 82. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2005.04.018 [11] Lu Sha, Guo Qiujuan, Tian Mingyan. Research on microstructure and carbide type of semi high speed steel roll[J]. Heavy Casting and Forging, 2017,2:3−6, 49. (鲁莎, 郭秋娟, 田明艳. 半高速钢轧辊显微组织和碳化物类型研究[J]. 大型铸锻件, 2017,2:3−6, 49. [12] Wu Qiong. Research on tempering microstructure transformation of nitrogen containing semi high speed steel cold roll material[J]. Heavy Machinery, 2020,2:25−31. (吴琼. 含氮半高速钢冷轧辊材料回火组织转变研究[J]. 重型机械, 2020,2:25−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-196X.2020.02.006 [13] Zhang Yu, Zhang Zhibo, Zhao Weidong. Effect of solution temperature on microstructure and properties of high temperature resistant bearing steel[J]. Metal Heat Treatment, 2015,40(3):151−154. (张瑜, 张志波, 赵卫东. 固溶温度对耐高温轴承钢组织与性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2015,40(3):151−154. [14] Ying Junlong, Shen Guoxi, Chao Minxuan, et al. Study on double refining process of solid solution cyclic phase transformation for CrMnMo die steel[J]. Hot Working Process, 2019,48:167−169. (应俊龙, 沈国喜, 巢昺轩, 等. CrMnMo模具钢固溶-循环相变双细化工艺研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2019,48:167−169. [15] (刘广超. MC5冷轧辊二次电渣重熔与碳化物超细化工艺开发[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2015.)Liu Guangchao. Development of secondary electroslag remelting and carbide superfine process for MC5 cold roll[D]. Shengyang: Northeast University, 2015. [16] Xu Hun, Hou Xinghui, Liu Xi, et al. Carbides ultrafine process of MC5 forged steel for cold roll, metal heat treatment[J]. Metal Heat Treatment, 2018,43(8):103−106. (徐锟, 侯兴慧, 刘喜, 等. 冷轧辊用MC5锻钢的碳化物超细化工艺[J]. 金属热处理, 2018,43(8):103−106. [17] Xu Jing, Yang Yitao. Study on carbide evolution in austenitizing process of MC5 cold roll steel[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2014,22(3):93−97. (徐京, 杨弋涛. MC5 冷轧辊钢奥氏体化过程碳化物演变的研究[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2014,22(3):93−97. doi: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20140316 [18] Mao Mingtao, Guo Hanjie, Sun Xiaolin, et al. High temperature behavior of liquidus carbide in H13 steel based on in-situ observation[J]. Acta Engineering Sinica, 2017,39:1174−1181. (毛明涛, 郭汉杰, 孙晓林, 等. 基于原位观察的 H13 钢中液析碳化物高温行为研究[J]. 工程科学学报, 2017,39:1174−1181. [19] Yin Zhongda, Liu Defu, Xu Dexiang, et al. Secondary hardening effect of semi high speed steel for cold rolling work roll[J]. Iron and Steel, 2006,41(2):72−75. (尹钟大, 刘德富, 徐德祥, 等. 冷轧工作辊用半高速钢的二次硬化效应[J]. 钢铁, 2006,41(2):72−75. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2006.02.018 -





 下载:
下载: