Effect of vanadium microalloying on properties of steel for automobile parts
-
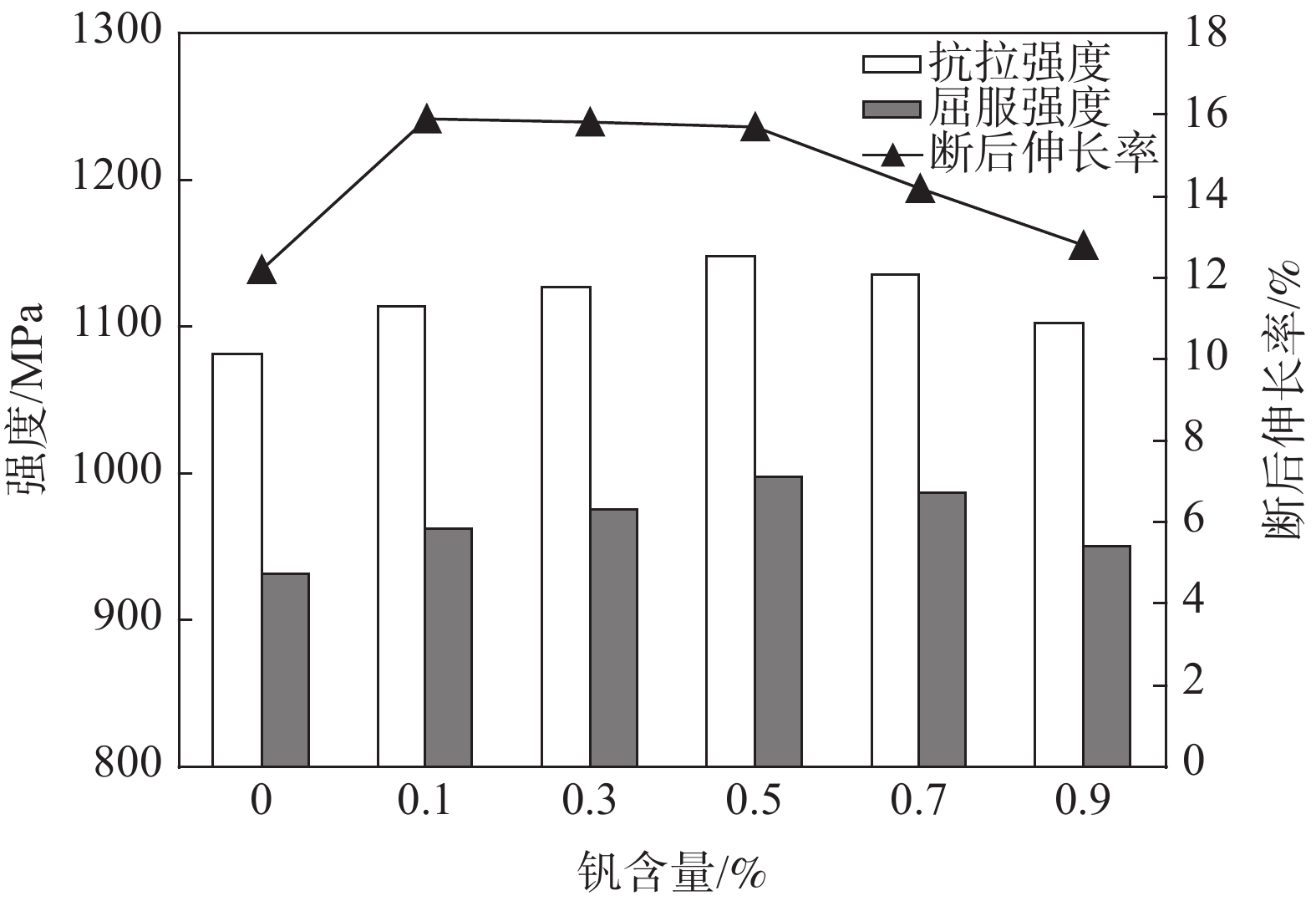
摘要: 制备了不同钒含量的钒微合金化汽车零部件用钢42CrMoVx(x=0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0.9),分析了钒微合金化对汽车零部件用钢拉伸性能、耐磨损和耐腐蚀性能的影响。结果表明,钒微合金化明显提高了汽车零部件用钢42CrMo的拉伸性能、耐磨损和耐腐蚀性能。随钒含量增加,钢拉伸性能、耐磨损和耐腐蚀性能均先提高后下降。与未添加钒的42CrMo钢相比,添加0.5%钒的汽车零部件用钢42CrMoV0.5的抗拉强度增大66 MPa、屈服强度增大67 MPa、断后伸长率增大3.5个百分点,磨损体积减小18×10−3 mm3,腐蚀电位正移88 mV、腐蚀电流减小了0.771 mA/cm2。汽车零部件用钢42CrMoV中钒含量优选0.5%。Abstract: Vanadium microalloyed steel 42CrMoVx (x=0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0.9) for automobile parts was prepared. The effects of vanadium microalloying on tensile strength, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the steel were analyzed. The results show that the tensile strength, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of 42CrMo steel for automobile parts are improved obviously by vanadium microalloying. With the increase of vanadium content, the tensile strength, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the steel increase first and then decrease. Compared with 42CrMo without vanadium, the tensile strength, yield strength and elongation after fracture of 42CrMoV0.5 steel increase by 66 MPa, 67 MPa and 3.5% respectively, while the wear volume and corrosion current of 42CrMoV0.5 steel separately decrease by 18×10−3 mm3 and 0.771 mA/cm2, with the corrosion potential positively shifted by 88 mV. The vanadium content in 42CrMoV steel used for auto parts is preferred to be 0.5%.
-
Key words:
- automobile parts steel /
- 42CrMoV /
- microalloying /
- vanadium content /
- tensile property /
- wear resistance /
- corrosion resistance
-
表 1 42CrMoVx试验钢化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of 42CrMoVx test steels
% 编号 C Mn Cr Mo Si V S P Fe 试样1(x=0) 0.42±0.05 0.75±0.05 1.1±0.05 0.25±0.05 0.20±0.05 0 <0.03 <0.03 Bal. 试样2(x=0.1) 0.42±0.05 0.75±0.05 1.1±0.05 0.25±0.05 0.20±0.05 0.1 <0.03 <0.03 Bal. 试样3(x=0.3) 0.42±0.05 0.75±0.05 1.1±0.05 0.25±0.05 0.20±0.05 0.3 <0.03 <0.03 Bal. 试样4(x=0.5) 0.42±0.05 0.75±0.05 1.1±0.05 0.25±0.05 0.20±0.05 0.5 <0.03 <0.03 Bal. 试样5(x=0.7) 0.42±0.05 0.75±0.05 1.1±0.05 0.25±0.05 0.20±0.05 0.7 <0.03 <0.03 Bal. 试样6(x=0.9) 0.42±0.05 0.75±0.05 1.1±0.05 0.25±0.05 0.20±0.05 0.9 <0.03 <0.03 Bal. 表 2 42CrMoVx试验钢电化学腐蚀试验结果
Table 2. Electrochemical corrosion results of 42CrMoVx test steels
编号 腐蚀电位/V 腐蚀电流/(mA·cm−2) 试样1(x=0) −0.499 1.305 试样2(x=0.1) −0.445 0.846 试样3(x=0.3) −0.421 0.751 试样4(x=0.5) −0.401 0.534 试样5(x=0.7) −0.418 0.722 试样6(x=0.9) −0.459 0.917 -
[1] Liu Qingmei, Feng Jiaojie. Development and current situation of advanced high-strength steel under the condition of automobile light weight[J]. Steel Rolling, 2020,37(4):65−70, 90. (刘清梅, 封娇洁. 汽车轻量化条件下先进高强钢的发展及现状[J]. 轧钢, 2020,37(4):65−70, 90. [2] Jin Xuejun, Gong Yu, Han Xianhong, et al. A review of current state and prospect of the manufacturing and application of advanced hot stamping automobile steels[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2020,56(4):411−428. (金学军, 龚煜, 韩先洪, 等. 先进热成形汽车钢制造与使用的研究现状与展望[J]. 金属学报, 2020,56(4):411−428. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2019.00381 [3] Zhang Chengcheng, Ma Xiaolei, Zhang Chaolei, et al. Evolution and control of surface decarburization in automobile front axle steel 42CrMoH[J]. Materials Review, 2020,34(12):127−131. (张成成, 马潇磊, 张朝磊, 等. 汽车前轴用42CrMoH钢表面脱碳演变规律及控制[J]. 材料导报, 2020,34(12):127−131. [4] Lu Junhui, Liu Jiaqi, Qiu Shengtao, et al. Determination of fatigue limit and analysis of fatigue fracture of 600 MPa automobile frame steel[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020,20(1):135−140. (卢军辉, 刘家琪, 仇圣桃, 等. 600 MPa级汽车大梁钢疲劳极限确定和疲劳断裂原因分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020,20(1):135−140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.01.021 [5] Chen Zezhong, Liu Huan, Xie Honghao, et al. Numerical simulation and process analysis of 22MnMoB steel in hot stamping for automobile rear floor crossmember[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2020,27(2):13−20. (陈泽中, 刘欢, 谢洪昊, 等. 22MnMoB钢汽车后地板横梁热冲压成形数值模拟和工艺研究[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2020,27(2):13−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2020.02.002 [6] Hou Yudong, Jing Cainian, Ding Xiaoyun, et al. Effect of strain rate on microstructure and properties of high strength steel for automobile[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2020,45(9):71−76. (候玉栋, 景财年, 丁啸云, 等. 应变速率对汽车用高强钢组织和性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2020,45(9):71−76. [7] Zhao Tiantian, Teng Lvdan, Jin Yangfan, et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of niobium-containing ferritic stainless steel suitable for automobile exhaust manifold[J]. Shanghai Metals, 2020,42(2):63−68. (赵天天, 滕铝丹, 金洋帆, 等. 适用于汽车排气歧管的含铌铁素体不锈钢的组织与力学性能[J]. 上海金属, 2020,42(2):63−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2020.02.011 [8] Lin Shaokai, Dong Xuanpu, Guo Ting, et al. 3Dp printing sand casting technology for high-graded automobile stamping die casting steel parts[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2020,40(4):392−395. (林少凯, 董选普, 郭艇, 等. 高端汽车冲压模铸钢件的3Dp打印砂型铸造技术[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2020,40(4):392−395. [9] Xue Feng, Sun Yan, Zhao Nan, et al. Study on formability of HC340LA low alloy high strength sheet for automobile[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2020,49(5):46−48. (薛峰, 孙岩, 赵楠, 等. 汽车用低合金高强度HC340LA钢板的成形性能研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2020,49(5):46−48. [10] Wang Cunyu, Chang Ying, Zhou Fengluan, et al. M3 microstructure control theory and technology of the third-generation automotive steels with high strength and high ductility[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2020,56(4):400−410. (王存宇, 常颖, 周峰峦, 等. 高强度高塑性第三代汽车钢的M3组织调控理论与技术[J]. 金属学报, 2020,56(4):400−410. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2019.00371 [11] Ye Yanxian, Yu Jiaojiao. Refining process optimization of vanadium-bearing steel 20CrMoV for automotive gear[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019,40(6):108−112. (叶燕仙, 于娇娇. 含钒汽车齿轮钢20CrMoV的精炼工艺优化[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2019,40(6):108−112. -





 下载:
下载: