Preparation of geopolymer for building by mechanical activation process
-
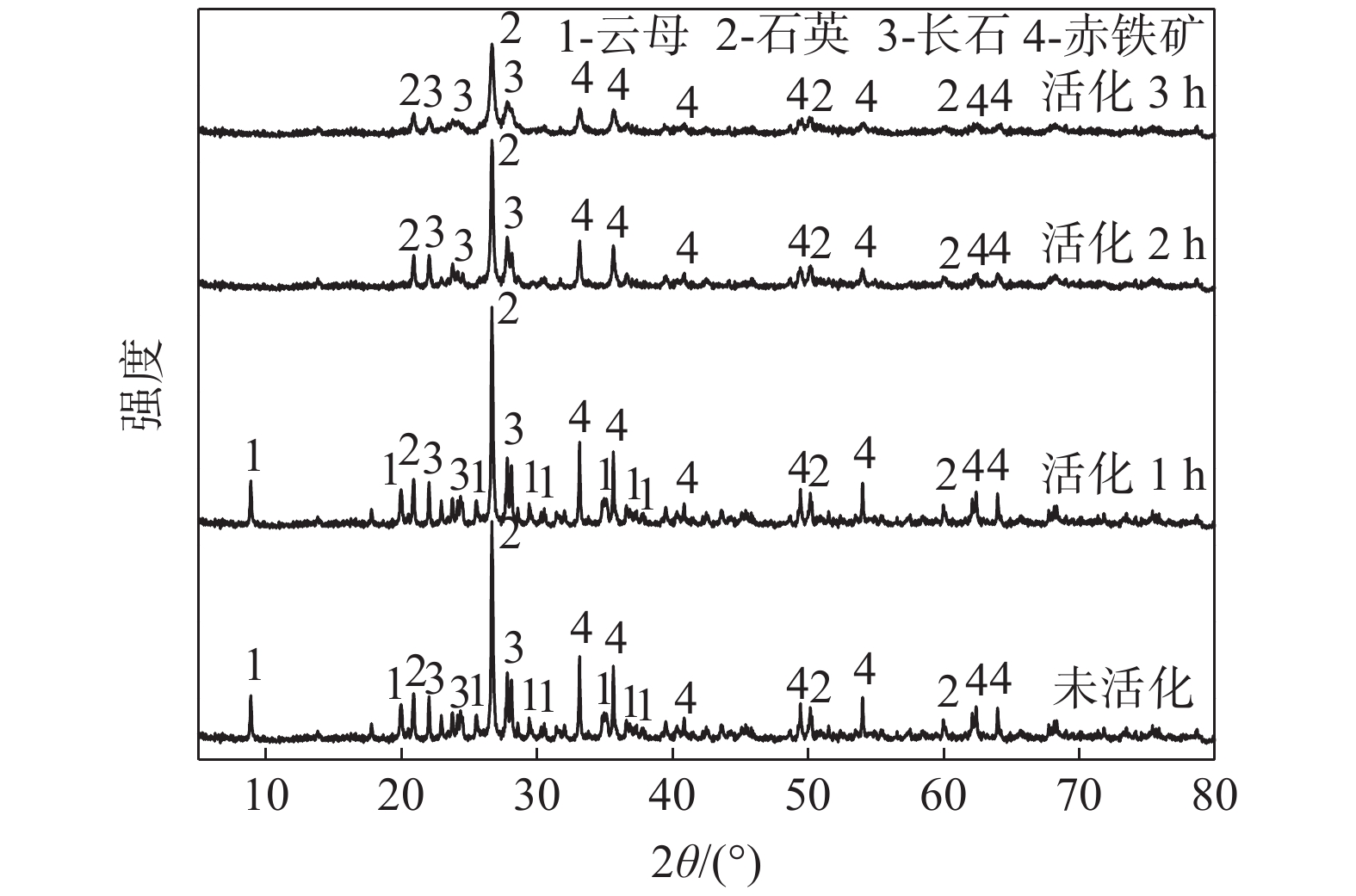
摘要: 利用钒钛磁铁矿尾矿制备地聚合物,既减轻了尾矿的污染,又实现了尾矿的高效利用。以承德某钒钛磁铁矿尾矿为主要原料,采用机械活化工艺制备地聚合物,探讨活化时间对尾矿的粒度、结构与地聚合物制品抗压强度的影响。结果表明:延长活化时间减小了尾矿粒度,破坏了矿物的晶体结构,从而增大了尾矿中活性硅与活性铝的浸出浓度,赋予地聚合物较高的抗压强度。当尾矿活化3.0 h后,采用尾矿与高岭土的质量比为6:4,Ca(OH)2和Na2SiO3的掺量均为10%、胶砂比为1∶1.5、液固比为0. 20的工艺条件,可制备出28 d 抗压强度高达50 MPa的地聚合物。样品的重金属离子浸出浓度符合国家标准。无定型的铝硅酸盐凝胶相及少量的沸石结合紧密,赋予制品较高的强度。Abstract: Using vanadium-titanium magnetite tailings for preparation of geopolymer can not only reduce pollution of the tailings, but also realize the efficient utilization of the tailings. The geopolymer was prepared from vanadium-titanium magnetite tailings in Chengde by mechanical activation process. The effect of activation time on the particle size and microstructure of the tailings and the compressive strength of the geopolymer products were investigated. The results show that prolonging the activation time can reduce the particle size and destroy the crystal structure of the tailings, which can increase the leaching concentration of active silicon and aluminum in the tailings and improve the compressive strength of the geopolymer. At the activation time of 3 h, mass ratio of tailings to kaolin of 6∶4, Ca(OH)2 and Na2SiO3 addition respectively of 10%, ratio of mortar to sand of 1∶1.5 and liquid-solid ratio of 0.20, the geopolymer with the 28-day compressive strength up to 50 MPa can be obtained. The leaching concentration of heavy metal ions in the sample meets the national standard. The amorphous aluminosilicate gel phase is tightly bonded with a small amount of zeolites, endowing the products with a high compressive strength.
-
表 1 尾矿和偏高岭土的化学组成
Table 1. Chemical compositions of tailings and kaolin
% 原料 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO Na2O K2O TiO2 SO3 V2O5 LOI 尾矿 56.89 12.56 6.39 9.65 1.26 2.63 1.69 1.50 5.39 0.02 2.02 高岭土 40.29 46.98 0.62 0.09 0.29 0.33 0.96 0.52 0.12 — 9.80 表 2 经机械活化后尾矿的粒度分布及比表面积
Table 2. Particle size distribution and specific surface area of tailings after mechanical activation
活化时间/h −10 µm含量/% d50/µm d90/µm 比表面积/
(m2·g−1)0 40.26 19.55 78.12 0.30 0.5 50.96 16.34 60.58 0.43 1.0 58.38 12.69 45.23 0.52 1.5 64.22 9.64 35.12 0.86 2.0 70.69 6.97 27.92 0.95 2.5 75.16 4.47 22.64 1.13 3.0 80.22 2.95 17.31 1.20 3.5 83.69 1.94 15.55 1.22 表 3 样品重金属浸出浓度与相关标准要求
Table 3. Leaching concentration of heavy metals of the sample and the related standard requirements
mg/L Cu Pb Cd Cr Zn 含量 2.33 3.69 0.67 11.06 19.28 标准限值 <3.00 <5.00 <1.00 <15.00 <100.00 -
[1] Zhang Jun. New light wall materials can be produced by low-temperature autoclaving process from low-lean vanadium ilmenite resources[J]. Building Materials Development Orientation, 2013,(5):107−108. (张均. 低贫钒钛铁矿资源可以采用低温蒸压工艺生产的新型轻质墙体材料[J]. 建材发展导向, 2013,(5):107−108. [2] (于明珠. 承德市尾矿库安全监管问题与对策研究[D]. 保定: 河北大学, 2014.)Yu Minzhu. Study on safety supervision and management of tailings pond in Chengde[D]. Baoding:Hebei University, 2014. [3] Zhang Shaomin. Recovery of iron and titanium from a vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate tailings in Chengde area[J]. Modern Mining, 2013,29(10):108−109. (张韶敏. 承德地区某钒钛磁铁矿选铁尾矿回收铁、钛试验[J]. 现代矿业, 2013,29(10):108−109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2013.10.038 [4] Song Xiaomin, Wang Yonggang. Comprehensive recovery of titanium and iron from a tailings in Twin Towers mountain in Chengde[J]. Modern Mining, 2015,(1):86−87. (宋晓敏, 王永刚. 承德双塔山某尾矿综合回收钛、铁试验[J]. 现代矿业, 2015,(1):86−87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2015.01.027 [5] Liu Changmiao, Wu Dongyin, Lv Zihu, et al. Study on Beneficiation of ilmenite in tailings of a vanadium titanium magnetite ore[J]. China Mining, 2015,(5):115−117. (刘长淼, 吴东印, 吕子虎, 等. 某钒钛磁铁矿尾矿中钛铁矿的选矿研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2015,(5):115−117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2015.05.025 [6] Fernández Jiménez A, Palomo A. Characterisation of fly ashes: Poten-tial reactivity as alkaline cements[J]. Fuel, 2003,82:2259−2265. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(03)00194-7 [7] Jiao Xiangke, Zhang Yimin, Chen Tiejun, et al. Research on utilizing low-reactive vanadium tailing as source material for geopolymer syn-thesis[J]. Non Metallic Mines, 2011,34(4):1−4. (焦向科, 张一敏, 陈铁军, 等. 利用低活性钒尾矿制备地聚合物的研究[J]. 非金属矿, 2011,34(4):1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2011.04.001 [8] Liu Xiang, Zhang Yimin, Bao Shenxu, et al. Activated vanadium tailing by different activation methods based gepolymer[J]. NonMetallic Mines, 2014,37(4):1−3. (刘 祥, 张一敏, 包申旭, 等. 不同活化方法活化钒尾渣制备地聚合物[J]. 非金属矿, 2014,37(4):1−3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2014.04.001 [9] Hu Fangfang, Zhang Yimin, Chen Tiejun, et al. Experimental study on alkali-activated stone coal aciding vanadium tailings based geopolymer[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2013,32(12):2449−2454. (胡芳芳, 张一敏, 陈铁军, 等. 石煤提钒尾渣制备地聚合物的研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2013,32(12):2449−2454. [10] (韩涛. 矿渣粉粒度分布特征及其对水泥强度的影响[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2004.)Han Tao. The distribute characteristic of slag powder and influence on strength of cement[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2004. [11] Wang Changlong, Ni Wen, Qiao Chunyu, et al. Preparation and properties of iron tailings aerated concrete[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2013,(2):157−162. (王长龙, 倪文, 乔春雨, 等. 铁尾矿加气混凝土的制备和性能[J]. 材料研究学报, 2013,(2):157−162. [12] (王斌. 铁尾矿加气混凝土的制备及其性能研究[D].沈阳: 沈阳建筑大学, 2015.)Wang Bin. Study on preparation and performance of iron tailings aerated concrete[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Construction University, 2015. [13] Jiao Xiangke, Zhang Yimin. Activation of a low-reactive and silica-rich tailing and evaluation of its reactivity in geopolymeric reaction[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2015,24(1):112−119. (焦向科, 张一敏. 低活性高硅尾矿的活化及其在矿物聚合反应中的活性评价[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2015,24(1):112−119. -





 下载:
下载: