Simulation on particle movement and pulverized coal jet combustion of titano-magnetite pellets during the reduction with coal in rotary kiln
-
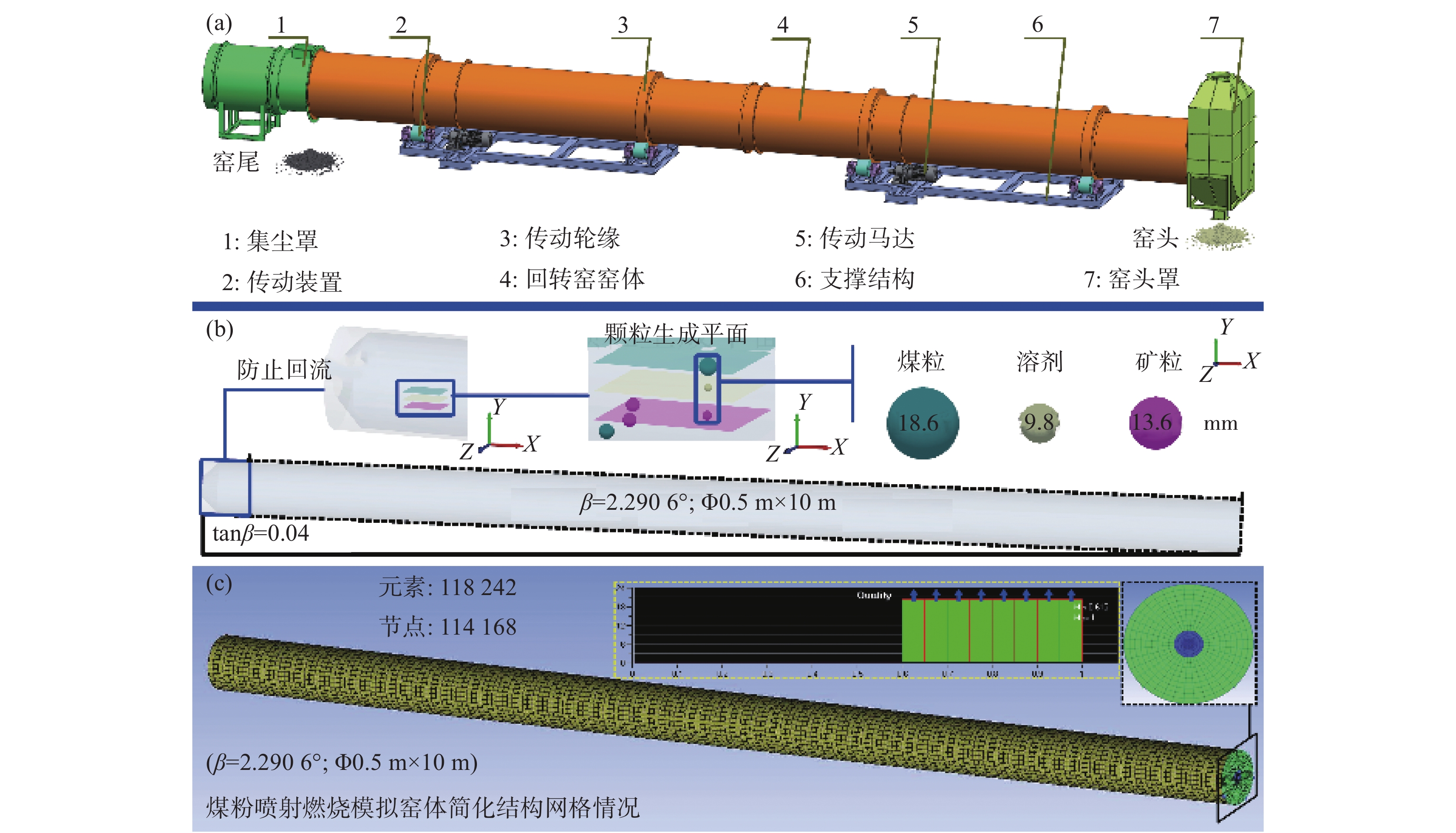
摘要: 开展了回转窑内钒钛磁铁矿球团煤基还原颗粒运动及煤粉喷射燃烧数值模拟研究。结果表明,回转窑内三种颗粒在运动过程中存在分层现象和离散料堆现象。离散料堆现象导致了颗粒数轴向周期性波动分布,并结合反应焓变推导出了单个周期内的平均波动能量为
$ \tilde {{E}}$ = 25.58 MJ;煤粉喷射燃烧过程中燃料射流在重力作用下会形成反弹效果,作用区间长度约2 m,该区域内传质传热过程被强化,易出现局部过热现象,可通过附着配碳和外配碳球团混合配碳的方式削弱能量波动与局部过热,矿石颗粒的附着配碳量约为18.9 g/kg。Abstract: In this paper, the numerical simulation of on particle movement and pulverized coal injection combustion duringin the coal coal-based reduction of titano-magnetite pellets in rotary kiln was carried out. The results show that there were delamination phenomenon and discrete pile phenomenon in the movement process of three kinds of particles in rotary kiln. The discrete particle piles led to the axial periodic fluctuation distribution of particle number. Combined with the change of reaction enthalpy, the average fluctuation energy in a single period was deduced as$\tilde {{E}}$ = 25.58 MJ; in the process of pulverized coal injection combustion, the fuel jet would form a rebound effect under the action of gravity, and the length of the action zone was about 2 m. The mass and heat transfer process in this zone was strengthened, and the local overheating phenomenon was readily to occur. The energy fluctuation and local overheating could be reduced by the way of attaching carbon with coal powder on the surface of ore pellets and mixing carbon with external coal pellets. The amount of carbon distribution by adhering to ore particles is about 18.9 g/kg.-
Key words:
- titanomagnetite /
- rotary kiln /
- reduction /
- simulation /
- particle movement /
- pulverized coal jet combustion
-
表 1 钒钛磁铁矿精矿主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of titano-magnetite concentrate
% Fe3O4 TiO2 Al2O3 SiO2 MgO CaO MnO Na2O Co3S4 ZnS CuS 68.51 13.41 5.00 6.77 4.45 1.17 0.29 0.16 0.15 0.050 0.019 表 2 模拟过程(颗粒运动)中的颗粒生成参数
Table 2. Particle formation parameters used in simulation study (particle motion)
实体密度
ρ/(g·cm−3)半径分布/
mm生成速率/
(kg·s−1)质量分数/
%煤粒 1.5 N(10,0.25) 0.2062 11.42 熔剂 2.6 N(5,0.25) 0.1461 11.50 矿粒 3.6 N(7.5,0.25) 1.2083 77.08 注:N(10,0.25)表示模拟过程中颗粒半径按正态分布生成,10 为半径平均值(单位:mm),0.25为标准差。 表 3 模拟过程中(煤粉喷射燃烧)燃料参数
Table 3. Fuel parameters used in simulation study (pulverized coal injection combustion)
燃料空气混合物组成/% 工业分析/% 元素分析w/% 煤粉 O2 CO2 H2O 挥发分 C固 灰分 水分 C H O N 20 18.4 0.1 0.1 10 75 10 5 90 5 4 1 注:燃料热值为29.67 MJ/kg。 表 4 模拟过程中(煤粉喷射燃烧)燃料喷射速度
Table 4. Fuel injection velocity used in simulation study (pulverized coal injection combustion)
煤粉喷射速度/(m·s−1) 质量流动/(kg·s−1) 6 0.0666691 7 0.0777806 8 0.0888922 9 0.100004 10 0.111115 -
[1] Guo X, Dai S, Wang Q. Influence of different comminution flowsheets on the separation of vanadium titano-magnetite[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2020,149:106−177. [2] Chen J, Chen W, Mi L, et al. Kinetic studies on gas-based reduction of V anadium titano-magnetite pellet[J]. Metals, 2019,9:145−158. doi: 10.3390/met9020145 [3] Hu T, Lv X, Bai C, et al. Reduction behavior of Panzhihua titanomagnetite concentrates with coal[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2013,44B:252−260. [4] Jiang T, Yu Z, Peng Z, et al. Preparation of BF burden from titanomagnetite concentrate by composite agglomeration process (CAP)[J]. ISIJ International, 2015,55:1599−1607. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2015-094 [5] Jiang T, Wang S, Guo Y, et al. Effects of basicity and MgO in slag on the behaviors of smelting vanadium titanomagnetite in the direct reduction-electric furnace process[J]. Metals, 2016,6:1−10. [6] Fu W, Wen Y, Xie H. Development of intensified technologies of vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite smelting[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2011,18:7−10. [7] Wang S, Guo Y, Jiang T, et al. Behavior of titanium during the smelting of vanadium titanomagnetite metallized pellets in an electric furnace[J]. JOM, 2019,71:323−328. doi: 10.1007/s11837-018-2932-y [8] Gan M, Sun Y, Fan X, et al. Preparing high-quality vanadium titano-magnetite pellets for large-scale blast furnaces as ironmaking burden[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2018,139:149−158. [9] Zeng R, Li W, Wang N, et al. Influence and mechanism of CaO on the oxidation induration of Hongge vanadium titanomagnetite pellets[J]. ISIJ International, 2020,142:1−10. [10] Hu T, Lv X, Bai C, et al. Carbothermic reduction of titanomagnetite concentrates with ferrosilicon addition[J]. ISIJ International, 2013,53:557−563. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.53.557 [11] Liu P, Zhang L, Liu B, et al. Determination of dielectric properties of titanium carbide fabricated by microwave synthesis with Ti-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2021,28:88−91. doi: 10.1007/s12613-020-1985-4 [12] Yang J, Tang Y, Yang K, et al. Leaching characteristics of vanadium in mine tailings and soils near a vanadium titanomagnetite mining site[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014,264:498−504. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.09.063 [13] Zeng R, Li W, Wang N, et al. Effect of Al2O3 on the gas-based direct reduction behavior of Hongge vanadium titanomagnetite pellet under simulated shaft furnace atmosphere[J]. Powder Technology, 2020,376:342−350. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2020.08.043 [14] Chen D, Zhao L, Liu Y, et al. A novel process for recovery of iron, titanium, and vanadium from titanomagnetite concentrates: NaOH molten salt roasting and water leaching processes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013,(244−245):588−595. [15] Adetoro A, Sun H, He S, et al. Effects of low-temperature pre-oxidation on the titanomagnetite ore structure and reduction behaviors in a fluidized bed[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2018,49B:846−857. [16] Dang J, Zhang G, Hu X, et al. Non-isothermal reduction kinetics of titanomagnetite by hydrogen[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2013,20:1134−1139. doi: 10.1007/s12613-013-0846-9 [17] Geng C, Sun T, Yang H, et al. Effect of Na2SO4 on the embedding direct reduction of beach titanomagnetite and the separation of titanium and iron by magnetic separation[J]. ISIJ International, 2015,55:2543−2549. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2015-420 [18] Du Q, Mo H, Tian L, et al. A preliminary control system on a barium sulphide rotary kiln process[J]. IEEE Computer Society, 2010,142:286−290. [19] Atmaca A, Yumrutas R. Analysis of the parameters affecting energy consumption of a rotary kiln in cement industry[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2014,66:435−444. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.02.038 [20] Mu J, Leder F, Park W C, et al. Reduction of phosphate ores by carbon: Part I. process variables for design of rotary kiln system[J]. Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1986,17B:861−868. [21] Boateng A A. Rotary kilns-transport phenomena and transport processes[M]. 2nd Edition. Elsevier, 2016. [22] Zhao S, Zhou X, Liu W. Discrete element simulations of direct shear tests with particle angularity effect[J]. Granular Matter, 2015,17:793−806. doi: 10.1007/s10035-015-0593-x [23] Yakhot V, Orszag S A. Renormalization group analysis of turbulence[J]. Journal of Scientific Computing, 1986,1:3−49. doi: 10.1007/BF01061452 [24] Wang S, Lu J, Li W, et al. Modeling of pulverized coal combustion in cement rotary kiln[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2006,20:2350−2356. [25] Escotet-Espinoza M, Foster C, Ierapetritou M. Discrete element modeling (DEM) for mixing of cohesive solids in rotating cylinders[J]. Powder Technology, 2018,335:124−136. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.05.024 [26] Ndiaye L, Caillat S, Chinnayya A, et al. Application of the dynamic model of saeman to an industrial rotary kiln incinerator: Numerical and experimental results[J]. Waste Management, 2010,30:1188−1195. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2009.09.023 [27] Ding Y, Wang J, She X, et al. Reduction characteristics and kinetics of bayanobo complex iron ore carbon bearing pellets[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2012,20:28−33. [28] Zhou L, Zeng F. Reduction mechanisms of vanadium-titanomagnetite-non-coking coal mixed pellet[J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2011,38:59−64. doi: 10.1179/030192310X12816231892549 -







 下载:
下载: