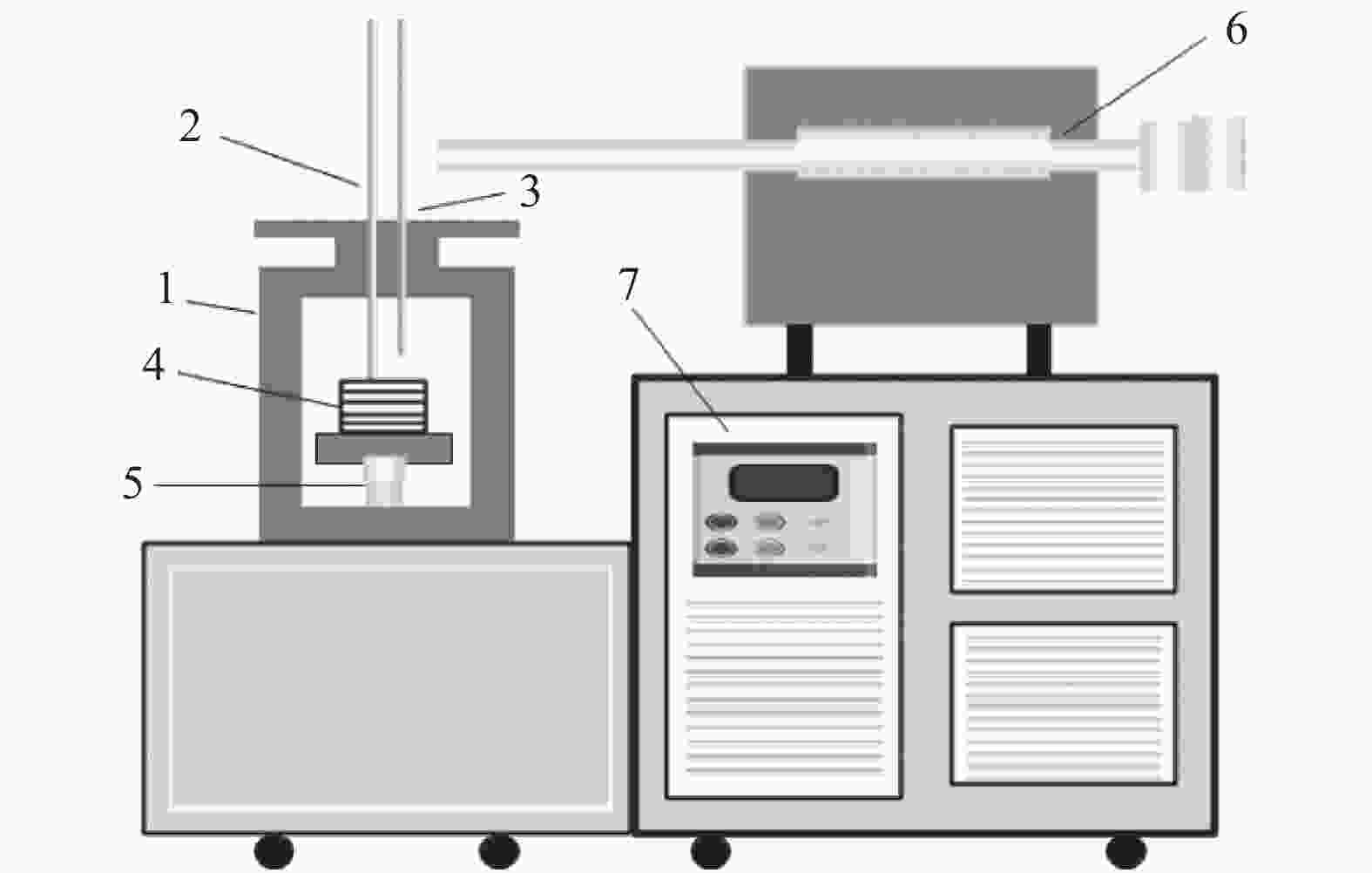
Study on the regulation mechanism of valuable elements in the reduction process of vanadium-titanium magnetite marine placer
-
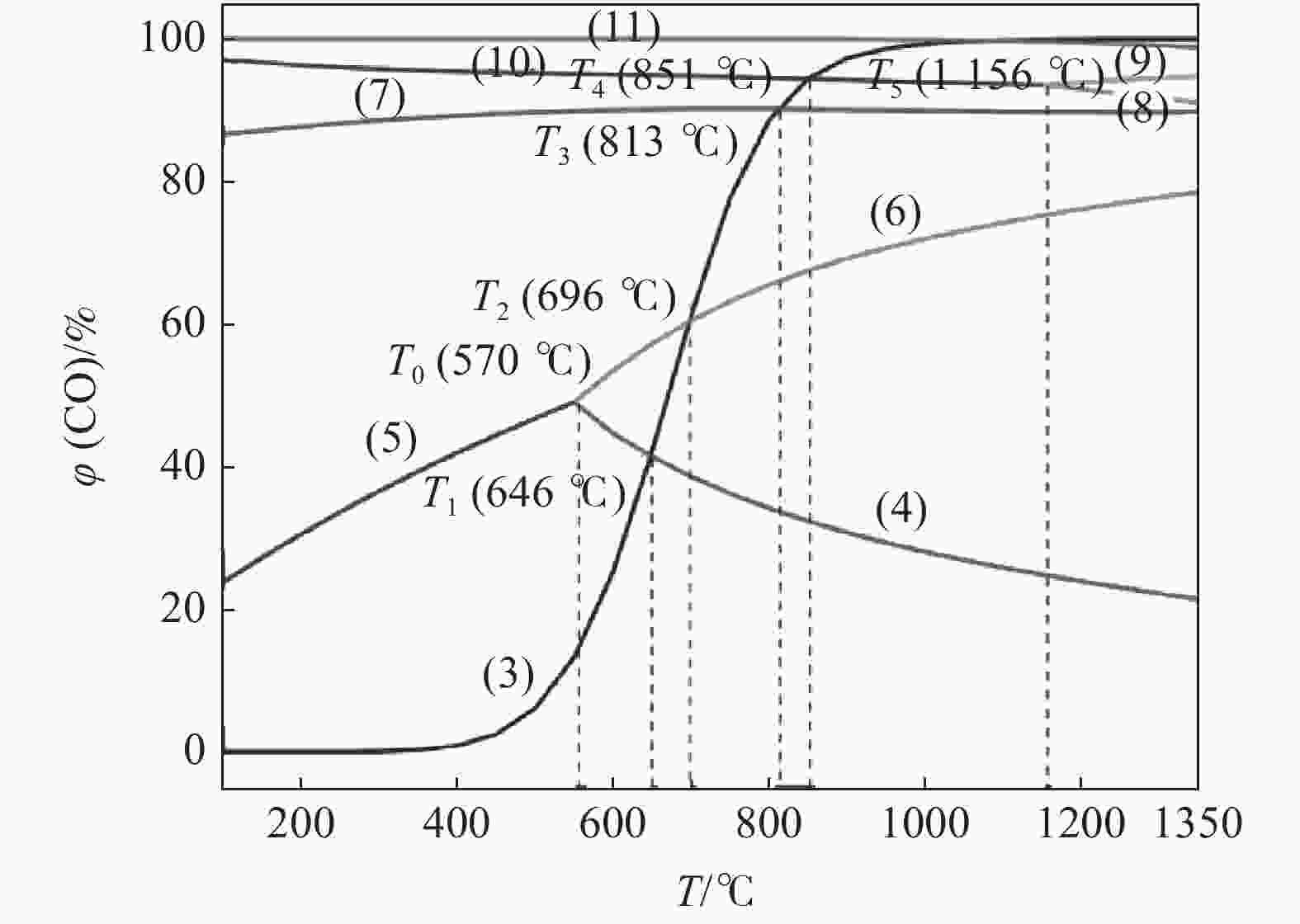
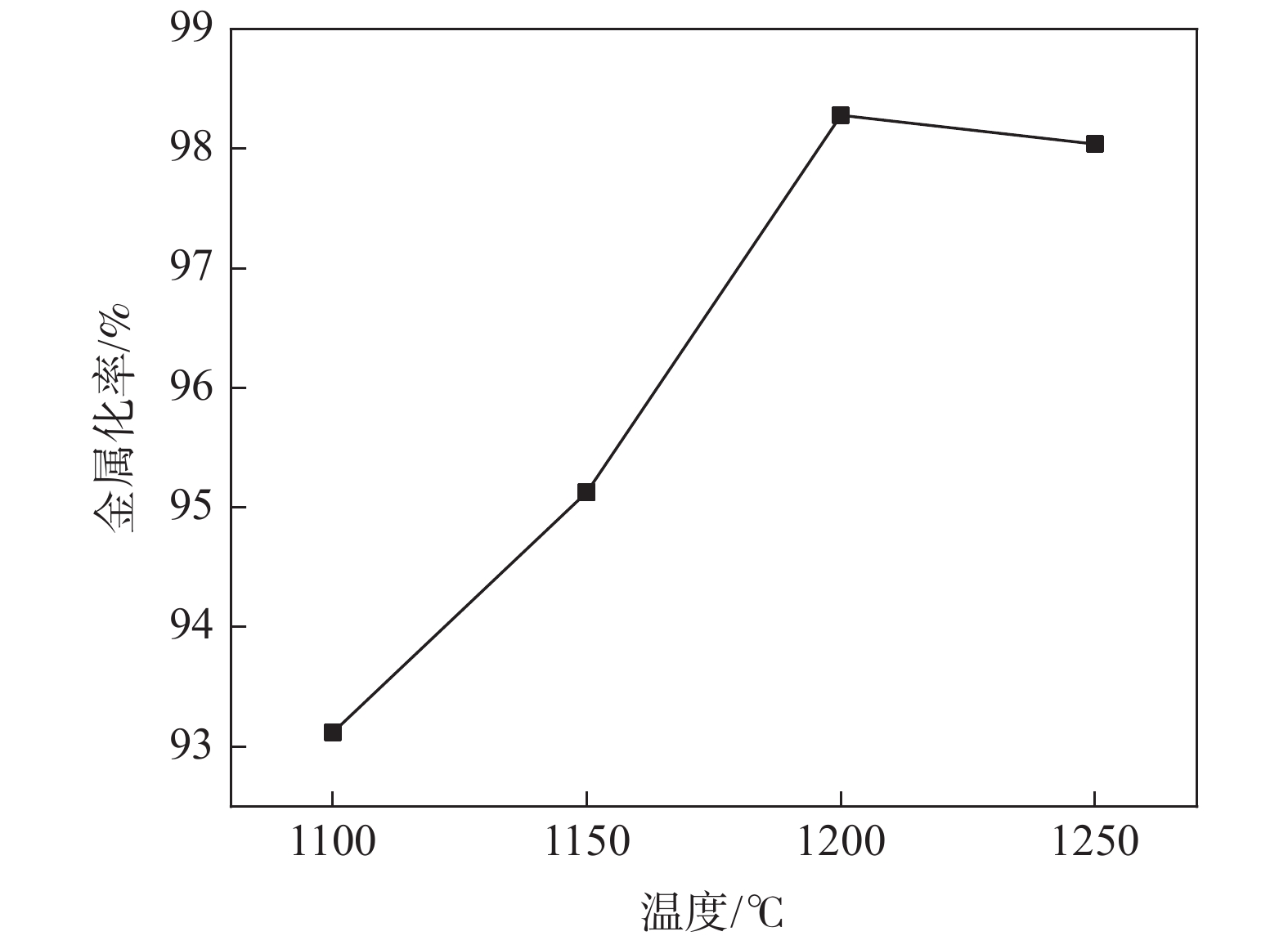
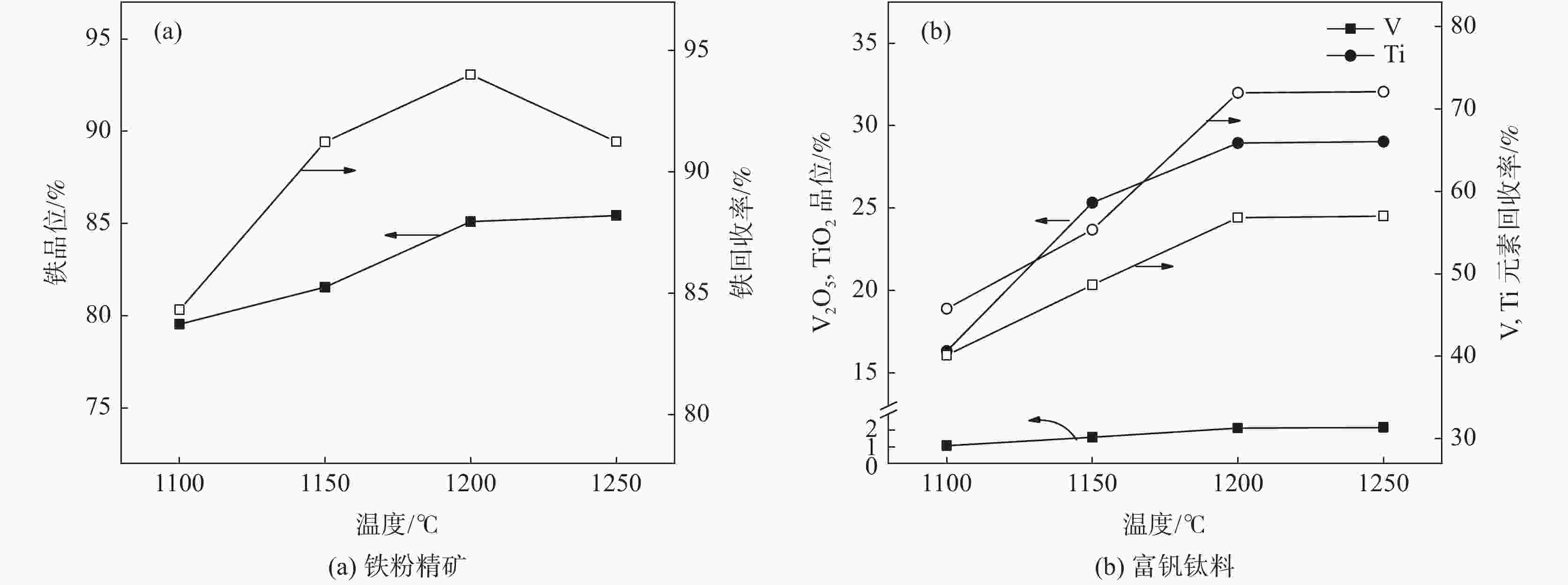
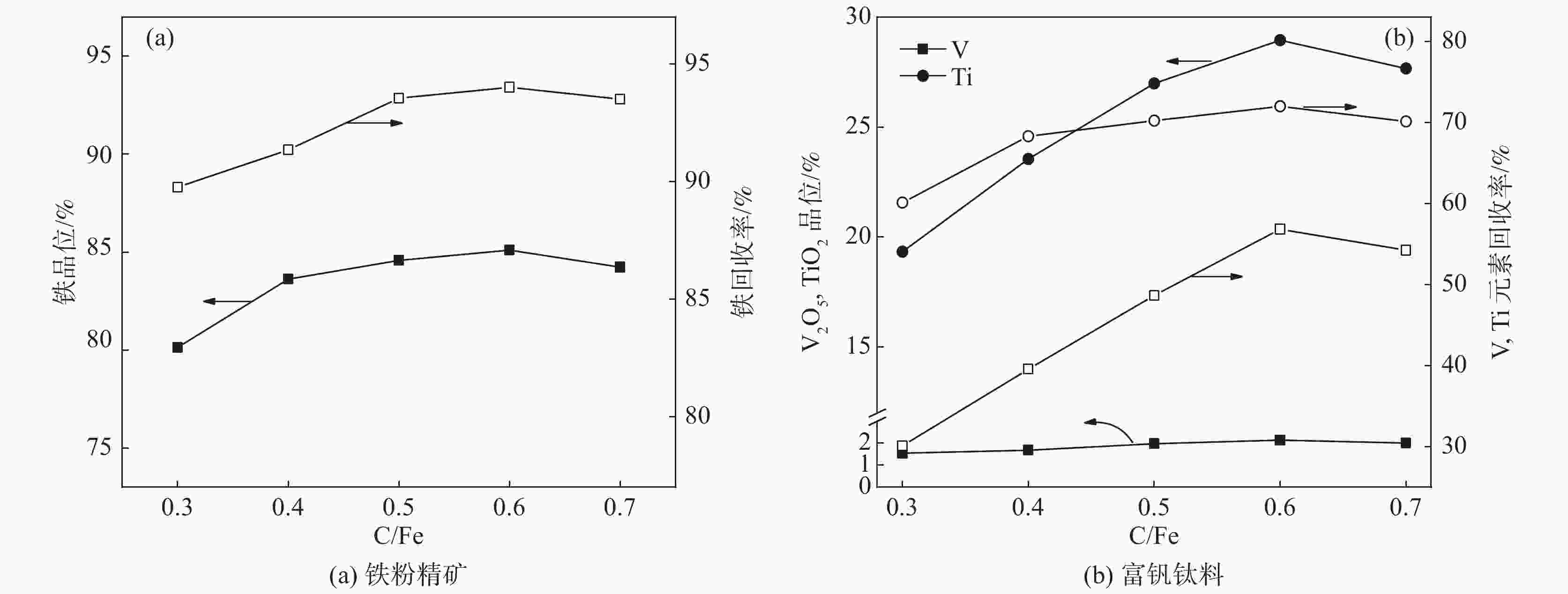
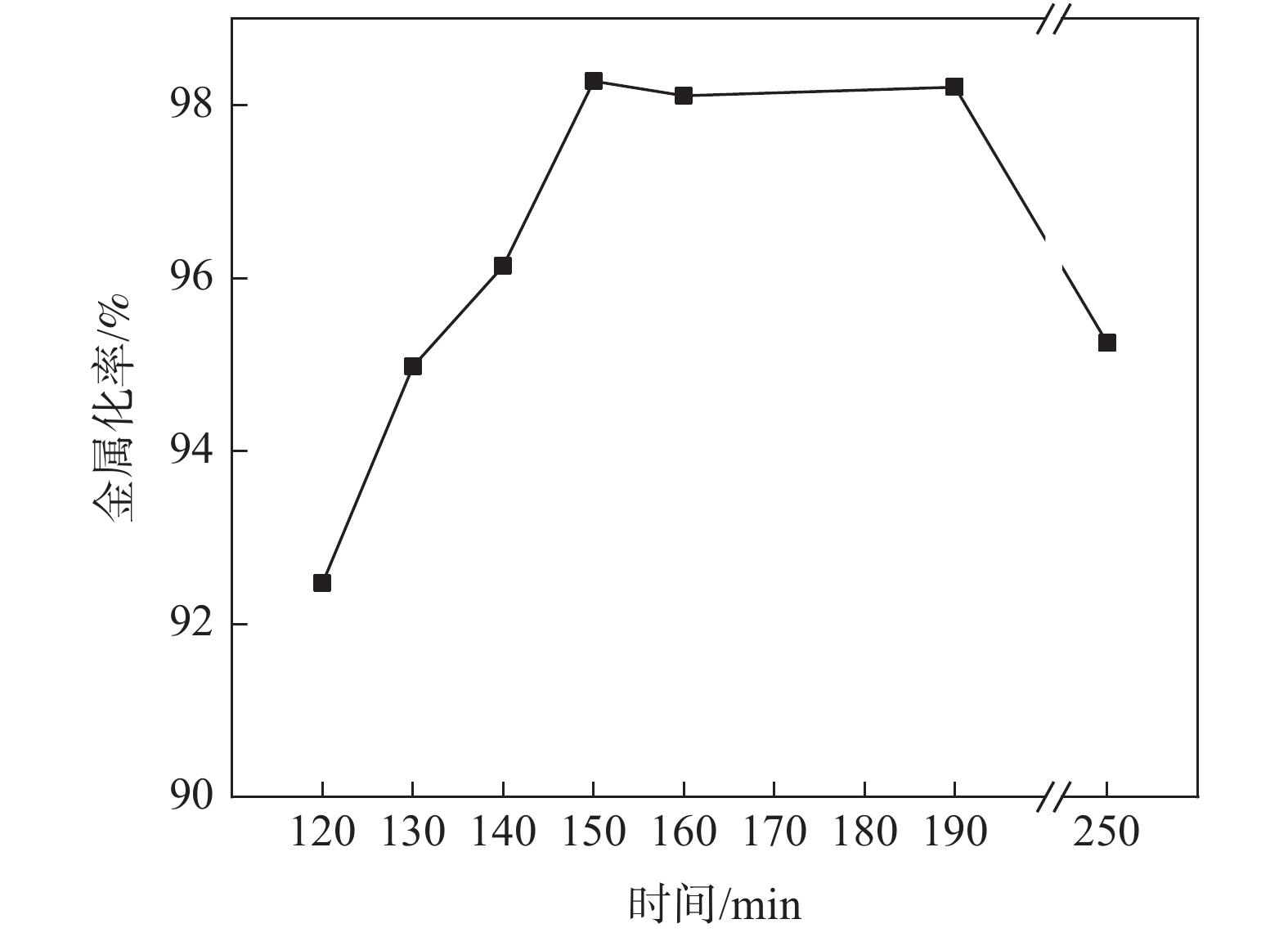
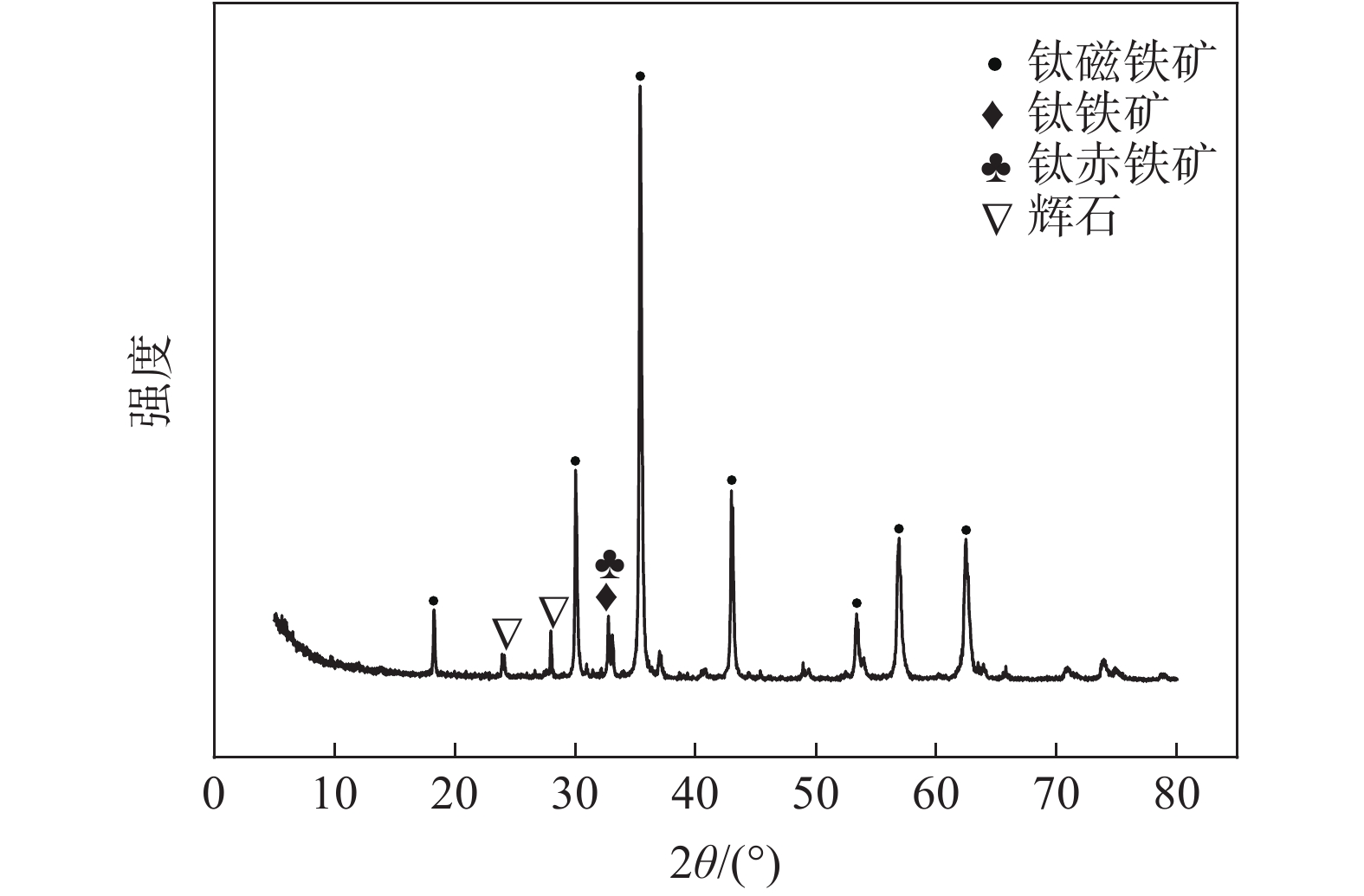
摘要: 以印尼某钒钛磁铁海砂矿为研究对象,通过XRD分析探明其主要成分和物相组成,并在热力学分析基础上探讨了该矿的还原特性和有价元素变化规律。利用微波加热同时以生物质炭作为直接还原的还原剂对海砂矿进行还原-磨选试验,微波加热有利于强化海砂矿的还原过程。结果表明,在C/Fe为0.6,还原焙烧温度1200 ℃下还原150 min,可获得金属化率为98.28%的还原产物;在矿浆浓度50%,磨矿时间为40 min,磁场强度为0.08 T的条件下,可获得铁品位为85.1%、铁回收率94.01%的精矿粉,以及TiO2品位为28.95%,回收率为71.98%,V2O5品位为2.14%,回收率为56.82%的尾矿粉,有效实现了铁和钒钛的分离富集。Abstract: In this paper, a marine placer from Indonesia is used as the testing material. Its chemical composition and mineral composition were analyzed by XRD, and the reduction characteristics and the regulation mechanism of the valuable elements of the ore are discussed on the basis of thermodynamics. The reduction and grinding experiments of marine placer were carried out by microwave heating with biochar as the reducing agent for direct reduction. Microwave heating is beneficial to strengthen the reduction process of marine placer. The results show that the reduction product with 98.28% metallization rate can be obtained with the C/Fe ratio of 0.6 and the reduction temperature of 1 200 ℃ for 150 min. Under the conditions of 50% pulp concentration, 40 min grinding time and 0.08 T magnetic field intensity, the refined powder with iron grade of 85.1% and iron recovery of 94.01%, tailings powder with TiO2 grade of 28.95% and recovery of 71.98%, V2O5 grade of 2.14% and recovery of 56.82% can be obtained. The separation and enrichment of iron and vanadium-titanium are effectively realized.
-
表 1 海砂矿的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of marine placer
% TFe FeO Fe2O3 TiO2 V2O5 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO MnO S P 54.27 29.08 45.27 10.88 0.68 4.01 3.67 0.48 3.68 0.44 0.06 0.03 表 2 海砂矿主要矿物含量
Table 2. Main mineral content of marine placer
% 钛磁铁矿 钛赤铁矿 钛铁矿 辉石 83.21 6.93 1.87 5.61 表 3 生物质炭工业分析
Table 3. Content analysis of the biochar
% 水分 固定碳 挥发分 灰分 6.51 80.81 15.65 3.54 -
[1] Liu S S, Guo Y F, Qiu G Z, et al. Solid-state reduction kinetics and mechanism of pre-oxidized vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014,24(10):3372-3377. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63479-8 [2] Yang Tao, Chen Hanyu, Song Fumei, et al. Research on developing and utilizing an indonesia beach iron sand[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2016,(2):29−33. (杨涛, 陈汉宇, 宋复梅, 等. 对印尼某海滨铁砂矿的开发利用研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2016,(2):29−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2016.02.006 [3] Sui Y L, Guo Y F, Travyanov A Y, et al. Reduction roasting-magnetic separation of vanadium tailings in presence of sodium sulfate and its mechanisms[J]. Rare Metals, 2016,(35):954−960. [4] Yang S P, Wang J, Du X, et al. Study on melting separation for metalized pellet of vanadium-titanium magnetite and TiO2 enrichment[J]. Mining & Metallurgical Engineering, 2014,(34):87−88. [5] Guo Y F, Tang M J, Jiang T, et al. Research on the slag phase type of vanadium-titanium magnetite in pre-reduction/electric furnace smelting[C]//Processing in: 4th International Symposium on High-temperature Metallurgical Processing, TMS Annual Meeting, San Antonio, Texas, USA, 2013: 87-94. [6] Jena M S, Tripathy H K, Mohanty J K, et al. Roasting followed by magnetic separation: A process for beneficiation of titano-magnetite ore[J]. Separation Science & Technology, 2015,50(8):1221−1229. [7] 王伟, 董辉, 赵亮, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿提钒工艺综述[C]//第十届全国能源与热工学术年会. 中国金属学会能源与热工分会, 杭州: 2019.Wang Wei, Dong Hui, Zhao Liang, et al. Review on vanadium extraction from vanadium-titanium magnetite[C]//The 10th National Conference on Energy and Thermal Engineering. Energy and Thermal Engineering Branch of China Metal Society, Hangzhou: 2019. [8] Xi Gan, Lei Ying, Hu Kejun, et al. Application of vanadium abroad[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2000,(2):13−21. (锡淦, 雷鹰, 胡克俊, 等. 国外钒的应用概况[J]. 世界有色金属, 2000,(2):13−21. [9] 范鑫. 稀土掺杂改性水热合成纳米V2O5及在硫酸钒催化剂中的应用[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2019.Fan Xing. Hydrothermal synthesis of nano-V2O5 doped with Rare earth and its application in vanadium sulfate catalyst[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2019. [10] Qu Mingjun, Zhu Quanfang. Analysis of vanadium catalyst heating up and blowing in sulphuric acid plant[J]. Sulfuric Acid Industry, 2018,(11):20−22. (瞿明军, 朱全芳. 浅谈硫酸装置钒催化剂的升温和吹除[J]. 硫酸工业, 2018,(11):20−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1507.2018.11.007 [11] Gao Yongzhang. Analysis of vanadium ore resources and supply and demand situation in China[J]. China Mining, 2019,28(z2):5−10. (高永璋. 中国钒矿资源及供需形势分析[J]. 中国矿业, 2019,28(z2):5−10. [12] Sun H Y, Adetoro A A, Pan F, et al. Effects of high-temperature preoxidation on the titanomagnetite ore structure and reduction behaviors in fluidized bed[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2017,48(3):1898−1907. doi: 10.1007/s11663-017-0925-9 -




 下载:
下载: