Effects of phase structure of vanadium slags with different calcium content on calcified vanadium extraction
-
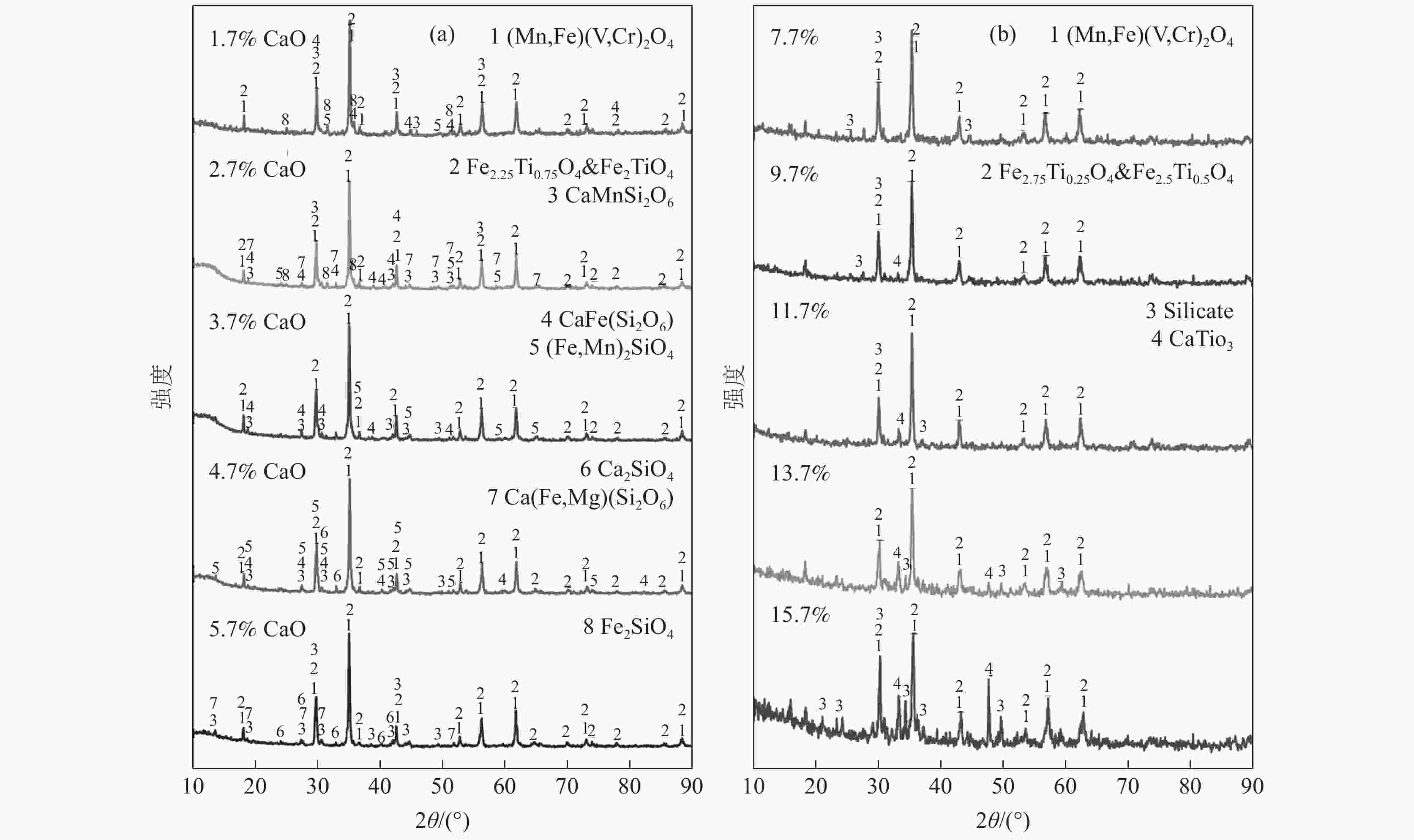
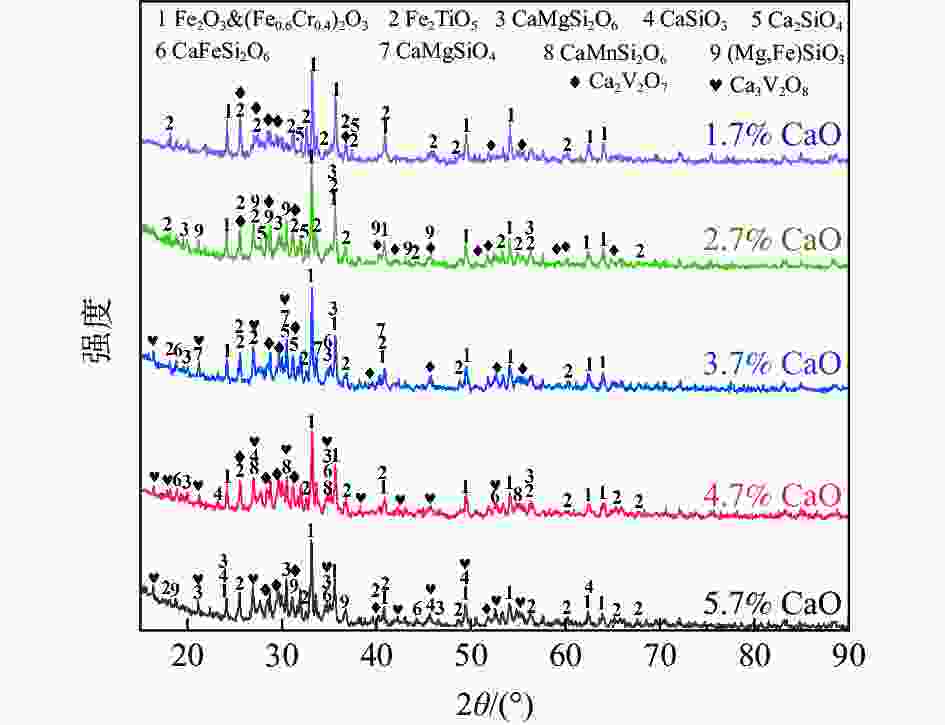
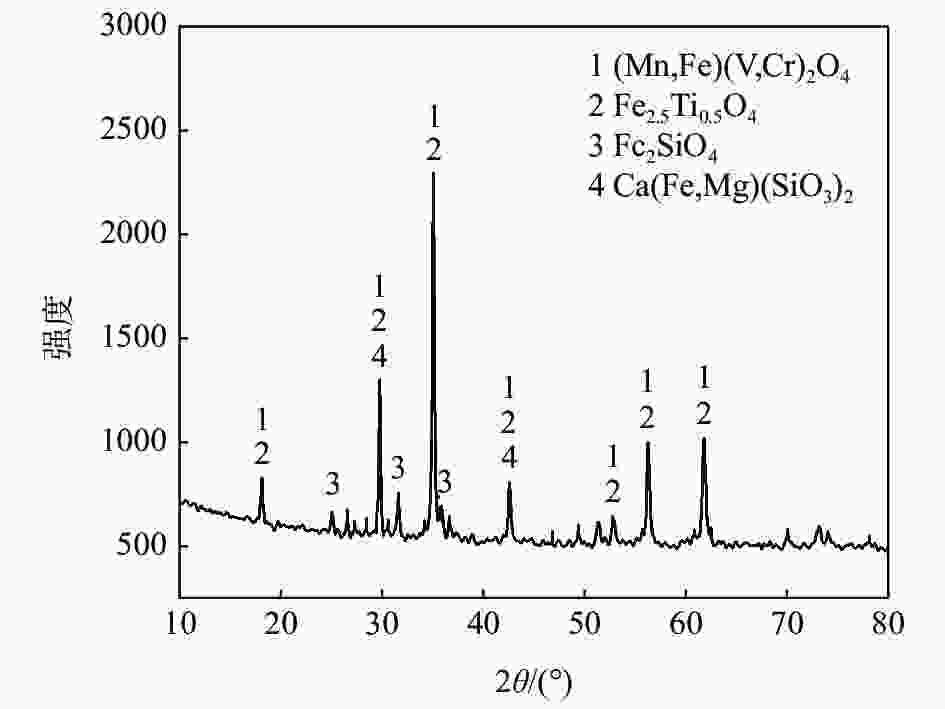
摘要: 以钙含量较低的西昌钒渣为基准,向其中添加不同含量CaO并重熔结晶得到不同钙含量的钒渣,利用XRD和SEM-EDS分析方法探究钒渣物相组成和微观结构随其钙含量变化的演变规律,查明不同钙含量钒渣钙化焙烧熟料的物相变化及对钒浸出率的影响。结果表明:随钒渣中CaO质量分数升高,尖晶石晶粒尺寸逐渐增大,橄榄石相Fe2SiO4逐渐转变为Ca2SiO4。当CaO含量升高至9.7%时,部分钛由钛铁尖晶石转移到钙钛矿。进一步升高CaO含量至13.7%时,尖晶石出现明显不规则化,且硅酸盐相逐渐复杂化。钙含量较低钒渣的钙化焙烧产物主要为焦钒酸钙,当钙含量超过3.7%后正钒酸钙开始生成。钙含量为2.7%的钒渣熟料钒浸出率最高为87.52%,进一步增加钙含量,钒浸出率略有下降,此时钒渣中原有的钙含量对钙盐焙烧添加剂用量和钒浸出率将产生影响。Abstract: In this paper, the vanadium slags with different calcium contents were obtained by remelting and crystallizing the mixture of CaO and Xichang vanadium slag with low-CaO contents. The changes of phase and micromorphology of vanadium slags with different calcium contents were observed by XRD and SEM-EDS. Furthermore, the law of phase changing of roasted samples and the impact on vanadium leaching rate were explored. The results showed that as the CaO mass fraction in vanadium slags rose, the spinel size gradually increased, and the olivine phase Fe2SiO4 gradually changed to Ca2SiO4. When the CaO content rose to 9.7%, part of Ti began to transfer from spinel to CaTiO3. When the CaO content further rose to 13.7%, the spinel shape became irregular, and the silicate was gradually complicated. V was produced as Ca2V2O7 for low-calcium contents in vanadium slags after calcification roasting. As the calcium content rose to 3.7%, Ca3V2O8 gradually generated. The highest vanadium leaching rate was 87.52% when the calcium content was 2.7%. As calcium content increased further, the vanadium leaching rate decreased slightly. The calcium contents in vanadium slags would influence the amount of calcium salt additives during the calcium roasting process and the vanadium leaching rate at this point.
-
Key words:
- vanadium slag /
- the calcium content /
- phase changes /
- micromorphology /
- calcified vanadium extraction
-
表 1 西昌钒渣化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of XCVS
% FeO V2O3 CaO Cr2O3 TiO2 SiO2 MnO 总计 38.19 15.44 1.70 1.42 14.6 13.16 9.90 94.41 -
[1] Fontana, Mars G. Vanadium alloy oxidation corrosion[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 1950,42(10):65−68. [2] Li Y, Mitchell P S, 龚维幂. 钒在钢中的应用[C]// 中国金属学会2003中国钢铁年会论文集. 北京: 中国金属学会, 2003: 2708−2712.Li Y, Mitchell P S, Gong Weimi. Use of vanadium in steel[C]// CMS 2003 annual meeting proceedings. Beijing: CMS, 2003: 2708−2712. [3] Moskalyk R R, Alfantazi A M. Processing of vanadium: A review[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2003,16(9):793−805. doi: 10.1016/S0892-6875(03)00213-9 [4] Hayes E. Chromium and vanadium[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 1961,53(2):105−107. [5] Jae-chun Lee, Kurniawan, Eun-young Kim, et al. A review on the metallurgical recycling of vanadium from slags: towards a sustainable vanadium production[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2021,12:343−364. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.02.065 [6] Chen Donghui. Annual evaluation for vanadiumindustry in 2018[J]. Hebei Metallurgy, 2019,(8):5−15. (陈东辉. 钒产业2018年年度评价[J]. 河北冶金, 2019,(8):5−15. [7] Jiang Tao, Wen Jing, Zhou Mi, et al. Phase evolutions, microstructure and reaction mechanism during calcification roasting of high chromium vanadium slag[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 742: 402-412. [8] Wen Jing, Jiang Tao, Zheng Xiaole, et al. Efficient separation of chromium and vanadium by calcification roasting–sodium carbonate leaching from high chromium vanadium slag and V2O5 preparation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020,230:115881. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115881 [9] Wen Jing, Jiang Tao, Liu Yajing, et al. Extraction behavior of vanadium and chromium by calcification roasting-acid leaching from high chromium vanadium slag: Optimization using response surface methodology[J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 2019,40(1):56−66. doi: 10.1080/08827508.2018.1481059 [10] 高官金. 高铬钒渣综合利用研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院过程工程研究所), 2017.Gao Guanjin. Study on comprehensive utilization of high-chromium vanadium slag[D]. Beijing:The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. [11] Yu Liang, Dong Yuanchi, Ye Guozhu, et al. Concentrating of vanadium oxide in vanadium rich phase(s) by addition of SiO2 in converter slag[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2007,34(2):131−137. [12] Feng Guangxi, He Jinqiu, Huang Xiangyu, et al. Study on vanadium extraction of high calcium vanadium containing slag by carbonation[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Science and Technology, 1979,(1):1−18. (冯光熙, 何晋秋, 黄祥玉, 等. 高钙含钒炉渣碳酸化提钒之研究[J]. 成都科技大学学报, 1979,(1):1−18. [13] 付自碧. 高钙高磷钒渣制备氧化钒工艺研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院过程工程研究所), 2017.Fu Zibi. Technological research on preparation of vanadium oxide from high calcium and high phosphorus vanadium slag[D]. Beijing: The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. [14] 余唐霞, 曹婧, 温婧, 等. 钒渣钙化焙烧添加剂选择及工艺优化[J], 材料与冶金学报, 2020, 19(3): 176-184.Yu Tangxia, Cao Jing, Wen Jing, et al. Selection of additives for vanadium slag calcification roasting and process optimization[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2020, 19(3): 176-184. [15] 周旺. 高钙高磷钒渣尖晶石结晶动力学及钒、磷选择性分离的研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2017.Zhou Wang. Investigate on crystallization kinetics of spinels and selective separating vanadium and phosphorus in vanadium slag with high CaO and P2O5 content[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2017. -




 下载:
下载: