Effect of crystallographic orientation on globularization during the rolling of a near α titanium alloy tube
-
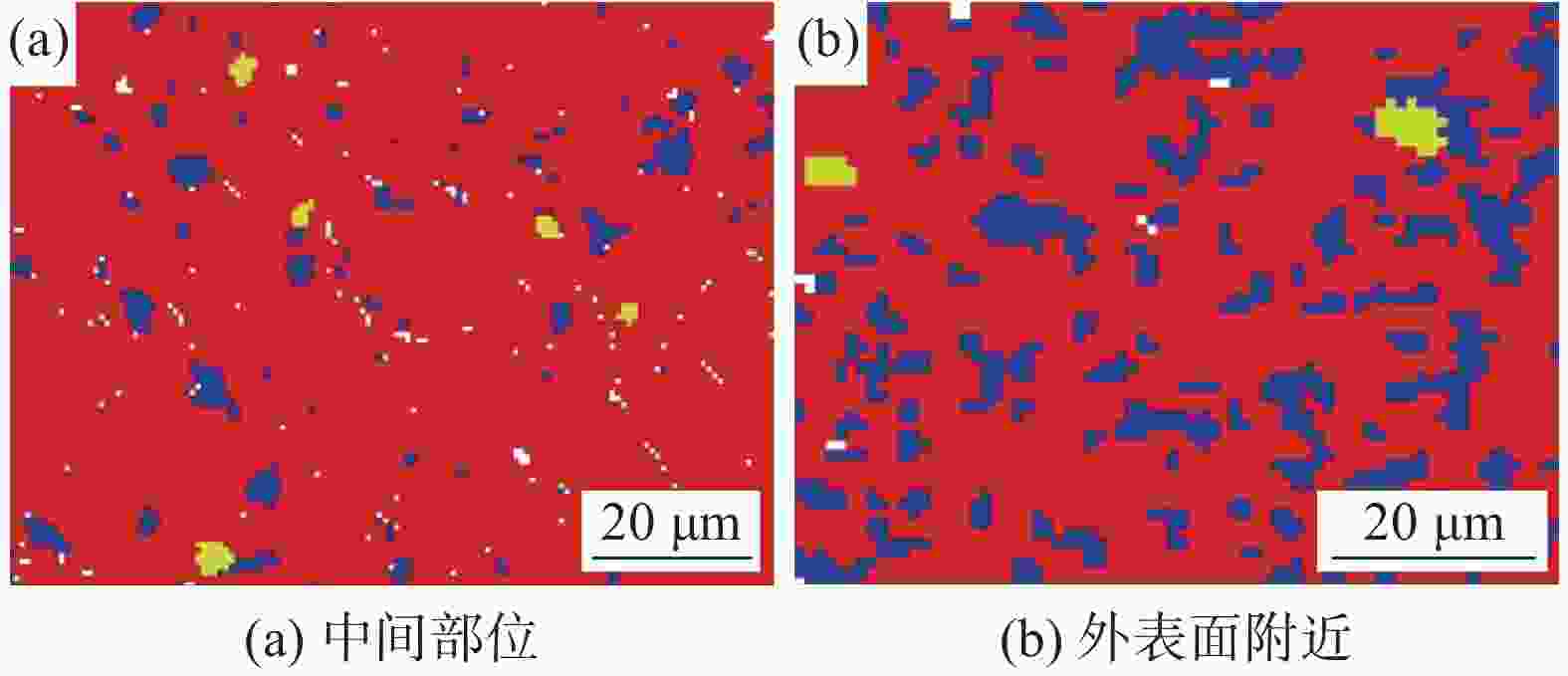
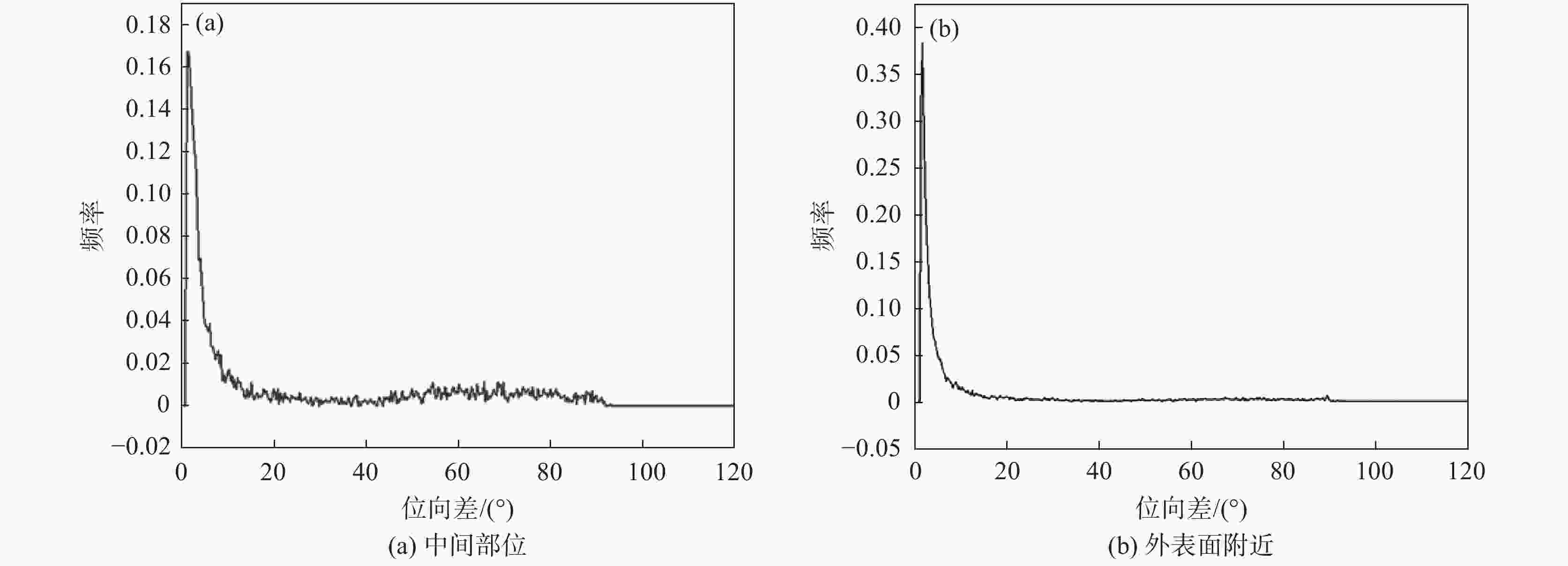
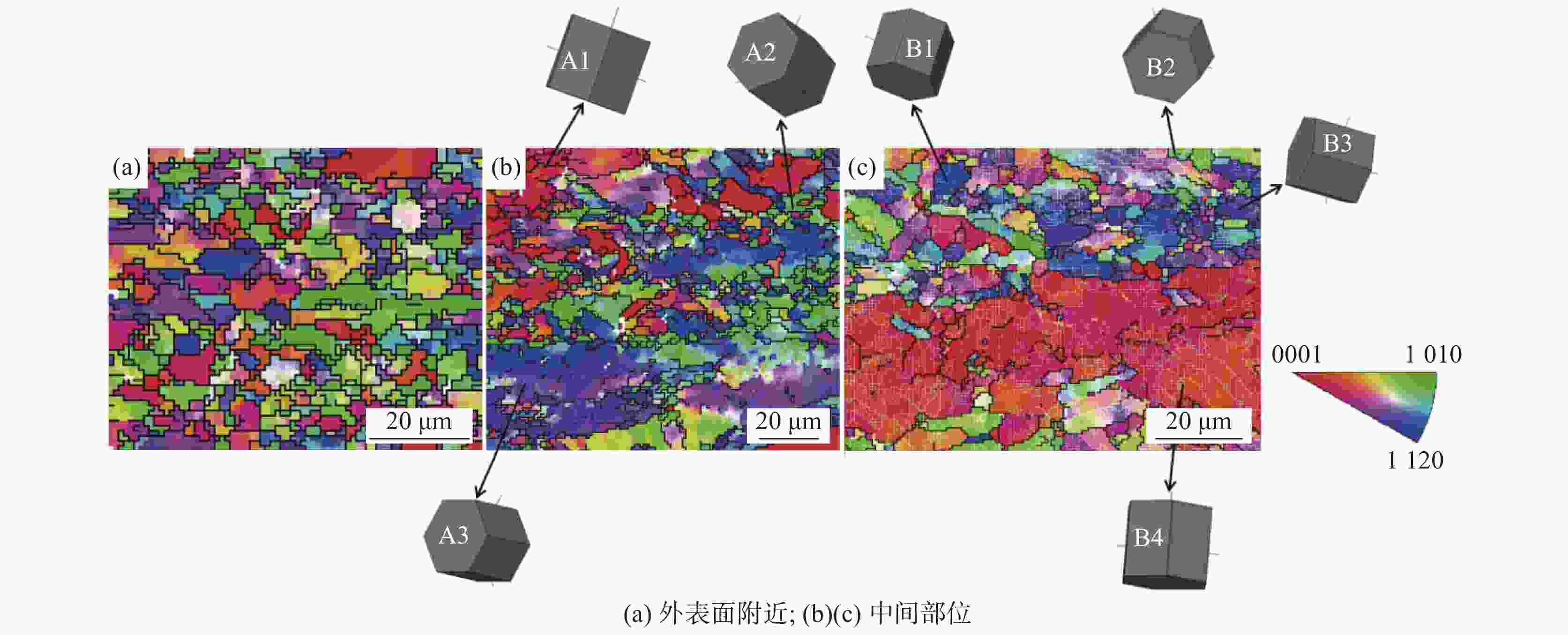
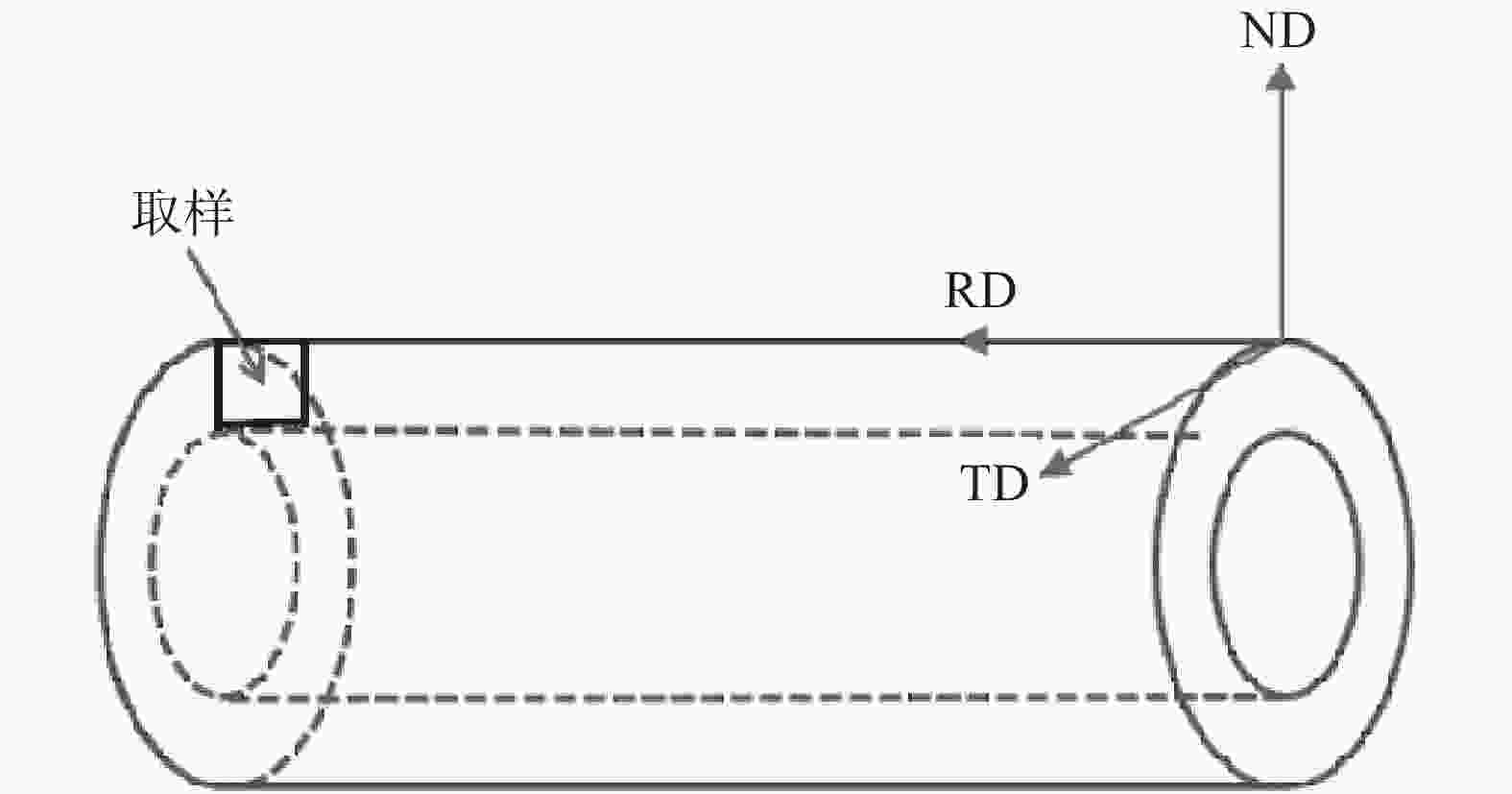
摘要: 研究了一种近α钛合金管在热轧过程中发生的动态球化规律。通过金相组织分析和电子背散射衍射(EBSD)技术对管材外表面附近和中间部位进行观察,结果发现:在热轧过程中,管材外表面附近的α相球化率很高,球化后的组织大角度晶界变多而小角度晶界变少;中间部位的α相球化程度受晶体学位向影响很大。通过计算不同晶体学取向α相的施密特因子,发现基面滑移和柱面滑移在轧向(RD)和弦向(TD)均有较大的施密特因子(>0.3)时,很容易发生球化。当α相仅有一种滑移系且仅在一个方向有较大的施密特因子时,则很难被球化。Abstract: The dynamic globularization of a near α titanium alloy tube during hot rolling was studied by observation of different regions of the pipe using metallographic analysis and electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) technology. The results showed that the fraction of globularized α phases near the outer surface of the tube was very high. After globularization, the large-angle grain boundaries increased and the small-angle grain boundaries decreased. The globularization of the α phases in the middle part was greatly affected by the crystal orientation. The Schmidt factor of α phase in different crystallographic orientations is calculated. It was found that the α phases were more prone to be globularized when the basal slips and prism slips have a larger Schmidt factor (> 0.3) in the rolling direction (RD) and transverse direction (TD), respectively. The globularization would be difficult when the α phase has only one slip system and the Schmidt factor was high only in one direction.
-
Key words:
- titanium alloys /
- tube /
- hot rolling /
- microstructures /
- globularization /
- crystallographic orientations
-
表 1 钛合金管材的实测成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of Ti80 pipe
% Ti Al Nb Zr Mo Si Fe C N O 87.614 6.12 3.1 2.07 0.94 0.03 0.02 0.005 0.001 0.10 表 2 不同晶粒在不同应变方向下的施密特因子
Table 2. Schmidt factors of different grains in different strain directions
滑移系 施密特因子 A1 A2 A3 B1 B2 B3 B4 基面滑移
{0001}RD 0.32 0.08 0.06 0.28 0.05 0.34 0.02 TD 0.35 0.34 0.10 0.37 0.36 0.27 0.05 柱面滑移
{10-10}RD 0.42 0.49 0.31 0.45 0.46 0.31 0.19 TD 0.50 0.28 0.20 0.40 0.08 0.41 0.45 -
[1] Boyer R R. An overview on the use of titanium in the aerospace industry[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1996,213(1−2):103−114. doi: 10.1016/0921-5093(96)10233-1 [2] Schutz R W, Watkins H B. Recent developments in titanium alloy application in the energy industry[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998,243(1−2):305. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5093(97)00819-8 [3] Gorynin I V. Titanium alloys for marine application[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999,263:112−116. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5093(98)01180-0 [4] Li Baoxia, Li Hongbo, Zhao Fuqiang, et al. Study on technology of large size TC4 seamless pipe[J]. Nonferrous Metals Processing, 2018,47(5):47−49. (李宝霞, 李红博, 赵富强. 大规格TC4无缝管材工艺研究[J]. 有色金属加工, 2018,47(5):47−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6795.2018.05.011 [5] Salem A A, Glavicic M G, Semiatin S L. The effect of preheat temperature and interpass reheating on microstructure and texture evolution during hot-rolling of Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008,496:169−176. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2008.05.017 [6] Bantounas I, Dye D, Lindley T C. The role of microtexture on the faceted fracture morphology in Ti–6Al–4V subjected to high-cycle fatigue[J]. Acta Materialia, 2010,58:3908−3918. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2010.03.036 [7] Humbert M, Germain L, Gey N. Study of the variant selection in sharp textured regions of bimodal IMI 834 billet[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006,430:157−164. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.05.047 [8] Zhu Zhishou, Wang Qingru, Zheng Yongling. Quasi-β forging processing of titanium alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2002,38:382−384. (朱知寿, 王庆如, 郑永灵. 准β锻造钛合金的组织与性能研究[J]. 金属学报, 2002,38:382−384. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2002.z1.117 [9] Lütjering G, Albrecht J, Sauer C, et al. The influence of soft, precipitate-free zones at grain boundaries in Ti and Al alloys on their fatigue and fracture behavior[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007,470:201−209. [10] Song Hongwu, Zhang Shihong, Cheng Ming. Dynamic globularization kinetics during hot working of a two phase titanium alloy with a colony alpha microstructure[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009,480:922−927. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.02.059 [11] Semiatin S L, Seetharaman V, Weiss I. Flow behavior and globularization kinetics during hot working of Ti-6Al-4V with a colony alpha microstructure[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999,263:257−271. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5093(98)01156-3 [12] Park C H, Won J W, Park J W. Mechanisms and kinetics of static spheroidization of hot-worked Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo-0.1Si with a lamellar microstructure[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2012,43:977−985. doi: 10.1007/s11661-011-1019-y [13] Bieler T R, Semiatin S L. The origins of heterogeneous deformation during primary hot working of Ti–6Al–4V[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2002,18:1165−1189. doi: 10.1016/S0749-6419(01)00057-2 [14] Roy S, Suwas S. Microstructure and texture evolution during sub-transus thermomechanical processing of Ti-6Al-4V-0.1B alloy: Part I. Hot rolling in (α+β) phase field[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2013,44:3303−3321. doi: 10.1007/s11661-013-1672-4 [15] Roy S, Suwas S. The influence of temperature and strain rate on the deformation response and microstructural evolution during hot compression of a titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V-0.1B[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013,548:110−125. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.08.123 [16] Roy S, Suwas S. Orientation dependent spheroidization response and macro-zone formation during sub β-transus processing of Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2017,134:283−301. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2017.04.071 [17] Shi Jiaxin, Yu Wei, Dong Entao. Hot continuous-rolling process for Ti alloy seamless pipe and its application[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2019,42:43−47. (史佳新, 余伟, 董恩涛. 钛合金无缝管热连轧工艺及应用[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2019,42:43−47. [18] Wang L, Fan X G, Zhan M, et al. The heterogeneous globularization related to crystal and geometrical orientation of two-phase titanium alloys with a colony microstructure[J]. Materials and Design, 2020,186:108338. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108338 -




 下载:
下载: