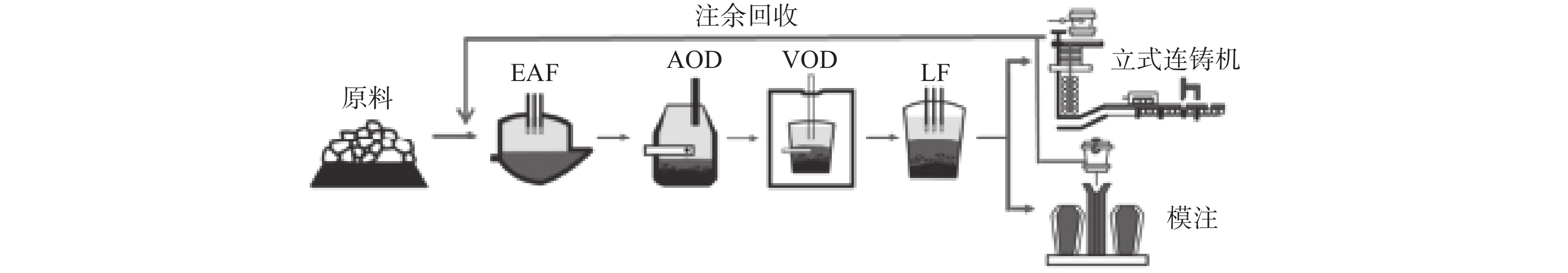
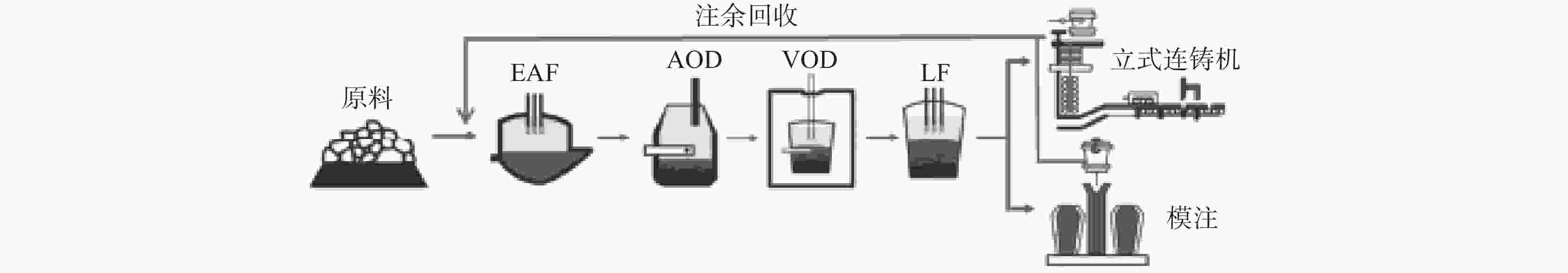
Test on the hot utilization of stainless steel refining slag in EAF
-
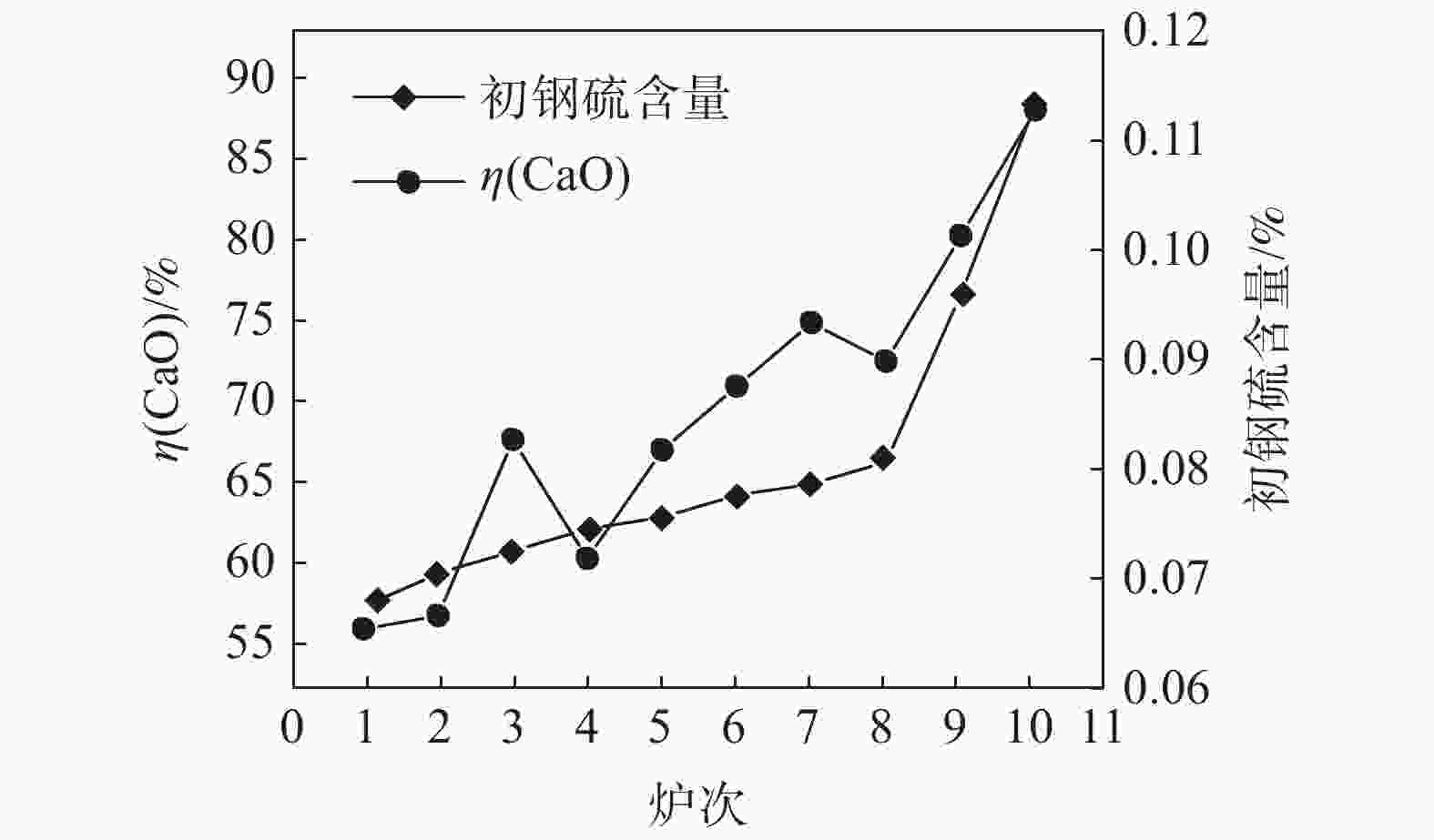
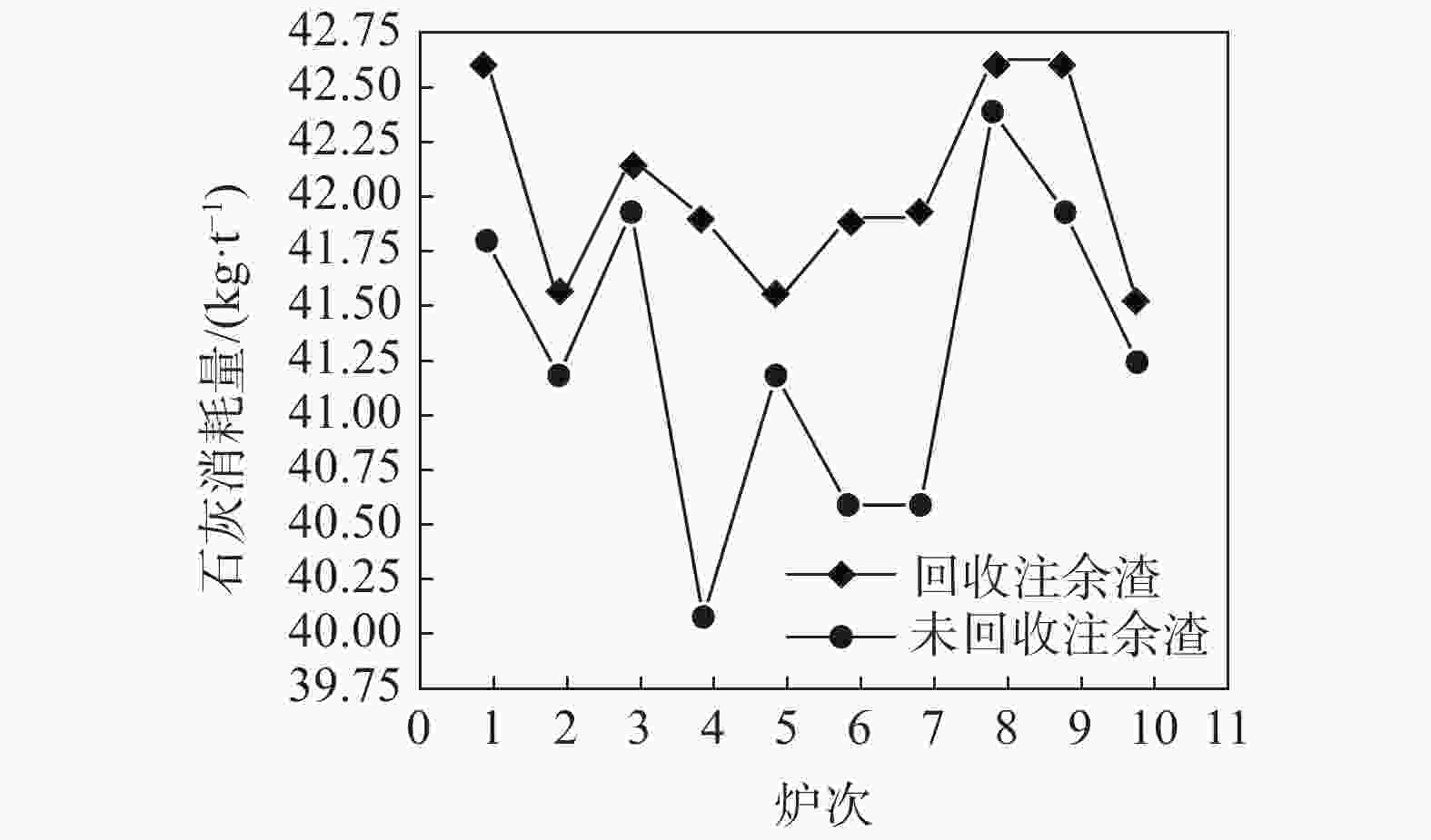
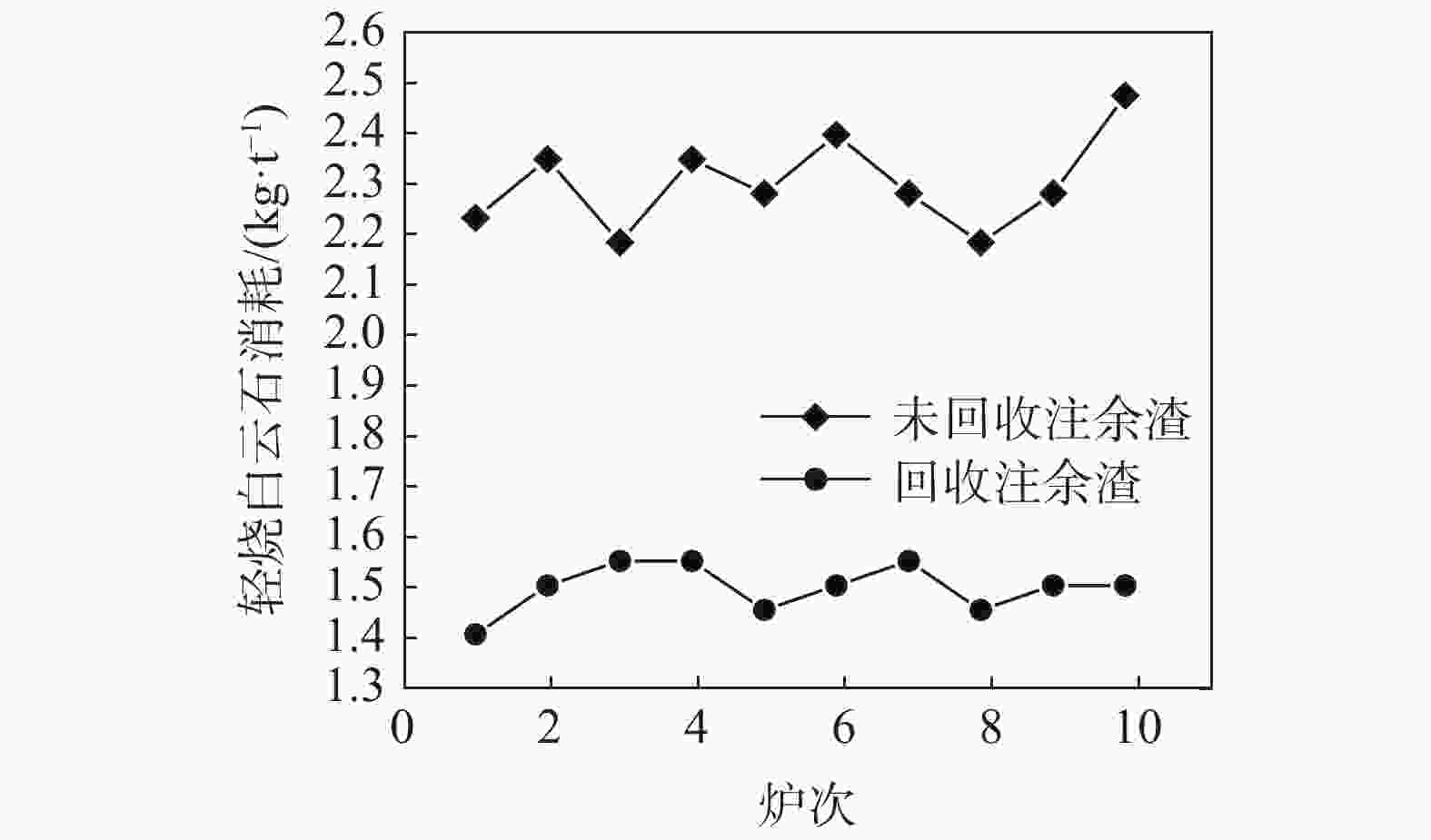
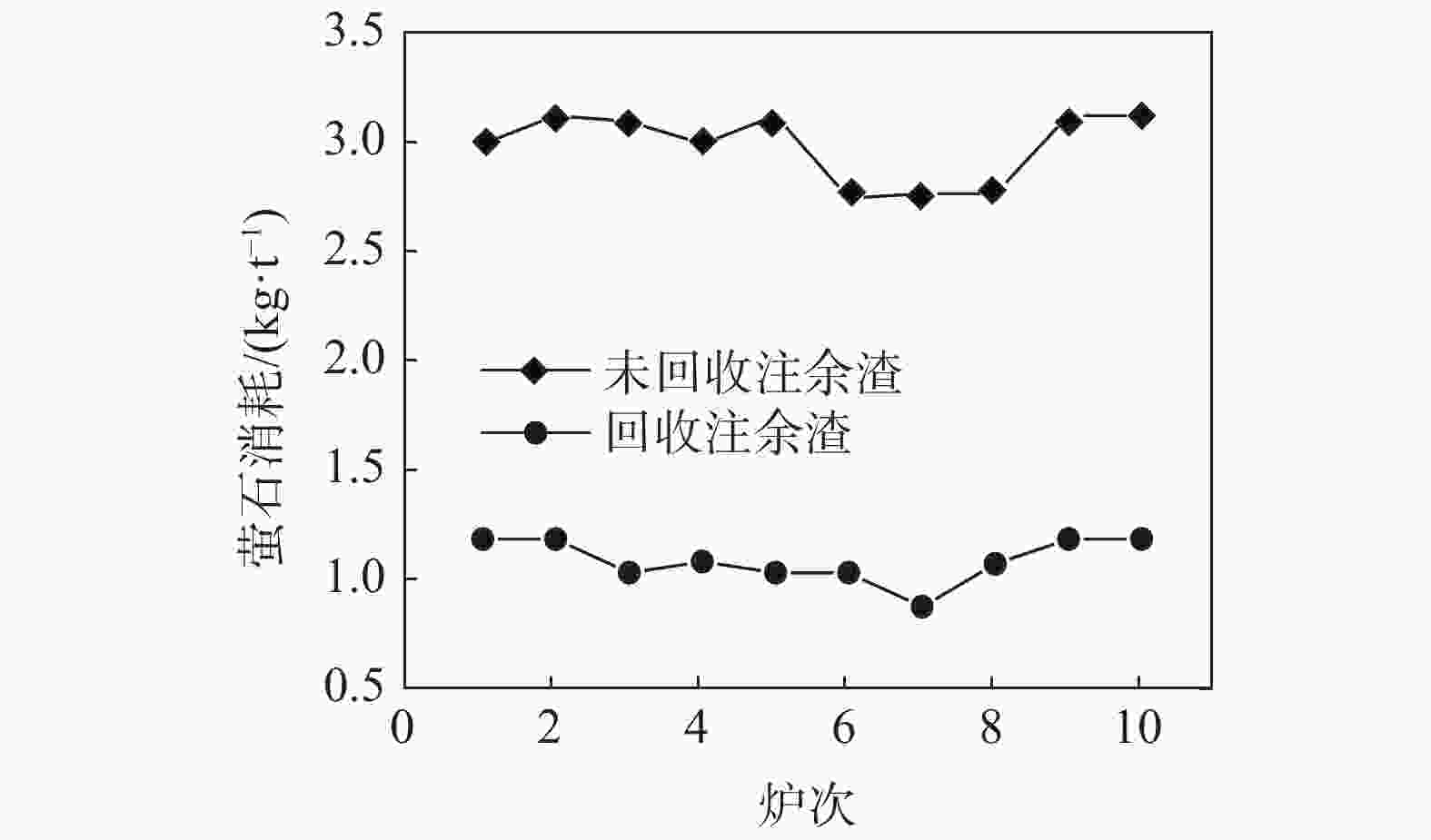
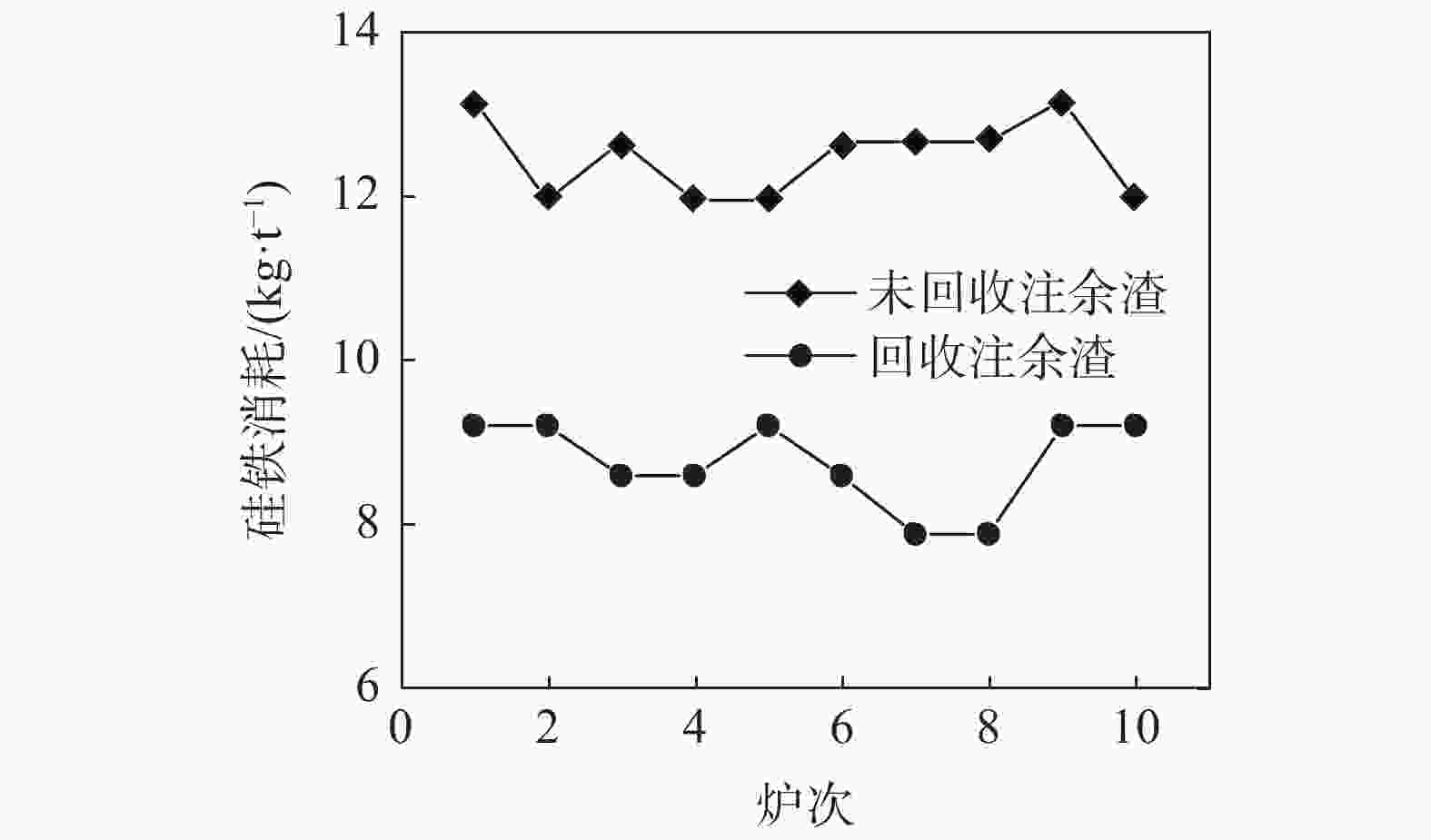
摘要: 在不锈钢精炼渣热态利用性质分析基础上,结合电炉为钢水粗炼、电能熔炼特点,开展了热态注余渣在电炉冶炼利用的试验研究。试验研究表明,电炉利用热态注余渣不仅有助于高碱度液渣快速形成,提高脱硫效率,降低石灰消耗3 kg/t,降低轻烧白云石1.2 kg/t,降低萤石消耗1.8 kg/t;而且回收了注余渣余热,吨钢电耗降低5~10 kWh,同时改善了EAF冶炼条件,降低了钢水氧化损耗,降低还原硅铁消耗1.5~2 kg/t,缩短了冶炼时间3~5 min/炉。就钢渣资源利用、节能减排方面,该研究成果对精炼渣利用发展具有借鉴作用。Abstract: Based on the analysis on hot utilization of stainless steel refining slag, considering the characteristics of electric furnace which it is primary steelmaking process and using electric power, a test on hot pouring residual utilization in electric furnace had been carried out. It is found out that hot pouring residual utilization in electric furnace can not only promote the rapid formation of high basicity slag and improve desulfurization efficiency, but also recycle waste heat and reduce power consumption. After hot utilization, the consumption of lime is reduced by 3 kg/t and lightly burned dolomite by 1.2 kg/t and fluorite by 1.8 kg/t as well, meanwhile electricity consumption is reduced by 5~10 kWh. Electric furnace conditions is improved significantly, where oxidation loss of molten steel is reduced, the consumption of ferrosilicon is reduced by 1.5~2 kg/t and smelting time is shortened by 3~5 minutes per heat. From the aspects of utilization of steel slag, energy conservation and emissions reduction, this research results can be helpful for the development of refining slag utilization.
-
Key words:
- electric furnace /
- LF refining slag /
- stainless steel /
- pouring residual /
- utilization of waste heat
-
表 1 国内某不锈钢厂LF精炼渣主要成分
Table 1. Main components of a domestic stainless steel factory LF refining slag
w(CaO)/% w(MgO) /% w(Al2O3) /% w(SiO2) /% w(MnO) /% w(FeO) /% R CS 60~67 5~8 2~4 15~20 0.2~0.5 0.3~0.5 3~4.5 0.015~0.25 表 2 EAF回收热态注余渣试验的消耗对比
Table 2. Comparison of consumption in test of recycling hot residual in EAF
试验 用量/(kg·炉−1) 电耗/
(kWh·t−1)冶炼时间/
(min·炉−1)石灰 萤石 轻烧 硅铁 未回收 6500~7500 450~500 350~400 1800~2000 310~330 50~55 回收 6300~6800 150~200 200~250 1300~1500 280~300 48~52 -
[1] Pan Congchao, Guo Peimin, Pang Jianming, et al. Research on six components slag system of stainless slag[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2013,25(7):5−10. (潘聪超, 郭培民, 庞建明, 等. 不锈钢渣六元渣系模型研究[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2013,25(7):5−10. [2] Zhang Yu, Zhang Jian, Zhang Tianyou, et al. Analysis of steel slag treatment technology and waste heat recovery technology[J]. China Metallurgy, 2014,24(8):33−37. (张宇, 张健, 张天有, 等. 钢渣处理与余热回收技术的分析[J]. 中国冶金, 2014,24(8):33−37. [3] Lv Yan, Yang Libin, Lin Lu, et al. Leaching characteristics and affecting factors of total chromium and chromium Ⅵ in chromium-containing special steel slag[J]. Iron and Steel, 2019,54(6):103−108. (吕岩, 杨利彬, 林路, 等. 含铬特殊钢渣中总铬及六价铬浸出特性及影响[J]. 钢铁, 2019,54(6):103−108. [4] Liu Yanqiang, Luo Lei, Zhang Peng, et al. Development of green recycling system of hot slag and molten steel at Shougang Jingtang[J]. China Metallurgy, 2018,28(6):25−31. (刘延强, 罗磊, 张鹏, 等. 首钢京唐热态渣、钢绿色循环利用体系开发[J]. 中国冶金, 2018,28(6):25−31. [5] Wang Zhengjie, Yang Jian, Pan De′an, et al. Present state of stainless steel slag reourses disposal technique[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2015,27(2):1−6. (汪正洁, 杨健, 潘德安, 等. 不锈钢渣资源化利用技术研究现状[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2015,27(2):1−6. [6] Lv Yan, Na Xianzhao, Qi Yuanhong, et al. Harmless treatment of stainless steel EAF slag and its engineering performance for using as cement-base materials[J]. Iron and Steel, 2014,49(4):90−96. (吕岩, 那贤昭, 齐渊洪, 等. 不锈钢EAF渣无害化处置及作为水泥基材料的工程性能[J]. 钢铁, 2014,49(4):90−96. [7] Xu Ying, Zhang Zizi, Wang Bian, et al. Cureing influence factors and mechanism of stainless steel slag in AOD[J]. Iron and Steel, 2017,52(8):43−47. (许莹, 张孜孜, 王变, 等. 不锈钢AOD渣固化效果影响因素及其机理[J]. 钢铁, 2017,52(8):43−47. [8] Feng Xiaoxia, Wang Qi, Tan Bo, et al. Effect of TiO2 in refining slag on inclusions in Ti-ferritic stainless steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(2):108−113. (冯晓霞, 王旗, 谭博, 等. 精炼渣中TiO2对含Ti铁素体不锈钢夹杂物的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(2):108−113. [9] Zhuang Ying, Li Jidong. Prediction model of GA-BP moltem slag activity and deoxidation mechanium of stainless steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2017,27(1):11−18. (庄迎, 李吉东. GA-BP渣系活度预测模型及不锈钢脱氧机理[J]. 中国冶金, 2017,27(1):11−18. [10] Han Shaowei, Guo Jing, Chen Xingrun, et al. Thermodynamics of desulfurization and industrial trials for refining of 304 stainless steel with low basicity slag[J]. Iron and Steel, 2018,53(6):47−52. (韩少伟, 郭靖, 陈兴润, 等. 低碱度渣冶炼304不锈钢脱硫热力学和工业试验[J]. 钢铁, 2018,53(6):47−52. [11] Chen Xingrun, Han Shaowei, Guo Jing, et al. Inclusion evolution of 304 stainless steel produced with different LF refining slag basicity[J]. Iron and Steel, 2019,54(11):40−48. (陈兴润, 韩少伟, 郭靖, 等. 304不锈钢不同精炼钢渣碱度下夹杂物的演变[J]. 钢铁, 2019,54(11):40−48. [12] Ding Guangyou, Xu Zhirong, Shi Cuiwei. Development and application of re-utilization technology of LF hot steel-making slag[J]. Steelmaking, 2006,22(4):12−15. (丁广友, 徐志荣, 史翠微. LF热态钢渣循环再利用技术的开发与应用[J]. 炼钢, 2006,22(4):12−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1043.2006.04.004 [13] Ma Yong, Zhao Chenglin, Chen Zhiwei. LF hot slag was used in desulfurization experiment of molten steel[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Liaoning, 2012,35(6):590−593. (马勇, 赵成林, 陈志威. LF热态铸余钢渣用于钢水脱硫实验[J]. 辽宁科技大学学报, 2012,35(6):590−593. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1048.2012.06.007 [14] Du Yuncong, Yi Yuanrong, Bai Shuqi, et al. Change of occurrence state in carbonation process of LF refing slag[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2020,32(3):195−203. (杜昀聪, 伊元荣, 白书齐, 等. LF精炼渣碳酸化过程Ca赋存状态转变[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2020,32(3):195−203. [15] Sun Zhongqiang, Jiang Maofa, Liang Lianke. Determination of sulfide capacity, sulfur distribution ratio and desulfurization percentage in ladle furnace refining process[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2004,16(3):23−26. (孙中强, 姜茂发, 梁连科. LF精炼过程中顶渣硫容量、分配比和脱硫率的确定[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2004,16(3):23−26. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0963.2004.03.006 [16] Li Taiquan, Bao Yanping, Wu Huajie. Controlling of super-low sulfide of high grade pipeline steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2009,44(5):35. (李太全, 包燕平, 吴华杰. 高级别管线钢超低硫控制研究[J]. 钢铁, 2009,44(5):35. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2009.05.009 [17] Liu Zhennan, Tao Dongping, Yao Chunling, et al. Phase equilibrium study and thermodynamic analysis on secondary refining process of titanium-microalloyed steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2019,31(8):702−711. (刘振楠, 陶东平, 姚春玲, 等. 钛微合金钢炉外精炼相平衡研究与热力学分析[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2019,31(8):702−711. [18] Li Shun, Zhang Gongduo, Li Xiaotang. Experiment for primary heat recovery in dry granulation molten blast furnace slag[J]. Industrial Heating, 2014,43(2):60−62. (李顺, 张功多, 李晓堂. 干式粒化熔渣余热初次回收试验研究[J]. 工业加热, 2014,43(2):60−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1639.2014.02.017 -




 下载:
下载: