FEM analysis and experimental study of microwave assisted separation of vanadium-titanomagnetite
-
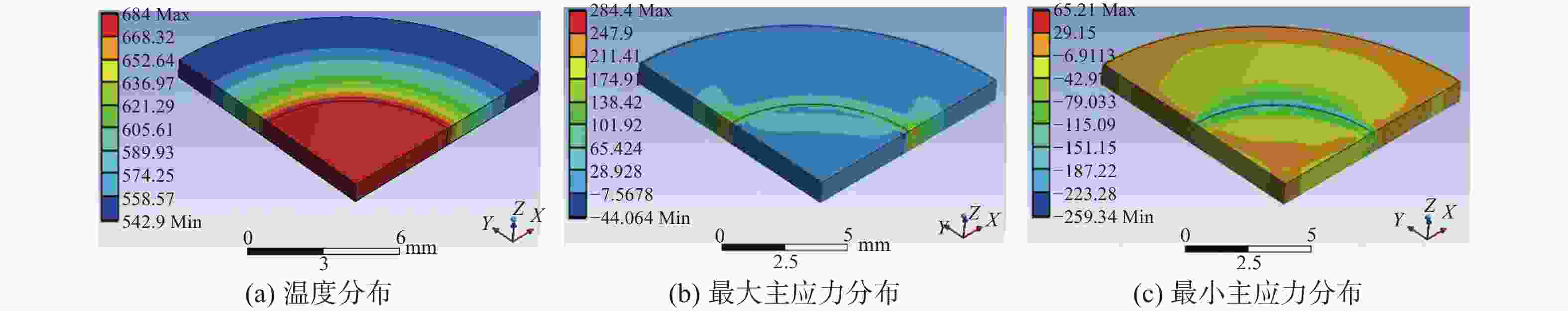
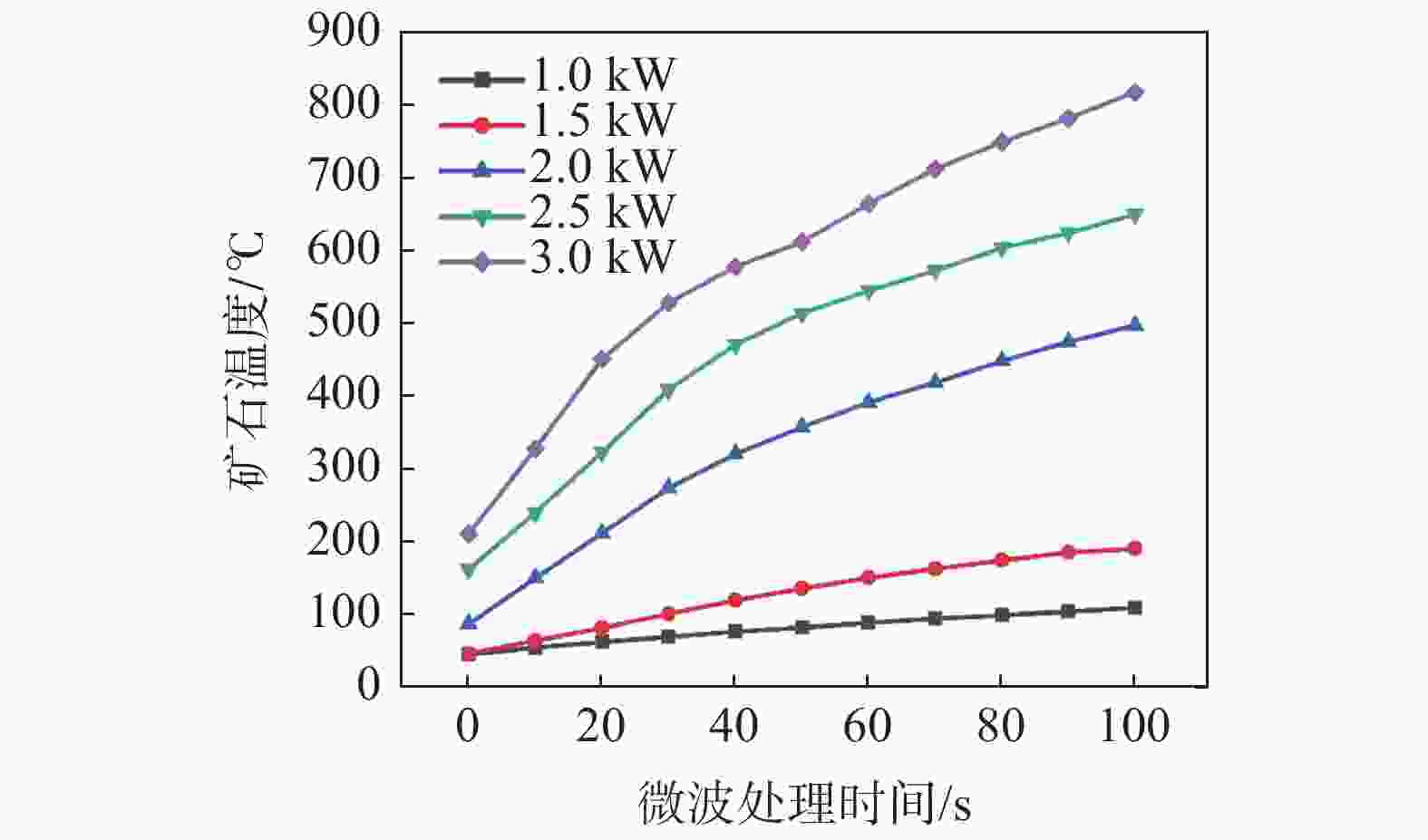
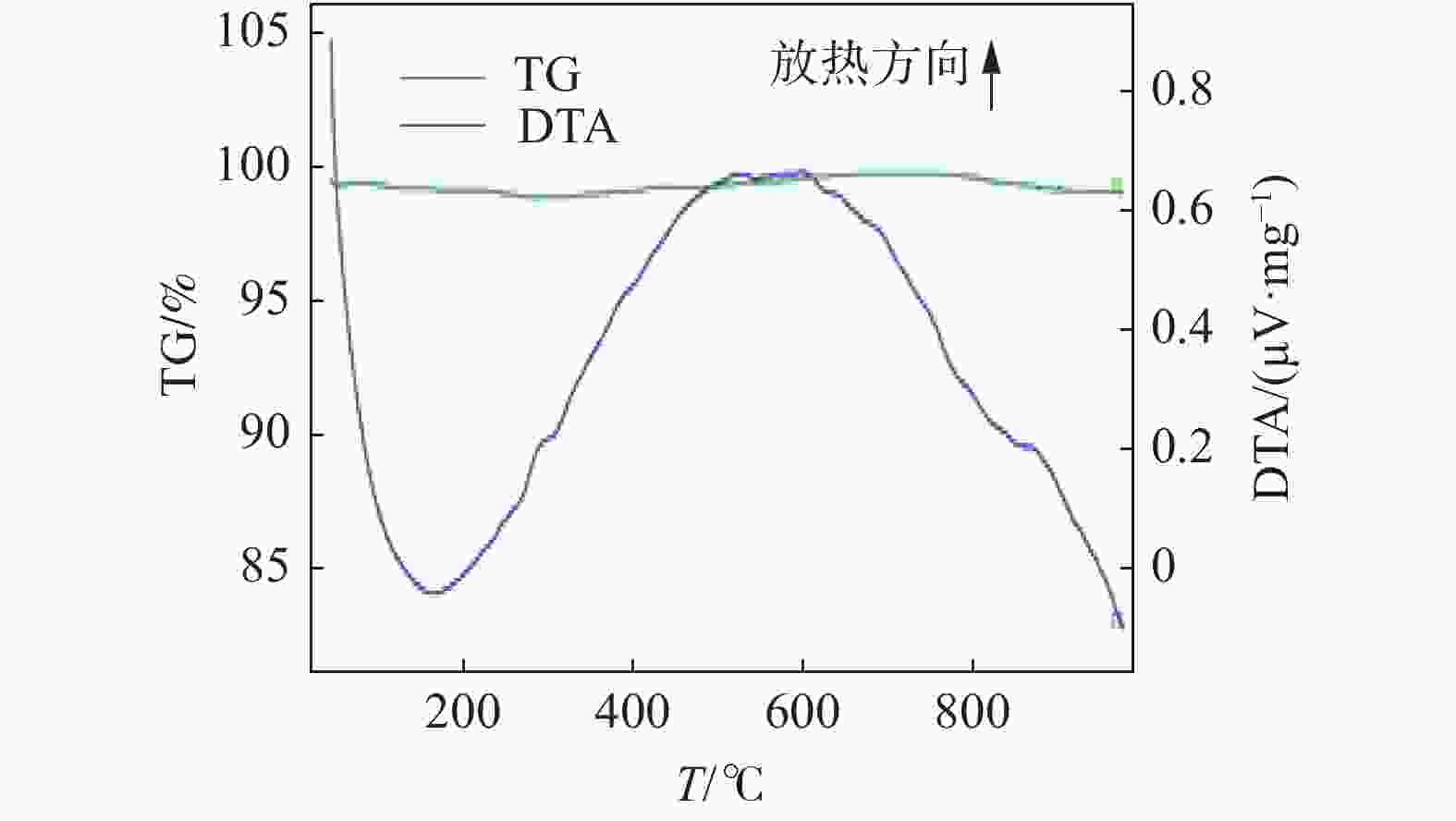
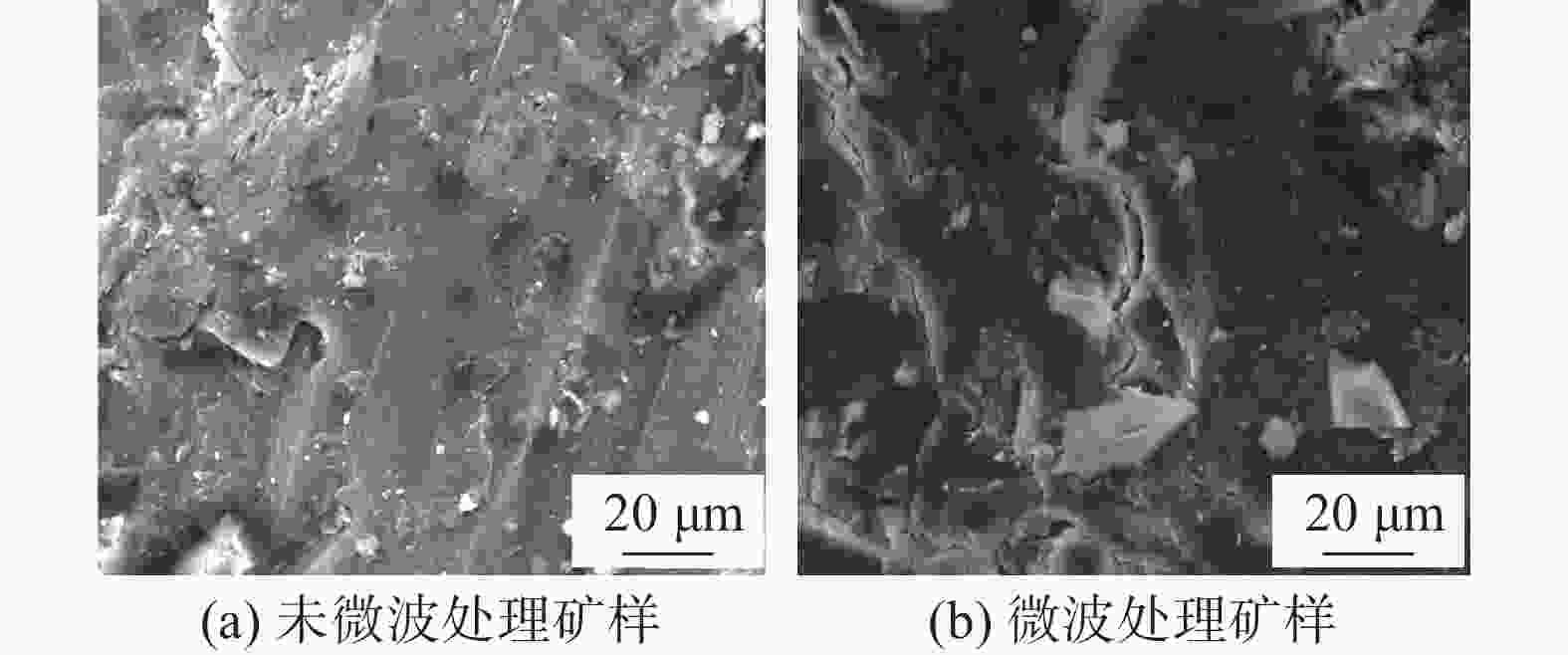
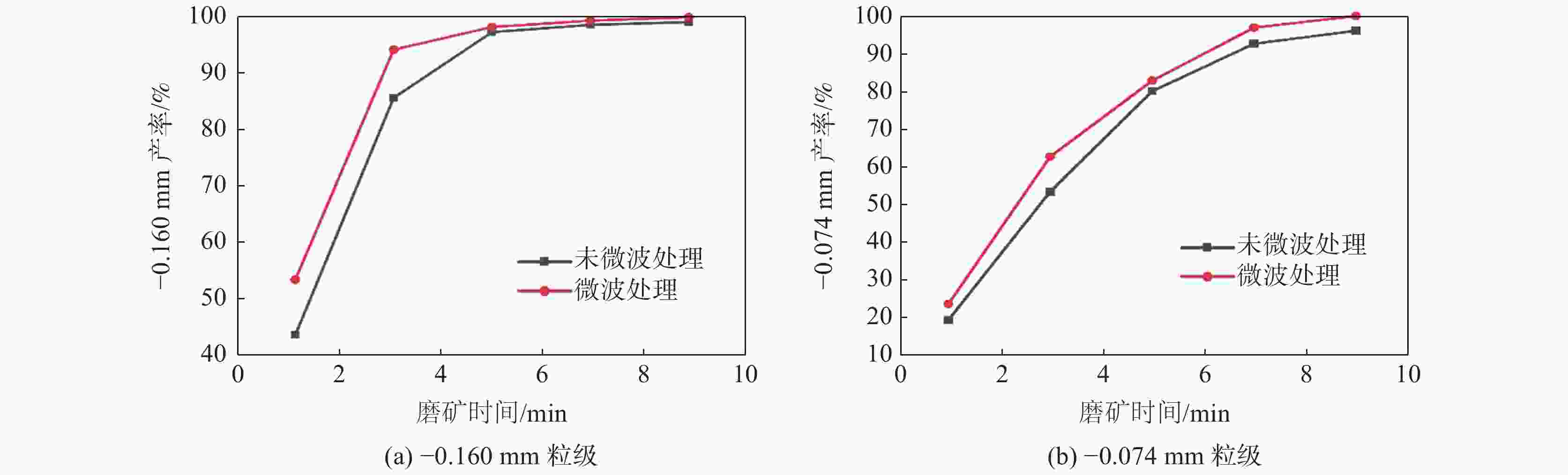
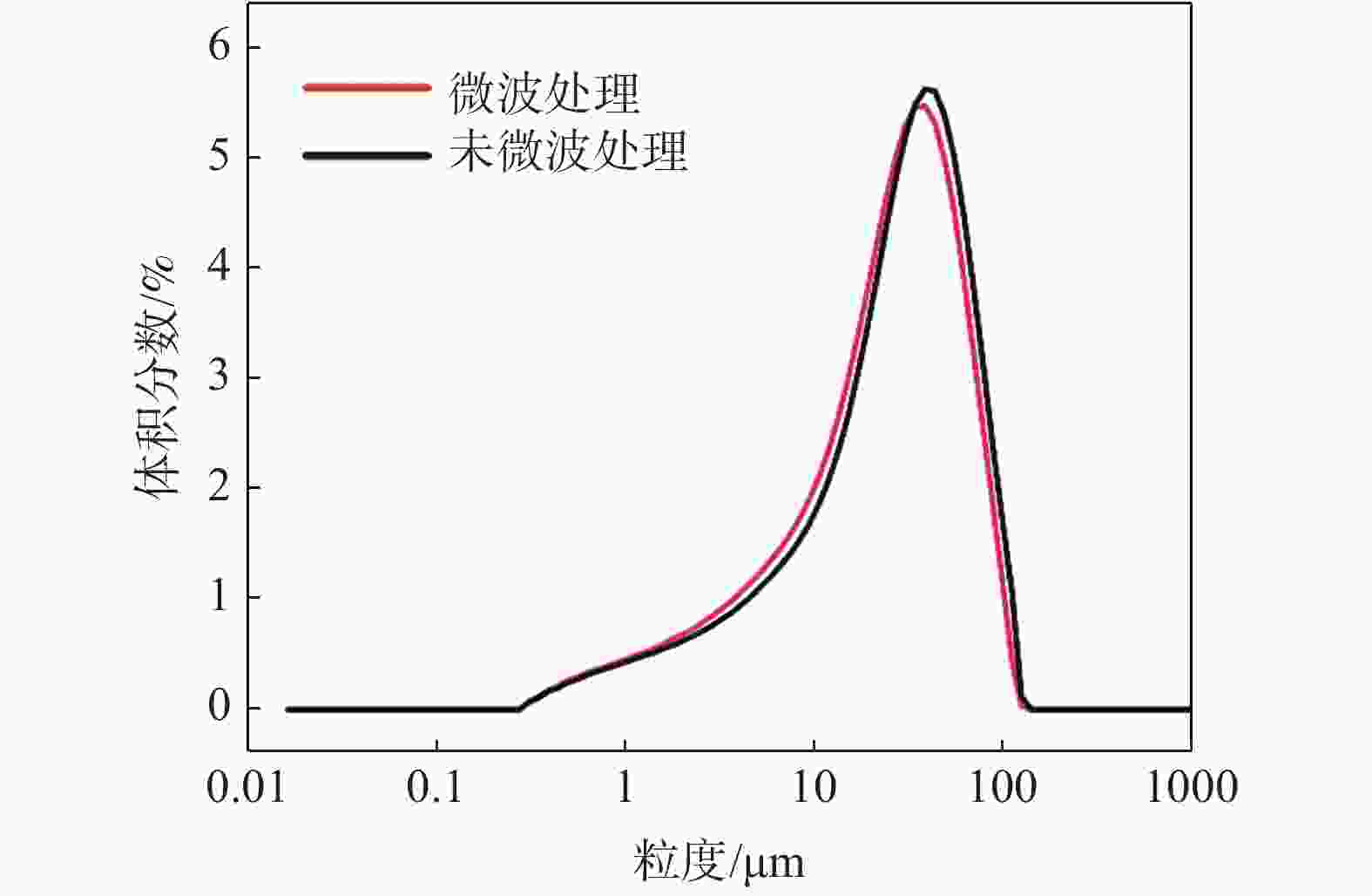
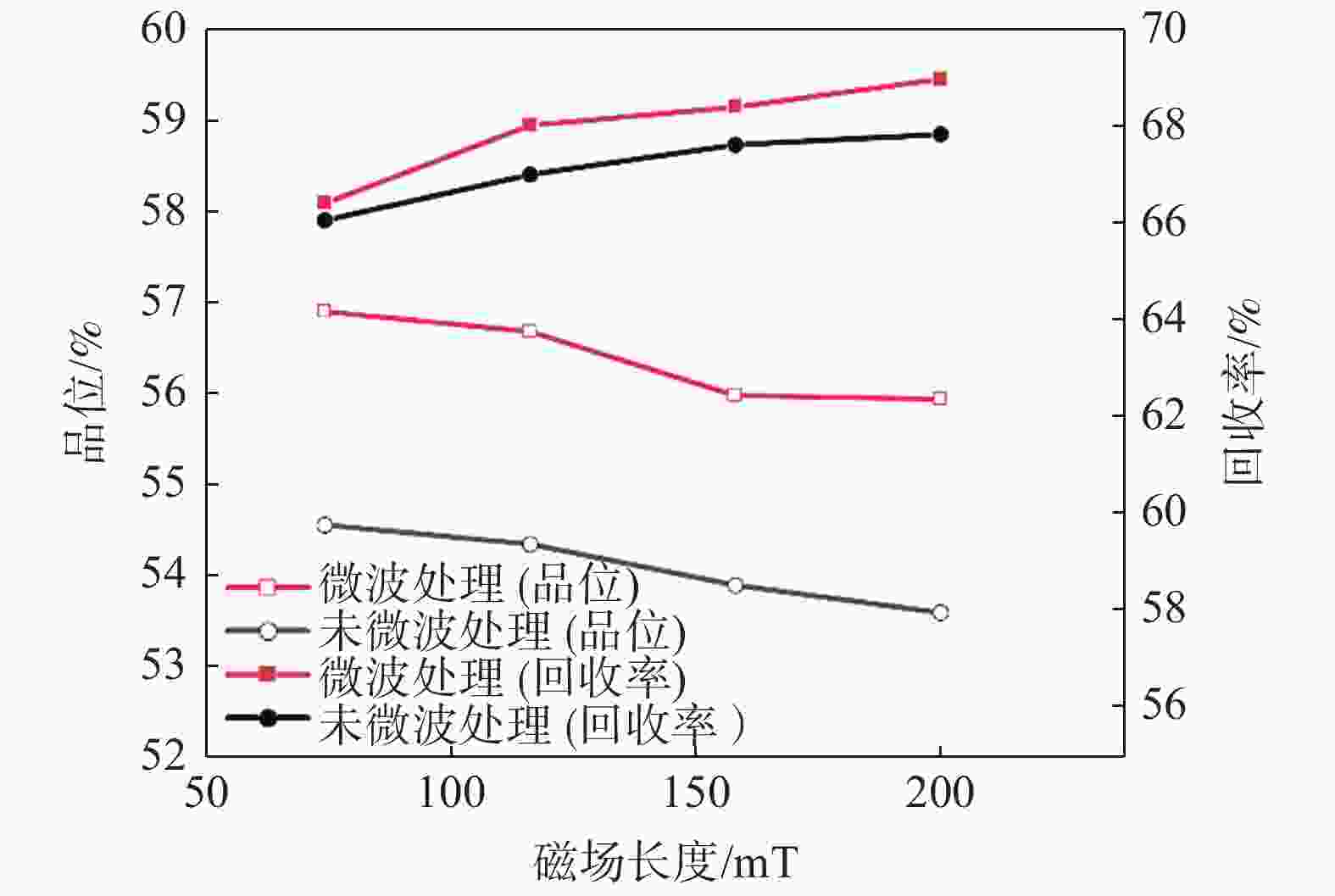
摘要: 以攀西钒钛磁铁矿为研究对象,通过有限元模拟,从理论上进行了微波对其选择性解离的可行性分析,开展了微波功率和处理时间对其解离的影响试验。采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、X射线衍射(XRD)、BET比表面积检测、粒度分析等方法探究了微波处理对钒钛磁铁矿解离特性的影响规律。结果表明,在微波功率3 kW,处理时间40 s的条件下,矿石可快速升温至600 ℃;经微波处理后,矿石内部出现许多明显裂纹,矿石比表面积和孔隙体积分别提高46.04%和83.45%;磨矿产品中−0.160 mm和−0.074 mm粒级的产率可分别提高21.47%和16.68%,邦德磨矿功指数下降8.13%。磁选试验表明,微波处理可使精矿铁品位提高2.34%,铁回收率提高1.13%。由此说明微波处理有助于钒钛磁铁矿的选择性解离,提高选别效果。Abstract: Taking vanadium-titanomagnetite (VTM) from Panxi zone as the investigation object, the feasibility of microwave selective separation of VTM was analyzed theoretically through finite element simulation, and the effects of microwave power and treatment time on its dissociation were investigated. The influence of microwave treatment on the separation characteristics of VTM were studied by using scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), BET specific surface area detection method (BET), particle size analysis and other methods. The results showed that the ore can be rapidly heated up to 600 ℃ under the condition of microwave power of 3 kW and treatment time of 40 s. After microwave treatment, many obvious cracks appeared in the ore, and the specific surface area and pore volume of VTM increased by 46.04% and 83.45%, respectively. The fractions of product with size of −0.160 mm and −0.074 mm in the grinding products increased by 21.47% and 16.68%, respectively, while the Bond grinding work index decreased by 8.13%. The magnetite separation test shows that the iron grade and recovery of concentrate can be increased by 2.34% and 1.13% respectively after microwave treatment. It is demonstrated that microwave treatment is positive to the selective separation of VTM and improve the separation effect.
-
表 1 钒钛磁铁矿的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of the VTM
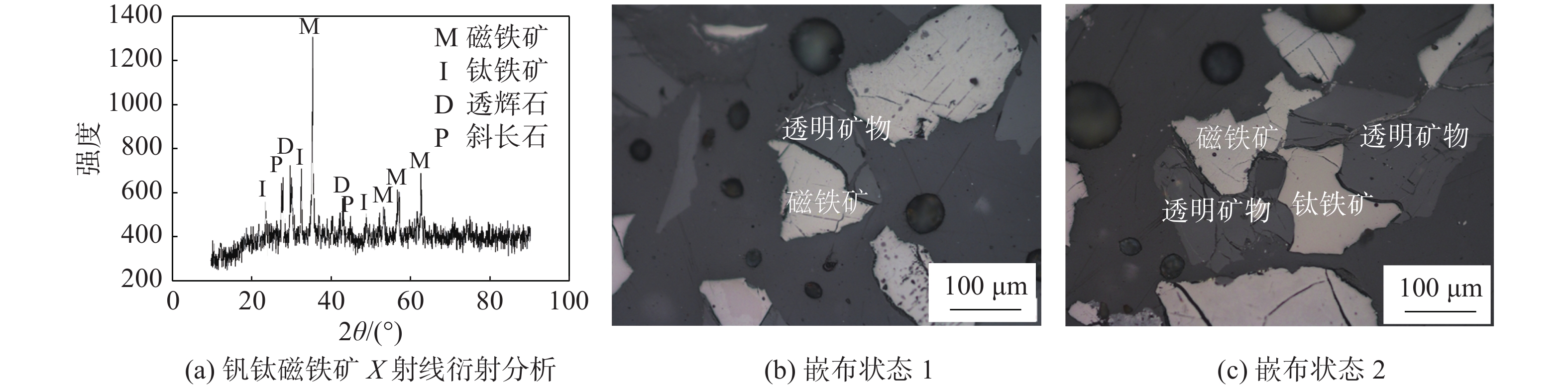
% SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO V2O5 TFe TiO2 25.59 9.94 7.95 6.72 0.35 30.53 11.52 表 2 矿物性能
Table 2. Properties of minerals used is this study
矿物 力学性能 热学性能 密度/(kg·m−3) 杨氏模量/GPa 泊松比 热膨胀系数
α×106热导率/(W·m−1·K−1) 比热容/
(J·kg−1·K−1)磁铁矿 5170 230.3 0.26 18.3 5.30 586.1 透辉石 3277 84.4 0.27 22.0 5.76 711.0 表 3 矿石的比表面积和孔隙体积
Table 3. Specific surface area and pore volume of VTM
样品 比表面积/(m2·g−1) 孔隙体积×103/(cm3·g−1) 未微波处理 0.5858 0.979 微波处理 0.8555 1.796 -
[1] Tromans D. Mineral comminution: energy efficiency considerations[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2008,21(8):613−620. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2007.12.003 [2] 段希祥. 选择性磨矿及其应用[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1991: 32−42.Duan Xixiang. Selective grinding and its application[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1991: 32−42. [3] 金钦汉. 微波化学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1999: 282−291.Jin Qinhan. Microwave chemistry[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1999: 282−291. [4] Stankiewicz A. Energy matters: Alternative sources and forms of energy for intensification of chemical and biochemical processes[J]. Chemical Engineering Research & Design, 2006,84(7):511−521. [5] Wei Z, Chen J, Chang X, et al. Effect of microwave irradiation on selective heating behavior and magnetic separation characteristics of Panzhihua ilmenite[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014,300(1):171−177. [6] Omran M, Fabritius T, Mattila R. Thermally assisted liberation of high phosphorus oolitic iron ore: A comparison between microwave and conventional furnaces[J]. Powder Technology, 2015,269:7−14. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.08.073 [7] Omran M, Fa Britius T, Elmahdy A M, et al. Effect of microwave pre-treatment on the magnetic properties of iron ore and its implications on magnetic separation[J]. Separation & Purification Technology, 2014,136:223−232. [8] Zhang Bo, Qian Gongming, Huang Zili, et al. Experimental study of microwave-acid leaching assisted grinding of oolitic hematite[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017,(5):41−44, 51. (张博, 钱功明, 黄自力, 等. 微波-酸浸方法助磨鲕状赤铁矿研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2017,(5):41−44, 51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2017.05.009 [9] Yang Yushan, Yu Qing, Hu Nan, et al. Heap leaching uranium ore pretreated by microwave radiation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2016,40(3):280−286. (杨雨山, 喻清, 胡南, 等. 微波加热预处理堆浸铀矿石[J]. 稀有金属, 2016,40(3):280−286. [10] Zhao Guojun, Zhao Qibin, Lan Jingzhi, et al. Characteristics of vanadium titanomagnetite resources and new benefication technology in Panxi area[J]. Modern Mining, 2017,33(7):198−200. (赵国君, 赵祺彬, 兰井志, 等. 攀西地区钒钛磁铁矿资源特点及选矿新技术[J]. 现代矿业, 2017,33(7):198−200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2017.07.060 [11] 刘全军, 陈景河. 微波助磨与微波助浸技术[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2005: 39−57.Liu Quanjun, Chen Jinghe. Microwave assisted grinding and microwave assisted leaching technology[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2005: 39−57. -




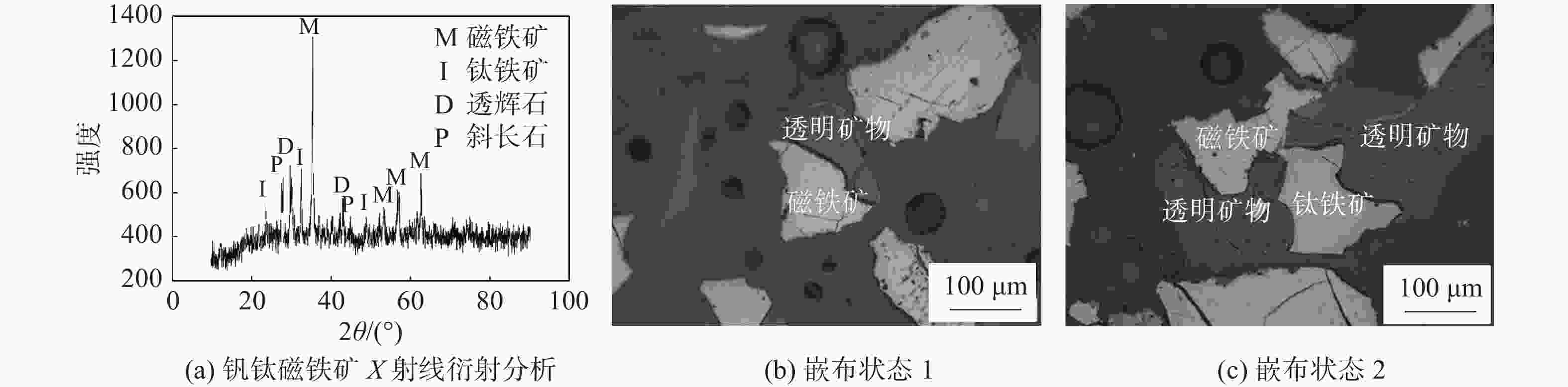
 下载:
下载: