Numerical simulation on interfacial behavior and mixing phenomena in three-phase argon-stirred ladles
-
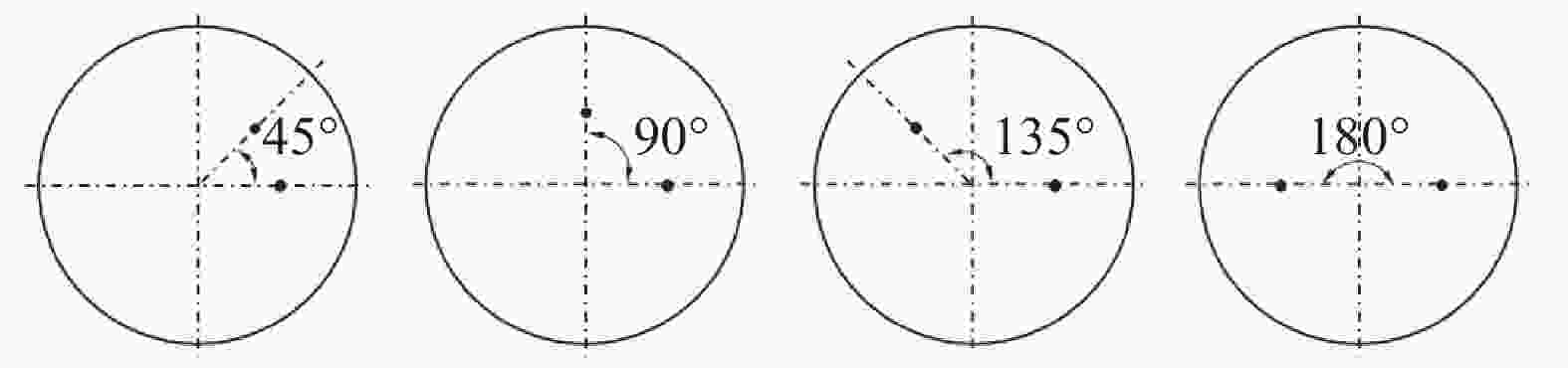
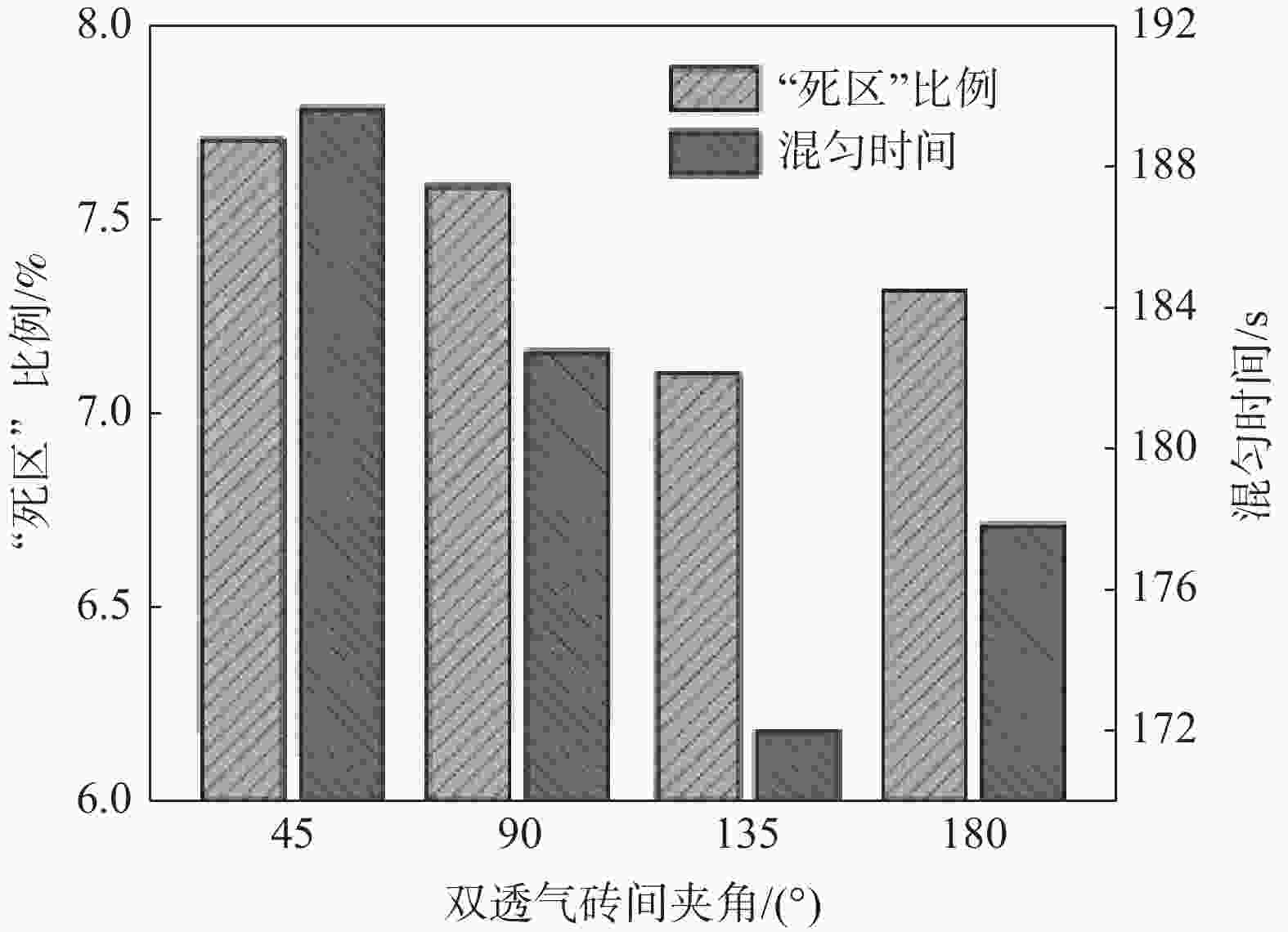
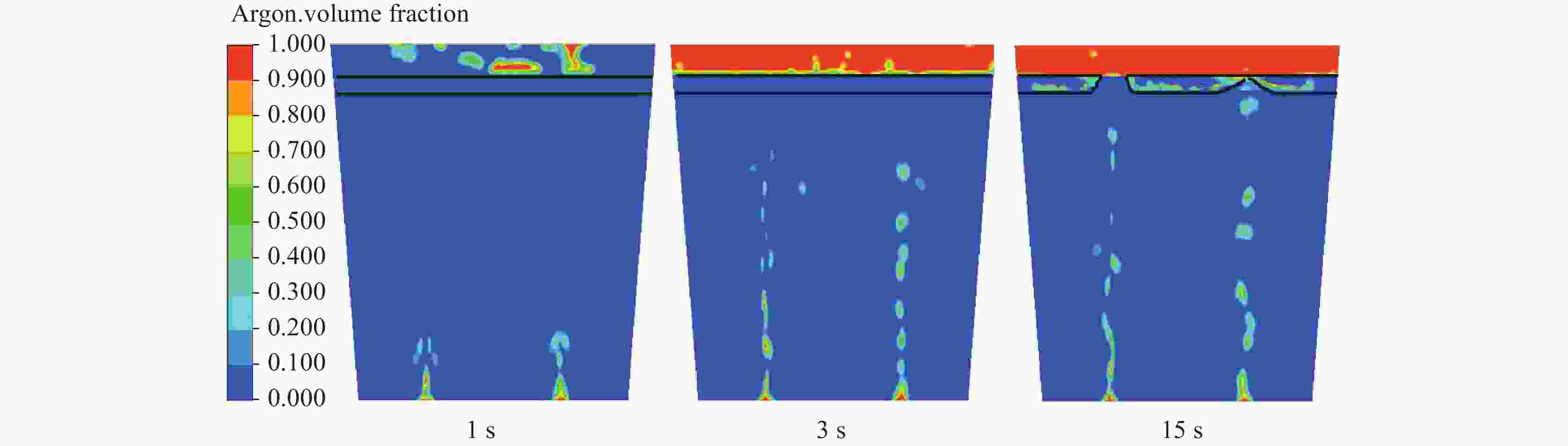
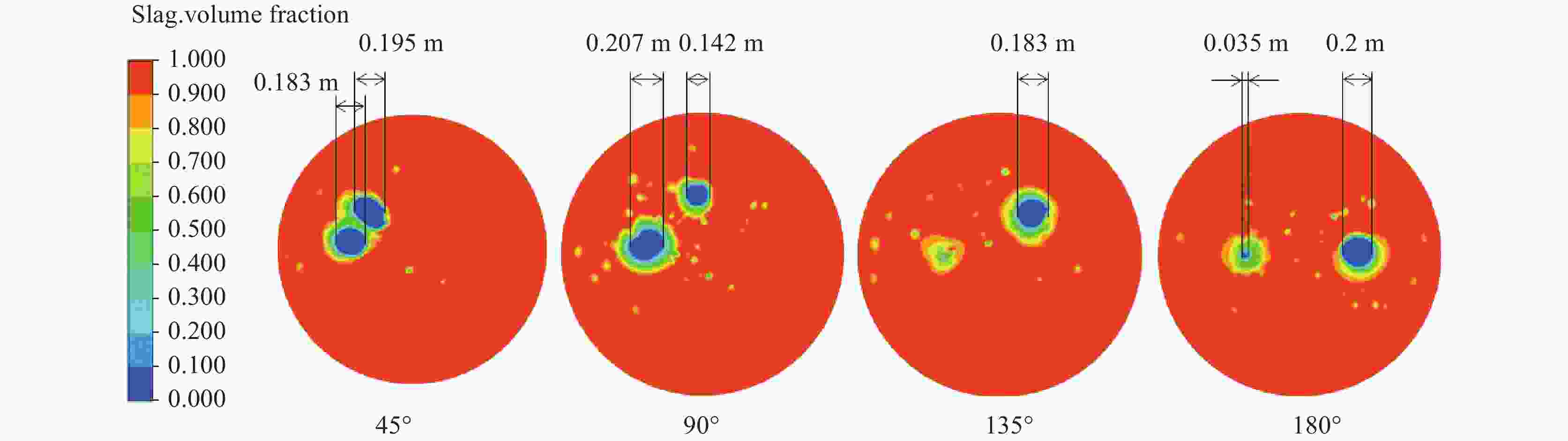
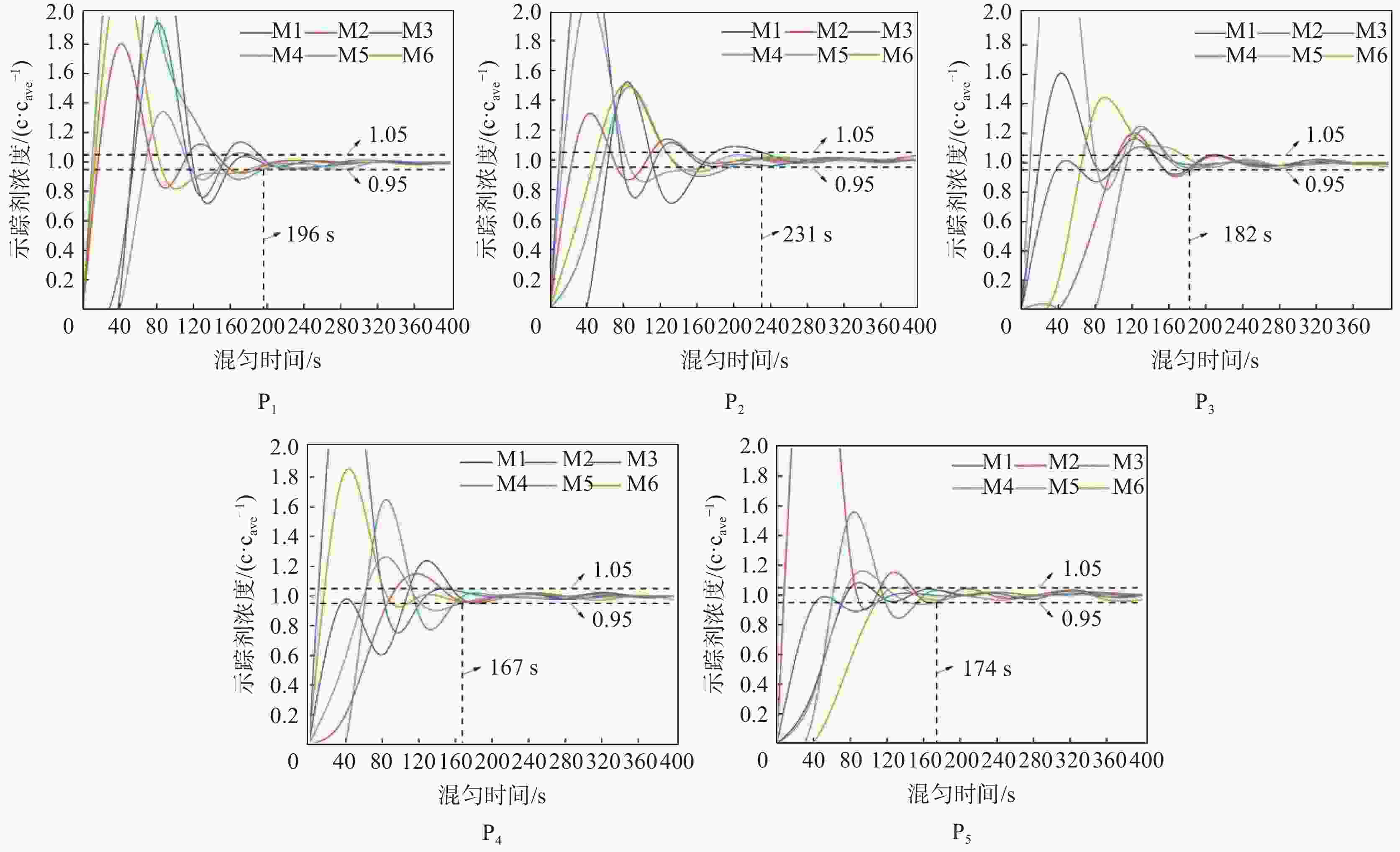
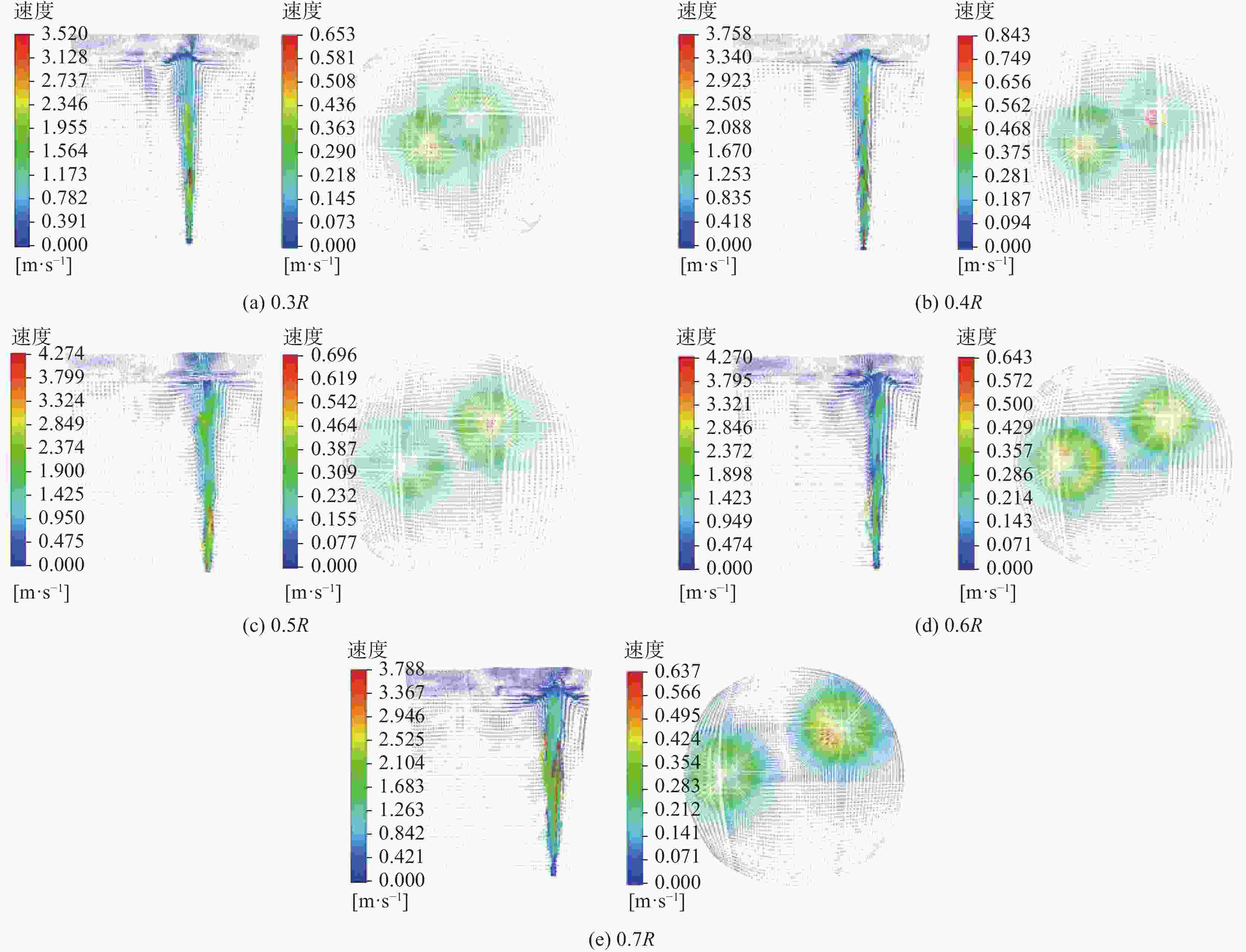
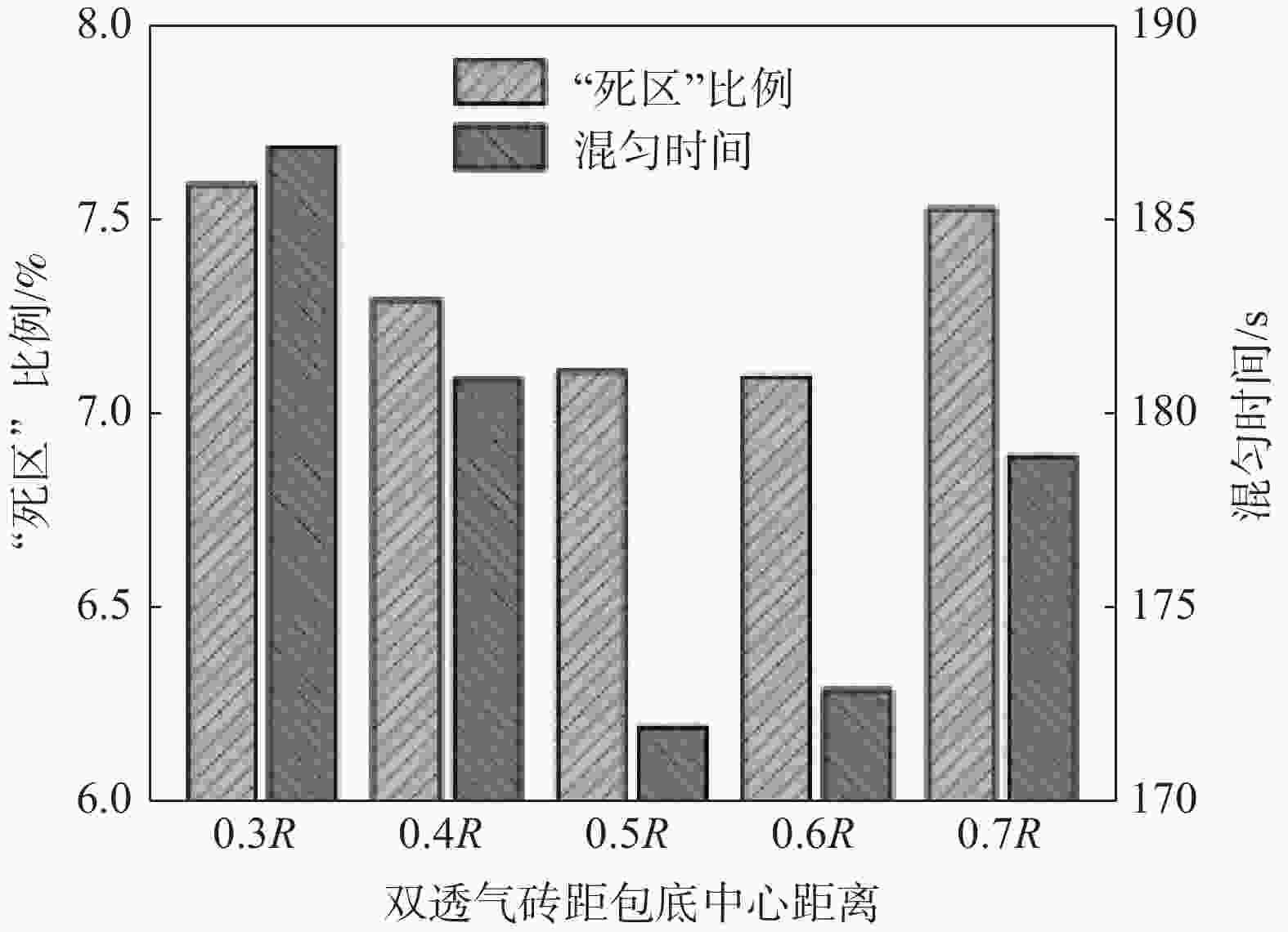
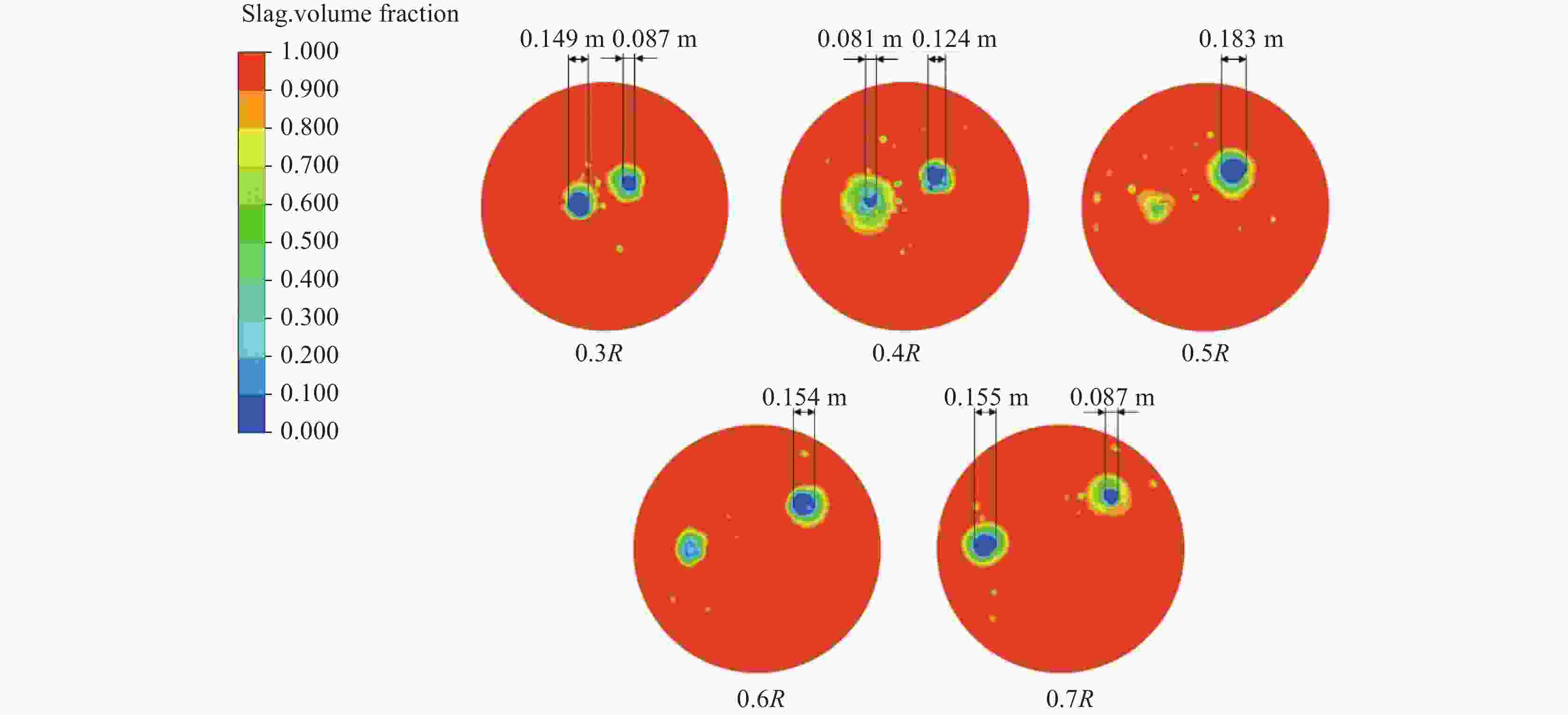
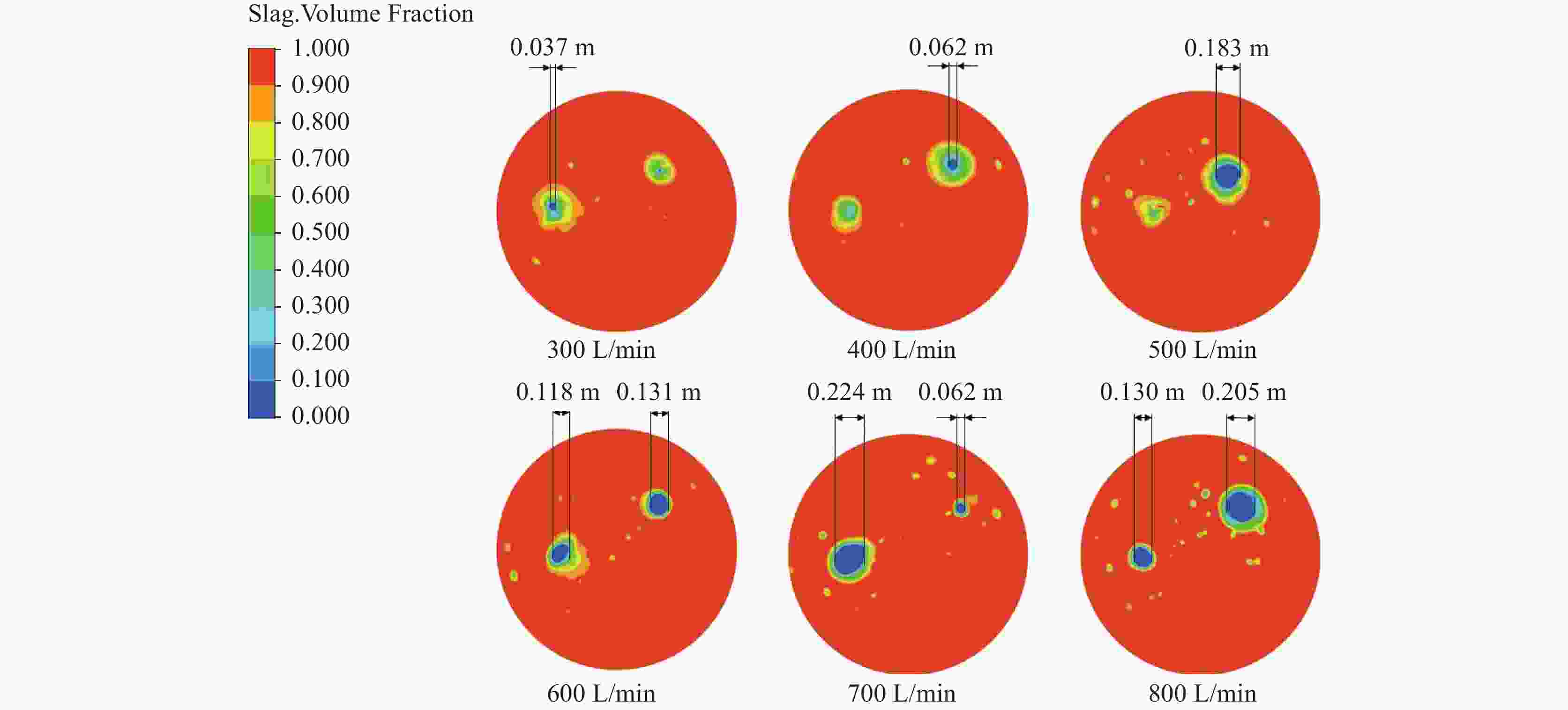
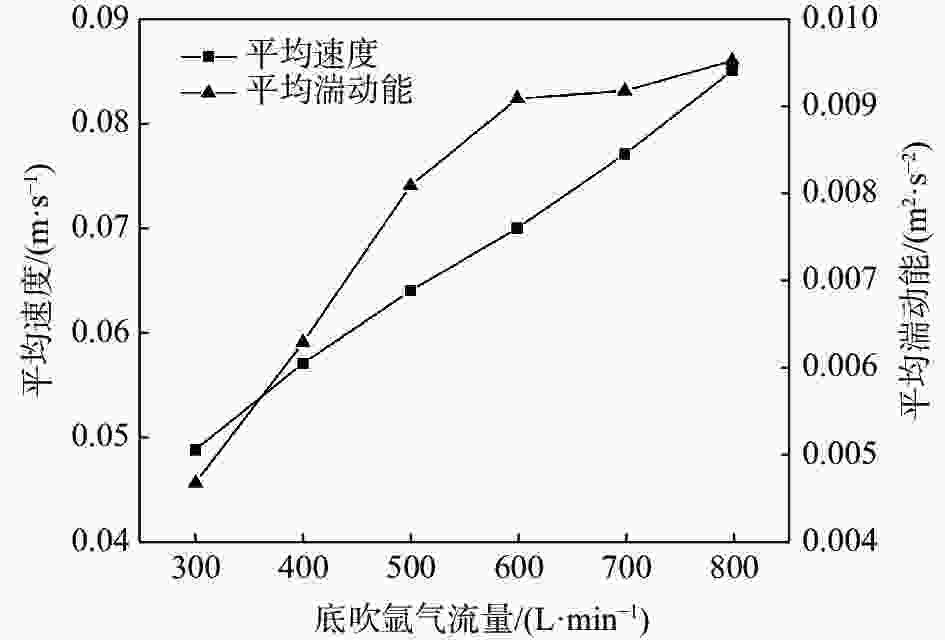
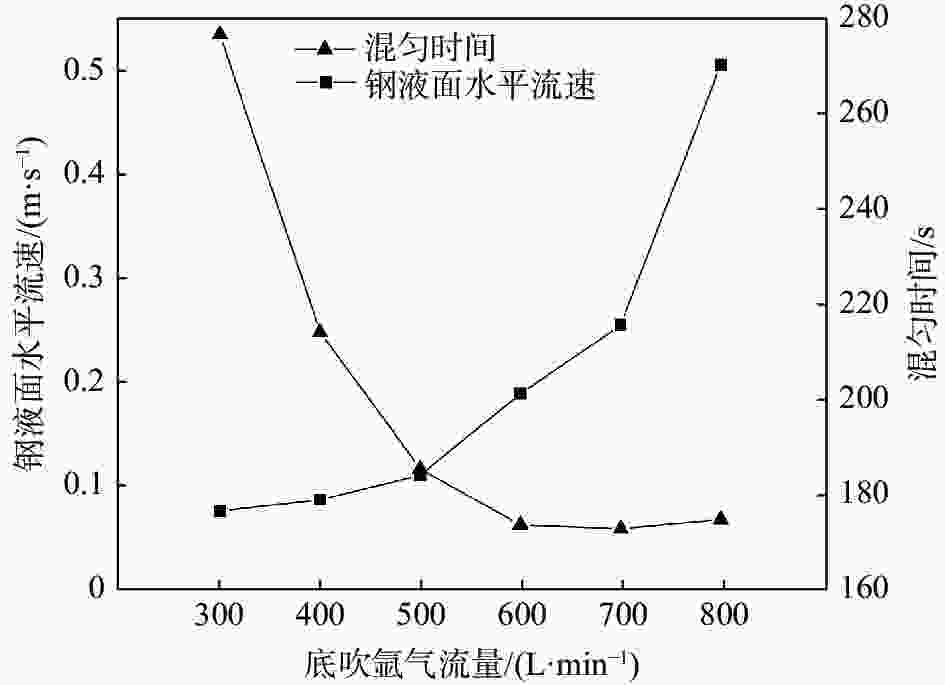
摘要: 采用多相流体积法,根据模型设计参数对某钢厂180 t钢包建立了氩气/钢液/钢渣三相流动数学模型,运用CFD软件Fluent模拟研究了钢包底吹氩气过程中的三相流界面行为及混合现象。基于流体力学理论,计算并分析了底吹氩搅拌钢液过程中双透气砖布置位置和底吹氩气流量对钢包内速度流场、钢-渣界面行为及混匀时间的影响规律。结果表明,在钢包底吹氩过程中,双透气砖的布置位置对钢包内流场效果影响较大,底吹氩气流量则对钢-渣界面行为及混匀时间影响较大。当双透气砖间夹角为135°、距包底中心距离为0.6R、底吹氩气流量为600 L/min时,钢包内流场分布较好,对钢液的搅拌效果最佳。Abstract: A three-phase flow mathematical model of argon/liquid steel/slag for a 180 ton ladle was established by using the multi-phase flow volume method according to design parameters of ladle. The interface behavior and mixing phenomena of three-phase flow in the process of bottom blowing argon in the ladle were simulated by CFD software Fluent. Based on the theory of hydrodynamics, the effects of arrangement of double permeable bricks and flow rate of bottom argon blowing on the velocity field, behavior of steel-slag interface and mixing time in ladle were calculated and analyzed. The results show that in the process of bottom argon blowing, the arrangement of double permeable bricks has a great influence on flow field in ladle, and the flow rate of bottom argon blowing has a great influence on behavior of steel slag interface and mixing time. When the angle between two permeable bricks is 135°, the distance from ladle bottom center is 0.6R, and argon flow rate is 600 L/min, flow field distribution in the ladle is better, which is beneficial to improve stirring efficiency of molten steel.
-
Key words:
- ladle /
- bottom blowing argon /
- three-phase flow /
- interfacial behavior /
- mixing time /
- numerical simulation
-
表 1 经验常数值
Table 1. Empirical constant values used in this study
$ {C}_{1\epsilon } $ $ {C}_{2\epsilon } $ $ {C}_{3\epsilon } $ $ {C}_{\mu } $ $ {\sigma }_{k} $ $ {\sigma }_{\epsilon } $ 1.44 1.92 1.2 0.09 1.0 1.3 表 2 钢包模型参数
Table 2. Ladle model parameters
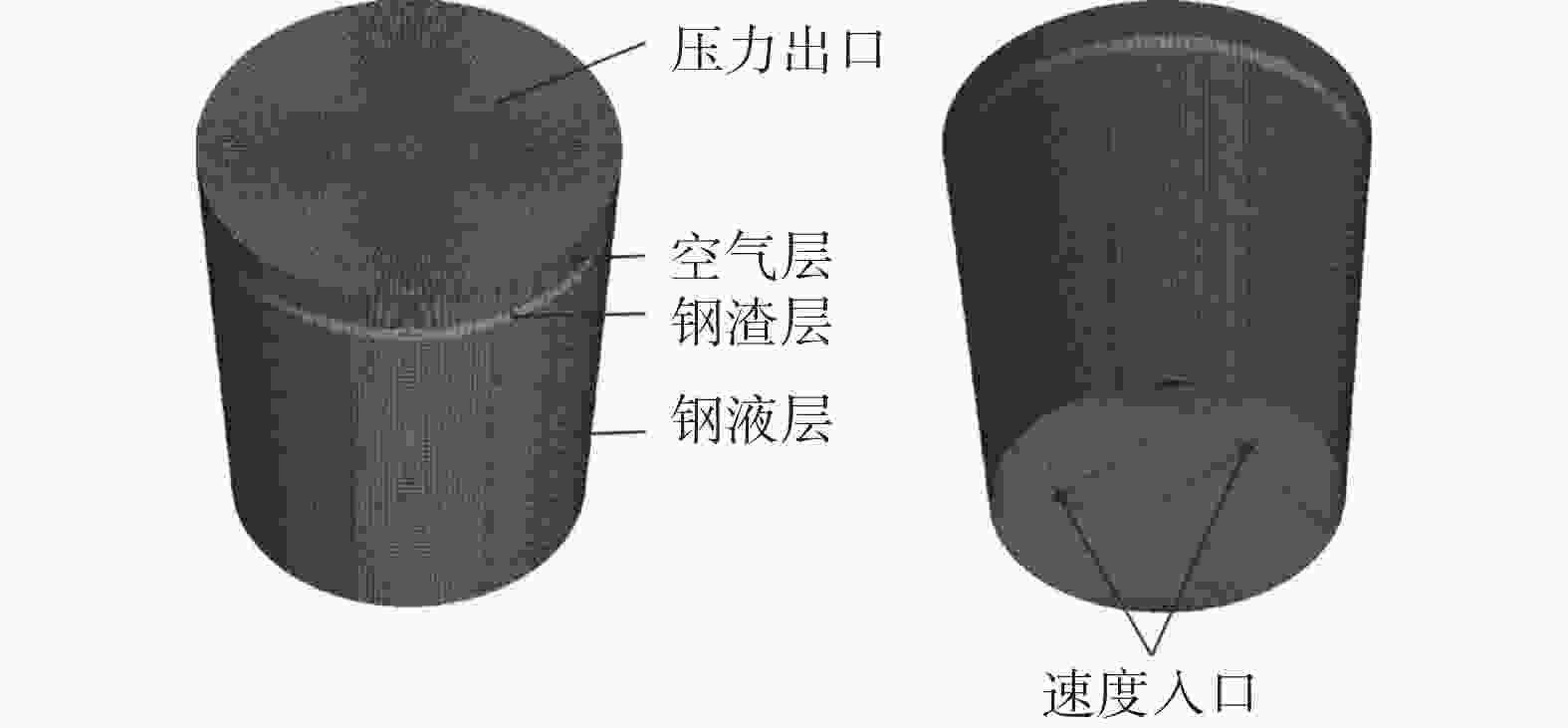
钢包顶部直径/mm 钢包底部直径/mm 钢液高度
/mm钢包高度
/mm渣层厚度
/mm透气砖直径
/mm3620 3000 3460 3960 150 120 表 3 流体材料的物性参数
Table 3. Physical parameters of fluid materials
密度/(kg·m−3) 粘度/(Pa·s) 表面张力/(N·m−1) 氩气 钢液 钢渣 空气 氩气 钢液 钢渣 空气 钢液-钢渣 钢液-空气 钢渣-空气 1.6228 7020 3500 0.5 2.125$ \times $10−5 0.0055 0.06 8.9$ \times $10−5 1.2 1.82 0.58 表 4 钢液表面水平流速度计算结果
Table 4. Calculation results of horizontal velocity on the surface of molten steel
渣/钢界面表面张力
($ {\sigma }_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{l}-\mathrm{s}\mathrm{l}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{g}} $)/($\mathrm{N}\cdot {\mathrm{m} }^{-1}$)钢液表面水平流速度
($ {v}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{l}} $)/($\mathrm{m}\cdot {\mathrm{s} }^{-1}$)1.2 0.59 0.12 0.34 0.012 0.18 -
[1] 殷瑞钰. 合理选择二次精炼技术推进高效率低成本“洁净钢平台”建设[J]. 炼钢2010, 26(2): 1−9.Yin Ruiyu. Reasonable selection of secondary refining technology to promote the construction of “clean steel platform” with high efficiency and low cost[J]. Steelmaking, 2010, 26(2): 1−9. [2] Yang Zhaojun, Zeng Yanan, Li Junguo. Numerical simulation on optimization design of constructional and technical parameters of 65 t ladle[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016,37(2):112−117. (杨赵军, 曾亚南, 李俊国. 65 t钢包精炼工艺参数优化数值模拟[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2016,37(2):112−117. [3] Lou W, Zhu M. Numerical simulations of inclusion behavior and mixing phenomena in gas-stirred ladles with different arrangement of tuyeres[J]. ISIJ International, 2014,54(1):9−18. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.54.9 [4] 蒋星亮. 70 t钢包底吹氩工艺优化及钢—渣界面行为研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2013.Jiang Xingliang. The research for optimization of 70 t ladle bottom argon blowing process and the interfacial behavior of steel-slags[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2013. [5] Zhang Jiangshan, Li Jingshe, Yang Jingbo. Numerical simulation of three-phase fluid flow in a bottom-blown steelmaking ladle[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2012,12(6):946−951. (张江山, 李京社, 杨静波. 底吹钢包三相流的数值模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2012,12(6):946−951. [6] Li Linmin, Liu Zhongqiu, Cao Maoxue, et al. Large eddy simulation of bubbly flow and slag layer behavior in ladle with discrete phase model (DPM)–volume of fluid (VOF) coupled model[J]. Jom, 2015,67:1459−1467. doi: 10.1007/s11837-015-1465-x [7] Li Baokuan, Gu Mingyan, Qi Fengsheng, et al. Modeling of three-phase(gas/molten steel/slag) flows and slag later behavior in an argon gas stirred ladle[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2008,44(10):1198−1202. (李宝宽, 顾名言, 齐凤升, 等. 底吹钢包内气/钢液/渣三相流模型及渣层行为的研究[J]. 金属学报, 2008,44(10):1198−1202. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2008.10.010 [8] Liu H, Qi Z, Xu M. Numerical simulation of fluid flow and interfacial behavior in three‐phase argon‐stirred ladles with one plug and dual plugs[J]. Steel Research International, 2011,82(4):440−458. doi: 10.1002/srin.201000164 [9] Cao, Qing, Nastac, et al. Mathematical investigation of fluid flow, mass transfer, and slag-steel interfacial behavior in gas-stirred ladles[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B Process Metallurgy & Materials Processing Science, 2018. [10] 崔东静. 精炼炉氩气流量的优化设定与控制[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2009.Cui Dongjing. The optimization and control of argon flux for refining furnace[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2009. [11] 李宝宽, 赫冀成. 炼钢中的计算流体力学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1998.Li Baokuan, He Jicheng. Computational fluid dynamics in steelmaking processes[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1998. [12] Asai S, Kawachi M, Muchi I. Mass transfer rate in ladle refining process[J]. Injection Metallurgy, 1983,12:4−9. -




 下载:
下载: