Effect of oxidizing atmosphere on scale formation of weathering steel containing Si
-
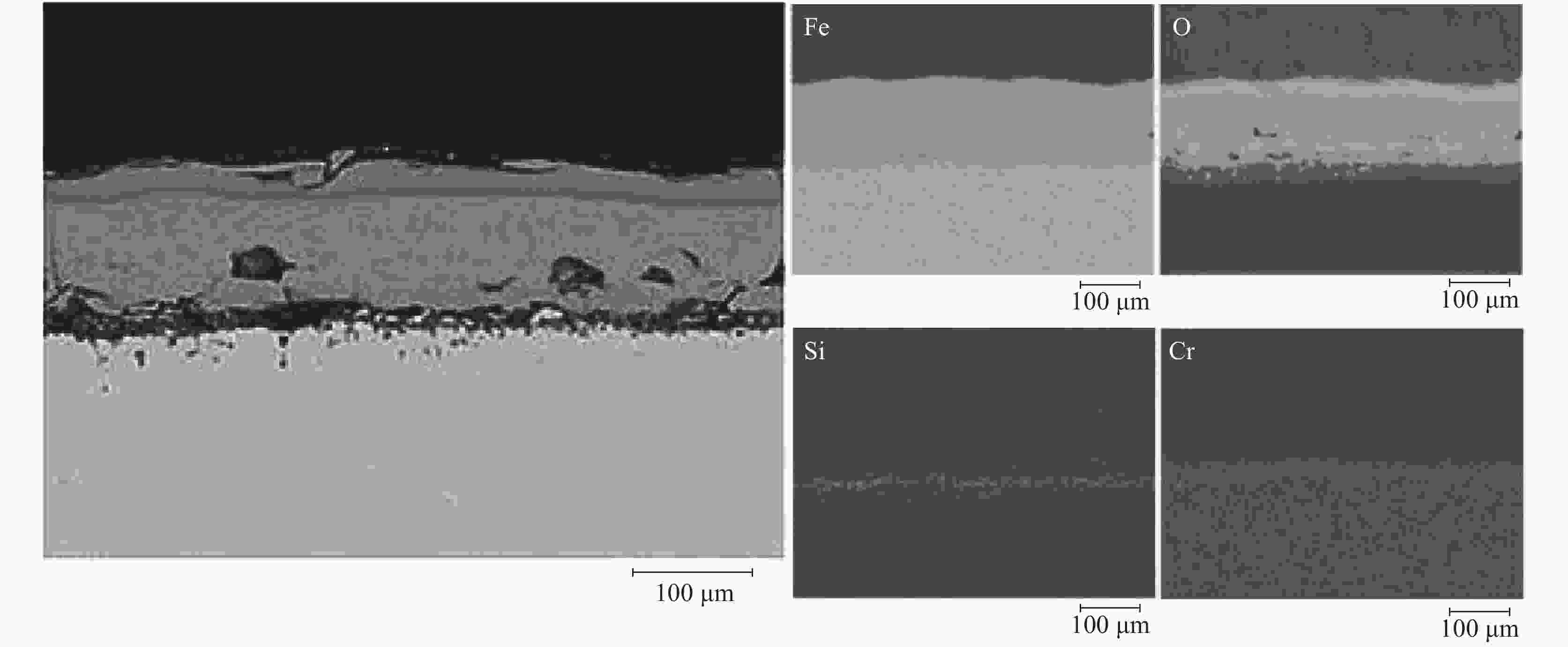
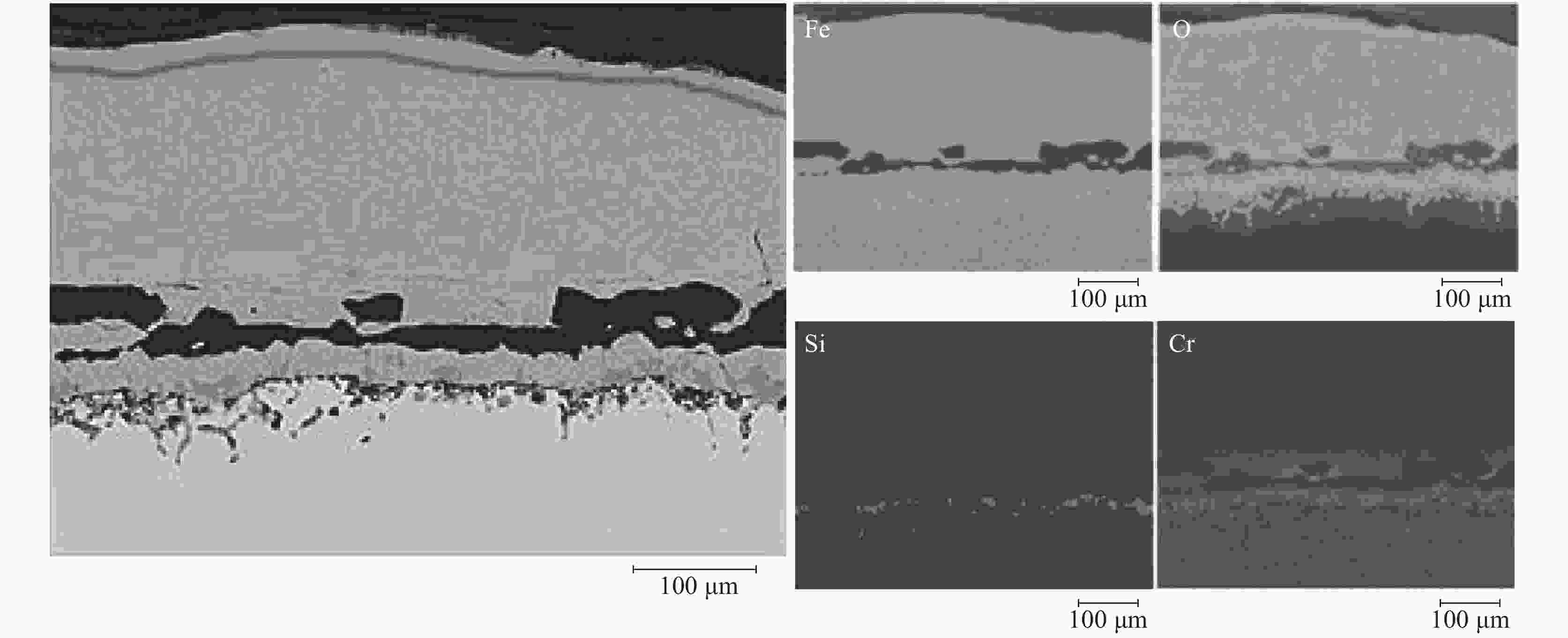
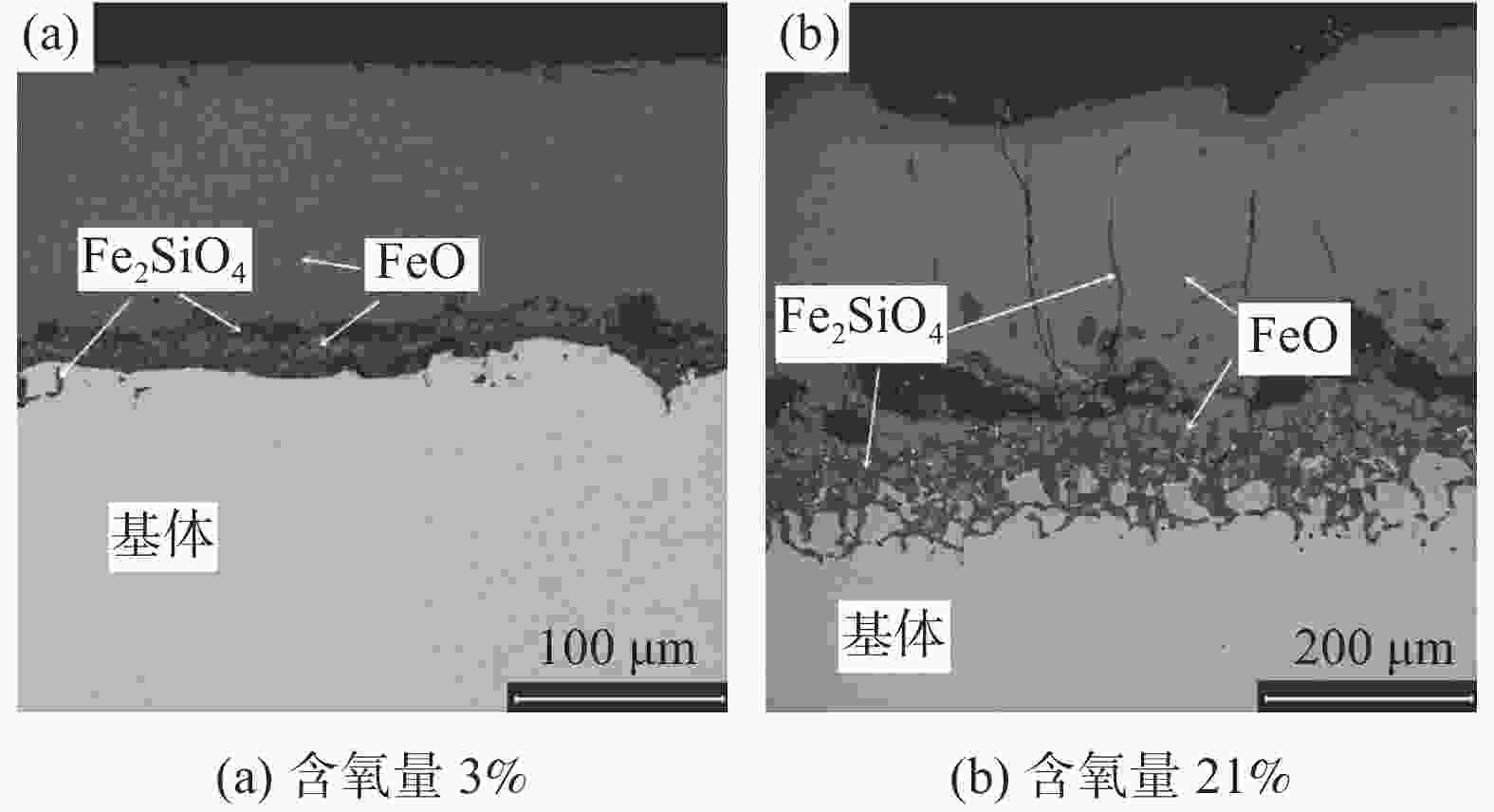
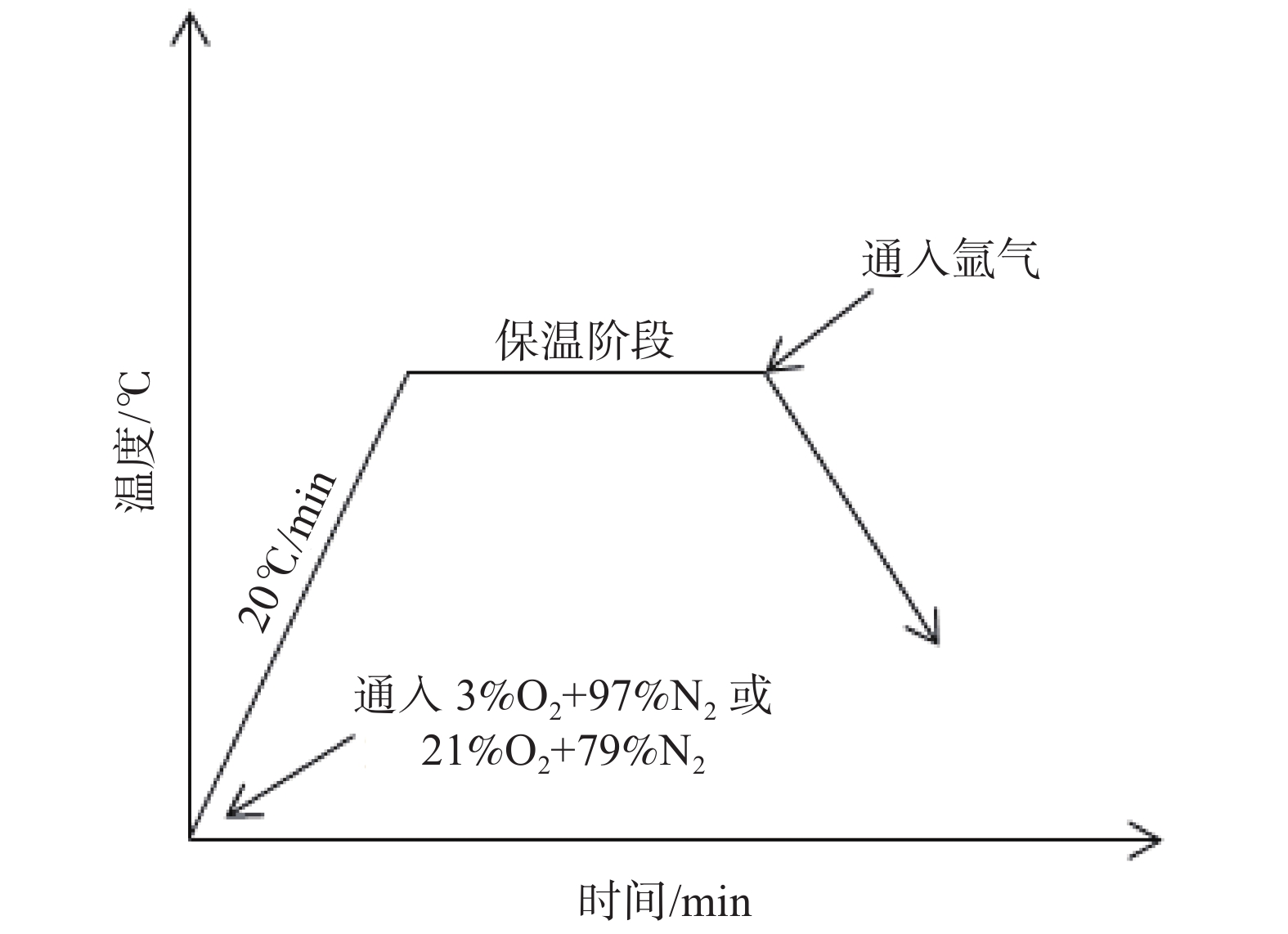
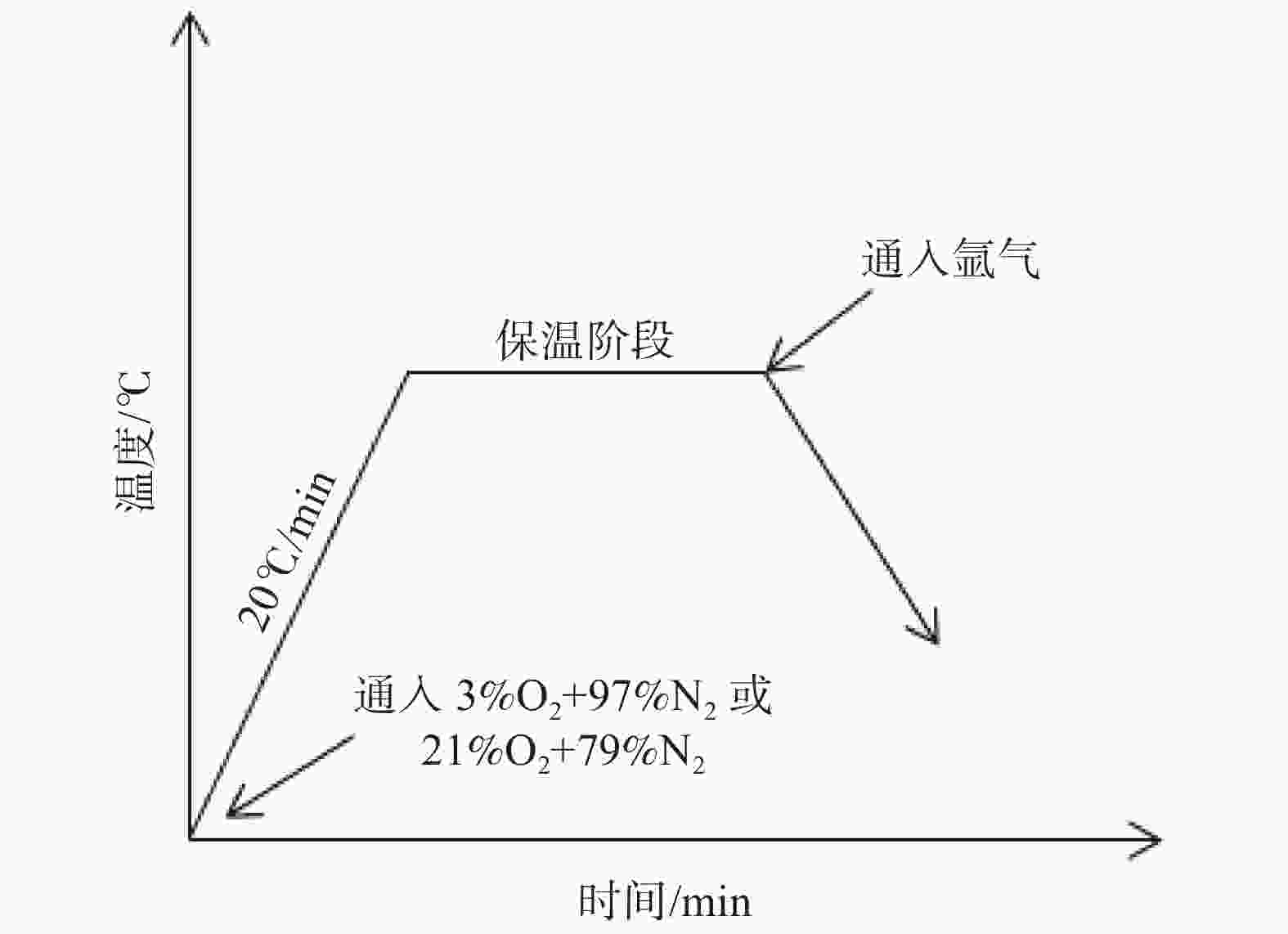
摘要: 模拟现场生产过程中温度较高时贫氧和空气条件下对氧化铁皮生成的影响,利用管式加热炉对试验钢种在含氧量3%和21%气氛中1150 ℃和1200 ℃加热时氧化铁皮的形成进行研究,采用SEM和EPMA对氧化铁皮的断面形貌进行观察和分析。结果表明:高于1150 ℃时不同氧化气氛条件下氧化增重曲线更符合线性规律,氧化气氛中含氧量增加,氧化增重和氧化速率都明显增加。试验钢种氧化铁皮结构与传统氧化铁皮结构相比,在氧化铁皮和基体之间出现了Fe2SiO4层,在含氧量3%,温度1150 ℃条件下Fe2SiO4未发生液相转变,其他条件下Fe2SiO4都发生了液相转变,温度升高和氧化气氛中含氧量增加都会使液态Fe2SiO4渗透度增加。现场结合试验结果对高温(高于1150 ℃)条件下加热炉中的残氧量进行合理控制,得到的成品样中未发现明显的红色氧化铁皮缺陷。Abstract: To simulate the influence of oxygen deficient and air conditions on the scale formation in the production process, the experimental steel was heated in 1150 ℃ and 1200 ℃ with oxygen content of 3% and 21% by tubular furnace to study the scale formation. The cross-section morphology of the scale was observed and analyzed by SEM and EPMA. The results show that when the temperature is higher than 1150 ℃, the oxidation weight gain curve under different oxidation atmospheres is more close to linear relation, and the oxidation weight gain and oxidation rate increase obviously with the increase of oxygen content in the oxidation atmosphere. Compared with the traditional scale structure, there are more Fe2SiO4 layers between the scale and the matrix. Fe2SiO4 does not undergo liquid phase transformation at 1150 ℃ except for 3% oxygen content. Liquid phase transformation occurs under other conditions. The permeability of liquid Fe2SiO4 increases with the increase of temperature and oxygen content in the oxygen atmosphere. Combined with the experimental results, the residual oxygen content in the heating furnace at high temperature (above 1150 ℃) was reasonably controlled, and no obvious red scale defect was found in the finished product.
-
Key words:
- weathering steel /
- oxidation atmosphere /
- red scale /
- Fe2SiO4
-
表 1 Q355NH钢主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of Q355NH
% C Si Cr Cu Ni Mn 0.09 0.32 0.48 0.29 0.15 0.87 表 2 不同氧化气氛下氧化层厚度及Fe2SiO4渗透度
Table 2. Thickness of oxide layer and permeability of Fe2SiO4 of samples under different oxidizing atmospheres
温度/℃ 含氧量/% 氧化铁皮厚度/μm Fe2SiO4渗透度/μm 1150 3 114.29 0 21 262.31 0.51 1200 3 126.32 15.77 21 326.38 60.28 -
[1] Li Shujia, Liu Yangbo, Zhang Wei, et al. Effect of Si on the oxidation rates of spring steels in atmosphere with O2 of 2%[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2015,27(5):55−60. (李舒笳, 柳洋波, 张玮, 等. 2%残氧气氛下硅对弹簧钢氧化速率的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2015,27(5):55−60. [2] Chen Guanghui, Xu Guang, Yuan Qing, et al. Study on isothermal oxidation behavior of Nb-containing high strength steel[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2019,48(6):76−79. (陈光辉, 徐光, 袁清, 等. 含Nb高强钢等温氧化行为研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2019,48(6):76−79. [3] Liang Weicheng, Xu Guang, Yuan Qing, et al. An experimental study on oxidation behavior in low carbon steel containing Si under non-isothermal oxidizing process[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2017,40(4):245−250. (梁伟成, 徐光, 袁清, 等. 非等温氧化工艺下含Si低碳钢氧化行为的实验研究[J]. 武汉科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2017,40(4):245−250. [4] Zhao Xiaolong, Wang Yongqi, Tang Xingchang, et al. Review on the oxidation mechanism and its research of steel billet in heating process[J]. Steel Rolling, 2019,36(6):66−68,82. (赵小龙, 王雍期, 唐兴昌, 等. 钢坯在加热过程中的氧化机理及其研究综述[J]. 轧钢, 2019,36(6):66−68,82. [5] 杨丽琴, 丁美良. 加热炉氧化烧损研究及改进措施[J]. 金属热处理, 2016, 41(9): 168-170.Yang Liqin, Ding Meiliang, Research on oxidizing burning loss of heating furnace and improvement measures[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2016, 41(9): 168-170. [6] Sun Bin, Cao Guangming, Liu Zhenyu. Formation mechanism of powered scale on hot rolled strip and flexible control method[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2013,25(10):53−57. (孙彬, 曹光明, 刘振宇. 热轧带钢粉状氧化铁皮的形成机制及柔性化控制[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2013,25(10):53−57. [7] Mouayd A A, Koltsov A, Sutter E, et al. Effect of silicon content in steel and oxidation temperature on scale growth and morphology[J]. Materials Chemistry & Physics, 2014,143(3):996−1004. [8] 袁清. 低碳含Si钢高温氧化行为及网格状Fe2SiO4/FeO形成机理研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2019.Yuan Qing. Research on the high-temperature oxidation behavior of low carbon silicon-containing steels and the formation mechanism of Net-like Fe2SiO4/FeO[D]. Hubei: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2019. [9] Sun Bin, Hao Mingxin, You Hongguang, et al. High temperature oxidation behavior of Fe-1 Cr-0.2 Si Steel[J]. Materials Reports, 2020,34(16):16131−16135. (孙彬, 郝明欣, 尤宏广, 等. Fe-1Cr-0.2Si钢的高温氧化行为[J]. 材料导报, 2020,34(16):16131−16135. doi: 10.11896/cldb.19060169 [10] Yan Lixin, Liang Liang, Cao Guangming, et al. High temperature oxidation behavior of low carbon steel with Cr element[J]. Steel Rolling, 2021,38(1):14−19. (严立新, 梁亮, 曹光明, 等. 含Cr低碳钢的高温氧化行为研究[J]. 轧钢, 2021,38(1):14−19. [11] Yuan Qing, Xu Guang, Hu Haijiang, et al. Effects of oxygen concentration on the passivation of Si-containing steel during high-temperature oxidation[J]. Corrosion Reviews, 2018,36(4):385−393. doi: 10.1515/corrrev-2017-0077 -




 下载:
下载: