Preparation and properties of porous Ti-Nb alloy materials
-
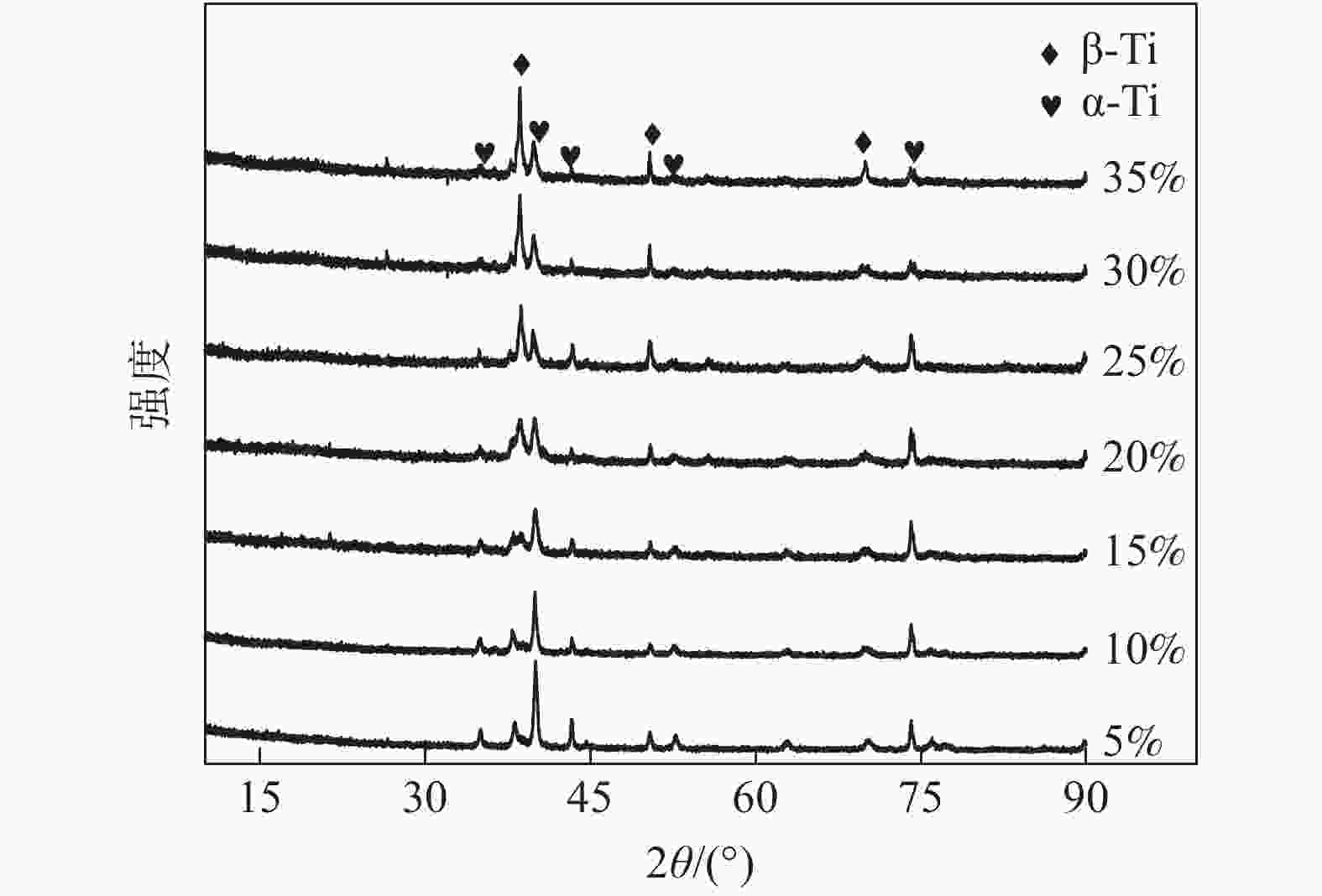
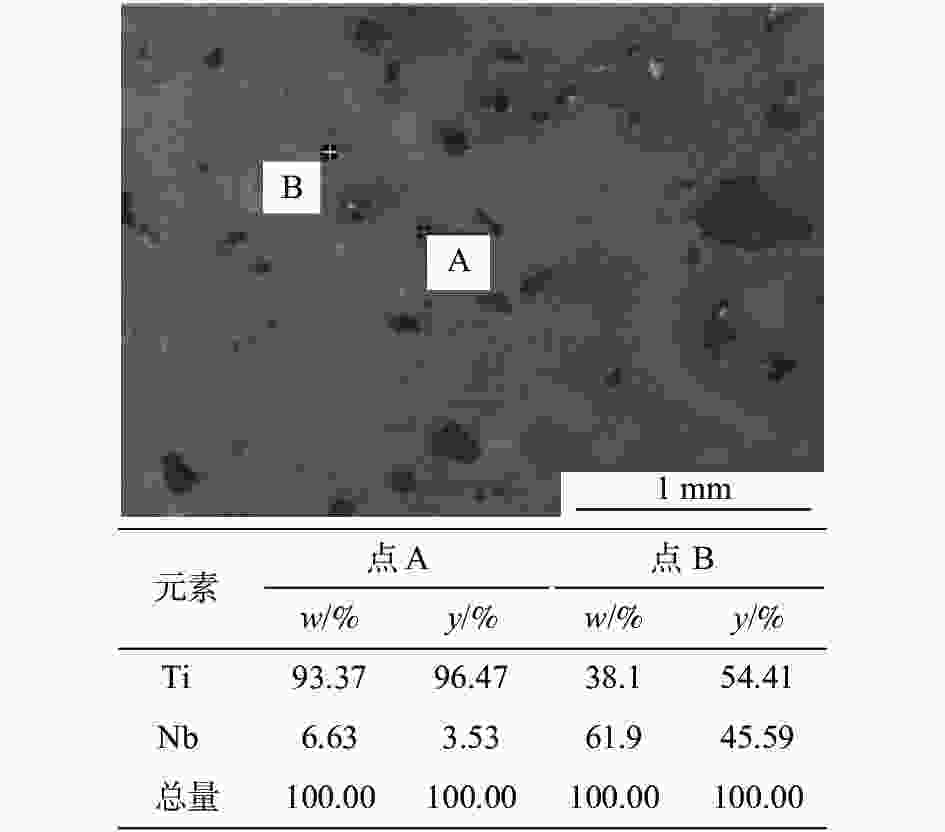
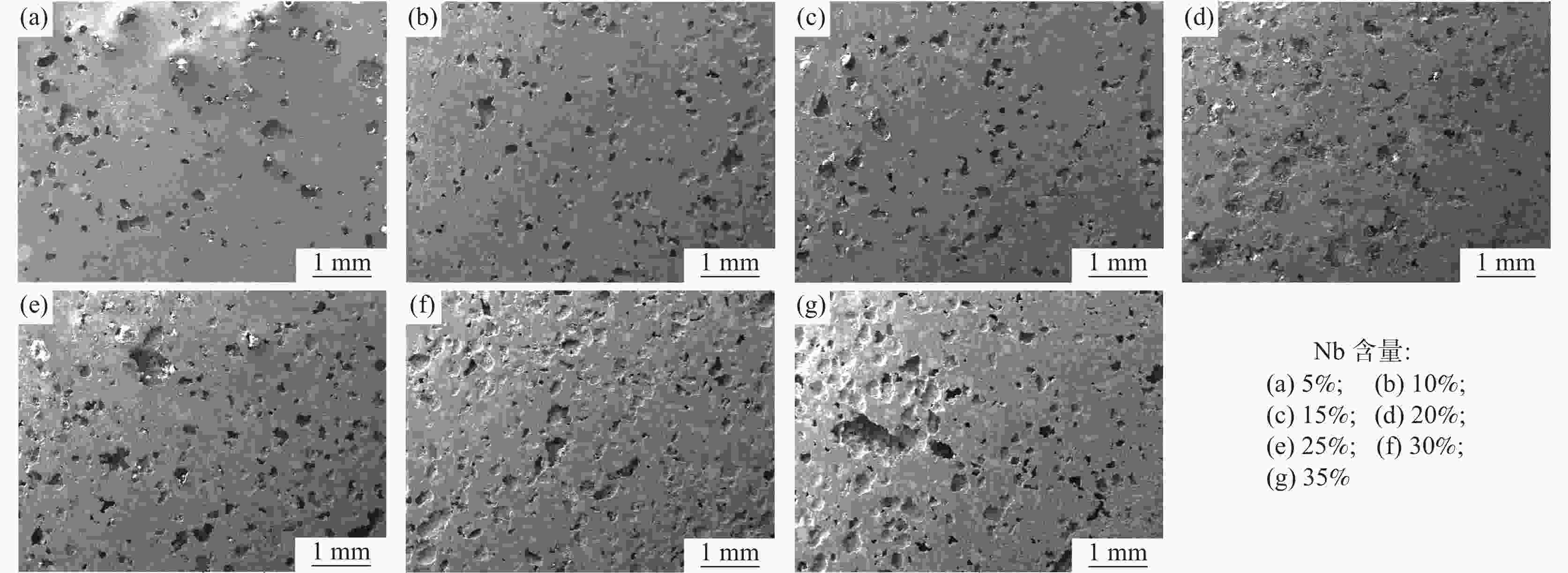
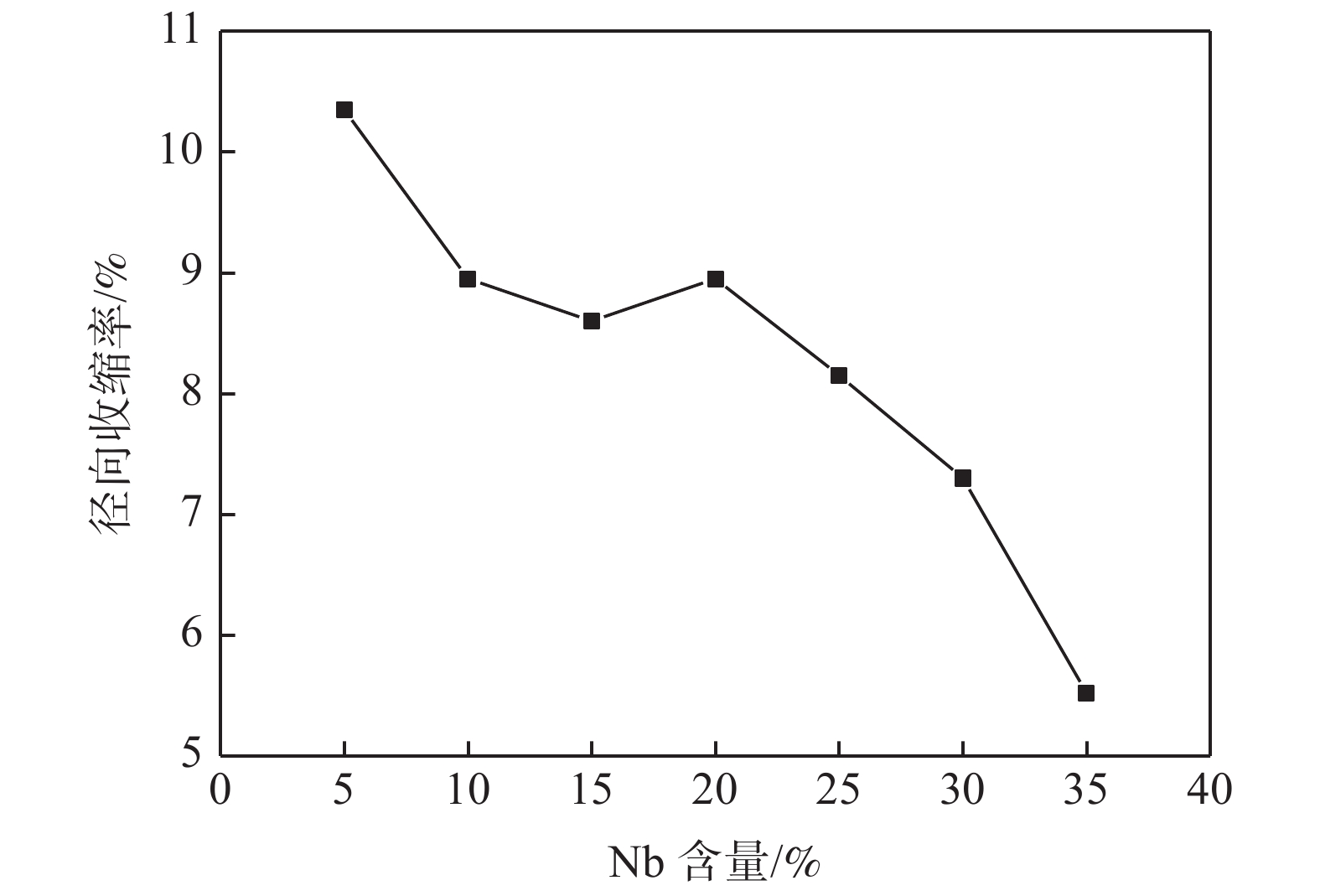
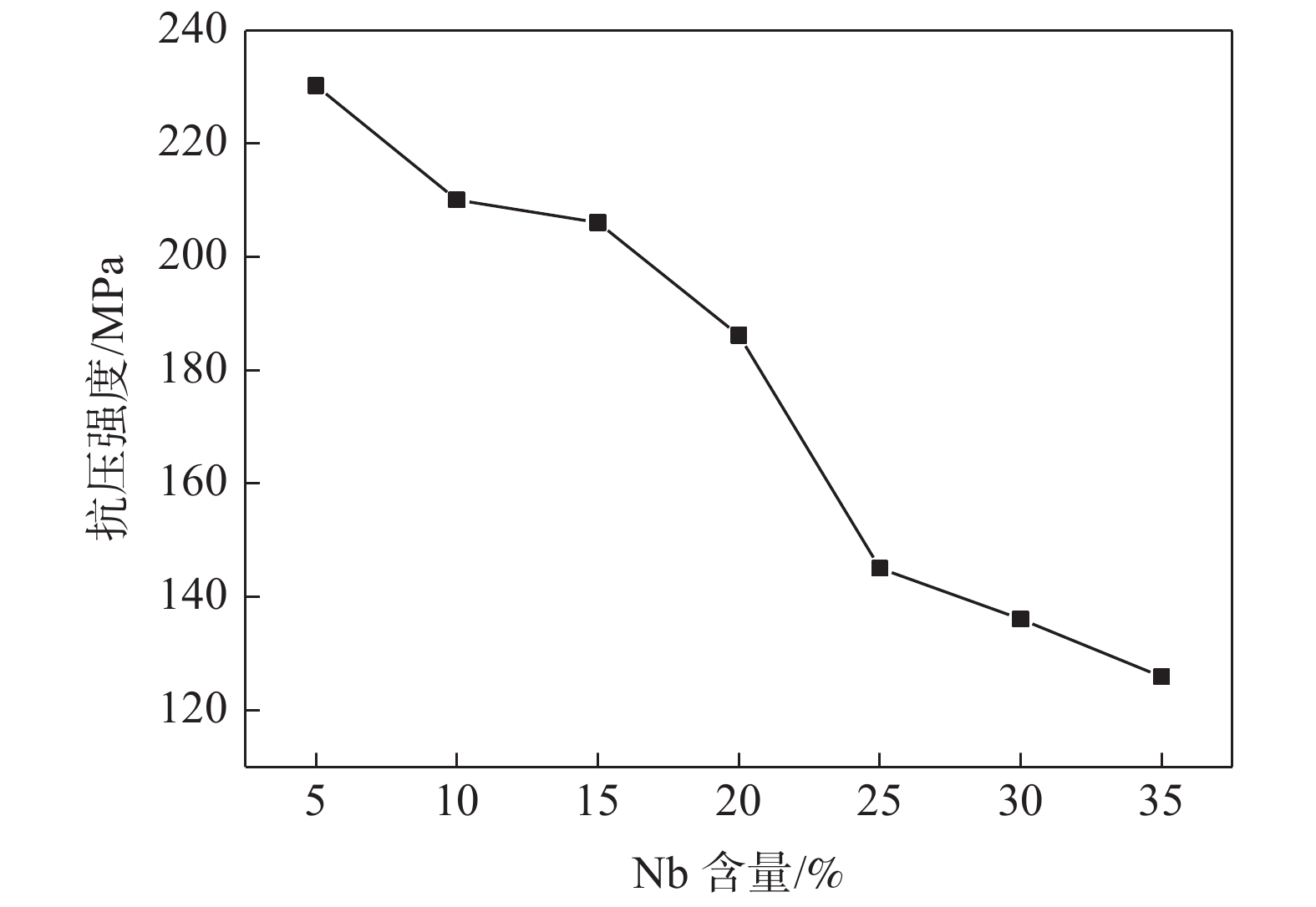
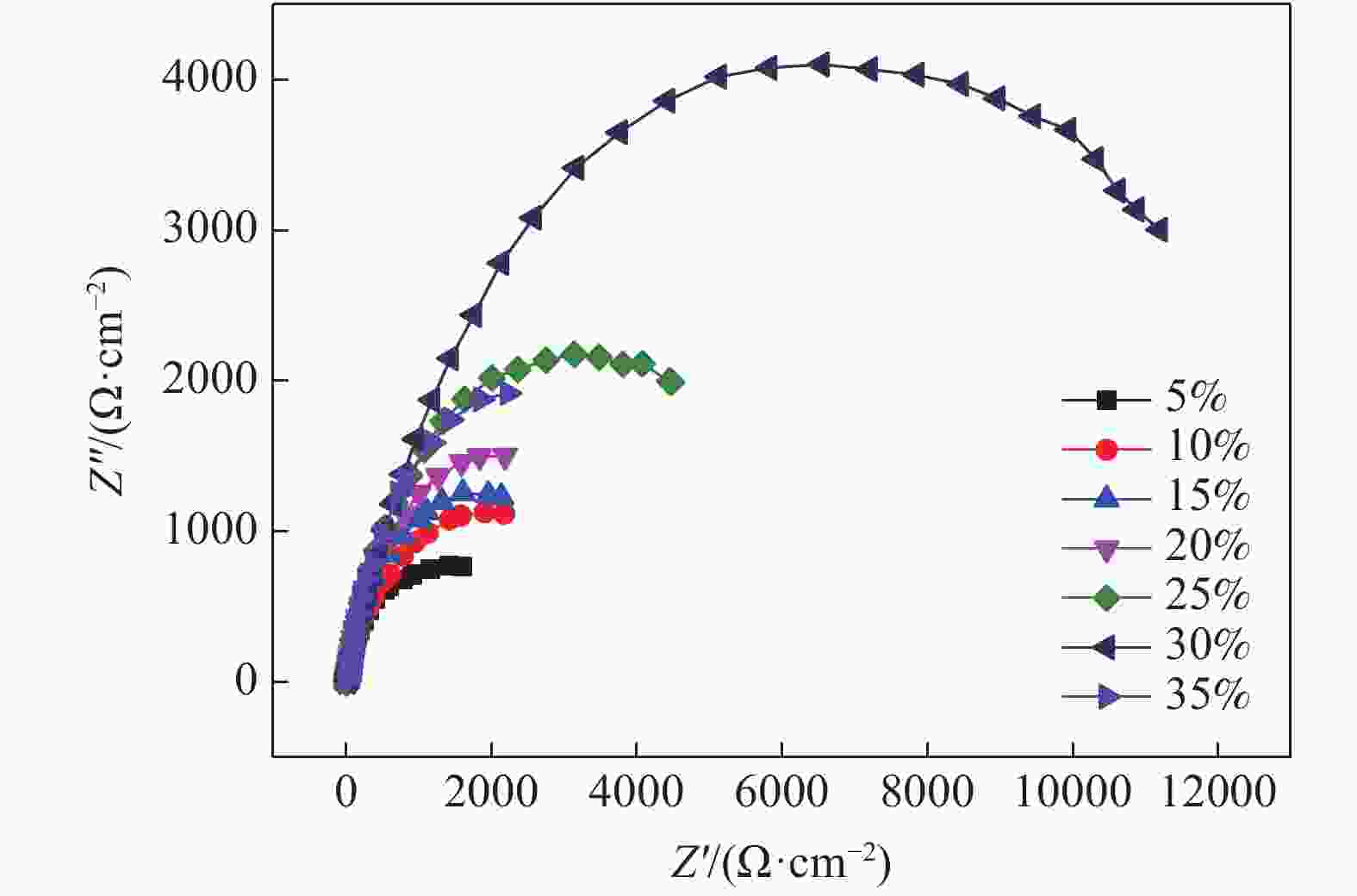
摘要: 采用粉末冶金添加造孔剂法制备多孔Ti-Nb合金,研究不同Nb含量对合金物相结构、微观孔隙形貌、孔隙率、抗压强度及耐腐蚀性能的影响。研究结果表明:多孔Ti-Nb合金具有α和β双相组织,随Nb含量的增加,材料中的 β 相含量逐渐增大,Nb含量为25%~30%时材料的孔隙大小和分布较均匀,平均孔径为300 μm左右;随Nb含量的增加,材料的孔隙率随之增大,径向收缩率和抗压强度逐渐减小,耐腐蚀性呈先增大后减小趋势,在Nb含量30%时材料的耐腐蚀性最强,其孔隙率为33.6%,径向收缩率为7.3%,抗压强度为130 MPa。Abstract: The porous Ti-Nb alloy was prepared by adding pore-forming agent in powder metallurgy. The effects of Nb content on the phase structure, pore morphology, porosity, compressive strength and corrosion resistance of the alloy were investigated. The results show that the porous Ti-Nb alloy has α and β phase structure. With the increase of Nb content, the content of β phase in the material increases gradually. When the content of Nb is 25% ~ 30%, the pore size and distribution of the material are more uniform, and the average pore size is about 300 μm. With the increase of Nb content, the porosity of the material increases, while the radial shrinkage rate and the compressive strength gradually decrease, and the corrosion resistance increases first and then decreases. When the Nb content is 30%, the corrosion resistance of the material is the strongest, with the porosity of 33.6%, the radial shrinkage rate of 7.3% and the compressive strength of 130 MPa.
-
表 1 多孔Ti-Nb合金的孔隙率和平均孔径
Table 1. Porosity and average pore size of porous Ti-Nb alloys
w(Nb)/% 孔隙率/% 平均孔径/μm 5 20.46 223 10 26.70 252 15 29.30 271 20 29.56 310 25 30.85 360 30 33.61 355 35 46.04 351 表 2 不同Nb含量多孔Ti-Nb合金的腐蚀电位
Table 2. The corrosion potential of porous Ti-Nb alloys with different Nb contents
w(Nb)/% 腐蚀电位/V 腐蚀电流/A 电流密度/(A·cm−2) 5 −0.86 −6.77 2.16 10 −0.77 −6.54 2.08 15 −0.71 −6.96 2.22 20 −0.71 −6.50 2.07 25 −0.75 −6.24 1.99 30 −0.76 −6.15 1.96 35 −0.95 −7.16 2.28 -
[1] Ren Junshuai, Zhang Yingming, Tan Jiang, et al. Current research status and trend of titanium alloys for biomedical applications[J]. Materials Review, 2016,30(2):384−388. (任军帅, 张英明, 谭江, 等. 生物医用钛合金材料发展现状及趋势[J]. 材料导报, 2016,30(2):384−388. [2] Yu Zhentao, Yu Sen, Cheng Jun, et al. Development and application of novel biomedical titanium alloy materials[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2017,53(10):1238−1264. (于振涛, 余森, 程军, 等. 新型医用钛合金材料的研发和应用现状[J]. 金属学报, 2017,53(10):1238−1264. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2017.00288 [3] Zhang L C, Chen L Y. A review on biomedical titanium alloys: Recent progress and prospect[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2019,21(4):1−29. [4] Zhang Erlin, Wang Xiaoyan, Han Yong. Research status of biomedical porous Ti and its alloy in China[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2017,53(12):1555−1567. (张二林, 王晓燕, 憨勇. 医用多孔Ti及钛合金的国内研究现状[J]. 金属学报, 2017,53(12):1555−1567. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2017.00324 [5] Xu L J, Xiao S L, Tian J, et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties and dry wear resistance of β-type Ti–15Mo–xNb alloys for biomedical applications[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013,23(3):692−698. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62518-2 [6] Wang Benli, Li Li, Zheng Yufeng, et al. Microstructure and wear behavior of biomedical Ti-Nb based alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010,20(S1):953−957. (王本力, 李莉, 郑玉峰. 生物医用Ti-Nb基合金的显微组织与耐磨性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010,20(S1):953−957. [7] 吴杰. 生物医用多孔Ti-Nb基记忆合金的制备及其性能优化[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2017.Wu Jie. Synthesis and properties optimization of porous Ti-Nb based memory alloys for biomedical application[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2017. [8] Zhang Meili, Pan Qi, Yang Tao, et al. Effect of Mo content on pore morphology and properties of porous Ti-Mo alloy[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2019,40(10):58−64. (张美丽, 潘旗, 杨涛, 等. 钼含量对多孔Ti-Mo合金孔隙形貌及性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2019,40(10):58−64. [9] Zou Liming, Yang Chao, Li Yuanyuan. Research progress on preparing Ti-based biomedical materials by powder metallurgy[J]. Materials Review, 2011,25(15):82−85. (邹黎明, 杨超, 李元元. 粉末冶金法制备钛基生物医学材料的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2011,25(15):82−85. [10] Li Yonghua, Chen Nan. Research on microstrructure and mechanical property of porous Ti-45Nb alloy[J]. Journal of Jinggangshan University (Natural Science), 2019,40(5):67−71. (李永华, 陈楠. 多孔Ti-45Nb合金的微观组织与力学性能研究[J]. 井冈山大学学报(自然科学版), 2019,40(5):67−71. [11] Liu Chao, Yang Hailin, Li Jing, et al. Porosity and mechanical properties of biomedical porous Nb-Ti alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014,24(3):752−757. (刘超, 杨海林, 李婧, 等. 生物医用多孔Nb-Ti合金的孔隙率和力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014,24(3):752−757. [12] Zhao Chaoyong, Kuang Lin, Zhang Xuefeng, et al. Preparation and mechanical properties of porous Ti-5Nb alloy with the elongated pores[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019,40(6):62−67. (赵朝勇, 匡林, 张雪峰. 细长孔的多孔Ti-5Nb合金制备及力学性能研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2019,40(6):62−67. [13] Ibrahim M K, Hamzah E, Saud S, et al. Parameter optimization of microwave sintering porous Ti-23%Nb shape memory alloys for biomedical applications[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018,28(4):700−710. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64702-8 [14] Liu Peisheng. Determining methods for porosity of porous materials[J]. Titanium Industry Progres, 2005,22(6):34−36. (刘培生. 多孔材料孔率的测定方法[J]. 钛工业进展, 2005,22(6):34−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2005.06.008 [15] 鲍路姿. 医用多孔Ti-Mo合金的微波烧结制备及水热活化处理[D]. 南昌: 南昌航空大学, 2016.Bao Luzi. Preparation and hydrothermal activation treatment of the microwave sintered biomedical porous Ti-Mo alloy[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang Hangkong University, 2016. [16] Xie Fangxia, He Xueming, Yu Jinghu, et al. Structural characteristics and mechanical behavior of selective laser sintered porous Ti-6Mo alloy for biomedical applications[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2016,45(6):1477−1482. (颉芳霞, 何雪明, 俞经虎, 等. 生物医用多孔Ti-6Mo合金选择性激光烧结的结构特征和力学行为[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2016,45(6):1477−1482. -




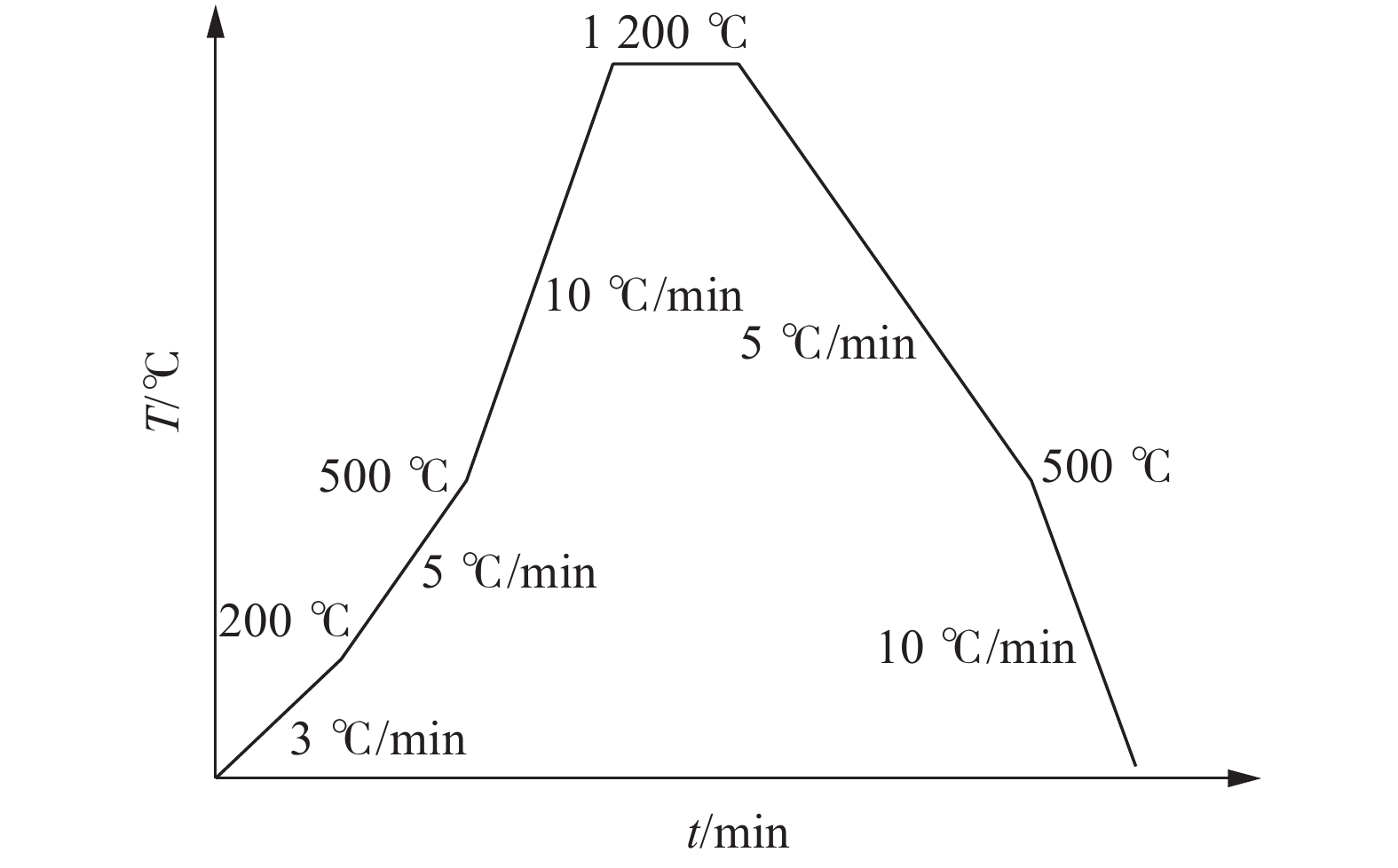
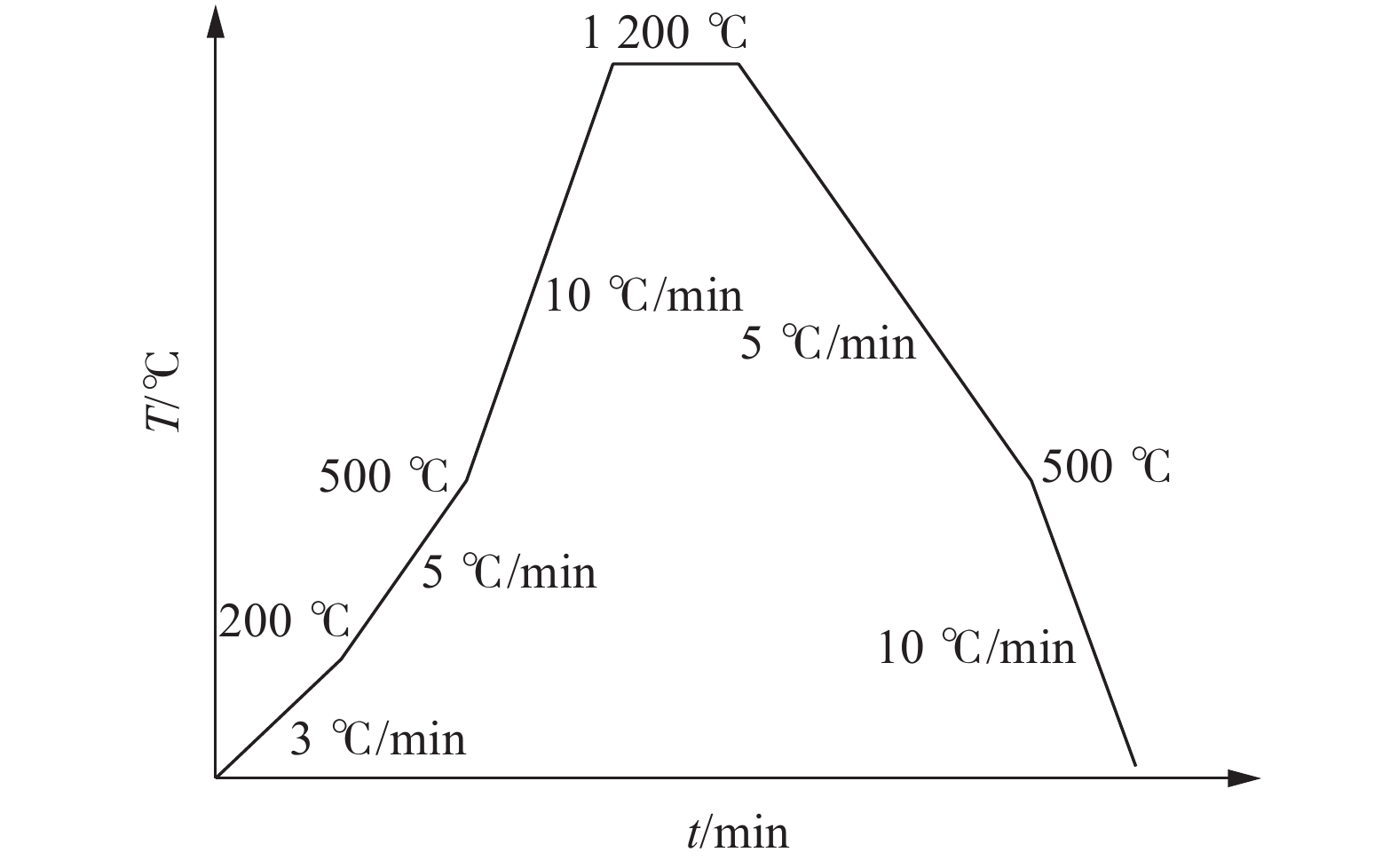
 下载:
下载: