Preparation of Ti60 high temperature titanium alloy ingot for aerospace
-
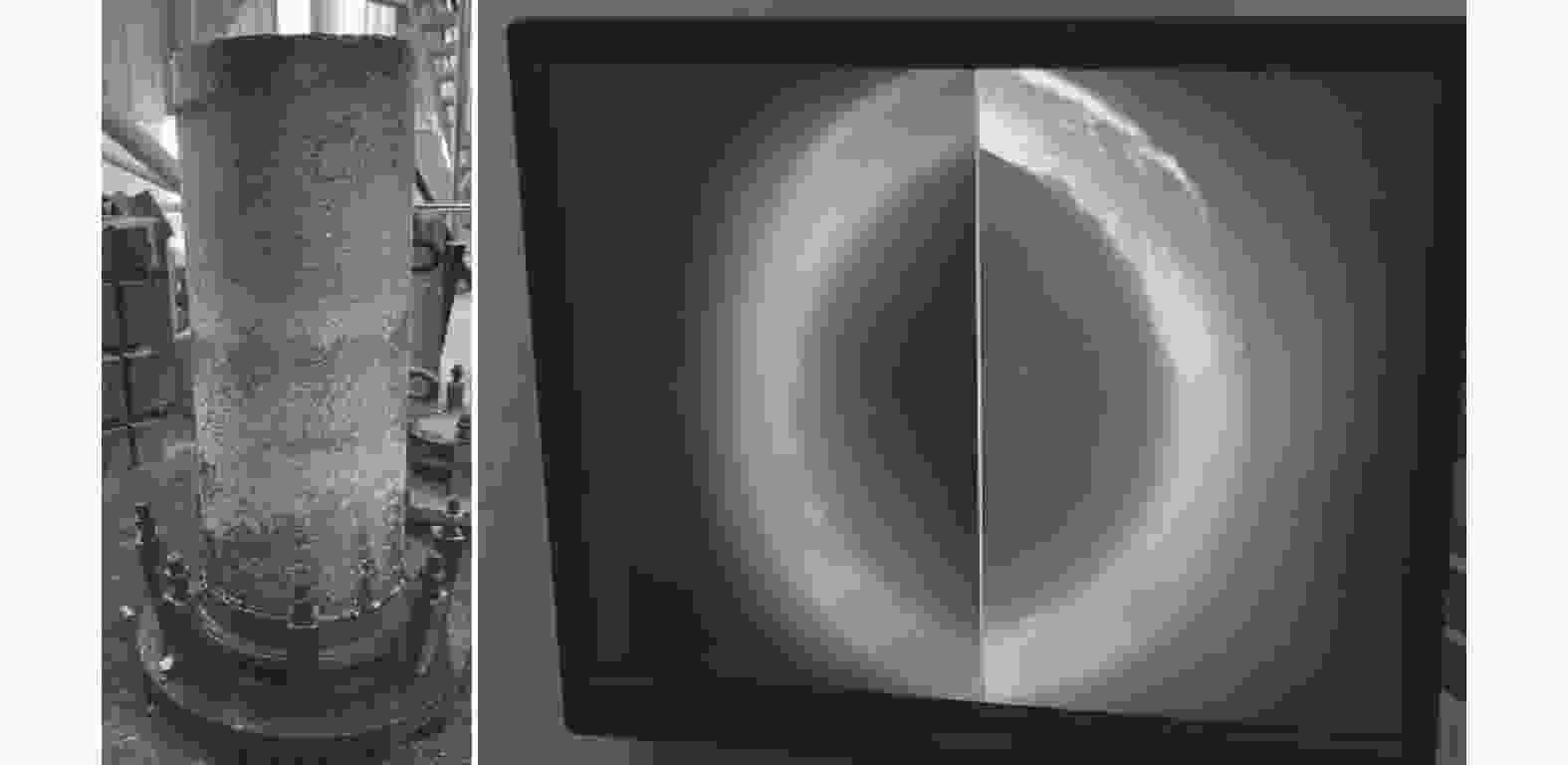
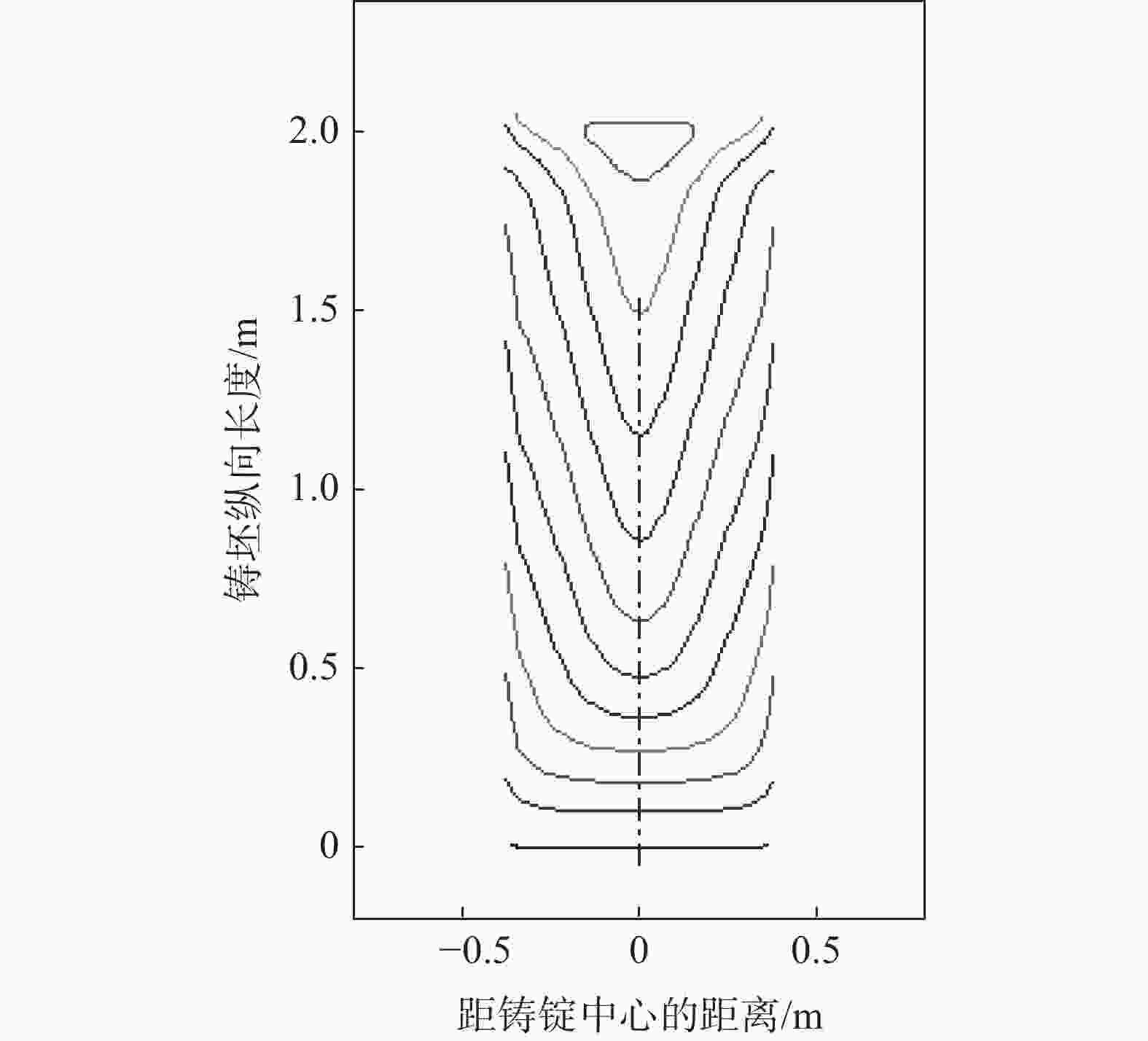
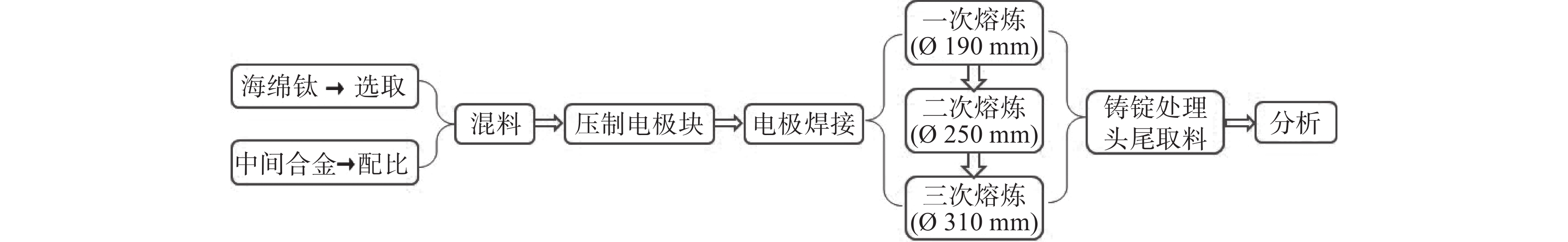
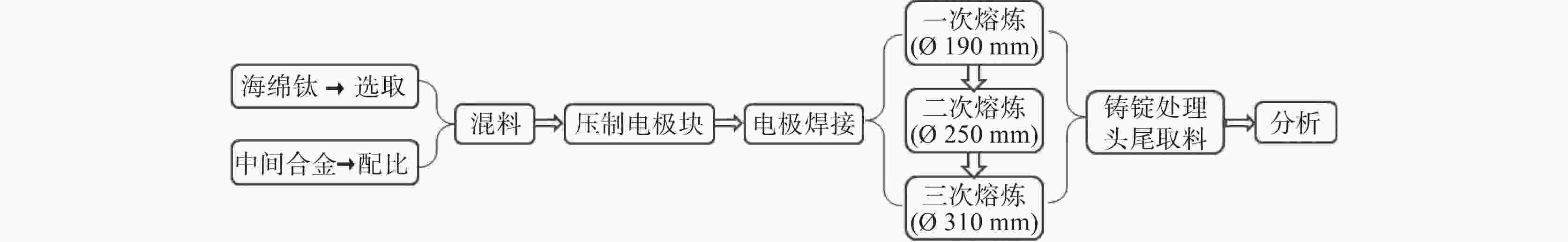
摘要: 针对Ti60高温钛合金在熔炼工艺上的关键技术,选用等级较高的0A级军工小粒海绵钛以及合适的中间合金,采用真空自耗电弧炉熔炼,通过控制熔炼电流电压等关键工艺参数,制备出Ø310 mm大型Ti60高温钛合金铸锭。铸锭表面质量良好,没有出现冷隔和不到边等缺陷。经检测,各合金元素在铸锭上均匀分布,杂质元素含量以及分布控制较好,系统研究了以中间合金方式添加的Nb、Ta、Mo等高熔点元素以及低熔点元素Sn的配入方式和熔炼电流、熔炼电压等工艺参数对合金铸锭的成分均匀性以及缺陷控制的影响。此铸锭通过后续工序所制出的锻件,经过力学性能以及超声探伤,均达到了行业要求。Abstract: Aiming at the key technology of Ti60 high temperature titanium alloy preparation by smelting process, 0A grade military granulated sponge titanium and appropriate master alloy were selected to prepare Φ310 mm large Ti60 high temperature titanium alloy ingot, via vacuum consumable arc furnace smelting. The prepared ingot has a well surface quality without defects such as cold isolation and missing edge. The alloy elements are evenly distributed in the ingot, and the impurities content and distribution are well controlled. The effects of the mixing mode of high melting point elements such as Nb, Ta, Mo and low melting point elements such as Sn, melting current and voltage on composition uniformity and defect control of the alloy ingot were systematically studied. The forgings made from the ingot through subsequent processes have met the industrial and technical requirements through mechanical properties test and ultrasonic flaw detection.
-
Key words:
- high temperature titanium alloy /
- Ti60 /
- master alloy /
- current /
- voltage /
- ingots /
- composition /
- uniformity
-
表 1 Ti60铸锭成分
Table 1. Composition of Ti60 ingot
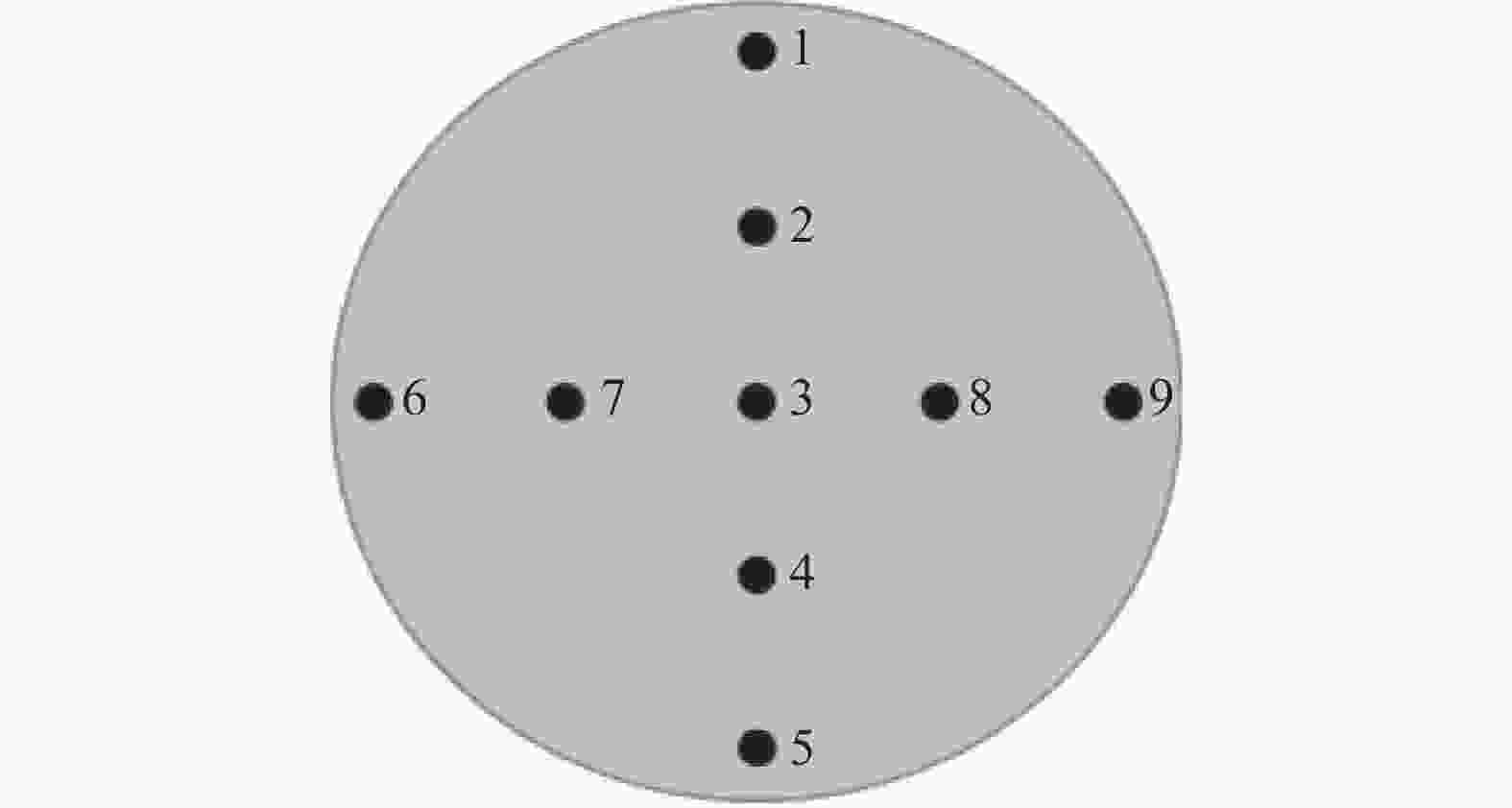
% Al Mo Nb Sn Si Ta 5.68~5.75 0.470~0.485 0.324~0.341 3.42~3.53 0.459~0.475 0.91~1 Zr C H O N Fe 3.48~3.53 0.059~0.063 0.0008~0.001 0.079~0.085 0.076~0.081 0.02~0.021 -
[1] Wang Qingjiang, Liu Jianrong, Yang Rui. Present situation and prospect of high temperature titanium alloys[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2014,34:1−25. (王清江, 刘建容, 杨锐. 高温钛合金的现状与前景[J]. 航空材料学报, 2014,34:1−25. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2014.6.001 [2] Wei Shouyong, Shi Weimin, Wang Dingchun, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of high temperature titanium alloy (Ti60) at 600 ℃[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010,20(S1):801−806. (魏寿庸, 石卫民, 王鼎春, 等. 600 ℃时高温钛合金(Ti60)的组织与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010,20(S1):801−806. [3] 李成功. 航空航天材料[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2002: 83.Li Chenggong, Aerospace materials[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2002: 83. [4] Sun Feng, Li Jinshan, Kou Hongchao, et al. Ti60 titanium alloy α phase dissolution kinetics and solid solution microstructure characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010,20(s1):437−441. (孙峰, 李金山, 寇宏超, 等. Ti60钛合金α相溶解动力学及固溶组织特征[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010,20(s1):437−441. [5] Wei Shouyong, He Yu, Wang Qingjiang, et al. Development of high temperature titanium alloys for aeroengines in Russia[J]. Aircraft Engine, 2005,31(1):52−58. (魏寿庸, 何瑜, 王清江, 等. 俄航空发动机用高温钛合金发展综述[J]. 航空发动机, 2005,31(1):52−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3147.2005.01.014 [6] Hong Quan, Zhang Zhenqi, Yang Guanjun. Hot working process, microstructure and properties of Ti600 alloy[J]. Journal of Metals, 2002,38(z1):135−137. (洪权, 张振祺, 杨冠军. Ti600合金的热机械加工工艺与组织性能[J]. 金属学报, 2002,38(z1):135−137. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2002.z1.039 [7] Li Xianjun. Control technology of chemical composition uniformity of large-scale pure titanium ingot[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2002,19(3):27−29. (李献军. 大规格纯钛铸锭化学成分均匀性控制技术[J]. 钛工业进展, 2002,19(3):27−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2002.03.009 -




 下载:
下载: