Research on microstructure and properties of TC4/ 6061 dissimilar metal resistance spot welding joint
-
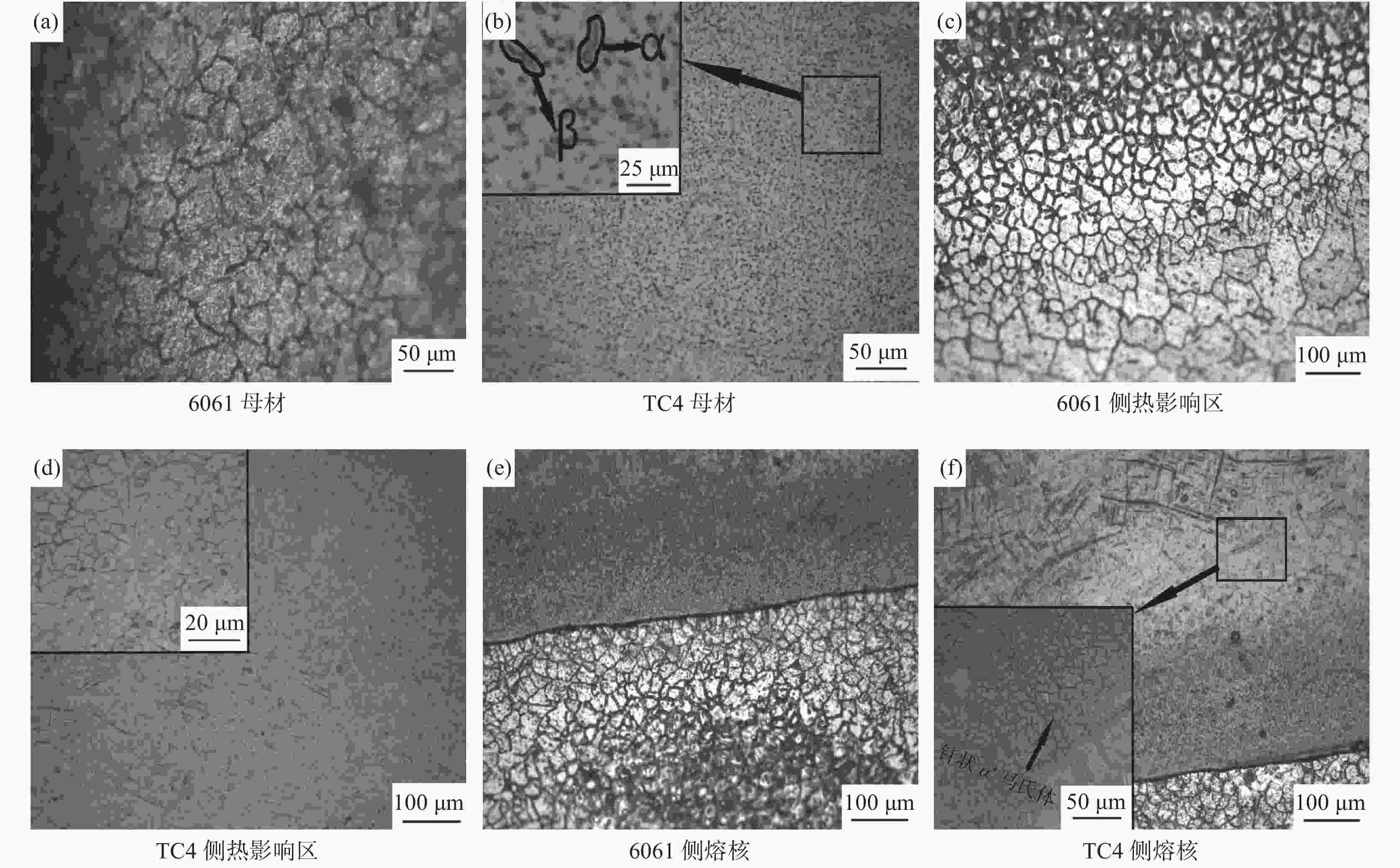
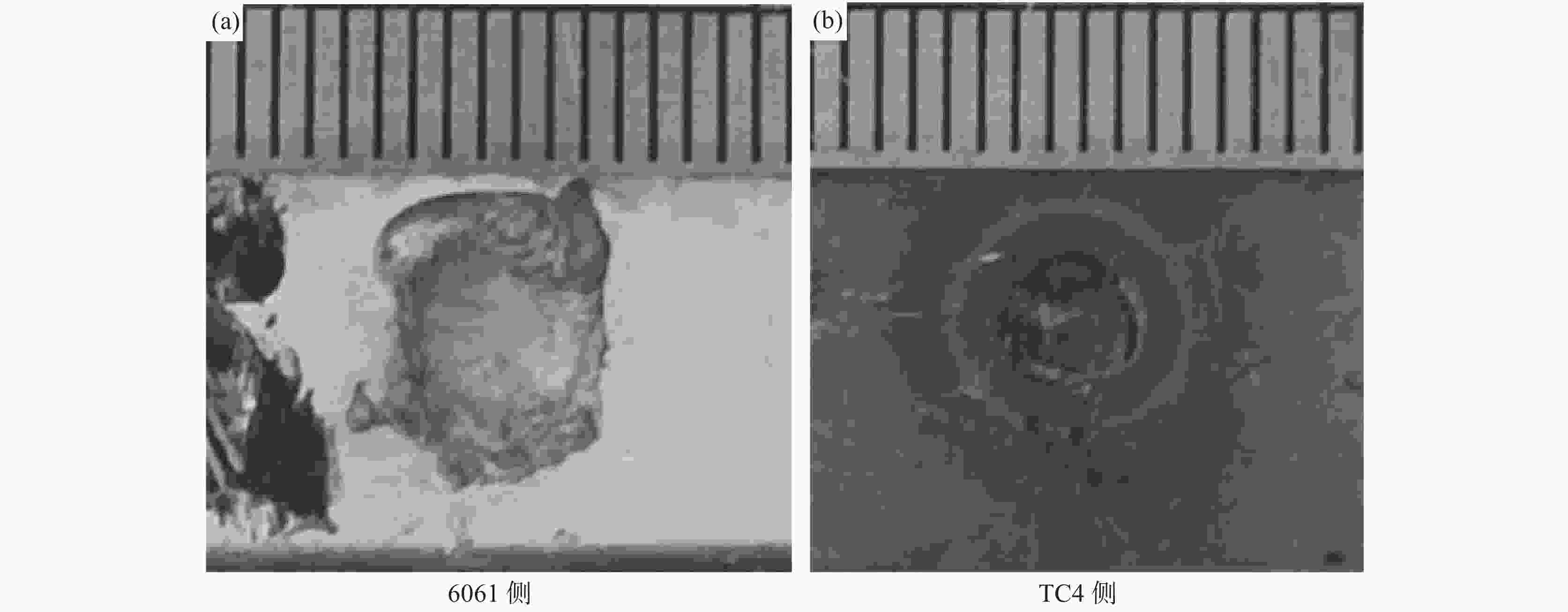
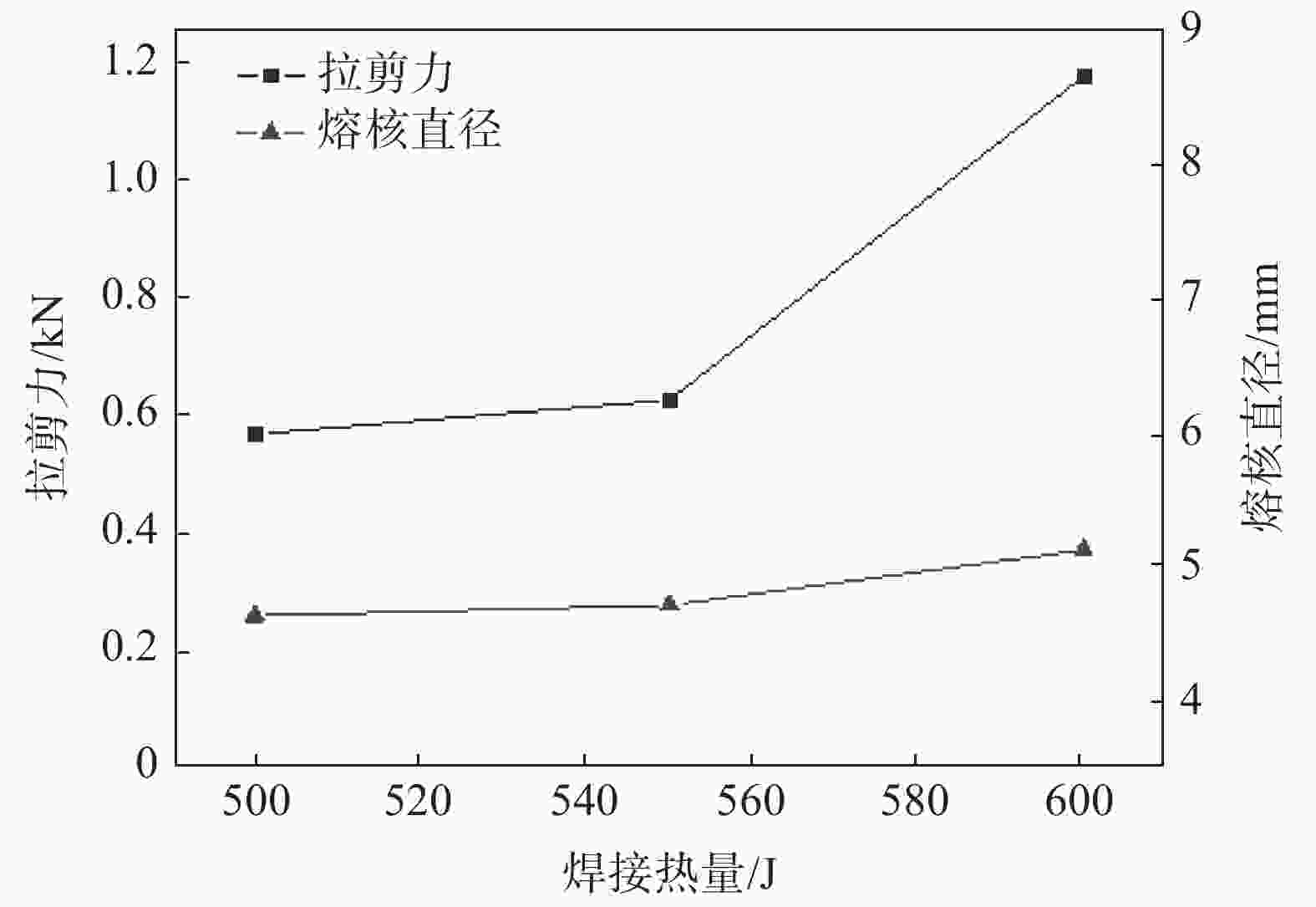
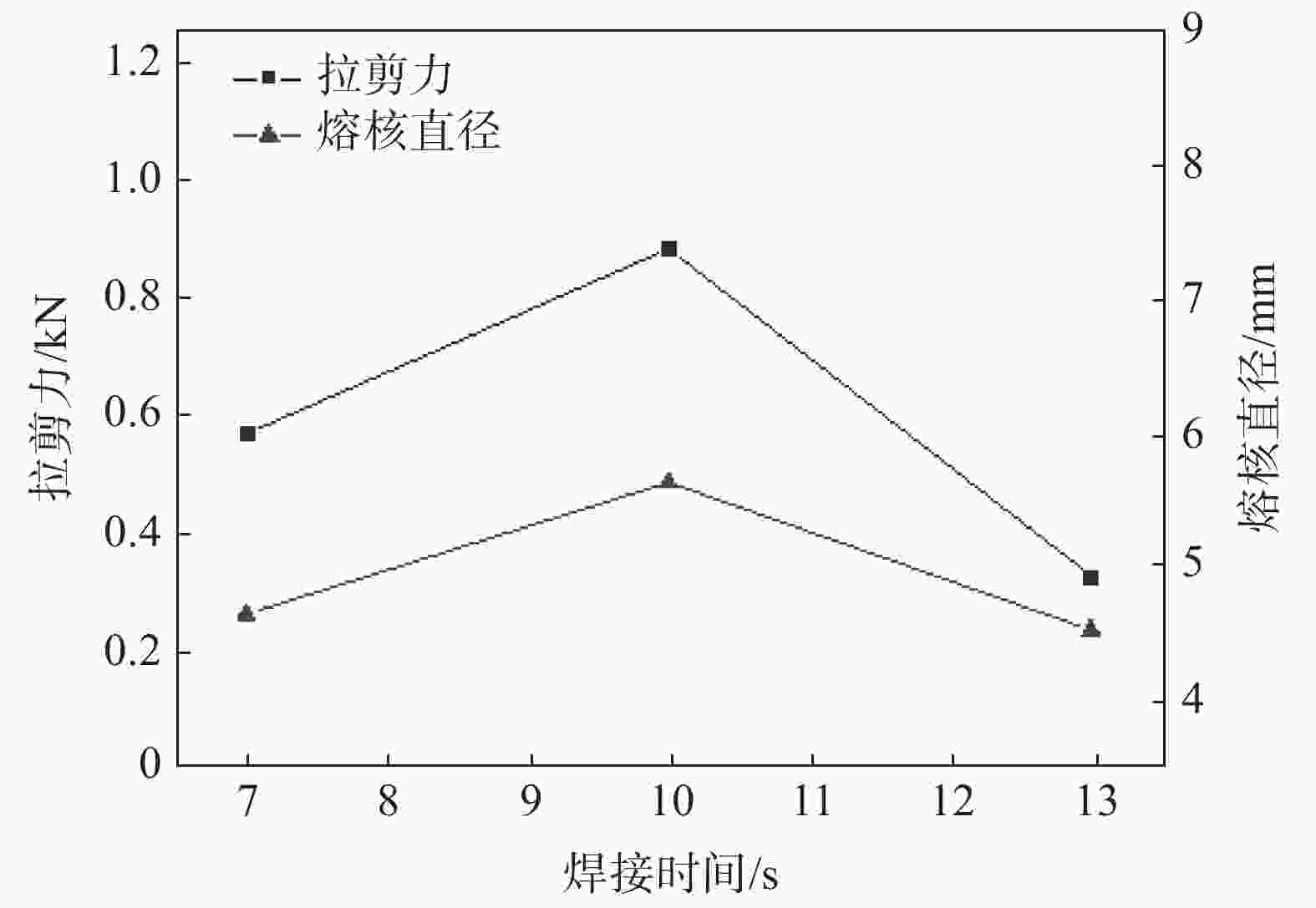
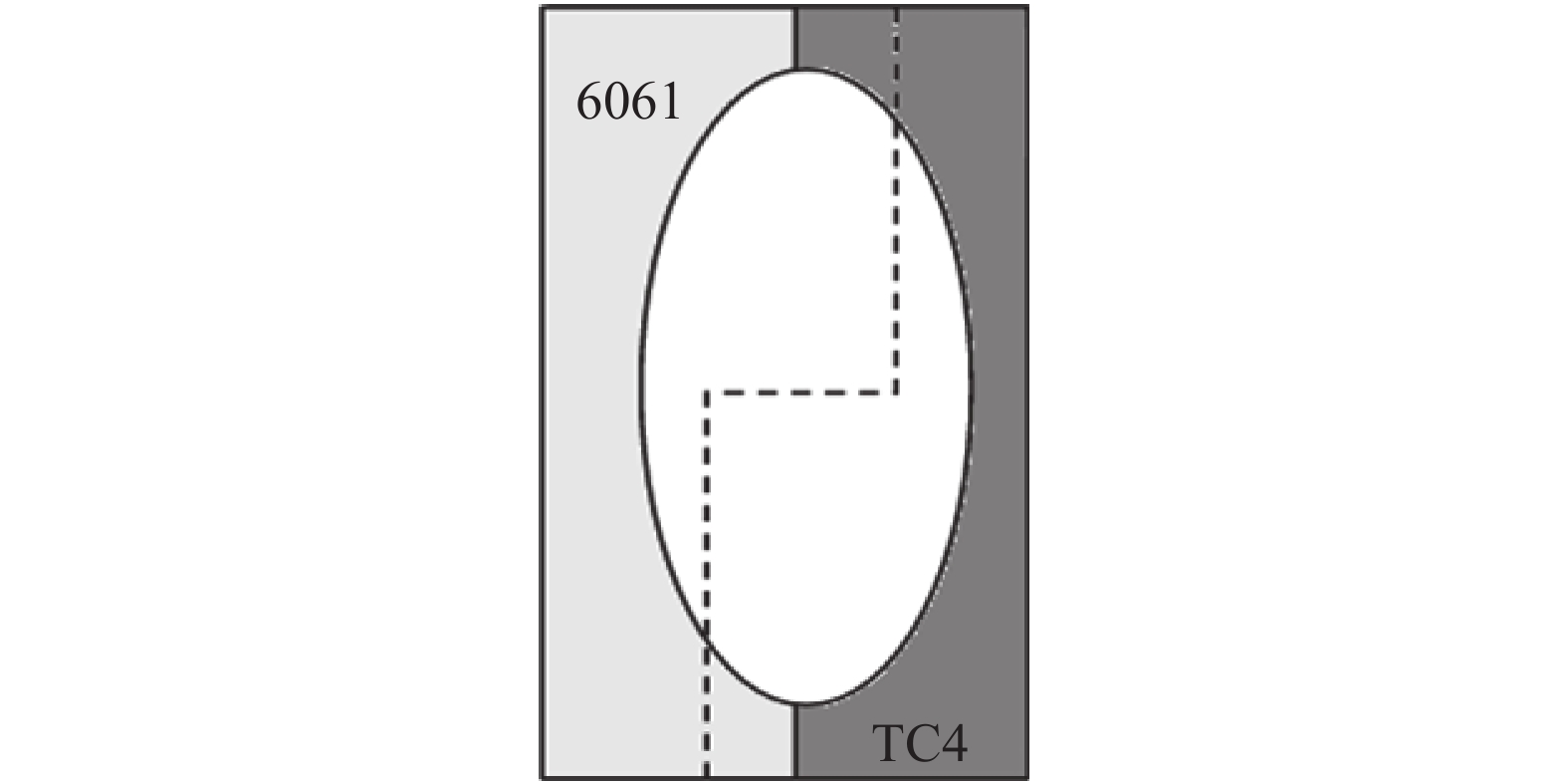
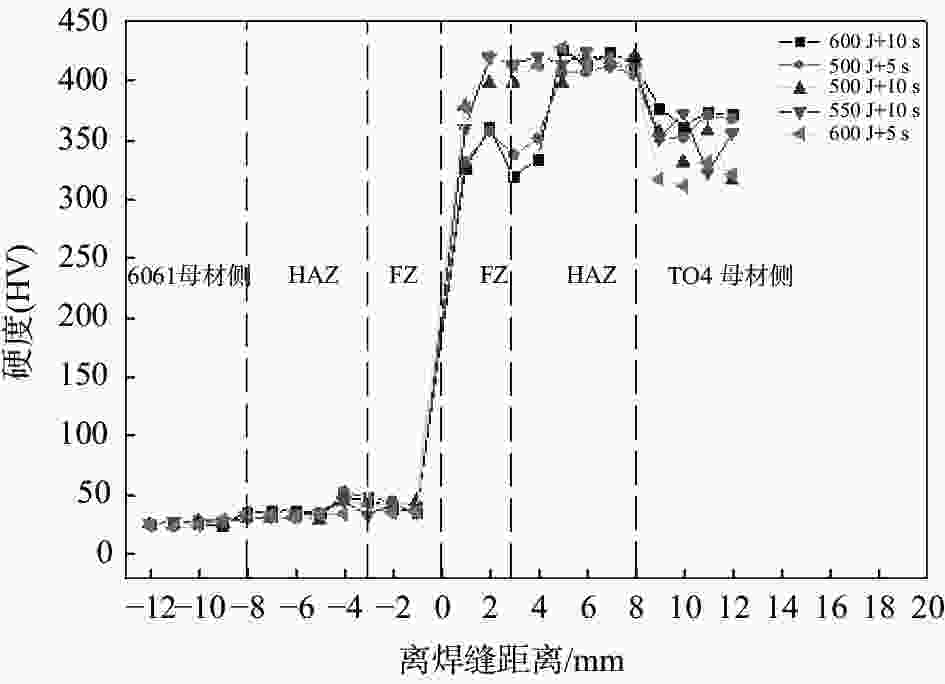
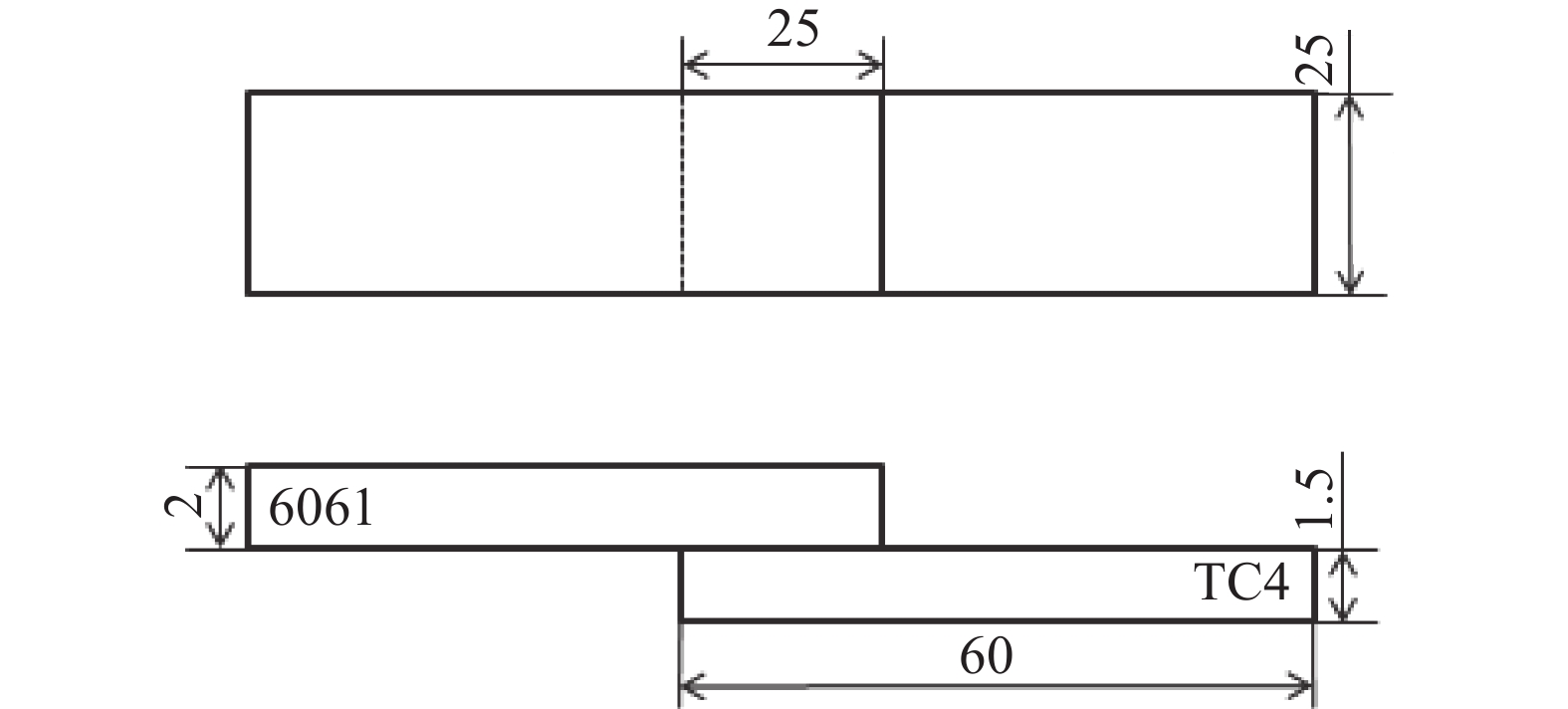
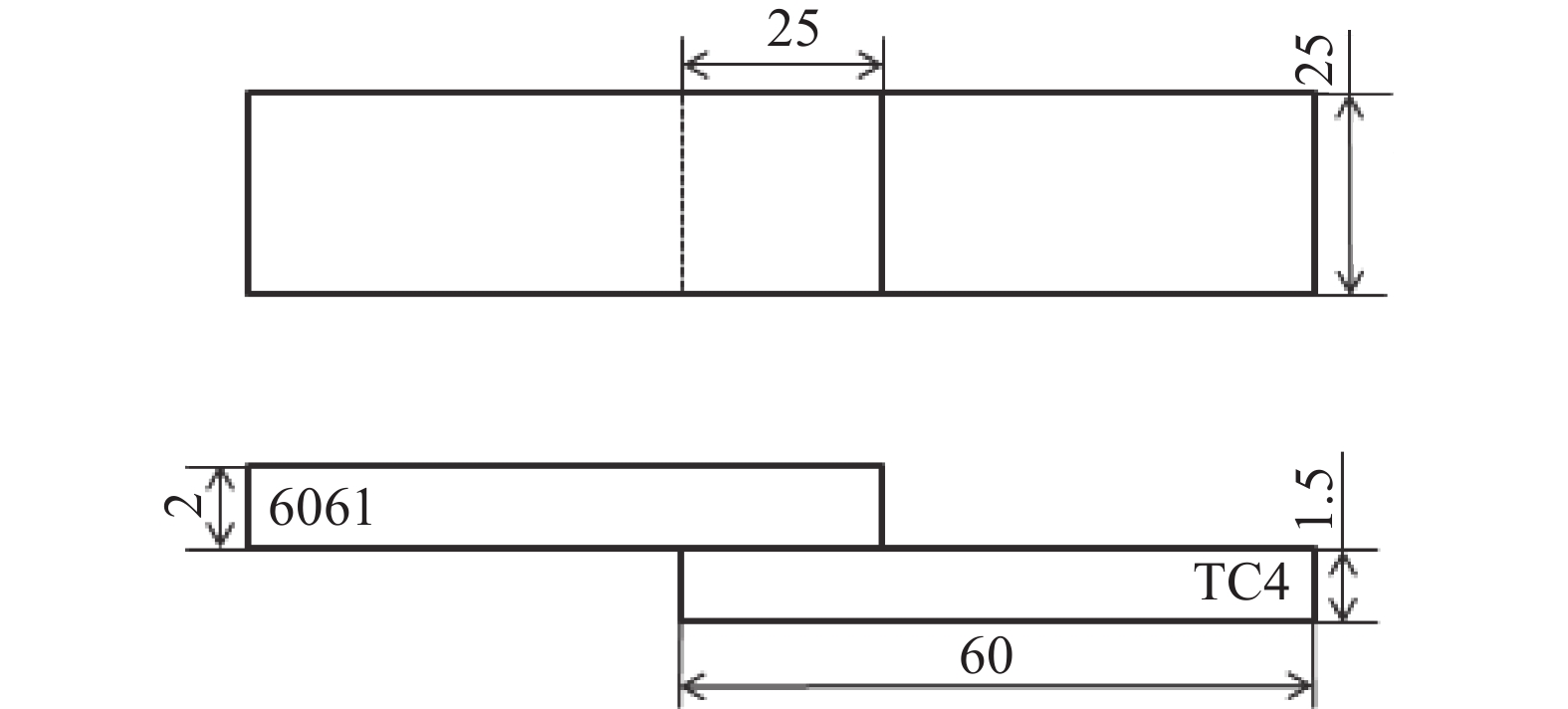
摘要: 采用2 mm厚的TC4钛合金和1.5 mm厚的6061铝合金进行电阻点焊,研究焊接热量与时间对接头拉剪力与熔核直径的影响,观察接头断裂特征并对接头进行了显微组织分析。试验结果表明:热影响区和熔核区的晶粒尺寸相对母材区变得粗大,靠近熔核的6061侧热影响区出现晶粒长大,TC4侧组织出现了细小的针状α'马氏体组织,并呈一定位向排列。随着焊接热量的增加,接头的拉剪力和焊核直径逐渐增加,随着焊接时间增加,接头的拉剪力和熔核直径先增加后减小;当Q=600 J时,接头的拉剪力最高,为1.17 kN。接头靠6061侧显微硬度无明显变化,靠TC4侧熔核区与热影响区硬度分布不均匀,当Q=550 J,t=10 s时硬度分布较理想。试验数据为钛/铝异种金属点焊提供理论指导。Abstract: Using 2 mm thick TC4 titanium alloy and 1.5 mm thick 6061 aluminum alloy as raw materials for resistance spot welding, the effects of heat and time on the tensile-shear force and nugget diameter of the joint were studied. The fracture characteristics of the joint were observed, and the microstructure of the joint was analyzed. The results show that the grain size of the heat affected zone and nugget zone become larger than the base material zone, the grain size of the heat affected zone for the 6061 aluminum alloy grows. The fine α' martensite structure of the TC4 side appears, and present directional distribution. With the increase of welding heat, the tensile shear and core diameter of the joint gradually increase. With the welding time prolonged, both of the tensile-shear force and core diameter of the joint increase first and then decrease. When Q=600 J, the highest tensile shear of the joint delivers is 1.17 kN. The microhardness of the 6061 aluminum alloy side of the joint has no obvious change, and the hardness distribution of the nugget zone and the heat affected zone of the TC4 alloy side is nonuniform. When Q =550 J and t =10 s, the ideal hardness distribution is obtained. These experimental data provide theoretical guidance for Ti/Al dissimilar metal spot welding.
-
Key words:
- titanium alloy /
- aluminum alloy /
- dissimilar metals /
- resistance spot welding
-
表 1 TC4钛合金的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of TC4 alloy
% Al V Fe C N O Ti 6.0 4.0 0.026 0.0150 0.008 0.06 余量 表 2 6061铝合金的化学成分
Table 2. Chemical compositions of 6061 alloy
% Cr Cu Ti Mg Si Mn Al 0.04 0.3 0.15 1 0.3 0.15 余量 表 3 点焊工艺参数
Table 3. Parameters of spot welding process
试验编号 焊接热量/J 焊接时间/s 1 500 10 2 500 5 3 600 5 4 550 10 5 600 10 -
[1] Ma Zhipeng, Zhang Xuyun, Guo Guangwei. Research status of dissimilar metal welding between titanium alloy and aluminum alloy[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2014,37(5):128−133. (马志鹏, 张旭昀, 郭光伟. 钛合金与铝合金异种金属焊接研究现状[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2014,37(5):128−133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2014.05.036 [2] Shao Lin, Cui Enhong. Different welding methods were used to weld Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy[J]. Materials China, 2019,38(3):286−290. (邵玲, 崔恩红. 不同焊接方法焊接Ti-22Al-25Nb合金[J]. 中国材料进展, 2019,38(3):286−290. [3] 苏居季. 钛合金激光点焊/双光束焊接头的力学性能研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳航空航天大学, 2019.Su Juji. Mechanical properties of laser spot welding/double beam welding joint of titanium alloy[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Aerospace University, 2019. [4] Liu Hao, Chen Yuhua, Zhang Wentao. Microstructure characteristics of Ti/Al needle-free friction stir lap welding joint[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020,42(6):64−73. (刘浩, 陈玉华, 章文滔. Ti/Al无针搅拌摩擦搭接点焊接头组织特征[J]. 航空学报, 2020,42(6):64−73. [5] Gao Yuan, Deng Huaibo, Chen Yuhua. Study on the formation process and mechanism of Ti/Al dissimilar metal micro-resistance spot welding joint[J]. Journal of Netshape Forming Engineering, 2018,10(5):50−53. (高原, 邓怀波, 陈玉华. Ti/Al异种金属微电阻点焊接头的形成过程及形成机理研究[J]. 精密成型工程, 2018,10(5):50−53. [6] 高原. Ti/Al异种金属微电阻点焊接头组织性能及形成机理[D]. 南昌: 南昌航空大学, 2018.Gao Yuan. Microstructure, properties and formation mechanism of Ti/Al dissimilar metal micro-resistance spot welding joint [D]. Nanchang: Nanchang Hangkong University, 2018. [7] Liu Hao, Chen Yuhua, Ji Di, et al. New progress in spot welding technology of titanium-aluminum dissimilar materials[J]. Journal of Netshape Forming Engineering, 2019,11(5):63−70. (刘浩, 陈玉华, 季迪, 等. 钛-铝异种材料的点焊技术研究新进展[J]. 精密成型工程, 2019,11(5):63−70. [8] Fan Dongchen, Chen Donghai, Chen Yiping, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of resistance spot joint of titanium alloy /aluminum alloy[J]. Welding & Joining, 2016,11(1):16−19. (范东晨, 程东海, 陈益平, 等. 钛/铝异种材料电阻点焊接头力学性能及显微组织[J]. 焊接, 2016,11(1):16−19. [9] 陈超. Ti/Al“搅拌摩擦点焊—钎焊”复合焊接工艺及机理研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.Chen Chao. Research on process and mechanism of friction stir spot welding-brazing of Ti/Al hybrid joint [D]. Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019. [10] Chen Yuhua, Li Shuhan, Liu Dongya, et al. Characteristics and properties of Ti/Al dissimilar metal micro-resistance spot welding joint[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2017,46(s1):37−39. (陈玉华, 李树寒, 刘东亚, 等. Ti/Al异种金属微电阻点焊接头的特征及性能[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2017,46(s1):37−39. [11] 刘东亚. Ti/Al异种金属电阻点焊工艺及接头形成机理研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌航空大学, 2016.Liu Dongya. Study on resistance spot welding technology and joint formation mechanism of Ti/Al dissimilar metals [D]. Nanchang: Nanchang Hangkong University, 2016. -




 下载:
下载: