Study on sodium roasting kinetics of vanadium removal slag of titanium tetrachloride
-
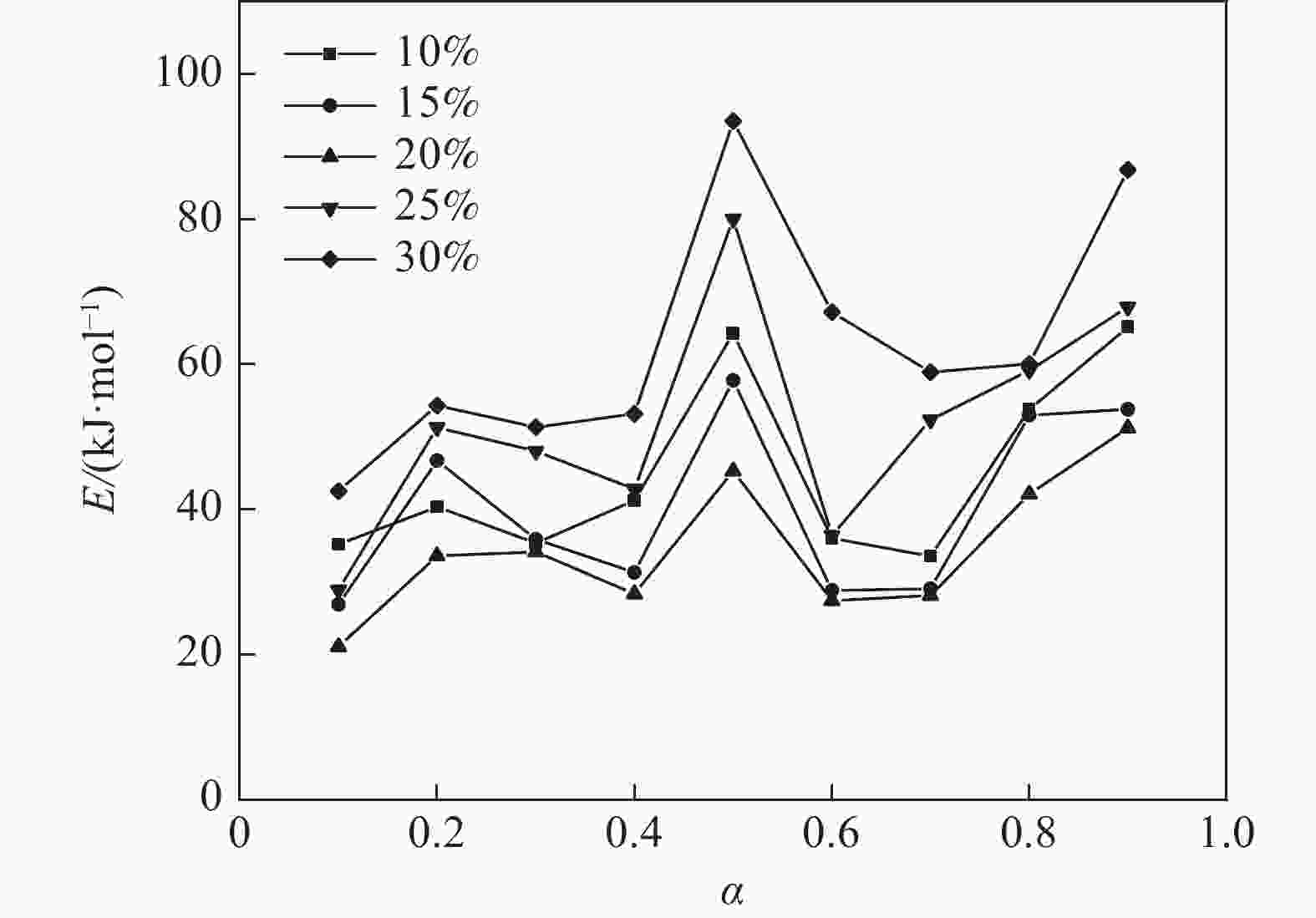
摘要: 基于非等温热重分析研究Na2CO3添加量和升温速率对含钒尾渣氧化的影响规律,采用Kissinger-Akahira-Sunose(KAS)法计算了含钒尾渣氧化过程活化能和指前因子,并通过Coats-Redfem法推断机理函数并建立不同阶段所适用的动力学方程。结果表明:含钒尾渣完全氧化的温度为700 ℃,随Na2CO3添加量增加,表观活化能逐渐降低,氧化速率提高;当Na2CO3添加量超过20%后,钒渣在氧化焙烧过程中出现玻璃相,产生烧结现象,表观活化能开始逐渐增大,氧化速率降低。钠化焙烧过程分为四个阶段,其动力学方程分别为:第一阶段二维扩散dα/dT=exp(−72.03/RT)4(1−α)1/2[1−(1−α)1/2]20.022/β,第二阶段三维扩散dα/dT=exp(−23.7/RT)3/2(1−α)4/3[(1−α)−1/3−1]−10.014/β,第三阶段化学反应dα/dT=exp(−27.91/RT) (1−α)20.06/β,第四阶段形核与长大dα/dT=exp(−12.09/RT)2(1−α)[−ln(1−α)]1/20.14/β。Abstract: Based on non-isothermal thermogravimetric analysis, the influences of Na2CO3 addition and heating rate on oxidation of vanadium removal slag of titanium tetrachloride (vanadium-containing tailings) were studied. The Kissinger-Akahira-Sunose (KAS) method was used to calculate the activation energy and pre-exponential factor of the oxidation process of vanadium-containing tailings. Through the Coats-Redfem method, the mechanism function was inferred and the kinetics equations of different stages were established. The results show that the temperature for complete oxidation of the vanadium-containing tailings is 700 ℃. With the increase of Na2CO3 addition, the apparent activation energy gradually decreases and the oxidation rate increases. While the Na2CO3 addition exceeds 20%, the glassy phase appears during the oxidation roasting process which results in sintering, and the apparent activation energy gradually increases with the oxidation rate decreased consequently. The sodium roasting process can be divided into four stages and the kinetics equations are as follows: the first stage of two-dimensional diffusion with dα/dT=exp(−72.03/RT)4(1−α)1/2[1−(1−α)1/2]20.022/β, the second stage of three-dimensional diffusion with dα/dT = exp (−23.7/RT)3/2(1−α)4/3[(1−α)−1/3−1]−10.014/β, the third stage of chemical reaction with dα/dT=exp(−27.91/RT)(1−α)20.06/β and the fourth stage of nucleation and growth with dα/dT=exp(−12.09/RT)2(1−α)[−ln(1−α)]1/20.14/β.
-
表 1 粗四氯化钛精制尾渣的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of vanadium removal slag of crude titanium tetrachloride
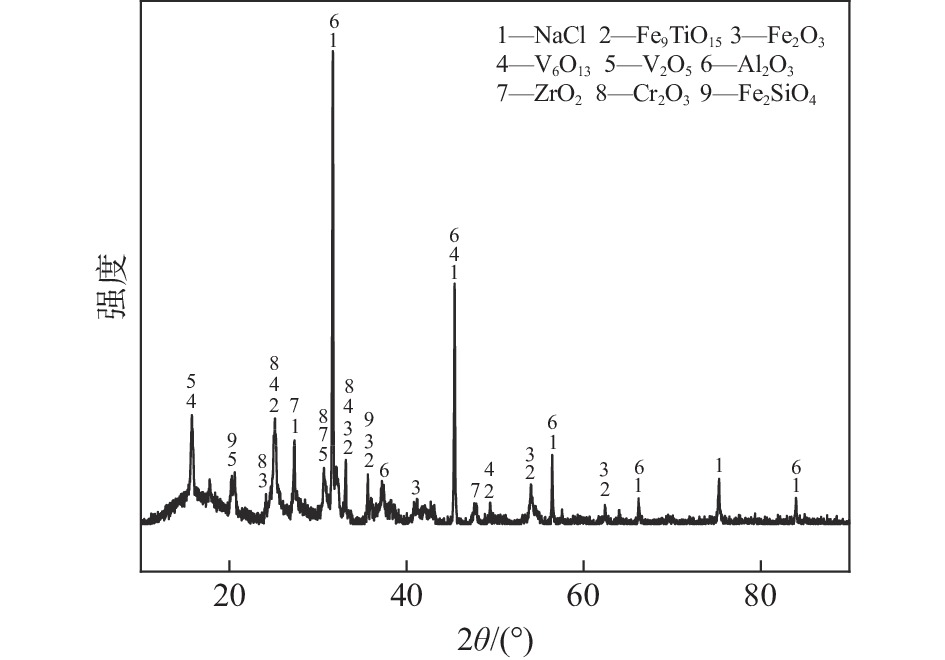
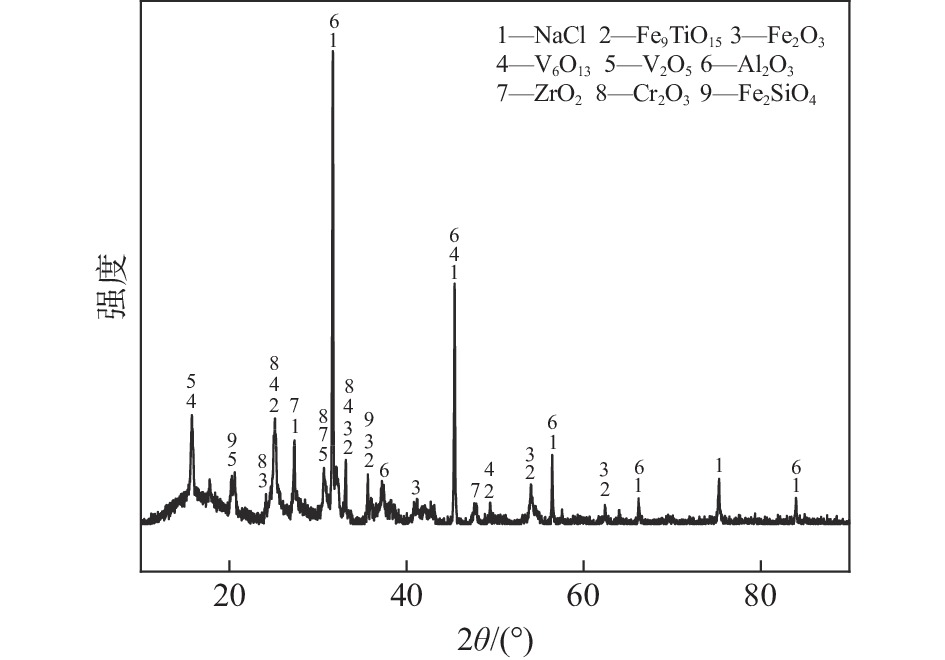
% Cl Fe2O3 TiO2 Al2O3 V2O5 ZrO2 C SiO2 Cr2O3 31.95 19.18 15.39 8.64 11.17 6.77 2.68 1.86 0.81 表 2 四氯化钛除钒尾渣添加20%Na2CO3钠化焙烧在不同阶段的表观活化能和指前因子
Table 2. Apparent activation energy and pre-exponential factor in different stages for sodium roasting of vanadium removal slag of titanium tetrachloride with 20% Na2CO3
阶段 不同升温速率时的活化能 活化能/(kJ·mol−1) 指前因子/min−1 10 K/min 15 K/min 20 K/min 活化能/(kJ·mol−1) 拟合度 活化能/(kJ·mol−1) 拟合度 活化能/(kJ·mol−1) 拟合度 第一阶段 77.66 0.99 71.98 0.99 66.44 0.99 72.03 0.022 第二阶段 24.81 0.99 21.78 0.99 24.51 0.98 23.7 0.014 第三阶段 33.67 0.98 26.04 0.99 24.03 0.99 27.91 0.06 第四阶段 13.43 0.98 10.21 0.99 12.64 0.99 12.09 0.14 -
[1] Qu Jinwei, Zhang Ting′an, Niu Liping, et al. Technical progress of comprehensive utilization of converter vanadium slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(5):1−7. (瞿金为, 张廷安, 牛丽萍, 等. 转炉钒渣的综合利用技术进展[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(5):1−7. [2] Xie Qichun. Research and application of reclaiming ilmenite from titanium tailings in Panxi[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2018,38(3):40−42. (谢琪春. 攀西选钛尾矿中再回收钛铁矿工艺研究与应用[J]. 矿冶工程, 2018,38(3):40−42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2018.03.009 [3] Li Liang, Zhou Li, Li Dongqin, et al. Research on the recovery and utilization of TiCl4 refined tailings[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016,7(5):76−79. (李良, 周丽, 李冬勤, 等. TiCl4精制尾渣的回收利用研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2016,7(5):76−79. [4] Zhou Li. Study on the vanadium removal process of the organic pretreatment of high vanadium content crude titanium tetrachloride[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(4):24−28. (周丽. 高含钒粗四氯化钛有机物预处理除钒工艺研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(4):24−28. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.04.005 [5] Yu Jing, Zhang Ping, Chen Tianxiang, et al. Research on the process of removing vanadium from crude titanium tetrachloride organics[J]. Journal of Guizhou University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2008,37(2):29−32. (于静, 章平, 陈天祥, 等. 粗四氯化钛有机物除钒工艺研究[J]. 贵州工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2008,37(2):29−32. [6] Shi Zhixin. Characterization of the variation law of vanadium spinel and fayalite during the sodium roasting of vanadium slag[J]. Non-ferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Part), 2018,(4):4−8,14. (史志新. 钒渣钠化焙烧过程中钒尖晶石和铁橄榄石的变化规律表征[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2018,(4):4−8,14. [7] Zhang Xinxia. Optimization of sodium roasting process for high silicon high calcium vanadium slag[J]. Ferro Alloys, 2013,44(1):22−24,29. (张新霞. 高硅高钙钒渣钠化焙烧工艺的优化研究[J]. 铁合金, 2013,44(1):22−24,29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1943.2013.01.006 [8] Yang Z, Li H Y, Yin X C, et al. Leaching kinetics of calcification roasted vanadium slag with high CaO content by sulfuric acid[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2014,133:105−111. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2014.10.011 [9] Pan Ziwei, Zheng Shili, Wang Zhongxing, et al. High-efficiency simultaneous extraction process of vanadium and chromium from high chromium vanadium slag by sub-molten salt method[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014,35(2):1−8. (潘自维, 郑诗礼, 王中行, 等. 亚熔盐法高铬钒渣钒铬高效同步提取工艺研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2014,35(2):1−8. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2014.02.001 [10] Gao Jian, Liu Xibin, Shi Zhixin. Phase changes and vanadium element migration characteristics of vanadium slag during sodium oxidation roasting[J]. Mining and Metallurgy, 2019,28(3):105−110. (高健, 刘希斌, 史志新. 钒渣氧化钠化焙烧过程中物相变化及钒元素迁移特征[J]. 矿冶, 2019,28(3):105−110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7854.2019.03.022 [11] Li Xinsheng, Xie Bing, Wang Guang, en, et al. Oxidation process of low-grade vanadium slag in presence of Na2CO3[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011,21(8):1860−1867. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60942-4 [12] Xie Zhaoming, Deng Rongrui, Liu Zuohua, et al. Evolutionary behavior of fractal growth of vanadium slag powder in sodium roasting converter[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry, 2019,70(5):1904−1912. (谢昭明, 邓容锐, 刘作华, 等. 钠化焙烧转炉钒渣粉体分形生长的演化行为[J]. 化工学报, 2019,70(5):1904−1912. [13] Wang Minghua, Zhao Hui, Liu Yan, et al. Semi-quantitative analysis of the sodiumization roasting process of vanadium slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(5):31−36. (王明华, 赵辉, 刘岩, 等. 钒渣钠化焙烧过程的半定量分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(5):31−36. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.05.006 [14] Lu X L, Zhu Q, Meng Y Z. Kinetic analysis of thermal decomposition of poly (propylene carbonate)[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2005,89(2):282−288. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2004.12.025 [15] Flynn J H, Wall L A. A quick, direct method for the determination of activation energy from thermogravimetric data[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part B:Polymer Letters, 1966,4(5):323−328. doi: 10.1002/pol.1966.110040504 [16] Criado J M, Sánchez-Jiménez P E, Pérez-Maqueda L A. Critical study of the isoconversional methods of kinetic analysis[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis & Calorimetry, 2008,92(1):199−203. [17] Kissinger H E. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1957,29(11):1702−1706. doi: 10.1021/ac60131a045 [18] Vyazovkin S, Chrissafis K, Lorenzo M L D, et al. ICTAC kinetics committee recommendations for collecting experimental thermal analysis data for kinetic computations[J]. Thermochimica ACTA, 2014,590:1−23. doi: 10.1016/j.tca.2014.05.036 [19] Coats A W, Redfern J P. Kinetic parameters from thermogravimetric data. II[J]. Nature, 1964,201:68−69. doi: 10.1038/201068a0 [20] Huang L, Chen Y C, Liu G, et al. Non-isothermal pyrolysis characteristics of giant reed using thermogravimetric analysis[J]. Energy, 2015,87:31−40. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2015.04.089 -




 下载:
下载: