Influence of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of ZTC4 titanium alloy
-
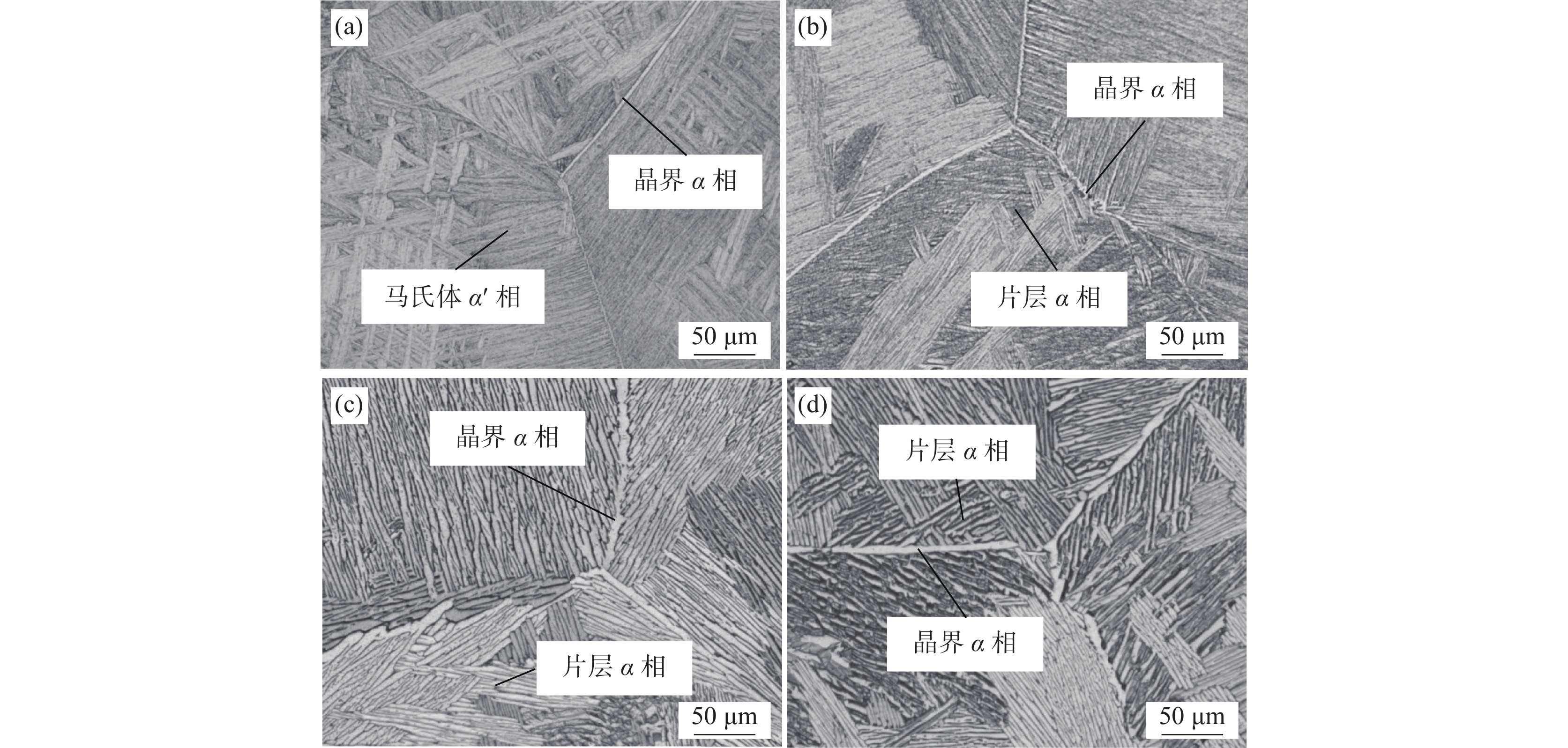
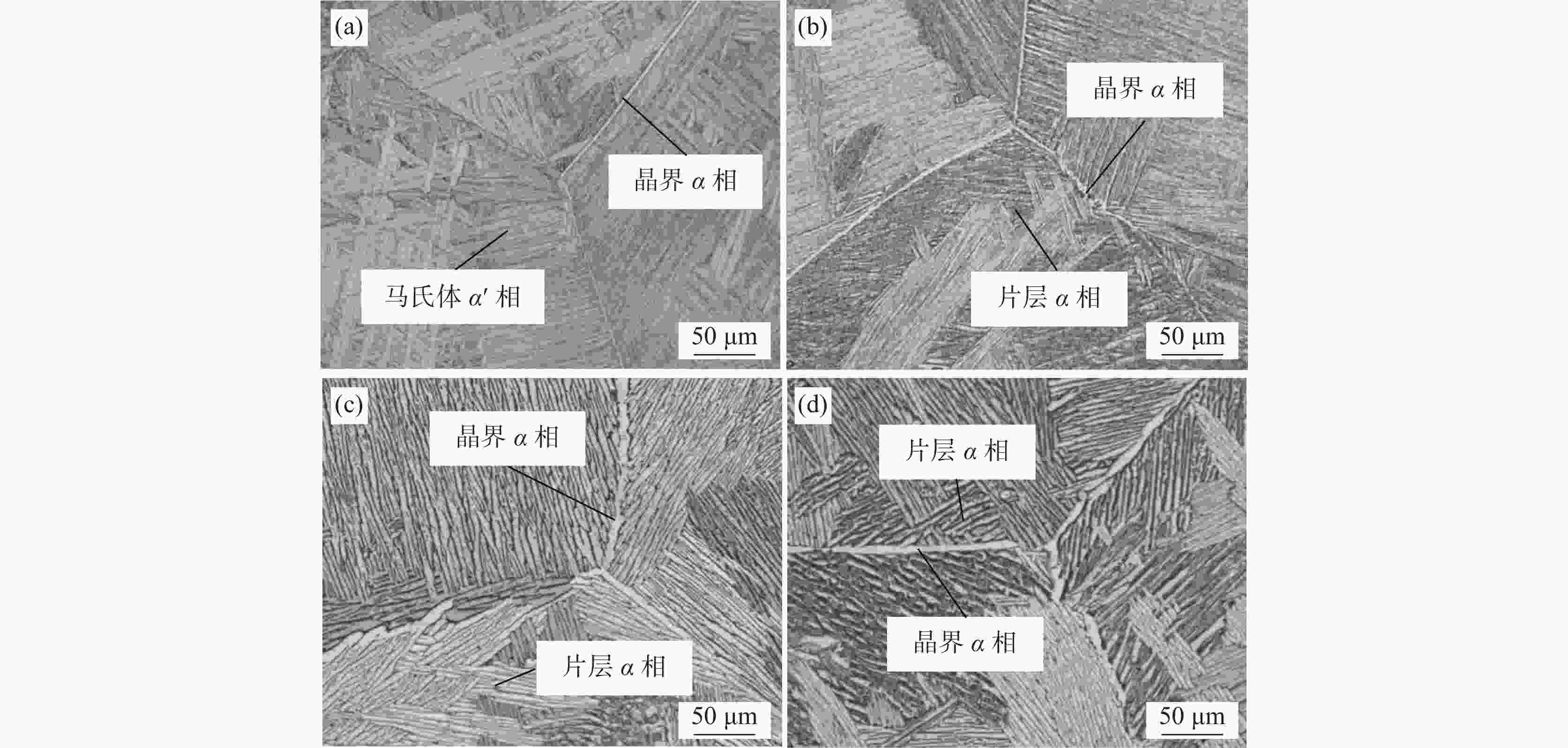
摘要: 采用金相显微镜(OM)研究了热处理制度对ZTC4钛合金显微组织的演变规律,以及显微组织对力学性能的影响关系。结果表明:ZTC4钛合金铸件由马氏体α′相组成,进行退火以及热等静压+退火热处理后,显微组织均为典型魏氏组织。ZTC4钛合金铸件退火后抗拉强度可达955 MPa,其延伸率和断面收缩率分别为8.8%和13.1%。采用热等静压+退火热处理后,抗拉强度降低至892 MPa,但其延伸率和断面收缩率升高至11.2%和21.4%。采用热等静压热处理,可破碎原始β相晶粒,形成破碎的晶界α相,提高ZTC4钛合金塑性性能。Abstract: The optical microscope (OM) was employed to investigate the influence of heat treatment on microstructure evolution of ZTC4 titanium alloy, and the relationship between microstructure and mechanical properties was discussed. The results showed that the ZTC4 titanium alloy casting was composed of martensitic phase α′. A typical Widmanstatten microstructure was always obtained after annealing or hot isostatic pressing followed by annealing heat treatment. The tensile strength of ZTC4 titanium alloy casting after annealing can reach 955 MPa, and its elongation and reduction of area were only 8.8% and 13.1%, respectively. After hot isostatic pressing followed by annealing heat treatment, the tensile strength was reduced to 892 MPa, but its elongation and reduction of area were increased to 11.2% and 21.4%. The hot isostatic pressing heat treatment can break the original β phase grains, which improve the plastic properties of ZTC4 titanium alloy.
-
Key words:
- ZTC4 titanium alloy /
- heat treatment /
- microstructure /
- mechanical properties
-
表 1 ZTC4钛合金铸件化学成分及验收标准
Table 1. Chemical compositions of ZTC4 titanium alloy casting and standard
% ZTC4钛合金 Ti Al V Fe Si C N H O 铸锭成分 Bal. 6.40 4.38 0.19 0.02 0.014 0.006 0.002 0.14 GB/T 15073—1994 Bal. 5.5~6.8 3.5~4.5 ≤0.3 ≤0.15 ≤0.10 ≤0.05 ≤0.015 ≤0.20 表 2 不同热处理工艺条件下ZTC4钛合金显微组织参数
Table 2. Microstructure parameters of ZTC4 titanium alloy at various heat treatments
热处理工艺 平均片层α相尺寸/μm 平均晶界α相尺寸/μm 铸态 1.1 3.5 退火态 2.5 4.8 热等静压态 4.6 7.6 热等静压+退火态 6.2 10.6 表 3 ZTC4钛合金在不同热处理工艺条件下的室温力学性能
Table 3. Mechanical properties of ZTC4 titanium alloy castings at various heat treatments
热处理工艺 Rm/MPa Rp0.2/MPa A/% Z/% 铸态 942 860 8.0 12.2 退火态 955 897 8.8 13.1 热等静压态 911 851 9.5 15.3 热等静压+退火态 892 834 11.2 21.4 -
[1] Tian Yongwu, Zhu Lele, Li Weidong, et al. Application and development of high temperature titanium alloys[J]. Hot Working Process, 2020,49(8):4−9. (田永武, 朱乐乐, 李伟东, 等. 高温钛合金的应用及发展[J]. 热加工工艺, 2020,49(8):4−9. [2] Semenova I P, Saitova L R, Raab G I, et al. Microstructural features and mechanical properties of the Ti-6Al-4V ELI alloy processed by severe plastic deformation[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2006,(1):128−131. [3] Ran Xing, Lv Zhigang, Cao Jian, et al. Investment casting technology for large complex titanium alloy castings[J]. Casting, 2021,70(2):8−13. (冉兴, 吕志刚, 曹建, 等. 大型复杂钛合金铸件熔模精密铸造技术[J]. 铸造, 2021,70(2):8−13. [4] Zhang W, Qin P, Wang Z, et al. Superior wear resistance in EBM-processed TC4 alloy compared with SLM and forged samples[J]. Materials, 2019,12(5):67−72. [5] Pan Bo, Huang Yichen, Li Liqun, et al. Effect of multiple laser repair on microstructure and hardness of ZTC4 titanium alloy[J]. China Laser, 2019,46(10):28−32. (潘博, 黄怡晨, 李俐群, 等. 多次激光修复对ZTC4钛合金组织与硬度的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2019,46(10):28−32. [6] Yin Zhongwei, Sun Yanbo, Zhang Xuhu, et al. Near net forming technology and development status of hot isostatic pressing of powder titanium alloy[J]. Material Guide, 2019,33(7):24−33. (阴中炜, 孙彦波, 张绪虎, 等. 粉末钛合金热等静压近净成形技术及发展现状[J]. 材料导报, 2019,33(7):24−33. [7] Xu Kaihua, Liu Haijun, Yan Jiangpeng, et al. Microstructure evolution of hot isostatic pressing TC4 titanium alloy during multi pass hot compression deformation[J]. Journal of Plastic Engineering, 2021,28(7):7−12. (徐凯华, 刘海军, 闫江鹏, 等. 热等静压态TC4钛合金在多道次热压缩变形中的组织演变[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2021,28(7):7−12. [8] Zhang Meijuan, Ying Xiwang, Nan Hai, et al. Study on interfacial fusion effect of ZTC4 / TA2 titanium alloy castings with slender holes[J]. Precision Forming Engineering, 2018,10(3):5−11. (张美娟, 郄喜望, 南海, 等. 含细长孔ZTC4/TA2钛合金铸件界面熔合效果研究[J]. 精密成形工程, 2018,10(3):5−11. [9] Feng Xin, Qiu Jianke, Ma Yingjie, et al. Effect of surface defects on fatigue crack propagation behavior of ZTC4 titanium alloy castings[J]. Special Casting and Nonferrous Alloys, 2019,(5):3−8. (冯新, 邱建科, 马英杰, 等. ZTC4钛合金铸件表面缺陷对疲劳裂纹扩展行为的影响[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2019,(5):3−8. [10] Ying Xiwang, Zhang Meijuan, Zou Chunyu, et al. Mechanical properties and failure analysis of ZTC4 laser cladding repair[J]. Welding, 2020,(1):29−35,41. (郄喜望, 张美娟, 邹纯昱, 等. ZTC4激光熔覆修复力学性能及失效分析[J]. 焊接, 2020,(1):29−35,41. [11] Liu Jixiong, Yang Qi, Guo Zhijun, et al. Microstructure evolution of ZTC4 titanium alloy treated by hot isostatic pressing during low temperature heat treatment[J]. Journal of Material Heat Treatment, 2015,(S1):5−10. (刘继雄, 杨奇, 郭志军, 等. 热等静压处理ZTC4钛合金低温热处理过程中组织演变[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2015,(S1):5−10. [12] Zhang Tingjie. Electron microscopic study of phase transformation in titanium alloys (Ⅲ): Martensitic transformation in titanium alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 1989,(4):71−78. (张廷杰. 钛合金相变的电子显微镜研究(Ⅲ): 钛合金中的马氏体相变[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 1989,(4):71−78. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.1989.04.016 [13] Wang Z, Wang X, Zhu Z. Characterization of high-temperature deformation behavior and processing map of TB17 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2017,692:149−154. [14] Zhu Liwei, Wang Xinnan, Zhu Zhishou. Microstructure and mechanical properties of TC4-DT titanium alloy under different heat treatment processes[J]. Progress of Titanium Industry, 2012,(1):14−17. (祝力伟, 王新南, 朱知寿. 不同热处理工艺下TC4-DT钛合金的显微组织及力学性能[J]. 钛工业进展, 2012,(1):14−17. [15] Tian Chenchao, Gao Yang, Zhang Juan, et al. Comparative analysis of fatigue crack growth rates of TC4-DT and TC21 titanium alloys[J]. Welded Pipe, 2019,42(11):31−34. (田晨超, 高阳, 张娟, 等. TC4-DT及TC21钛合金疲劳裂纹扩展速率的对比分析[J]. 焊管, 2019,42(11):31−34. [16] Wang B H, Cheng L, Bao X C. Effect of heat treatment on very high cycle fatigue properties of TC4[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2021,881:3−11. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.881.3 [17] Liu G, Huang C, Sun S, et al. Effect of microstructure on high-speed cutting modified anti-fatigue performance of Incoloy A286 and titanium alloy TC17[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2021,113(3):855−866. [18] Wang Xinnan, Zhu Zhishou, Shang Guoqiang, et al. Effect of heat treatment process on mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V ELI alloy thick section forgings[J]. Progress of Titanium Industry, 2019,(2):29−33. (王新南, 朱知寿, 商国强, 等. 热处理工艺对Ti-6Al-4V ELI合金厚截面锻件力学性能的影响[J]. 钛工业进展, 2019,(2):29−33. -




 下载:
下载: