Study on microstructure and properties of low-alloy steel fabricated by laser wire-feed additive manufacturing
-
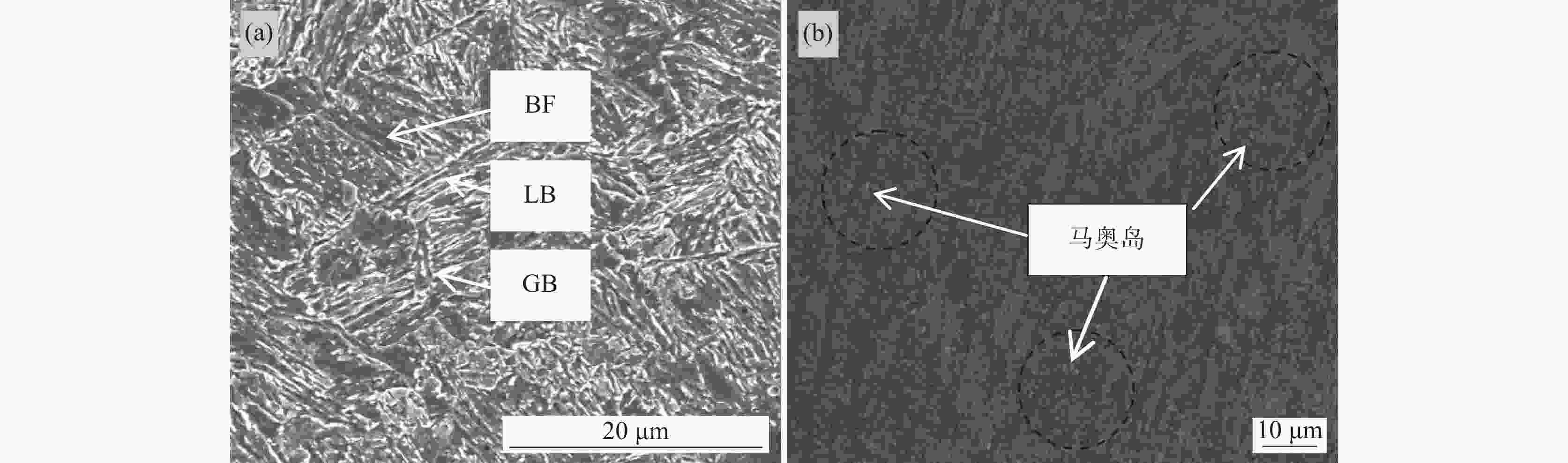
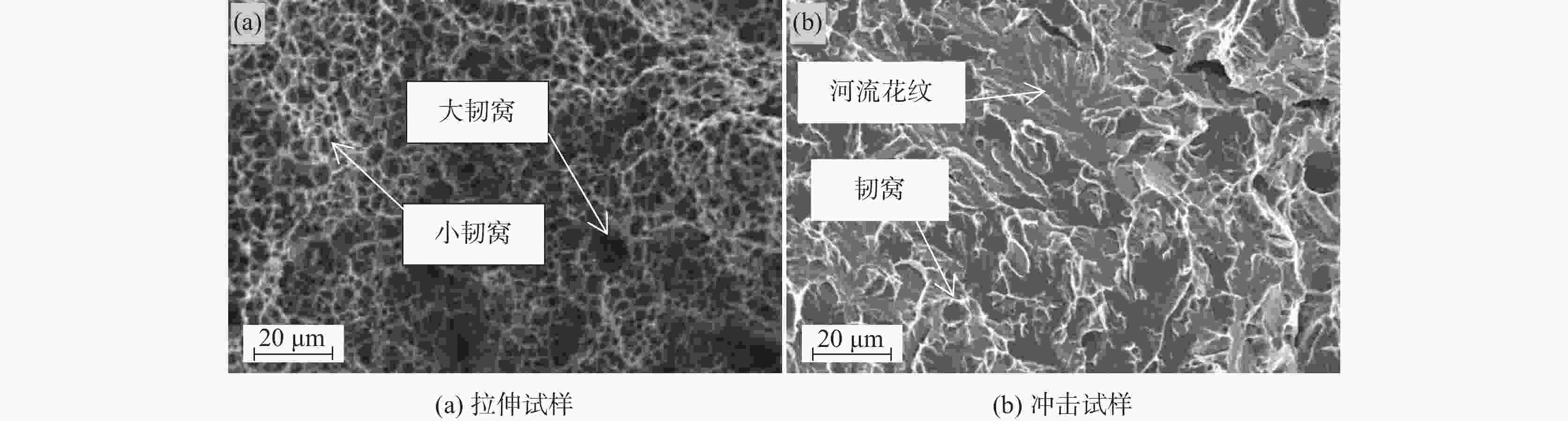
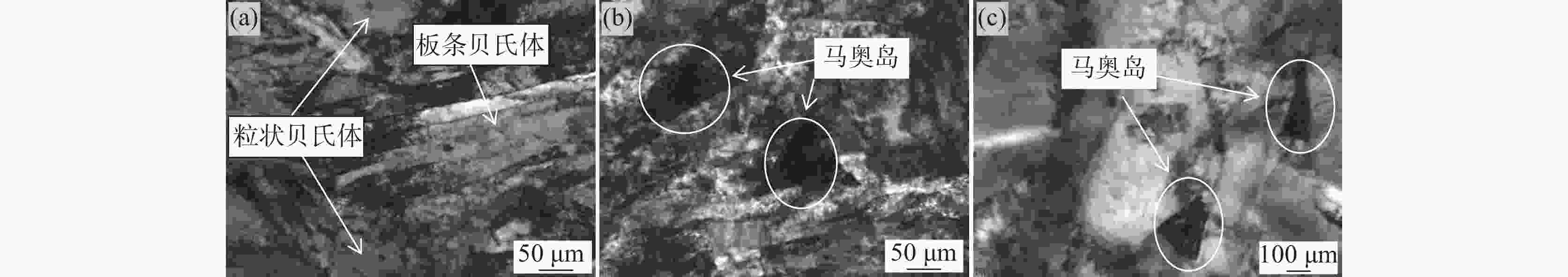
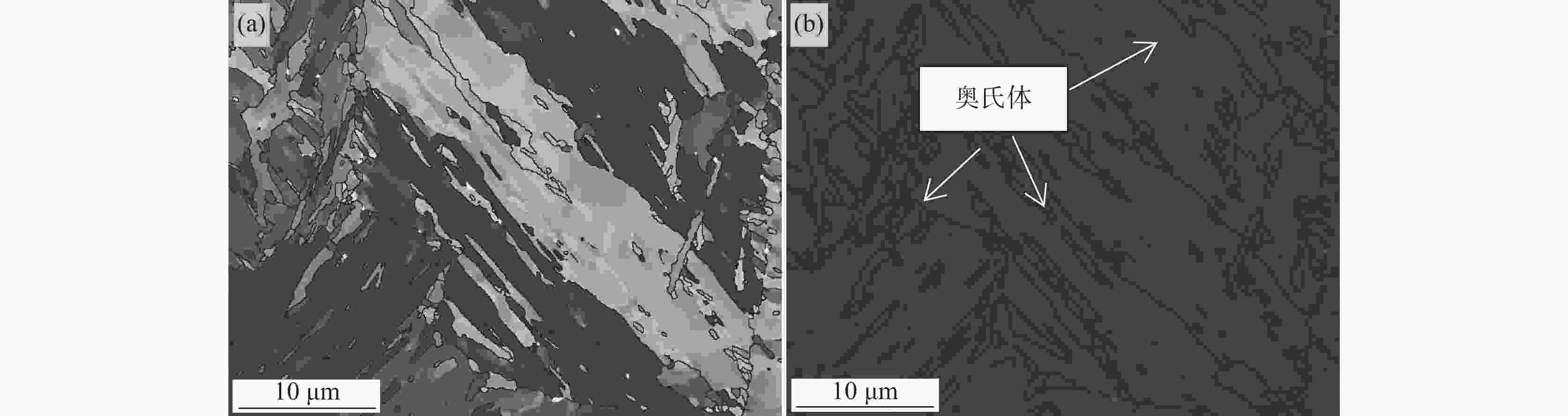
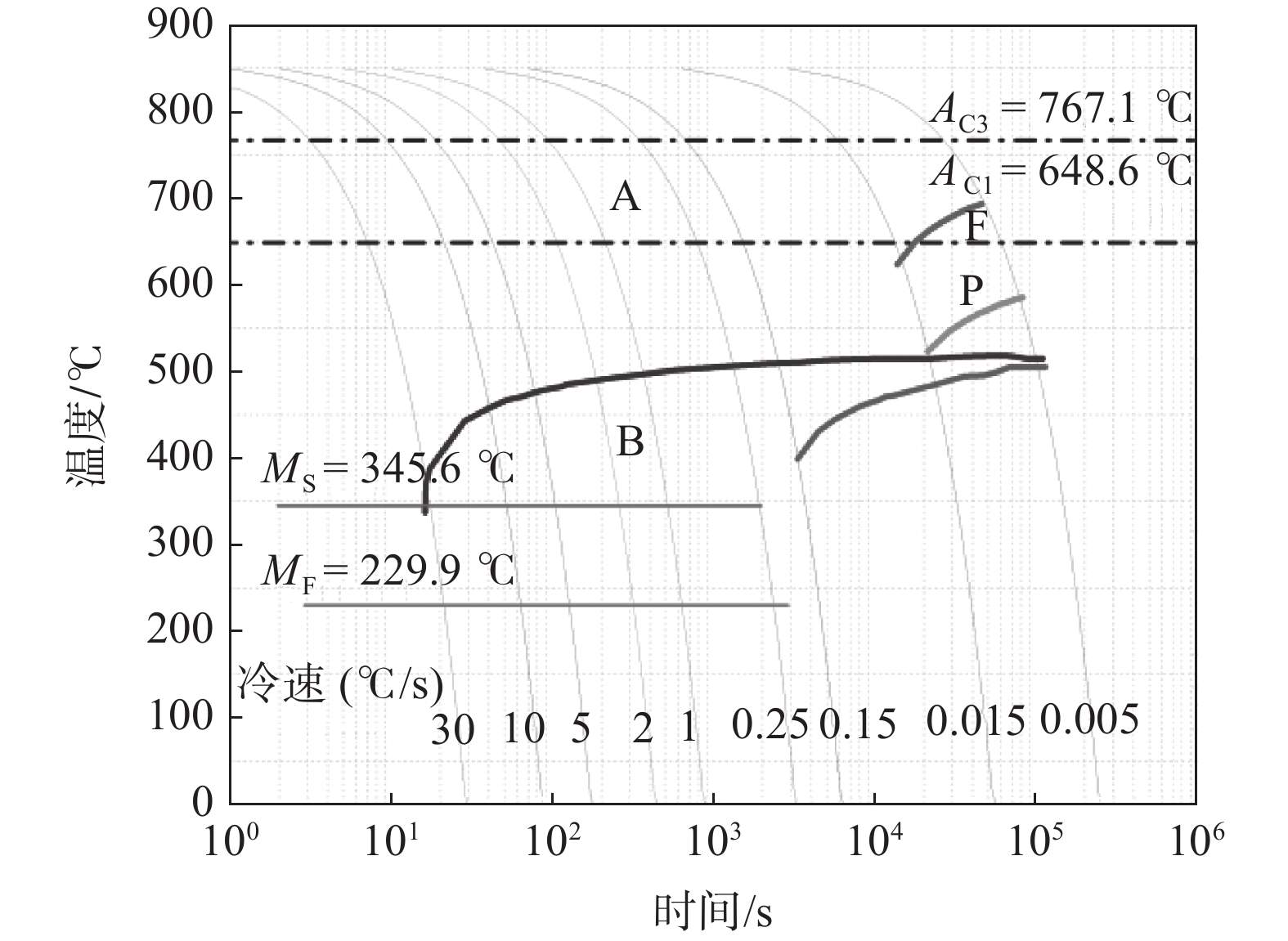
摘要: 通过清洁炼钢、热轧、拉拔工艺开发了增材制造专用的低合金钢丝,并用此钢丝进行了激光3D打印试验。打印件的力学性能分别为屈服强度857 MPa、抗拉强度930 MPa、延伸率18%,−40℃的平均低温冲击韧性达到了118 J,可以满足900 MPa级海工用增材制造的使用。通过扫描电镜、透射电镜对打印件微观组织的分析,发现微观组织为粒状贝氏体、板条状贝氏体和弥散分布的马奥岛(M-A)组织,在贝氏体基体上弥散分布的马奥岛组织可以同时提高打印件的拉伸性能和冲击性能。Abstract: In this investigation, the low-alloy steel wire applied in additive manufacturing was made by clean steelmaking, hot rolling and drawing; subsequently, laser wire-feed additive manufacturing was carried out with this steel wire. The mechanical properties of the 3D printed parts are the yield strength of 857 MPa, the tensile strength of 930 MPa and the elongation of 18%, the average low-temperature impact toughness of −40 ℃ reaches 118 J, respectively, whose can meet the requirements of 900 MPa class in the marine engineering field by the method of additive manufacturing. In terms of scanning electron micrograph (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM), and analysis of the microstructure of the printed pieces, the results showed that the microstructure was composed of granular bainite, lath bainite and diffusely distributed martensite-austenite constituents on the bainitic matrix, whose could improve the tensile property and impact property simultaneously.
-
Key words:
- additive manufacturing /
- low alloy steel /
- steel wire /
- bainite /
- martensite-austenite constituent /
- impact toughness
-
表 1 钢丝主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of wire
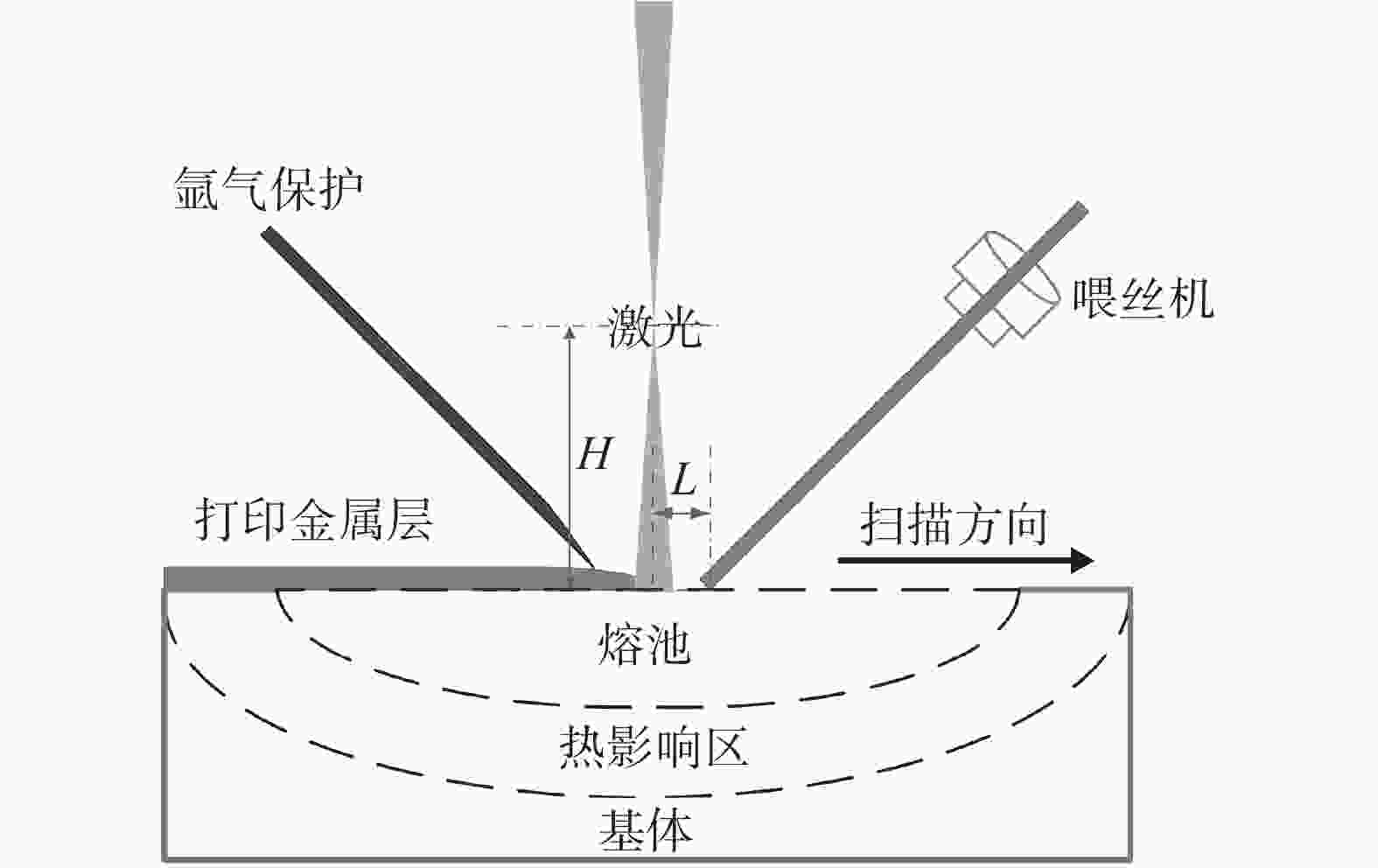
% C Si Mn Ni Cr Mo O N H P S 0.07 0.38 1.76 2.51 0.49 0.50 ≤0.005 ≤0.005 ≤0.002 0.006 0.003 表 2 激光熔丝增材制造试验技术参数
Table 2. Technical parameters of laser wire-feed additive manufacturing
光丝距/
mm扫描速度/
(mm·s−1)喂丝速度/
(mm·s−1)功率/
kW离焦量/
mm前2.0 10 30 3.2 50 表 3 打印金属拉伸性能
Table 3. Tensile properties of printed metal
牌号 屈服强度/
MPa抗拉强度/
MPa延伸率/
%断面收缩率/
%AFEW 6-86 857 930 18 35 表 4 打印金属冲击性能
Table 4. Impact properties of printed metal
牌号 −40 ℃冲击功(Ak)/J 1 2 3 4 5 均值 AFEW 6-86 112 111 122 121 123 118 -
[1] Lu Bingheng, Li Dichen. Development of additive manufacturing (3D printing) technology[J]. Machine Building & Automation, 2013,42(4):1−4. (卢秉恒, 李涤尘. 增材制造 (3D 打印) 技术发展[J]. 机械制造与自动化, 2013,42(4):1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5276.2013.04.001 [2] Yang Jiaoxi, Ke Hua, Cui Zhe, et al. Research status and application of laser metal deposition technology[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2020,63(10):14−22. (杨胶溪, 柯华, 崔哲, 等. 激光金属沉积技术研究现状与应用进展[J]. 航空制造技术, 2020,63(10):14−22. [3] Zhou Changping, Lin Feng, Yang Hao, et al. Application progress of additive manufacturing technology in shipbuilding field[J]. Ship Engineering, 2017,39(2):80−87. (周长平, 林枫, 杨浩, 等. 增材制造技术在船舶制造领域的应用进展[J]. 船舶工程, 2017,39(2):80−87. [4] Guo Chunhuan, Wang Zechang, Yan Jiayin, et al. Research progress in additive-subtractive hybrid manufacturing[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Science, 2020,42(5):540−548. (果春焕, 王泽昌, 严家印, 等. 增减材混合制造的研究进展[J]. 工程科学学报, 2020,42(5):540−548. [5] Guo Chunhuan, Yan Jiayin, Wang Zechang, et al. Research progress on metal laser fuse additive manufacturing process[J]. Hot WorkingTechnology, 2020,49(16):5−10. (果春焕, 严家印, 王泽昌, 等. 金属激光熔丝增材制造工艺的研究进展[J]. 热加工工艺, 2020,49(16):5−10. [6] Li Binzhou, Li Changsheng, Jin Xin, et al. Effect of M-A constituents formed in TMCP on toughness of 20 CrNi2 MoV steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2019,26:1340−1349. doi: 10.1007/s42243-019-00244-8 [7] Hu H, Xu G, Wang L, et al. The effects of Nb and Mo addition on transformation and properties in low carbon bainitic steels[J]. Materials & Design, 2015,84(5):95−99. [8] Wang B X, Liu X H, Wang G D. Correlation of microstructures and low temperature toughness in low carbon Mn–Mo–Nb pipeline steel[J]. Materials Science & Technology, 2013,29(12):1522−1528. [9] Yao Xiuquan, Yang Jianying, Han Dan, et al. Study on CCT curve of Si-Mn-Cr-Mo ultra-high strength steel[J]. Physical Test, 2018,36(4):1−5. (要秀全, 杨剑英, 韩丹, 等. Si-Mn-Cr-Mo超高强钢的 CCT 曲线的探讨[J]. 物理测试, 2018,36(4):1−5. [10] Jiang Zhouhua, Gong Wei, Wang Cheng, et al. High purity smelting technology for ultra-high strength steels[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2017,37(6):7−15. (姜周华, 龚伟, 王承, 等. 超高强度钢高纯净熔炼技术[J]. 航空材料学报, 2017,37(6):7−15. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2017.000147 [11] Dong Zhihong, Kang Hongwei, Xie Yujiang, et al. Effect of O content on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser additive 12CrNi2 alloy steel[J]. Applied Laser, 2018,38(1):1−6. (董志宏, 亢红伟, 谢玉江, 等. O含量对激光增材制造12CrNi2合金钢组织结构及力学性能的影响[J]. 应用激光, 2018,38(1):1−6. [12] Zhou Yun, Zhang Yu, Guo Huiying, et al. Effect of trial production and annealing on microstructure and properties of Mn-Mo low alloy wire rod[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2017,42(3):23−28. (周云, 张宇, 郭慧英, 等. Mn-Mo系低合金焊丝盘条的试制及退火对组织性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2017,42(3):23−28. [13] 冯帅. 合金钢激光熔丝沉积工艺及回火处理研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2019.Feng Shuai . Study on laser fuse deposition process and tempering treatment of alloy steel [D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2019. [14] Nazmul Hudaa, Abdelbaset R H, Midawia James, et al. Influence of martensite-austenite (MA) on impact toughness of X80 line pipe steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2016,662(26):481−491. [15] Zeng Yanping, Zhu Pengyu, Tong Ke. Effect of microstructure on mechanical properties of X70 pipeline steel[J]. Journal of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2015,36(3):45−50. (曾燕屏, 朱鹏宇, 仝珂. 显微组织对X70管线钢力学性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2015,36(3):45−50. [16] Liu Qingyou, Jia Shujun, Ren Yi. Study on control technology of low temperature fracture toughness of high grade thick wall pipeline steel[J]. Welded Pipe and Tube, 2019,42(7):39−47,54. (刘清友, 贾书君, 任毅. 高钢级厚壁管线钢低温断裂韧性控制技术研究[J]. 焊管, 2019,42(7):39−47,54. [17] Qi Liang, Peng Kai, Zhou Jun, et al. Effect of TMCP process on M/A island of X100 pipeline steel[J]. Journal of Materials Review, 2016,30(2):95−98. (齐亮, 彭凯, 周军, 等. TMCP工艺对X100管线钢M/A岛的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2016,30(2):95−98. [18] Huda N, Wang Y, Li L, et al. Effect of martensite-austenite (MA) distribution on mechanical properties of inter-critical reheated coarse grain heat affected zone in X80 linepipe steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2019,765:138301. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2019.138301 [19] Xu Rongjie, Yang Jing, Yan Pingyuan, et al. Study on microstructure of ultra-low carbon bainite steel with high strength by electron microscopy[J]. Physical Measurement, 2007,25(1):10−20. (徐荣杰, 杨静, 严平沅, 等. 高强度超低碳贝氏体钢显微组织电镜研究[J]. 物理测试, 2007,25(1):10−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0777.2007.01.003 -





 下载:
下载: