Review on development of metal solidification process under vibration
-
摘要: 介绍了振动被引入金属凝固过程的发展历程,重点归纳了机械振动技术、振动激发形核技术、超声振动技术和脉冲磁致振荡技术运用于金属凝固过程控制的振动方式、应用领域、冶金效果及优缺点,总结了四种振动产生的方式和机理,概述了振动对金属液凝固的影响及具体形式,总结了现有振动改善凝固组织的机理和振动技术在金属凝固过程中的研究现状,最后对几种控制金属凝固的振动技术做了简要分析,并对其后续发展做了简单的展望,为以后研究振动技术在凝固过程中应用的学者提供一个参考。Abstract: The development of vibration introduced into the metal solidification process was reviewed and the vibration methods, application fields, metallurgical effects, and advantages/disadvantages of mechanical vibration technology, vibration excitation nucleation technology, ultrasonic vibration technology and pulsed magnetic oscillation technology used for controlling metal solidification process were mainly summarized. Meanwhile, the modes and mechanisms of four kinds of vibration techniques were explored, and the impact of vibration on the solidification of molten metal and the specific forms were discussed. The mechanism of the existing vibration techniques improving solidification structure was discussed, and recent development of vibration technology used in the metal solidification process were summarized. A brief analysis and prospect of several vibration technologies for controlling metal solidification were also presented.
-
Key words:
- continue casting /
- vibration /
- solidification process /
- grain refinement /
- quality
-
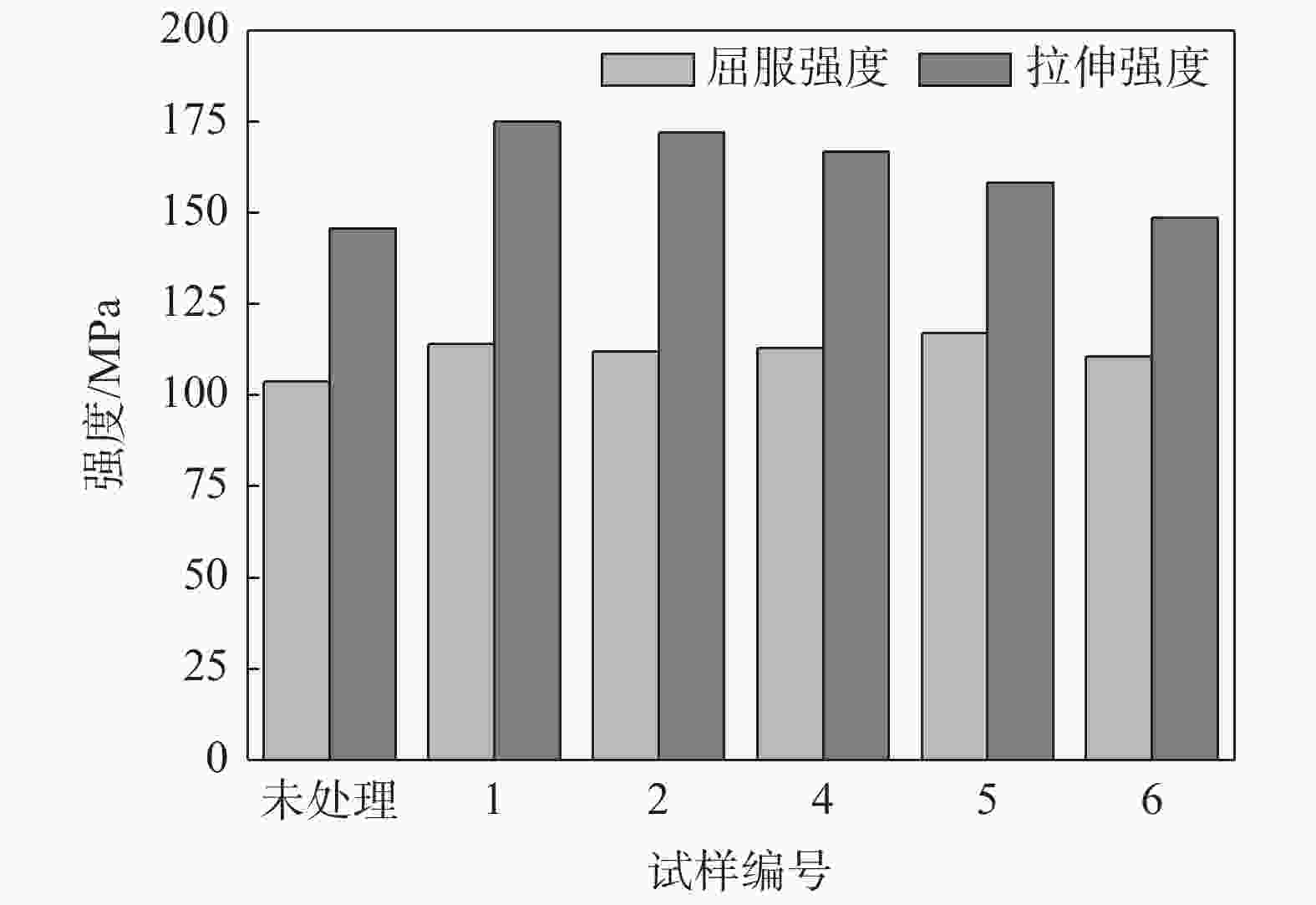
图 4 356 Al合金力学性能检测结果[24]
1,2号试样振动频率分别为100 Hz和150 Hz;4号试样为使用超细粉改性剂;5,6号试样分别为使用超细粉改性剂后再施加频率为100 Hz和150 Hz的振动
Figure 4. Mechanical properties of Al356 alloy
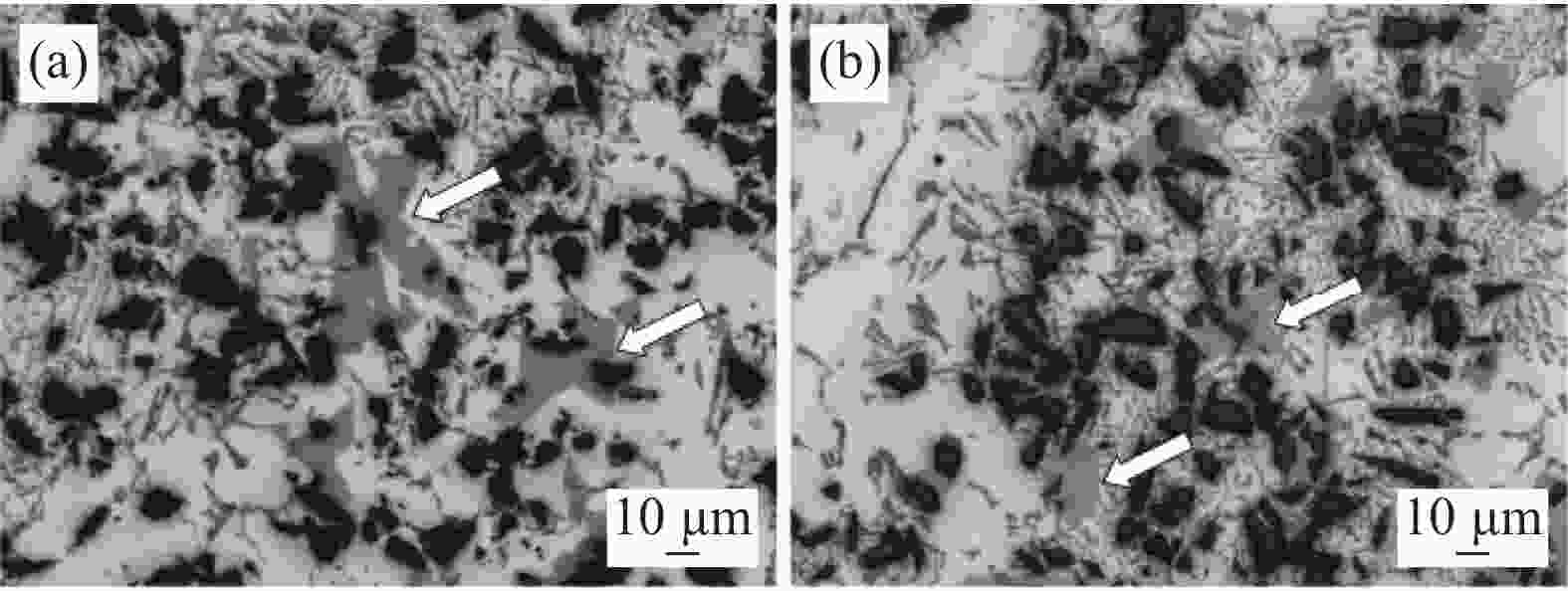
图 5 A360-10%SiC合金微观组织[22]
(a)未振动的微观组织;(b)振动后的微观组织。箭头所指为α-Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2粒子
Figure 5. Microstructures of the as-solidified A360-10%SiC composite
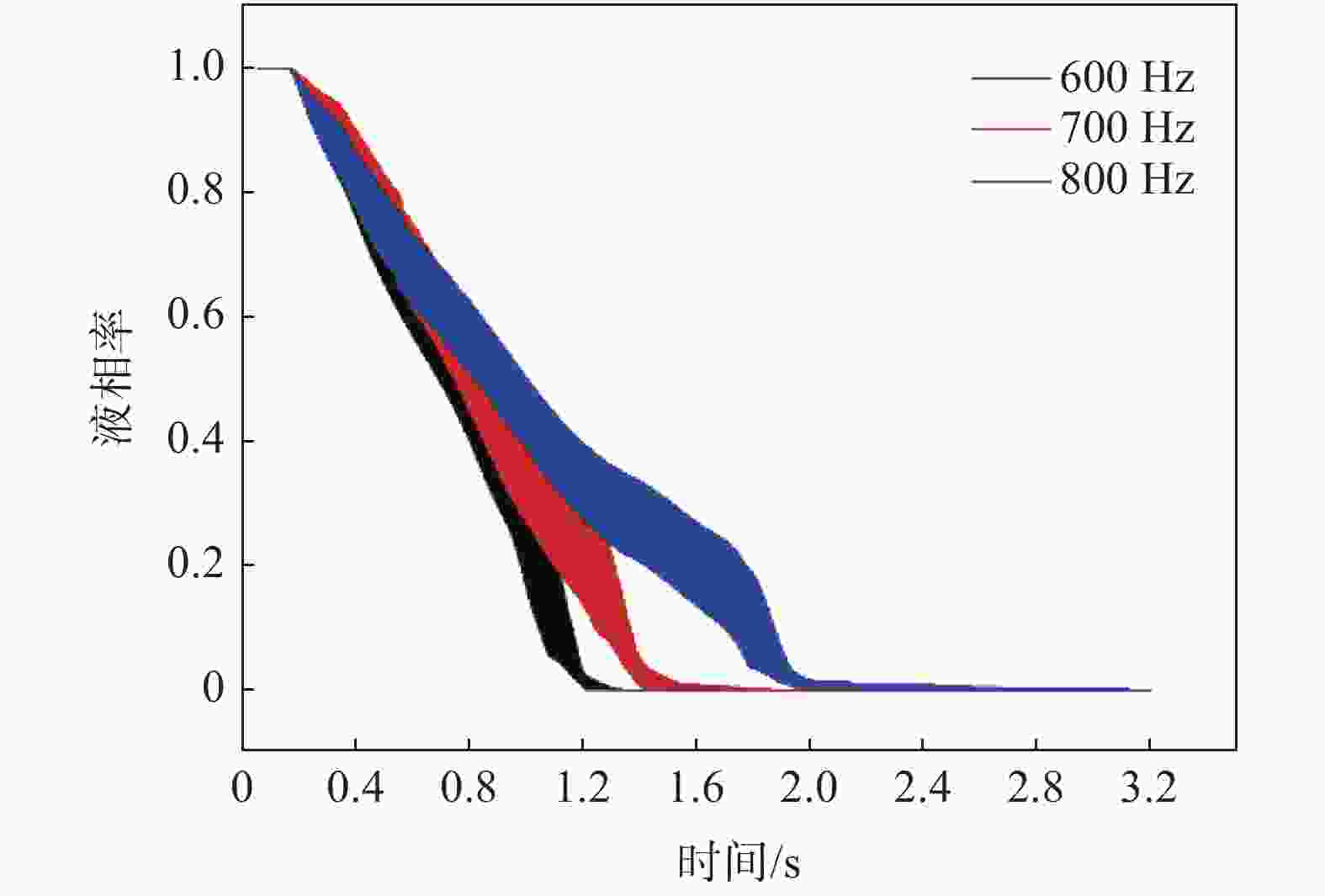
图 6 振动发射器某点液相率随时间变化曲线[34]
Figure 6. Variation curve of liquid phase ratio with time at a certain point of vibration emitter
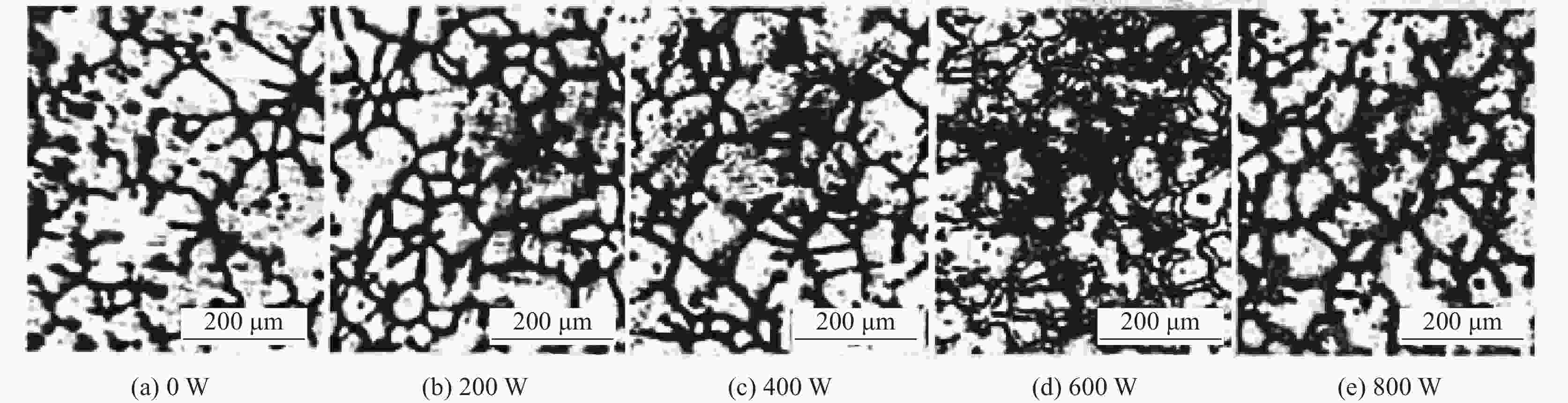
图 7 不同超声功率下AZ31镁合金铸锭的微观组织[37]
Figure 7. Microstructure of AZ31 magnesium alloy ingot produced through vibration under different ultrasonic power
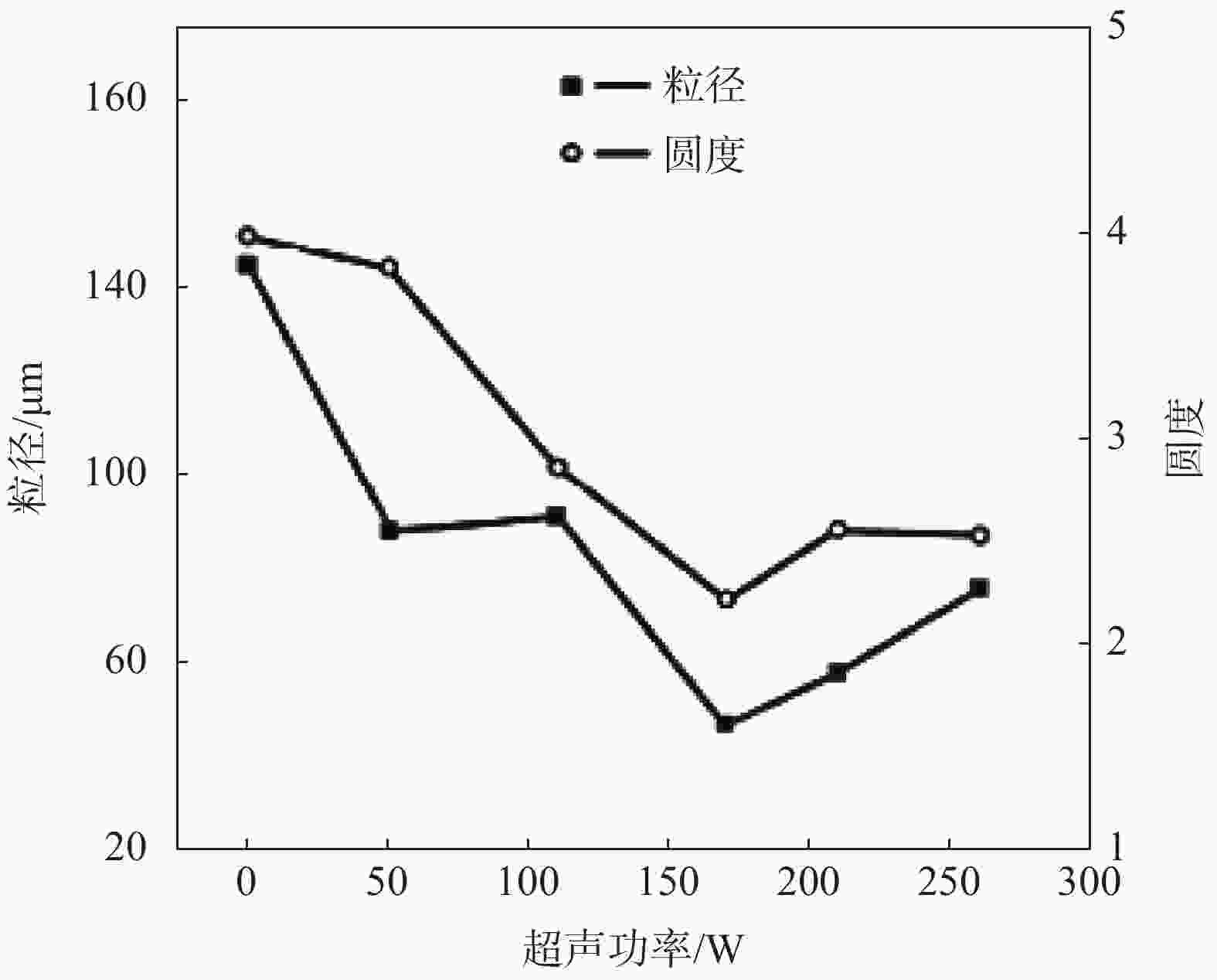
图 8 超声振动功率对α相粒径和圆度的影响[40]
Figure 8. Effects of ultrasonic vibration power on particle size and roundness of α phase
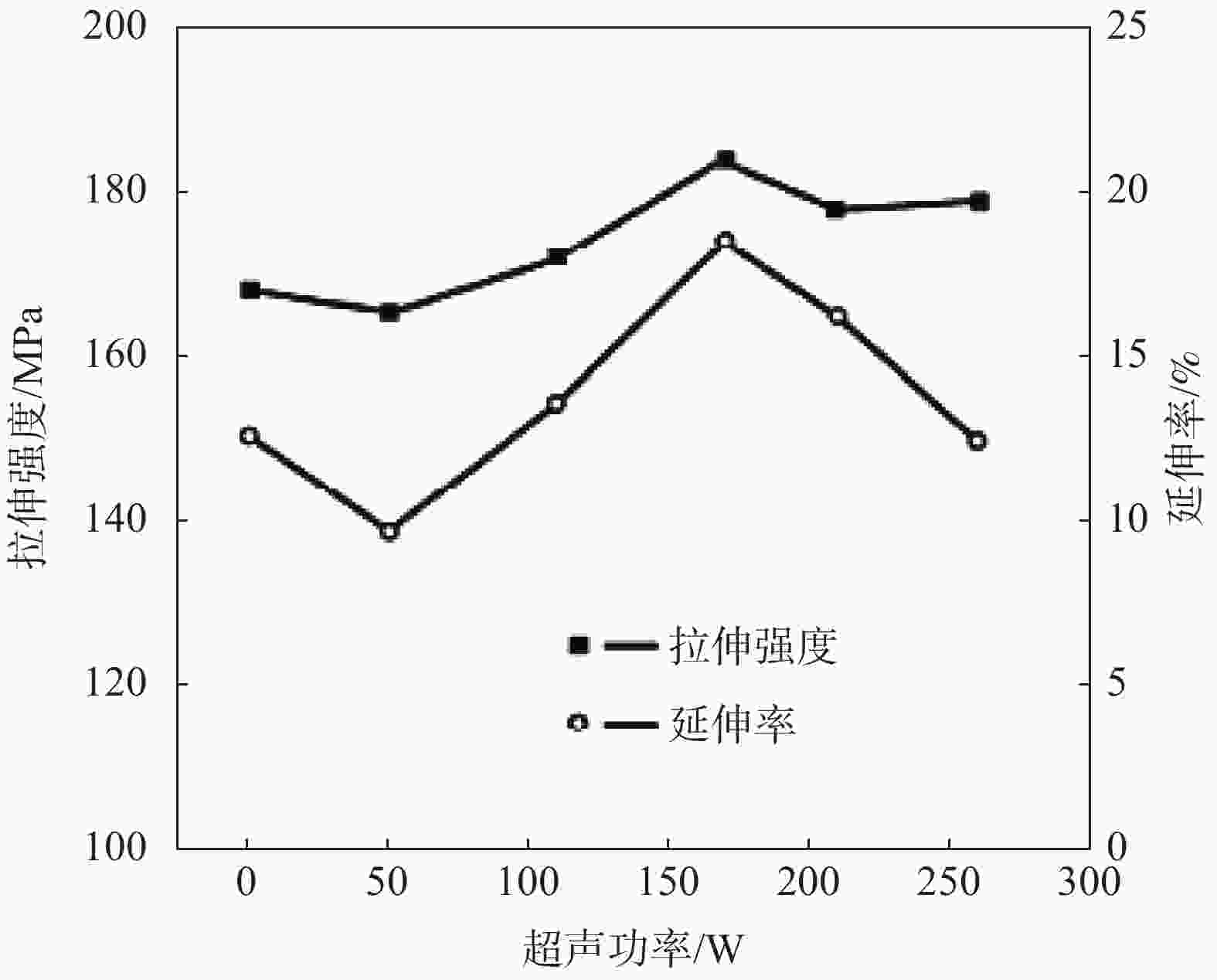
图 9 不同功率下Mg-8Li-3Al合金力学性能[40]
Figure 9. Mechanical properties of Mg-8Li-3Al alloys by ultrasonic vibration treatment
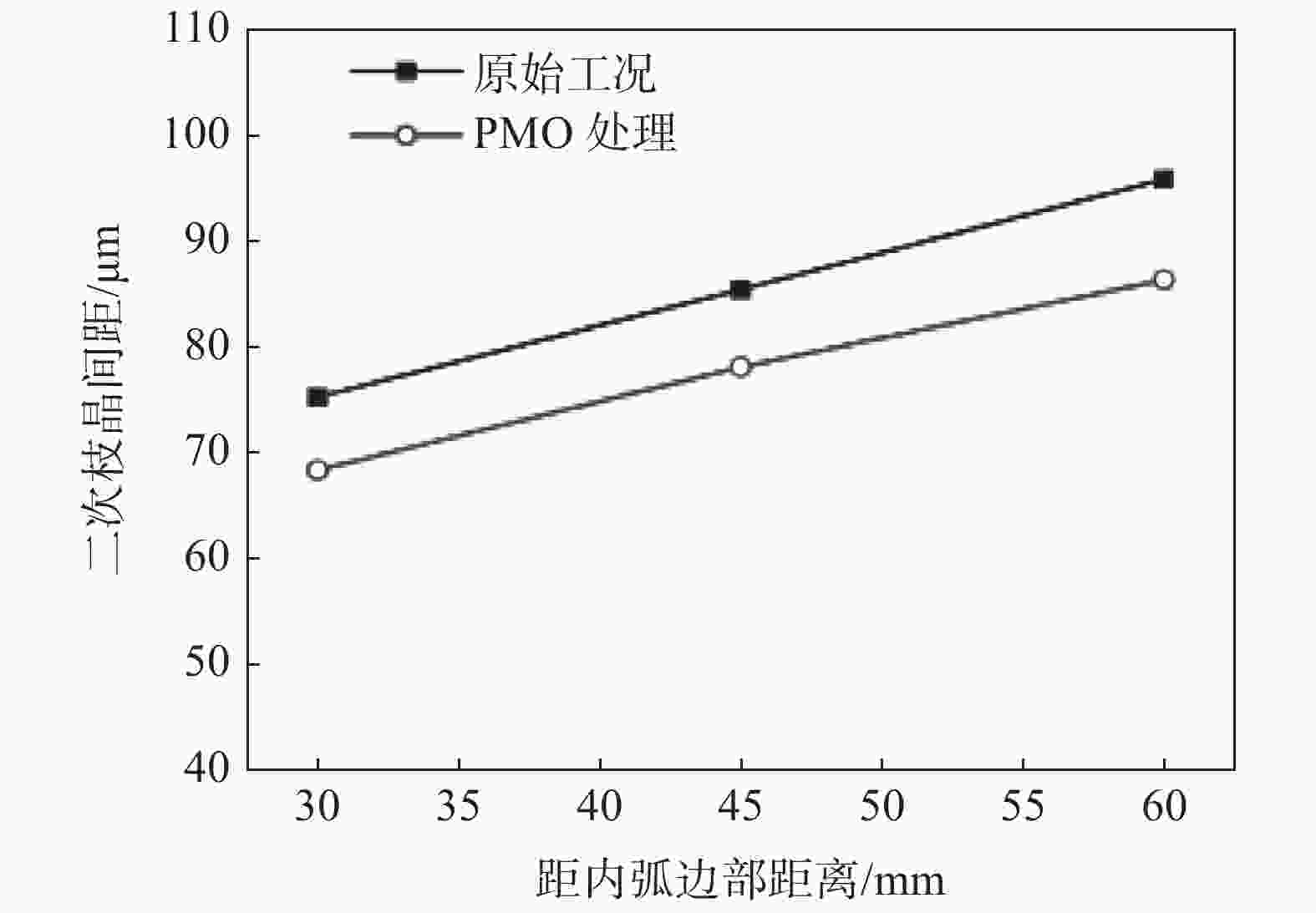
图 10 二次枝晶臂间距的比较[54]
Figure 10. Comparison of the secondary dendrite aria spacing
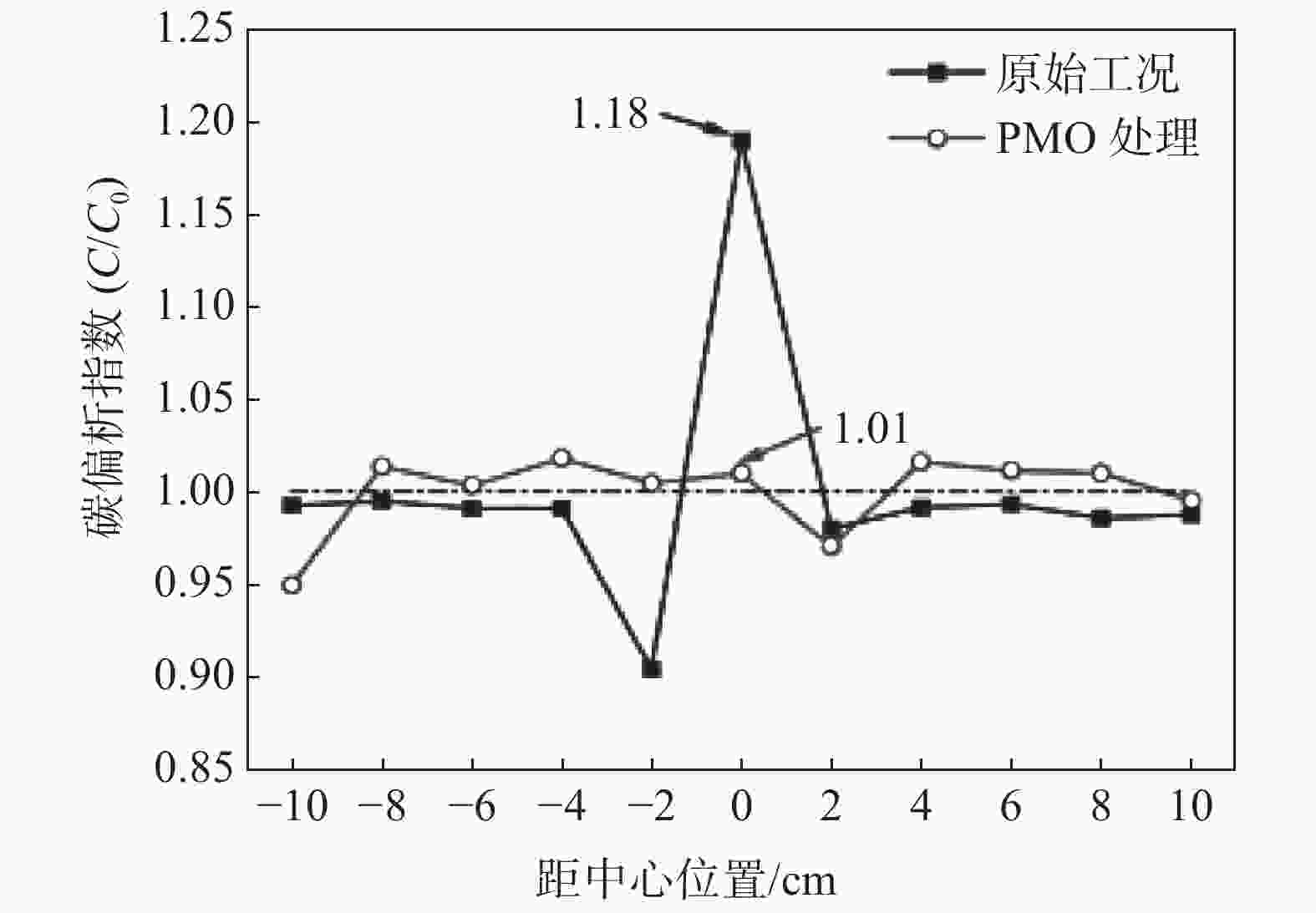
图 11 碳偏析指数分布曲线[54]
Figure 11. Distribution curves of the carbon segregation index
表 1 振动技术的特点
Table 1. Characteristics of vibration technology
类型 动力源 振动方式 接触类型 振动频率级别 应用项目 冶金效果 优点 缺点 机械振动 电、液压或压缩气体驱动 间歇或
连续式接触或
间歇接触中低频振动 模铸,连铸结晶器 细化晶粒;改善铸件力学性能;消除铸件疏松缩孔,减少渣气孔和裂纹;改变微观相的形貌 设备简单,易于操作,能耗低 频率较低,对铸件力学性能提升不明显,晶粒细化作用较弱 振动激发形核 电驱动 间歇式 接触 高频振动 模铸 促进金属液形核、细化晶粒 形核效果明显,适用于钢锭组织改善 应用面窄,设备造价高,易引起金属液污染,能耗高 超声振动 电驱动 间歇式或
连续式非接触 高频振动 模铸 改善铸件的耐腐蚀性、拉伸率和拉速强度;消除残余应力,提效降本;细化晶粒 对钢液无污染、细晶效果明显 设备造价高,能耗高 脉冲磁致振荡 电驱动 间歇式 非接触 高频振动 模铸,连铸结晶器,二冷区 提高等轴晶区占比,降低铸坯中心偏析和缩孔;提升铸坯中心致密度 操作便利,应用面较广 设备复杂,造价高,能耗较高 -
[1] Low W, Schieber M, Chalmers B. Principles of solidification[C]// Applied Solid State Physics.Springer, 1995: 161−170. [2] 知水. 机械振动对钢锭结晶过程的影响[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1959.Zhi Shui. Influence of mechanical vibration on crystallization process of steel ingot [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1959. [3] Fan Jinhui, Zhai Qijie. Effect of physical field on microstructure of metal solidification[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002,16(9):5−6,32. (范金辉, 翟启杰. 物理场对金属凝固组织的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002,16(9):5−6,32. [4] Kang Yan, Mao Weimin, Xu Dusheng, et al. Effect of mechanical vibration on microstructure and properties of investment casting 0Cr17 stainless steel[J]. Special Casting and Nonferrous Alloys, 2015,35(10):1073−1077. (康燕, 毛卫民, 许杜生, 等. 机械振动对熔模铸造0Cr17不锈钢组织与性能的影响[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2015,35(10):1073−1077. [5] Wang Chao, Zhang Hui, Wang Minglin, et al. Application of vibration excitation nucleation technology in 45 tQ345B steel ingot casting process[J]. Special Steel, 2014,35(4):20−23. (王超, 张慧, 王明林, 等. 振动激发形核技术在45 tQ345B钢锭浇铸过程的应用[J]. 特殊钢, 2014,35(4):20−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2014.04.006 [6] 李开晔. 直入式超声波施振铸造试验及其凝固动力学机理研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012.Li Kaiye. Study on the experiment of direct induction ultrasonic vibration casting and the kinetic mechanism of solidification [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012. [7] Li H C, Liu Y X, Zhang Y H, et al. Effects of hot top pulsed magneto-oscillation on solidification structure of steel ingot[J]. China Foundry, 2018,15(2):110−116. doi: 10.1007/s41230-018-7198-z [8] Zhong Honggang, Liu Haining, Xu Zhishuai, et al. Solidification homogenization technology and equipment of pulsed magnetically oscillated solidification[J]. Iron and Steel, 2019,54(8):174−180. (仲红刚, 刘海宁, 徐智帅, 等. 脉冲磁致振荡凝固均质化技术及装备[J]. 钢铁, 2019,54(8):174−180. [9] Wang Hongxia, Zhang Guoping, Xu Chunxiang, et al. Effect of mechanical vibration on grain refinement and solidification shrinkage of pure A1[J]. Foundry Equipment Research, 2007,(1):28−31. (王红霞, 张国平, 许春香, 等. 机械振动对纯A1晶粒细化及凝固收缩的影响[J]. 铸造设备研究, 2007,(1):28−31. [10] Gan Yong, Zhao Pei, Zhang Hui, et al. Physical simulation of in-situ nucleation of metal liquid excited by vibration[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2006,18(8):9−13. (干勇, 赵沛, 张慧, 等. 振动激发金属液原位形核的物理模拟[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2006,18(8):9−13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0963.2006.08.003 [11] Gong Yongyong, Cheng Shumin, Zhong Yuyi, et al. Pulsed magnetooscillation solidification technology[J]. Acta Metall Sinica, 2018,54(5):757−765. (龚永勇, 程书敏, 钟玉义, 等. 脉冲磁致振荡凝固技术[J]. 金属学报, 2018,54(5):757−765. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2017.00536 [12] Le Q C, Guo S J, Zhang Z Q, et al. Study on electromagnetic vibration casting (Evc) of magnesium alloys[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2007,546-549:207−210. [13] Jiang Fan, Feng Junming, Wang Yijun, et al. Small casting technology for optimization of casting structure parameters based on vibration casting[J]. Foundry Technology, 2014,35(1):90−93. (江帆, 冯均明, 王一军, 等. 基于振动铸造的铸件结构参数优化小铸造技术[J]. 铸造技术, 2014,35(1):90−93. [14] Wu S, Xie L, Zhao J, et al. Formation of non-dendritic microstructure of semi-solid aluminum alloy under vibration[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2008,58(7):556−559. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2007.11.010 [15] Zhao Zhong, Fan Zitian, Cheng Ping, et al. Microstructure and properties of Al-Si-Mg-Y alloy solidified by vibration pressure in EPC casting[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010,20(8):1520−1526. (赵忠, 樊自田, 成平, 等. Al-Si-Mg-Y合金消失模铸造振动压力凝固的组织与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010,20(8):1520−1526. [16] He Deping, Chen Feng. Effect of vibration anthology on dendritic growth[J]. Journal of Artificial Crystals, 1989,4:262−266. (何德玶, 陈锋. 振动干扰波形对枝晶生长的影响[J]. 人工晶体学报, 1989,4:262−266. [17] 陈翔. 机械振动改善等离子熔覆涂层组织及性能的机理与应用研究[D]. 青岛: 山东科技大学, 2009.Chen Xiang. Mechanical vibration improving microstructure and properties of plasma cladding coating [D]. Qingdao: Shandong University of Science and Technology, 2009. [18] 李峰. 振动激发金属液形核理论基础研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2008.Li Feng. Fundamental research on the nucleation theory of liquid metal excited by vibration[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2008. [19] 陈锋. 振动作用下铝合金的凝固、组织及性能特点[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 1990.Chen Feng. Solidification, microstructure and properties of aluminum alloy under vibration [D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 1990. [20] Liu Y C, Yu W C, Roux B, et al. Thermal-solutal flows and segre gation and their control by angular vibration in vertical Bridgman crystal growth[J]. Chem. Eng. Sci., 2006,61:7766. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2006.09.002 [21] Lyubimov D V, Lyubimova T P, Parshakova Y N, et al. Effect of high-frequency vibrations on oriented crystalization of binary alloys[J]. J. Surf. Invest. X-Ray, Synchrotron Neutron Tech., 2009,3:116. doi: 10.1134/S1027451009010194 [22] Timelli G, Della Corte E, Bonollo F. Effect of mechanical mould vibration on solidification behaviour and microstructure of A360-SiCp metal-matrix composites [C]//Materials Science Forum. Zurich: Trans Tech Publications, 2011, 678: 105-114. [23] 郭志远. 双辊薄带振动铸轧数值模拟及实验研究[D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2016.Guo Zhiyuan. Numerical simulation and experimental research on twin roll thin strip vibration casting [D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2016. [24] Vadim Selivorstov, Yuri Dotsenko, Konstantin Borodianskiy. Influence of low-frequency vibration and modification on solidification and mechanical properties of Al-Si casting alloy[J]. Materials, 2017,10(5):560−570. doi: 10.3390/ma10050560 [25] Numan Abu-Dheir, Marwan Khraisheh, Kozo Saito. Silicon morphology modification in the eutectic Al-Si alloy using mechanical mold vibration[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, Structural Materials, 2005,A393(1/2):109−117. [26] Gencalp S, Saklakoglu N. Effects of low-frequency mechanical vibration and casting temperatures on microstructure of semisolid AlSi-8Cu-3Fe alloy[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2012,37(8):2255−2267. doi: 10.1007/s13369-012-0316-0 [27] Li Jian, Li Yongying, Liu Feiyang. Influence of casting temperature and vibration direction on mechanical properties of aluminum alloy in vibration casting[J]. Foundry Technology, 2016,37(2):302−305. (李健, 李永英, 刘飞扬. 振动铸造中浇注温度及振动方向对铝合金力学性能的影响[J]. 铸造技术, 2016,37(2):302−305. [28] Zhang Hui, Tao Hongbiao, Li Feng, et al. Research on mechanism of metal liquid nucleation process excited by vibration[J]. Iron and Steel, 2008,43(8):20−24. (张慧, 陶红标, 李峰, 等. 振动激发金属液形核过程机理的研究[J]. 钢铁, 2008,43(8):20−24. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2008.08.005 [29] Tao Hongbiao, Zhang Hui, Wang Mei, et al. Effect of vibration excitation on solidification microstructure of zinc[J]. China Metallurgy, 2007,17(11):45−49. (陶红标, 张慧, 王玫, 等. 振动激发金属液形核对锌凝固组织的影响[J]. 中国冶金, 2007,17(11):45−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9356.2007.11.012 [30] 张慧, 陶红标, 王超, 等. 振动激发金属液形核技术在钢锭凝固过程中的应用探讨[C]//2012年钢锭制造技术与管理研讨会论文集. 唐山: 中国金属学会, 2012.Zhang Hui, Tao Hongbiao, Wang Chao, et al. Discussion on the application of vibration excitation metal liquid nucleation technology in the solidification process of steel ingot [C]//Proceedings of the 2012 Ingots Manufacturing Technology and Management Symposium . Tangshan: CSM, 2012. [31] Tao Hongbiao, Zhang Hui, Wang Chao, et al. Application of metal liquid nucleation technology excited by vibration in solidification process of ingots and slab[J]. Special Steel, 2012,33(6):18−21. (陶红标, 张慧, 王超, 等. 振动激发金属液形核技术在铸锭和板坯凝固过程中的应用[J]. 特殊钢, 2012,33(6):18−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2012.06.006 [32] Wang Chao, Zhang Hui, Zhu Xinkun, et al. Research on heat transfer in metal liquid nucleation process excited by vibration[J]. Iron and Steel, 2010,45(10):37−40. (王超, 张慧, 朱心昆, 等. 振动激发金属液形核过程的传热研究[J]. 钢铁, 2010,45(10):37−40. [33] Chang Xuejun, Wang Wenli, Xu Ruichao, et al. Research on heat transfer of ferritic stainless steel during vibration excitation nucleation process[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2015,44(3):104−106. (常雪君, 王文礼, 徐瑞朝, 等. 振动激发形核过程中铁素体不锈钢的传热研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2015,44(3):104−106. [34] Jia Jingda, Yan Xin, Qiu Yulong. Numerical simulation of liquid metal nucleation and shell formation process excited by vibration[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2019,48(15):78−81. (贾京达, 闫新, 邱玉龙. 振动激发金属液形核结壳过程的数值模拟[J]. 热加工工艺, 2019,48(15):78−81. [35] Shin S S, Kim W C, Kim K H, et al. Improvement of riser efficiency using high intensity ultrasonic treatment in A356 alloy[J]. Mater. Trans., 2015,56:1605. doi: 10.2320/matertrans.M2015141 [36] Jiang Ripeng, Li Xiaoqian, Hu Shicheng, et al. Effect of ultrasonic vibration treatment on microstructure of industrial pure aluminum during solidification[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2008,32(10):14−18. (蒋日鹏, 李晓谦, 胡仕成, 等. 凝固时超声振动处理对工业纯铝显微组织的影响[J]. 机械工程材料, 2008,32(10):14−18. [37] Bi Qiu, Li Ke, Gao Ting, et al. Effect of ultrasonic vibration power on solidification microstructure of AZ31B magnesium alloy iningot[J]. Special Casting and Nonferrous Alloying, 2009,29(6):576−581. (毕秋, 李克, 高挺, 等. 超声振动功率对AZ31B镁合金铸锭凝固组织的影响[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2009,29(6):576−581. doi: 10.3870/tzzz.2009.06.028 [38] Wang Shan, Wu Liangce, Zheng Lijing. Effect of ultrasonic vibration on solidification microstructure of Zn-55Al-1.6Si alloy[J]. Special Casting and Nonferrous Alloys, 2011,31(3):285−289. (王姗, 吴良策, 郑立静. 超声振动对Zn-55Al-1.6Si合金凝固组织的影响[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2011,31(3):285−289. doi: 10.3870/tzzz.2011.03.030 [39] Feng Danyan. Effect of ultrasonic vibration on solidification structure of ZL101 aluminum alloy melt[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2019,48(3):89−92. (冯丹艳. 超声振动对ZL101铝合金熔体凝固组织的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2019,48(3):89−92. [40] Yao Lei, Hao Hai, Ji Shouhua, et al. Effects of ultrasonic vibration on solidification structure and properties of Mg-8Li-3Al alloy[J]. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2011,21:1241−1246. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60848-0 [41] Li Xiaoqian, Li Kaiye, Chen Ming, et al. Effect of ultrasonic vibration on cooling time and solidification structure of 7050 aluminum alloy melt[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2011,16(2):249−244. (李晓谦, 李开晔, 陈铭, 等. 超声振动对7050铝合金熔体冷却时间及凝固组织的影响[J]. 粉末治金材料科学与工程, 2011,16(2):249−244. [42] Liu Fang, Zhang Luyun. Numerical simulation of solidification magnetic field and flow field distribution of pure aluminum under pulsed magnetooscillation[J]. Casting, 2012,21:285. (刘芳, 张璐云. 脉冲磁致振荡下纯铝凝固磁场与流场分布的数值模拟[J]. 铸造, 2012,21:285. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4977.2012.03.011 [43] Liang D, Liang Z Y, Sun J, et al. Grain refinement of commercial pure AI treated by pulsed magneto-oscillation on the top surface of melt[J]. China Foundry, 2015,12:48. [44] Zhao J, Yu J, Li Q, et al. Structure of slowly solidified 30Cr2Ni4MoV casting with surface pulsed magneto-oscillation[J]. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2015,31:1589. doi: 10.1179/1743284715Y.0000000040 [45] Zhao J, Cheng Y F, Han K, et al. Numerical and experimental studies of surface pulsed magneto-oscillation on solidification[J]. J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2016,229:286. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.09.027 [46] Liu T Y, Sun J, Sheng C, et al. Influence of pulse magneto-oscillation on the efficiency of grain refiner[J]. Adv. Manuf., 2017,5:143. doi: 10.1007/s40436-017-0175-8 [47] Gong Y Y, Luo J, Jing J X, et al. Structure refinement of pure aluminum by pulse magneto- oscillation[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2008,497A(1):147. [48] Yin Z X, Gong Y Y, Li B, et al. Refining of pure aluminum cast structure by surface pulsed magneto-oscillation[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2012,212(12):2629. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2012.07.013 [49] Liang D, Sun J, Liu T, et al. Enhanced heterogeneous nucleation by pulsed magneto-oscillation treatment of liquid aluminum containing A13Ti1B additions[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2015,17(10):1465. doi: 10.1002/adem.201400488 [50] Liu Haining, Li Renxing, Teng Lihong, et al. Application of PMO solidification homogenization technology on 20CrMnTi gear steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2019,54(6):69−78. (刘海宁, 李仁兴, 滕力宏, 等. PMO凝固均质化技术在20CrMnTi齿轮钢上的应用[J]. 钢铁, 2019,54(6):69−78. [51] Xu Zhishuai, Li Qixin, Liang Zhuyuan, et al. Microstructure morphology of A1-4.5%Cu alloy under pulsed magnetooscillation[J]. Shanghai Metal, 2015,(2):31. (徐智帅, 李祺欣, 梁柱元, 等. 脉冲磁致振荡下A1-4.5%Cu合金微观组织形态[J]. 上海金属, 2015,(2):31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2015.02.008 [52] Cheng Yong, Xu Zhishuai, Zhou Zhan, et al. Application of PMO solidification homogenization technology in production of continuous casting GCr15 bearing steel[J]. Shanghai Metal, 2016,38(4):54. (程勇, 徐智帅, 周湛, 等. PMO凝固均质化技术在连铸GCr15轴承钢生产中的应用[J]. 上海金属, 2016,38(4):54. [53] Edry I, Mordechai T, Frage N, et al. Effects of treatmentduration and cooling rate on pure aluminum solidification upon pulse magneto-oscillation treatment[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions, 2016,47A(3):1261. [54] Xu Heng, Li Lijuan, Cai Changqing, et al. Application of mold PMO to improve the quality of continuous casting billets[J]. Shanghai Metal, 2019,41(4):75−79. (徐衡, 李莉娟, 蔡常青, 等. 应用结晶器PMO提高连铸小方坯质量研究[J]. 上海金属, 2019,41(4):75−79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2019.04.015 -




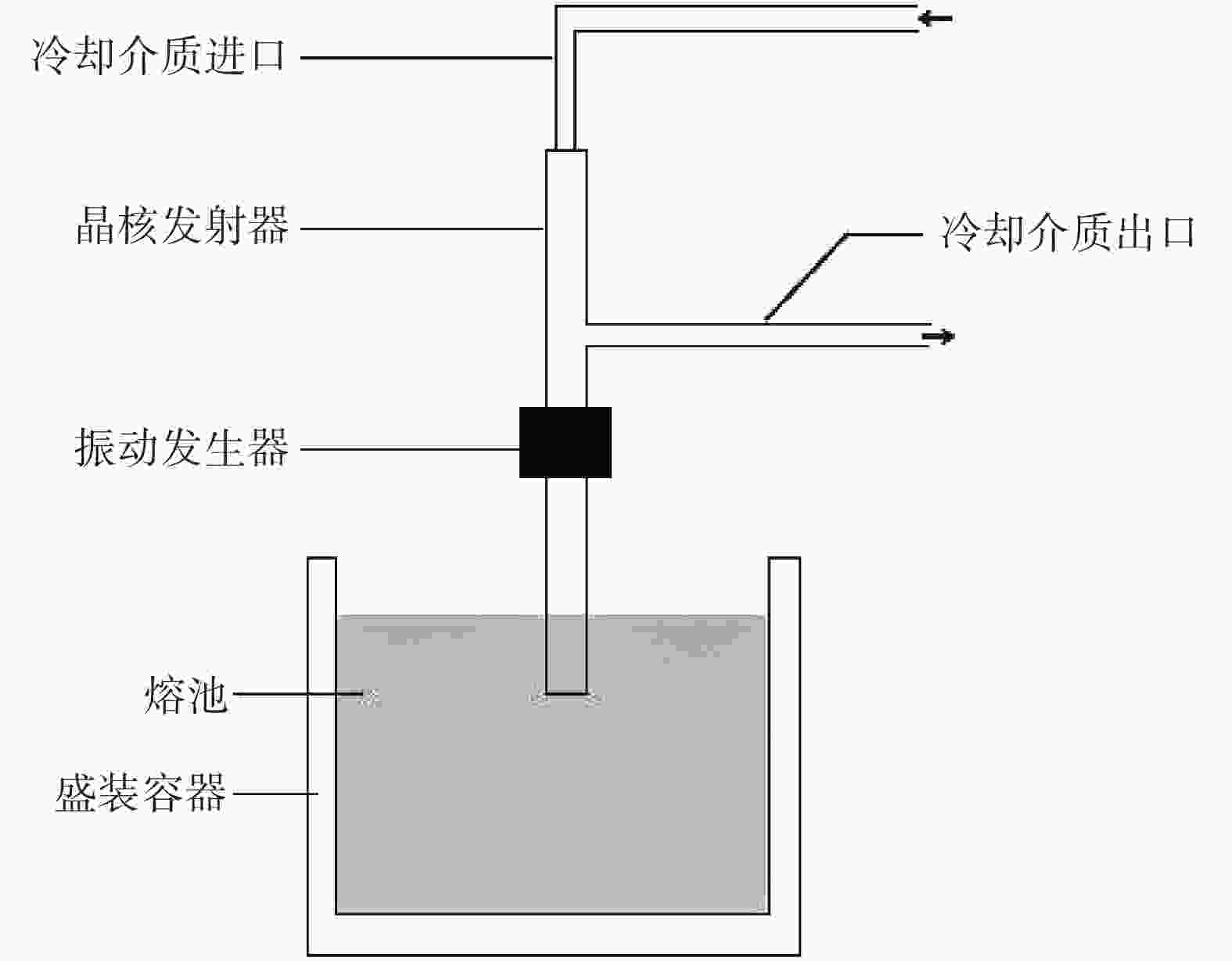
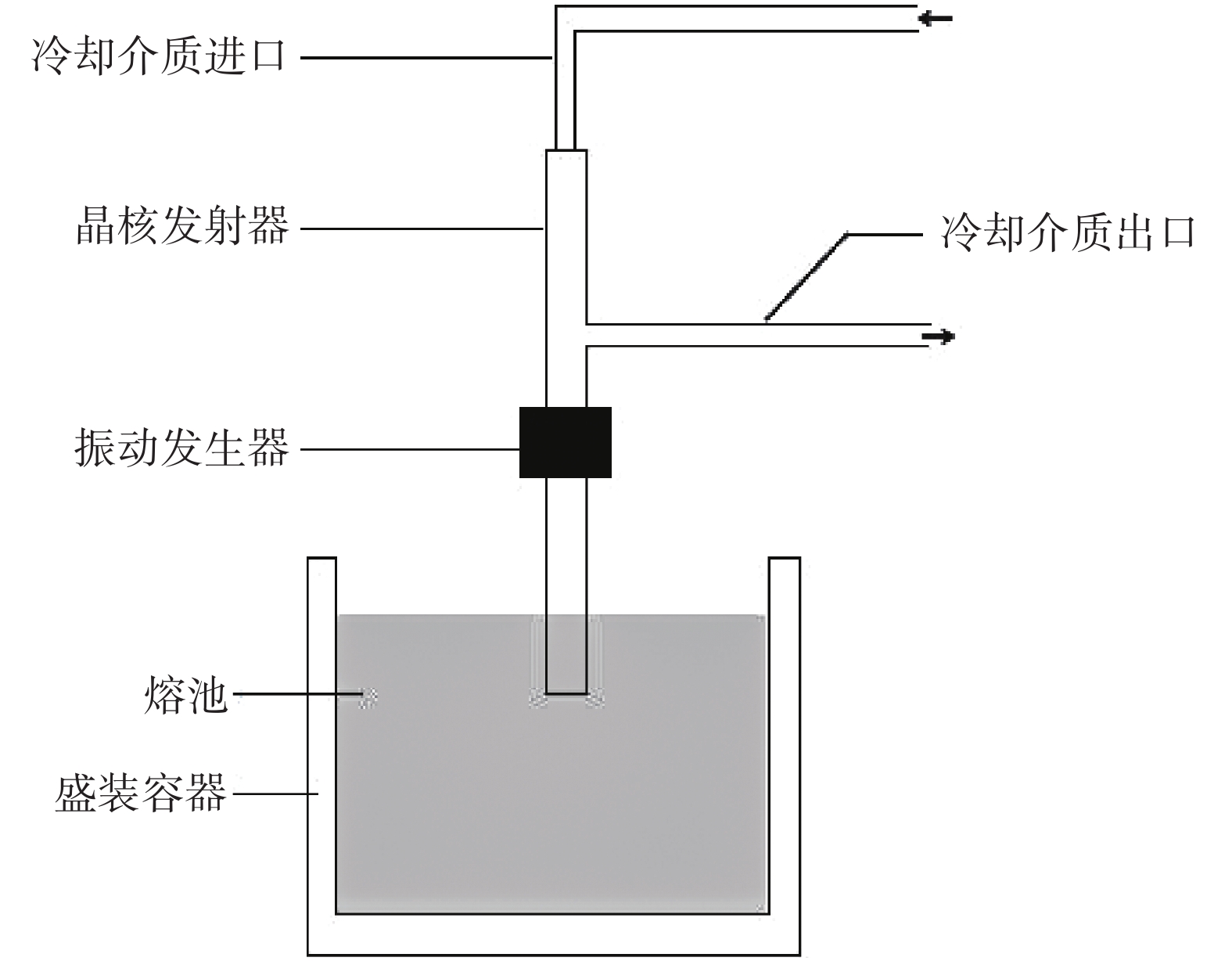
 下载:
下载: