Effect of high temperature and high strain rate on the dynamic mechanical properties of 06Cr19Ni10 austenitic stainless steel
-
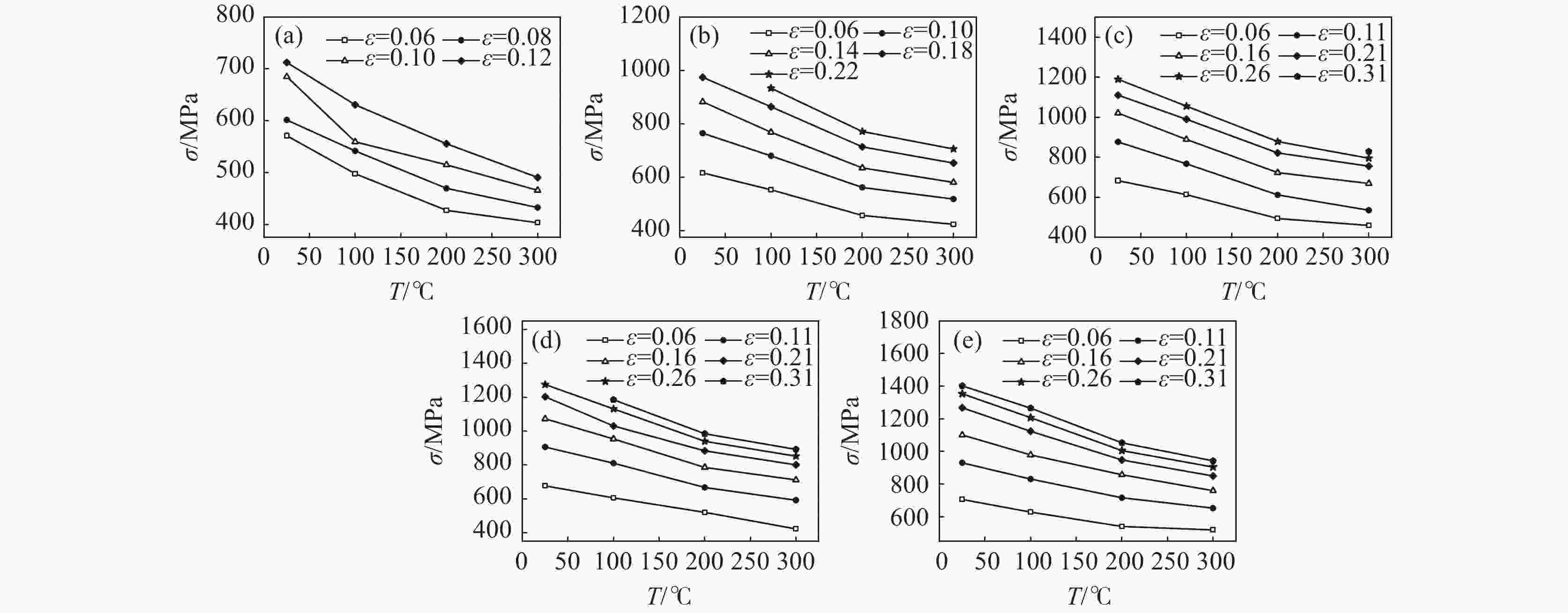
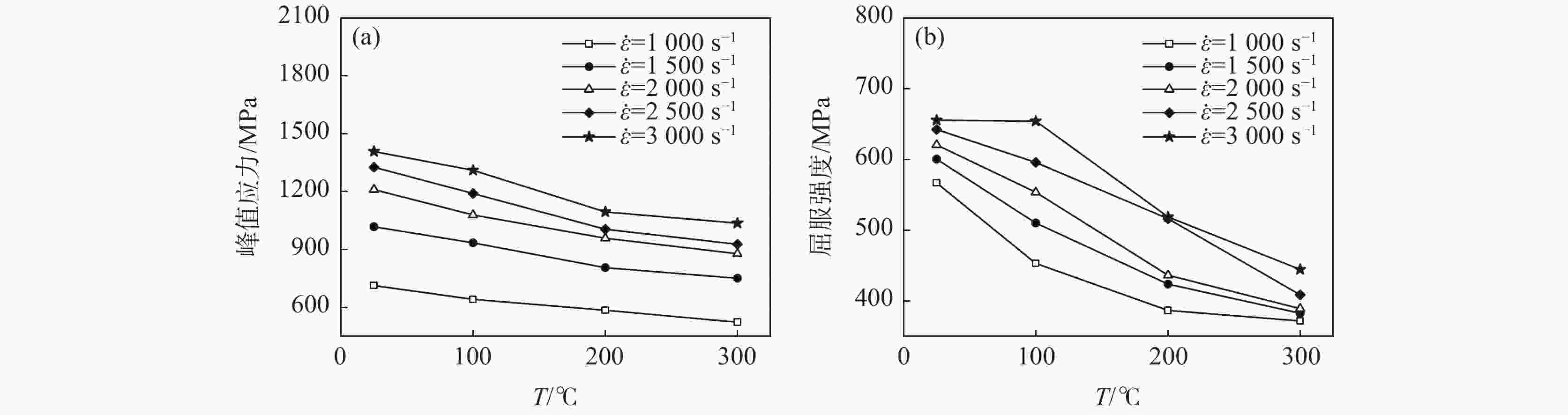
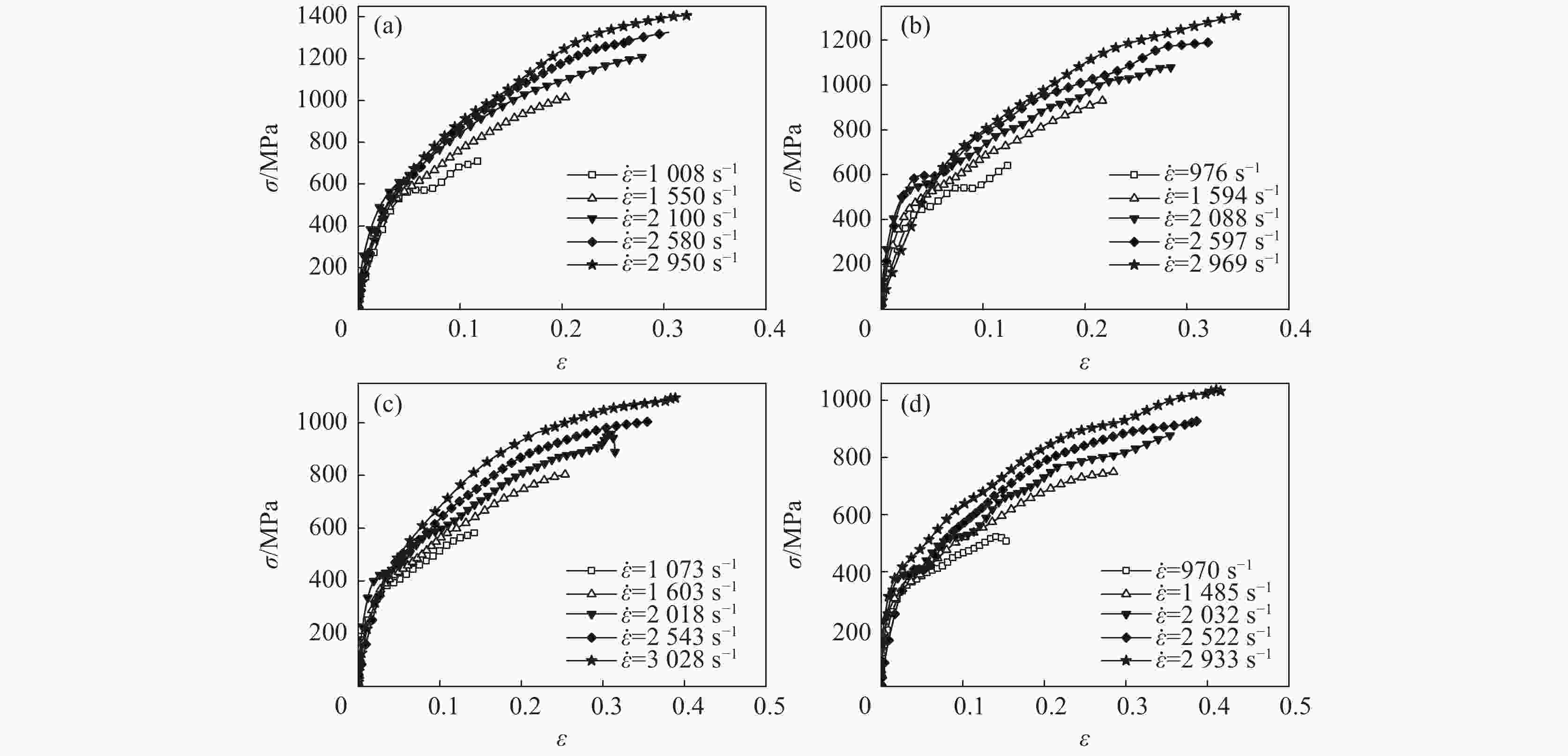
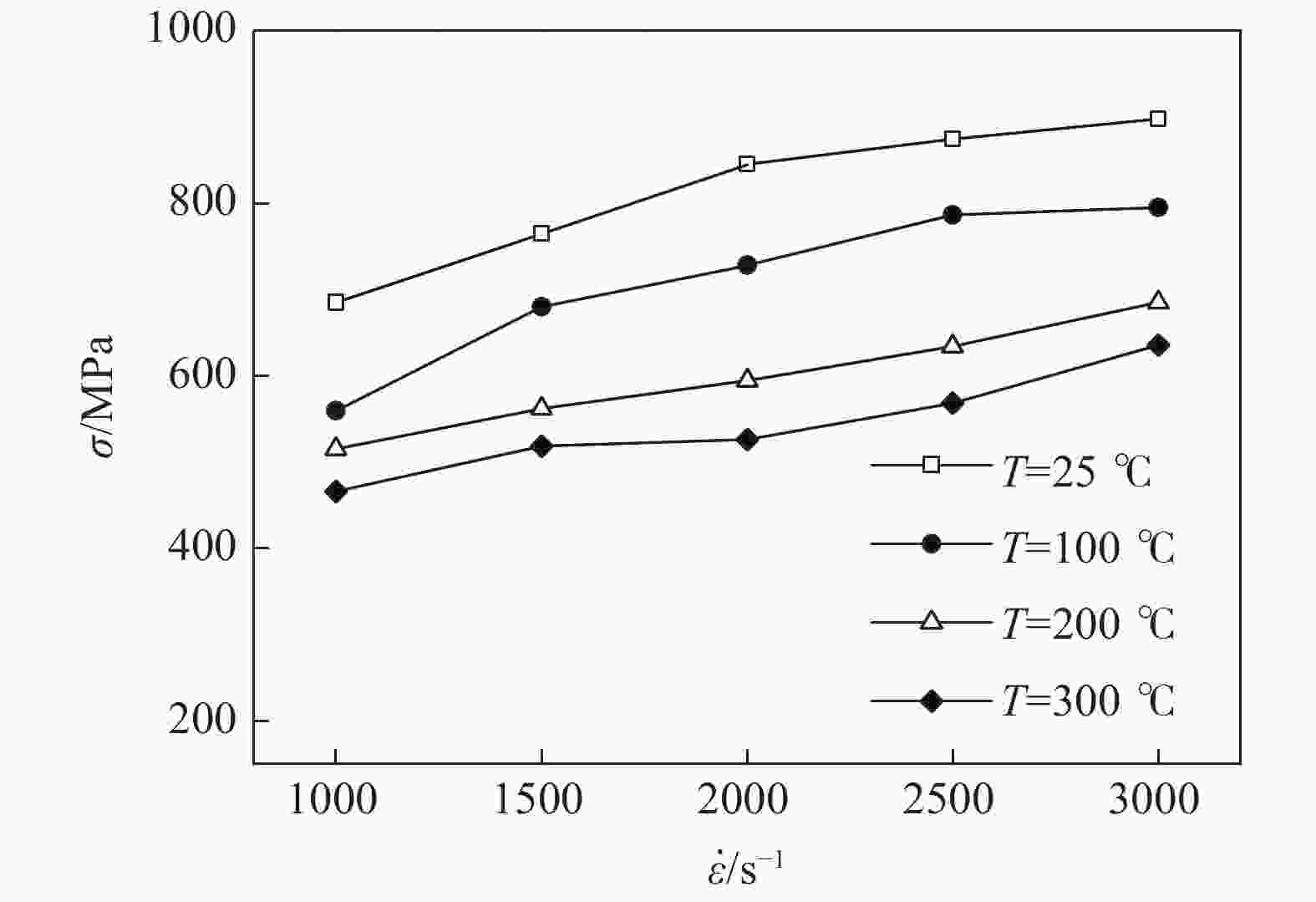
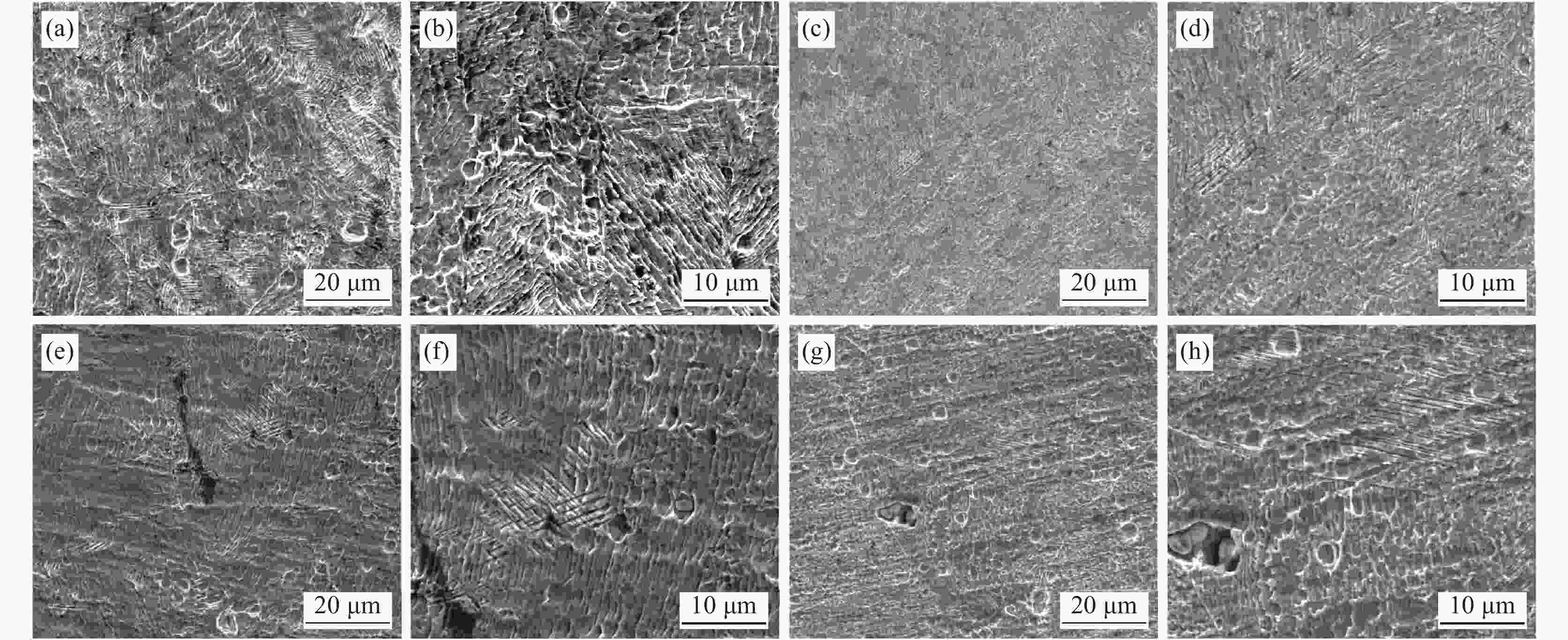
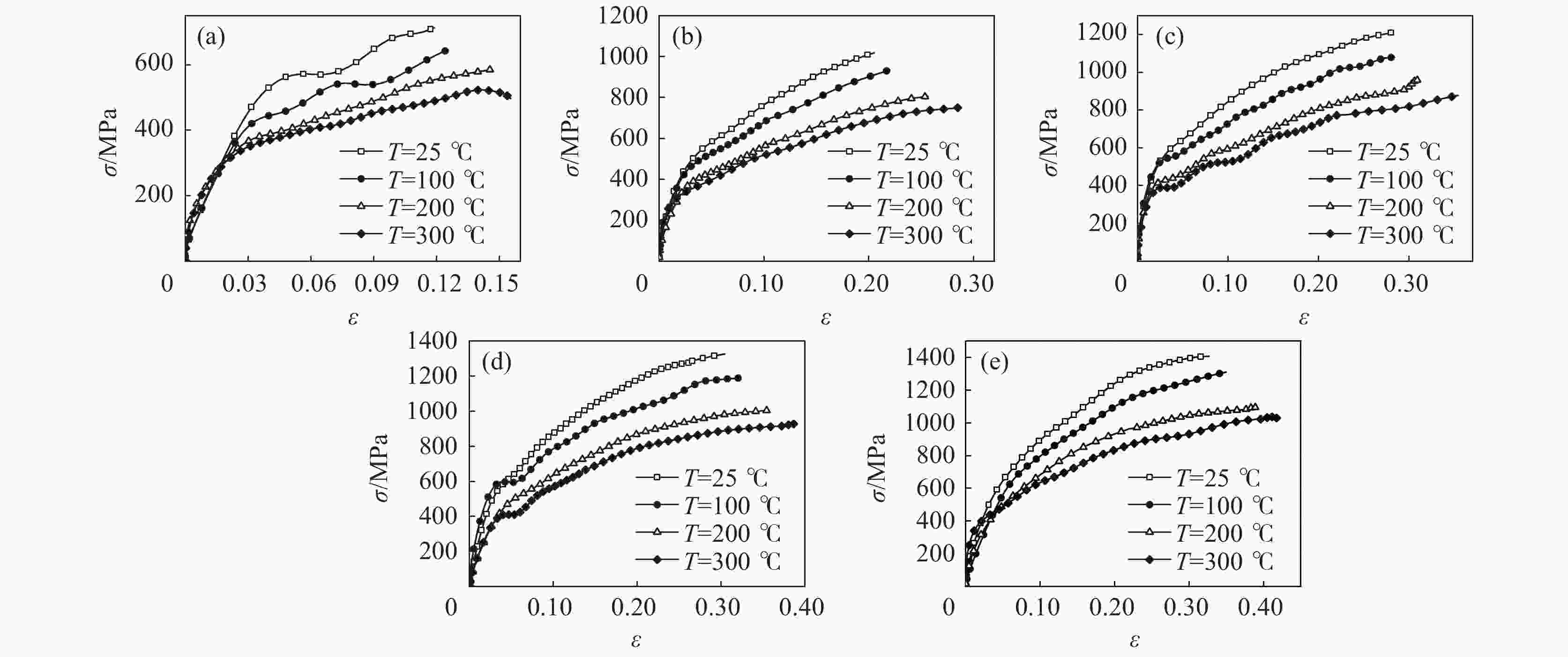
摘要: 采用高温分离式霍普金森(High Temperature Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar)动态试验装置,研究了06Cr19Ni10奥氏体不锈钢在温度25~300 ℃和应变率1000 ~3000 s−1下的动态力学性能。结果表明,06Cr19Ni10奥氏体不锈钢在1000~3000 s−1范围内表现出应变率强化效应,在25~300 ℃范围内表现出温度软化效应。利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)对应变率为3000 s−1的变形试样进行微观组织研究。结果表明,高应变率下,变形带密度大,随着变形温度的增加变形带密度降低。
-
关键词:
- 奥氏体不锈钢 /
- 06Cr19Ni10 /
- 高应变 /
- 温度软化 /
- 动态力学性能
Abstract: The dynamic mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steel 06Cr19Ni10 were studied by a high temperature split-Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) at temperatures of 25–300 ℃ and strain rates of 1000–3000 s−1. The austenitic stainless steel 06Cr19Ni10 shows strain rate strengthening effect in the range of 1000–3 000 s−1, and temperature softening effect in the range of 25–300 ℃. A scanning electron microscope (SEM) was used to observe microstructure of deformed sample at strain rate of 3 000 s−1. It is found that under high strain rate, the deformation zone density is high, and decreases as the deformation temperature increases. -
表 1 06Cr19Ni10奥氏体不锈钢主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of 06Cr19Ni10 stainless steel
% C Si Mn P S Ni Cr 0.08 0.75 2.00 0.045 0.03 8.22 18.89 -
[1] 刘勇. 密封唇焊结构奥氏体不锈钢阀门焊接性能研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2017.Liu Yong. Studies on welding properties for sealing lip welding structure austenitic stainless steel valve[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2017. [2] 黄超. 316 L不锈钢力学性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2016.Huang Chao. Analysis on the mechanical properties of 316 L stainless steel [D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2016. [3] Mei Rong, Ren Zhijun, Chou Wei. Hot deformation behavior of 06Cr18Ni11Ti austenitic stainless steel[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2019,42(6):88−92. (梅荣, 任志俊, 仇伟. 06Cr18Ni11Ti奥氏体不锈钢热变形行为研究[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2019,42(6):88−92. [4] 戴哲峰. 316 L不锈钢在复杂介质环境中的应力腐蚀试验研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2009.Dai Zhefeng. Stress corrosion test research on 316 L austenitic stainless steel in complex medium condition [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2009. [5] Dong Hanshan, Li Xiaoying. Surface engineering for joint prosthesis: State-of-the-art and future directions[J]. China Surface Engineering, 2008,21(5):1−14. (董汉山, 李小英. 人造关节材料表面工程的现状及前瞻[J]. 中国表面工程, 2008,21(5):1−14. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-9289.2008.05.001 [6] 凌玲, 李星星, 王学林, 等. 0Cr18Ni9不锈钢本构模型及其对切削力预测影响分析[J]. 中国机械工程, 2012,23(18): 2243-2248.Ling Ling, Li Xingxing, Wang Xuelin, et al. Constitutive model of stainless steel 0Cr18Ni9 and its influence on cutting force prediction [J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 23(18): 2243-2248. ) [7] Wang Yan, Wang Mingjia, Cai Dayong, et al. Effect of deformation parameters on microstructure evolution of medium carbon steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2005,26(4):65−68. (王艳, 王明家, 蔡大勇, 等. 高强度奥氏体不锈钢的热变形行为及其热加工图[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2005,26(4):65−68. [8] Wang Y L, Jia G Z, Zhang T, et al. Dynamic mechanical behaviors of high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel under high temperature and its constitutive model[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018,38(4):835−840. [9] Zhang Jing, Jiang Chunxia, Qiao Bangwei. Deformation behavior and constitutive equation of 14Cr17Ni2 steel at high temperature[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2018,47(14):38−43. (张静, 蒋春霞, 乔帮威. 14Cr17Ni2 钢高温变形行为及本构方程的研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2018,47(14):38−43. [10] Wu Liang, Hu Yiseng, Ji Xiang, et al. Dynamic mechanical behavior and constitutive model of FV520B martensitic precipitation-hardening steel[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2018,40(3):584−588. (吴亮, 胡毅森, 纪翔, 等. 马氏体沉淀硬化不锈钢 FV520B 动态力学性能及本构模型的研究[J]. 机械强度, 2018,40(3):584−588. [11] Zhang Hong, Suo Tao, Li Yulong. Mechanical behavior of a stainless steel material at elevated temperatures and high strain rates[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2012,31(1):78−83. (张红, 索涛, 李玉龙. 不锈钢材料高温、高应变率下动态力学性能的试验研究[J]. 航空材料学报, 2012,31(1):78−83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2012.1.016 [12] Xu Zejian, Li Yulong, Liu Mingshuang, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties of stainless steel 0Crl8Nil0Ti welded joint at elevated temperratures and high strain rates[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2008,44(1):98−104. (许泽建, 李玉龙, 刘明爽, 等. 不锈钢0Crl8Ni10Ti焊接头高温、高应变率下的动态力学性能[J]. 金属学报, 2008,44(1):98−104. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2008.01.019 [13] Shang Bing, Sheng Jing, Wang Baozhen, et al. Dynamic mechanical behavior and constitutive model of stainless steel[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2008,28(6):527−531. (尚兵, 盛精, 王宝珍, 等. 不锈钢材料的动态力学性能及本构模型[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2008,28(6):527−531. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2008.06.008 [14] He Zhu, Zhao Shougeng, Yang Jialing, et al. Experimental investigation of the dynamic material property of stainless steel: 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2007,25(3):418−421. (何著, 赵寿根, 杨嘉陵, 等. 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb不锈钢动态力学性能研究[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2007,25(3):418−421. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2812.2007.03.024 [15] 魏玉伟, 李宁, 文玉华, 等. 马氏体含量对1Cr17Ni1双相不锈钢动态和准静态力学性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2012, 37(11): 6-10.Wei Yuwei, Li Ning, Wen Yuhua, et al. Effect of martensite content on dynamic and quasi-static mechanical properties of 1Cr17Ni1dual-phase stainless steel [J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2012, 37(11): 6-10. [16] Xu Z, Li Y. Dynamic behaviors of 0Cr18Ni10Ti stainless steel welded joints at elevated temperatures and high strain rates[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2009,41(2):121−130. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2008.10.005 [17] Lee W S, Chen T H, Lin C F, et al. Dynamic mechanical response of biomedical 316 L stainless steel as function of strain rate and temperature[J]. Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications, 2011,(12):1−13. [18] Xiong Z P, Ren X P, Bao W P, et al. Effect of high temperature and high strain rate on the dynamic mechanical properties of Fe-30Mn-3Si-4Al TWIP steel[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2009,20(9):835−841. [19] Li Guohe, Wang Minjie. Dynamic mechanical properties and constitutive relationship of hardened steel (45 HRC) under high temperature and high strain rate[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2010,30(4):433−438. (李国和, 王敏杰. 淬硬45钢在高温高应变下的动态力学性能及本构关系[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2010,30(4):433−438. doi: 10.11883/1001-1455(2010)04-0433-06 [20] Bao Weiping, Ren Xueping, Zhang Yi. The characteristics of flow stress and dynamic constitutive model at high strain rates for pure iron[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2009,16(5):125−129. (包卫平, 任学平, 张毅. 纯铁在高应变率下的流动应力特征及其动态塑性本构关系[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2009,16(5):125−129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2009.05.024 [21] Yan Qiushi, Sun Bowen, Yang Lu. Study on dynamic mechanical behavior of structural stainless steel at elevated temperature and high strain rate[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019,47(5):128−132. (闫秋实, 孙博文, 杨璐. 高温高应变率下建筑不锈钢动态力学性能研究[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2019,47(5):128−132. [22] 周惠久, 黄明志. 金属材料强度[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989.Zhou Huijiu, Huang Mingzhi. Strength of metal materials[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989. [23] Mi Z L, Tang D, Dai Y J, et al. In-situ observation on the deformation behaviors of Fe-Mn-C TWIP steel[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2009, 16(6): 646-649. [24] Li D Z, Wei Y H, Liu C Y, et al. Effects of high strain rate on properties and microstructure evolution of TWIP steel subjected to impact loading[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2010,17(6):67−73. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(10)60116-1 [25] Xiong R G, Fu R Y, Su Y, et al. Tensile properties of TWIP steel at high strain rate[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2009,16(1):81−86. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(09)60015-7 [26] Xiong Z P, Rrn X P, Bao W P, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties of the Fe-30Mn-3Si-4Al TWIP steel after different heat treatments[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2011,530(12):426−431. -




 下载:
下载: