Process parameter optimization of 1725/WC composite coating on cast iron surface by laser cladding
-
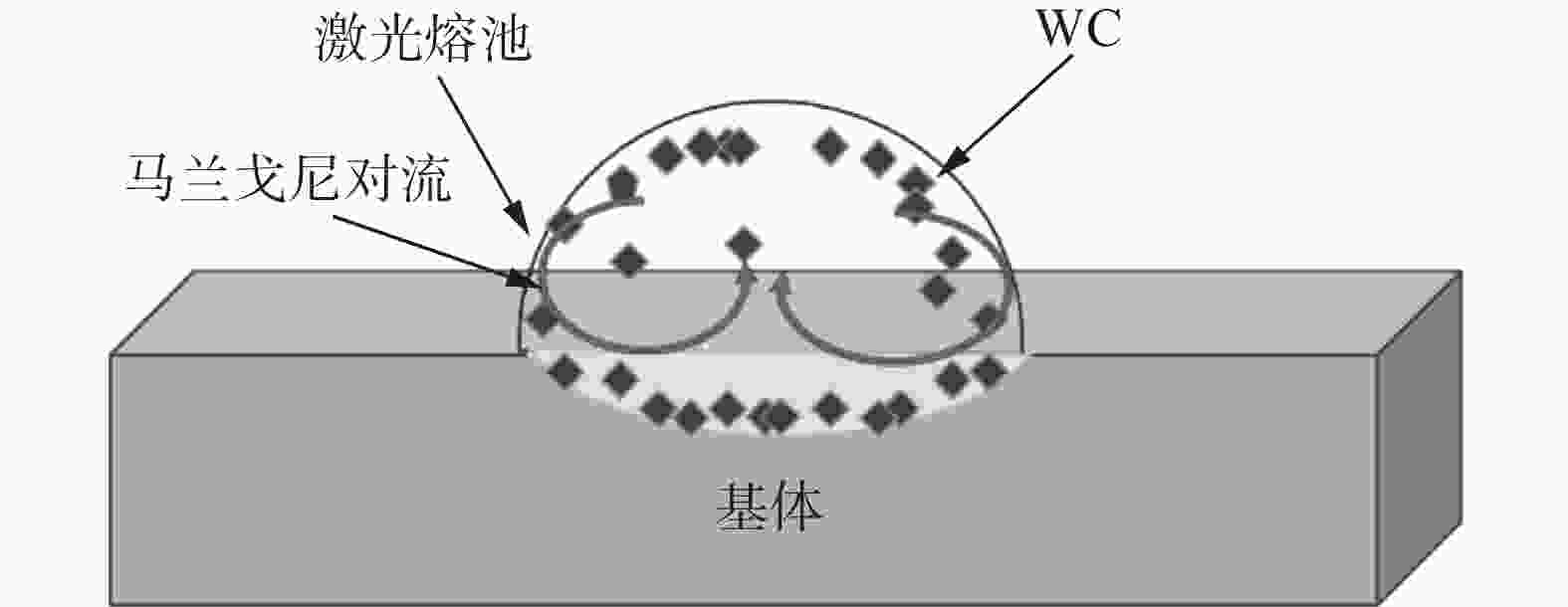
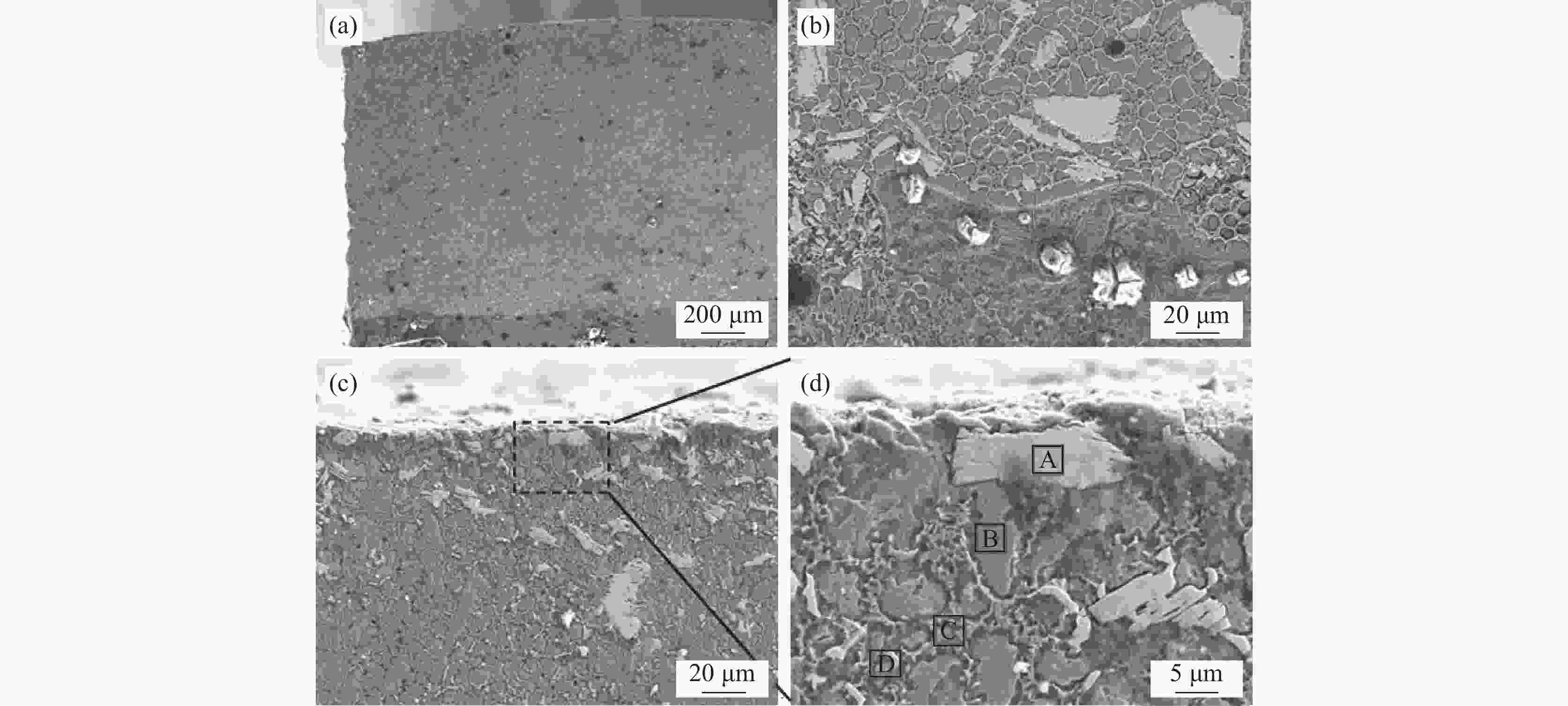
摘要: 采用激光熔覆技术在铸铁表面制备了1725/WC复合涂层,利用正交试验考察了激光功率、扫描速度及送粉率等因素对熔覆层稀释率和硬度的影响。结果表明:各因素对熔覆层稀释率影响的主次顺序为激光功率>送粉率>扫描速度。对熔覆层表面显微硬度影响的主次顺序为送粉率>激光功率>扫描速度。最优工艺参数为激光功率2 000 W,扫描速度15 mm/s,送粉率10 g/min。按最优工艺制备的1725/WC复合涂层成形质量较好,WC分布较均匀,熔覆层的平均硬度(HV0.2)为483.0。
-
关键词:
- 铸铁 /
- 激光熔覆 /
- 1725/WC复合涂层 /
- 稀释率 /
- 硬度
Abstract: 1725/WC composite coatings were prepared on the surface of cast iron by laser cladding. The effects of process parameters including laser power, scanning speed and powder feed rate on dilution ratio and hardness of the cladding coating were studied through orthogonal experiments. The results showed that the laser power had the greatest effect on the dilution rate of the cladding layer, followed by powder feeding rate and scanning speed, respectively. And the primary and secondary order sequence of these three factors on the surface microhardness were power feeding rate, laser power and scanning speed. The optimum process parameters were as follows: laser power was 2 000 W, scanning speed was 15 mm/s, powder feed rate was 10 g/min. The 1725/WC composite coating generated under the optimized process had good forming quality and WC had a uniform distribution. The average hardness of the cladding coating was 483.0HV0.2.-
Key words:
- cast iron /
- laser cladding /
- 1725/WC composite coatings /
- dilution ratio /
- hardness
-
表 1 球墨铸铁QT400-15化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of QT400-15 nodular cast iron
% C Si Mn P S Mg Cu Fe 3.6 2.6 0.28 ≤0.05 ≤0.02 0.035 ≤0.1 Bal. 表 2 1725粉末化学成分
Table 2. Chemical compositions of 1725 powder
% Cr Si B Al Fe C Ni 3.22 2.58 1.09 0.42 1.86 0.11 Bal. 表 3 L9(34)正交试验因素水平
Table 3. Orthogonal factors and levels of L9(34)
水平 A
功率
/ WB
扫描速率
/( mm·s−1)C
送粉速率
/( g·min−1)1 1500 10 10 2 2 000 15 14 3 2500 20 18 表 4 L9(34)正交试验结果及极差分析
Table 4. Experimental results and range analysis of L9(34) orthogonal test
编号 A B C H
/mmh
/mmB
/mmb
/mmγ
/%硬度
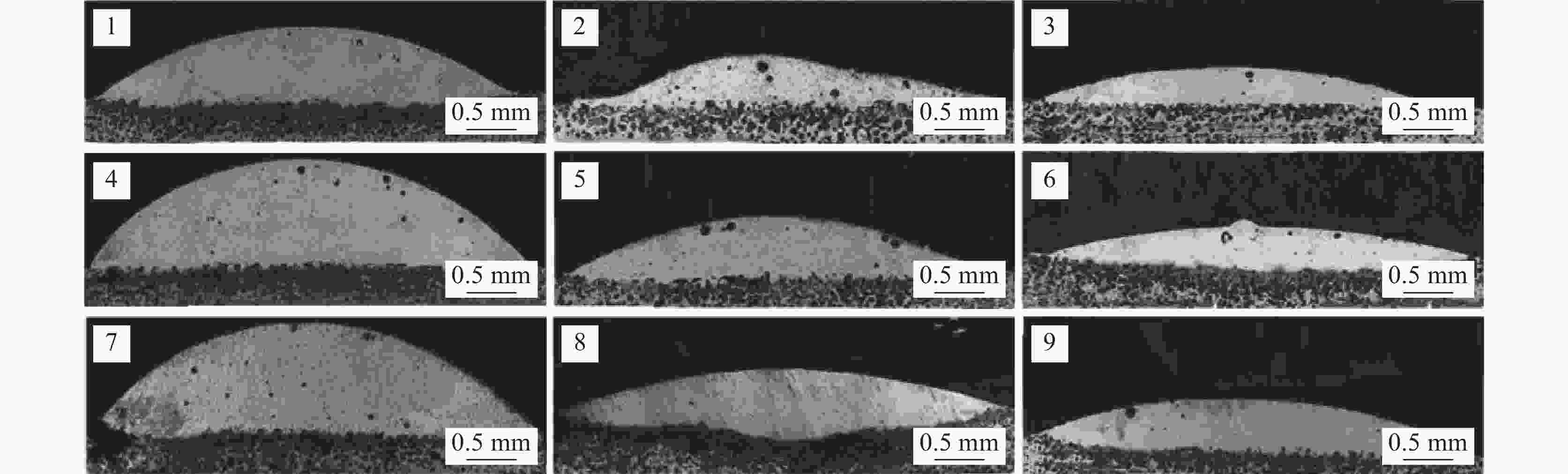
(HV0.2)1 1500 10 10 0.83 0.19 4.88 4.72 18.13 539.4 2 1500 15 14 0.51 0.12 4.77 4.67 18.72 454.4 3 1500 20 18 0.47 0.08 4.52 4.52 14.55 465.2 4 2000 10 14 1.25 0.26 5.32 5.32 17.22 447.4 5 2000 15 18 0.68 0.13 5.26 5.26 16.05 455.5 6 2000 20 10 0.50 0.20 5.01 5.01 28.57 455.1 7 2500 10 18 1.40 0.40 6.01 5.95 22.05 446.1 8 2500 15 10 0.90 0.42 5.80 5.80 31.82 472.5 9 2500 20 14 0.61 0.20 5.50 5.50 24.69 430.5 γ k1 17.13 19.13 26.17 k2 20.61 22.20 20.21 k3 26.18 22.60 17.55 R 9.05 3.47 8.62 硬度 k1 486.3 477.6 489.0 k2 452.7 460.8 444.1 k3 449.7 450.3 455.6 R 36.6 27.3 44.9 -
[1] Zhang Kaiyi, Han Hongsheng, Yang Chuan, et al. Microstructures and properties of hastelloy C276 on cast iron surface by laser cladding[J]. Surface Technology, 2021,50(6):109−115. (张凯奕, 韩宏升, 杨川, 等. 铸铁表面激光熔覆哈氏合金C276组织及性能[J]. 表面技术, 2021,50(6):109−115. [2] Schoenborna S, Kaufmanna H, Sonsinoa C M, et al. Cumulative damage of high-strength cast iron alloys for automotive applications[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2015,101:440−449. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2015.02.053 [3] Maraveas C, Wanga Y C, Swailes T, et al. An experimental investigation of mechanical properties of structural cast iron at elevated temperatures and after cooling down[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2015,71(1):340−352. [4] Sun T, Song R B, Wang X, et al. Abrasive wear behavior and mechanism of high chromium cast iron[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2015,22(1):84−90. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(15)60014-0 [5] Feng Xiaoli, Wang Haifeng, Liu Xuechao, et al. Effect of Al content on wear and corrosion resistance of Ni-based alloy coatings by laser cladding[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2021,412:1−12. [6] Zhang Shuling, Qiu Mingkun, Chen Weiye, et al. Preparation technology of wear resistant coatings[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2019,48(10):25−30. (张树玲, 邱明坤, 陈炜晔, 等. 耐磨涂层的制备技术[J]. 热加工工艺, 2019,48(10):25−30. [7] Akash Vyas, Jyoti Menghani. Parametric investigation of laser assisted cladding process: A review[J]. Materials Today:Proceedings, 2021,44:1828−1832. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.010 [8] Anas Ahmad Siddiqui, Avanish Kumar Dubey. Recent trends in laser cladding and surface alloying[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021,134:1−20. [9] Farahmand P, Liu S, Zhang Z, et al. Laser cladding assisted by induction heating of Ni-WC composite enhanced by nano-WC and La2O3[J]. Ceramics International, 2014,40(10):15421−15438. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.06.097 [10] Qiao Lei, Wu Yuping, Hong Sheng, et al. Wet abrasive wear behavior of WC-based cermet coatings prepared by HVOF spraying[J]. Ceramics International, 2021,47(2):1829−1836. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.09.009 [11] Wang Hui, Xia Weiming, Jin Yuansheng. A study on abrasive resistance of Ni-based coatings with a WC hard phase[J]. Wear, 1996,195(1−2):47−52. doi: 10.1016/0043-1648(95)06762-0 [12] Dong Dongmei, Chen Jufang, Lei Weining. Investigation on forming effect and dilution rate of laser cladding coating on 45 steel surfaces[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2019,48(4):163−166,169. (董冬梅, 陈菊芳, 雷卫宁. 45钢表面激光熔覆层成形效果及稀释率研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2019,48(4):163−166,169. [13] Lee Y S, Nordin M, Babu S S, et al. Influence of fluid convection on weld pool formation in laser cladding[J]. Welding Journal, 2014,93(8):292−300. [14] Singh A K, Bal K S, Dey D, et al. Experimental investigation and parametric optimization for minimization of dilution during direct laser metal deposition of tungsten carbide and cobalt powder mixture on SS304 substrate[J]. Powder Technology, 2021,390:339−353. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2021.05.056 -





 下载:
下载: