Effect of Ti treatment process on inclusions in steel
-
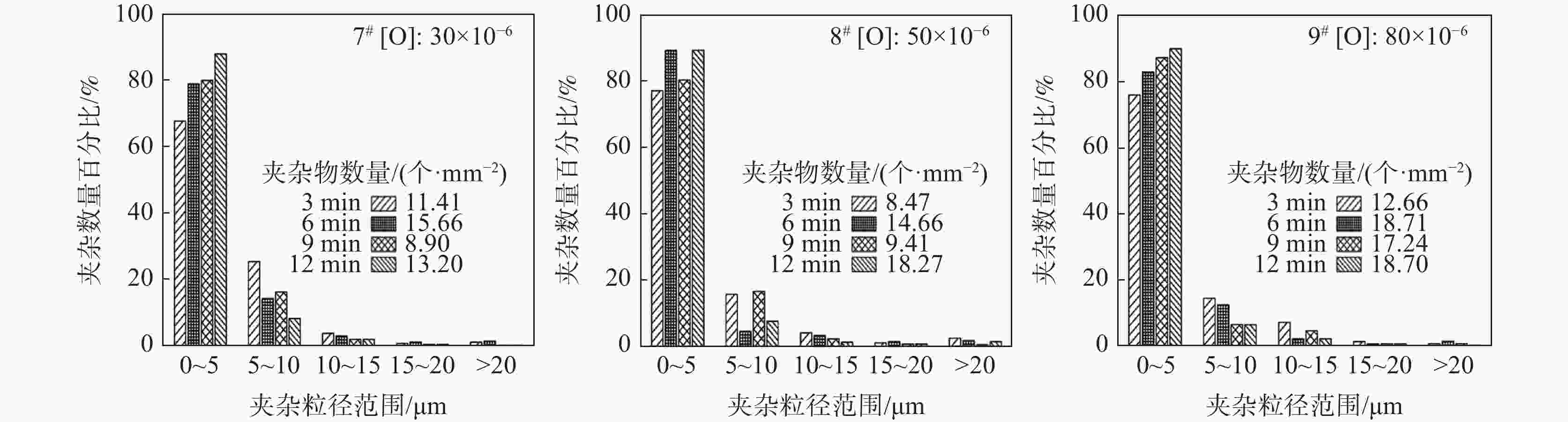
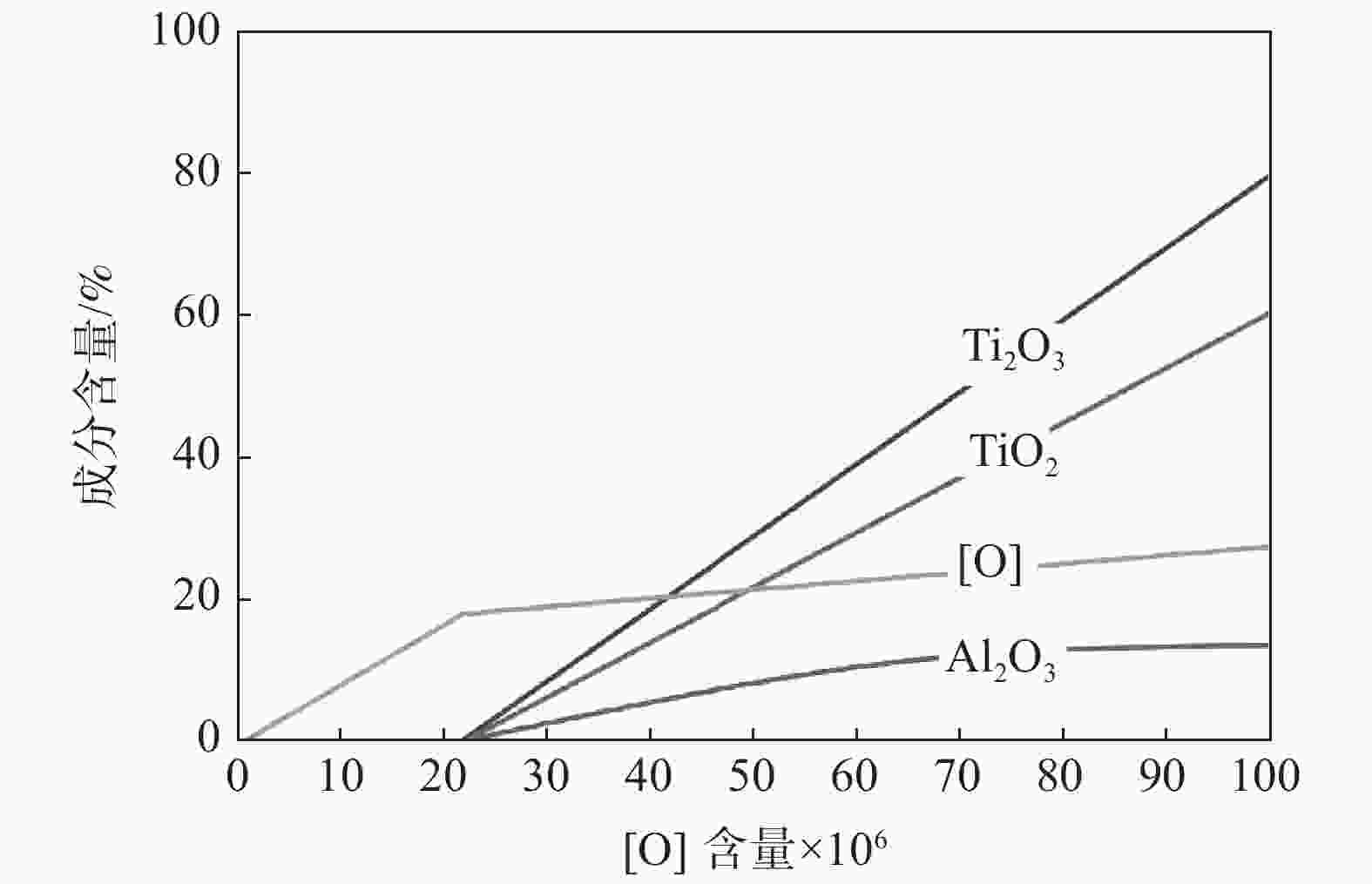
摘要: 采用模拟计算和试验相结合的方式研究了加Ti处理对钢中夹杂物的影响,探明了含Ti氧化物夹杂物的形成条件及演变过程。研究结果表明:在1600 ℃温度下,当钢中[O]含量大于22×10−6时,才会生成含Ti氧化物夹杂物。同时,由于钢中[Als]的存在会抑制含Ti氧化物夹杂的生成,要求在冶炼过程中尽可能避免采用金属Al进行脱氧处理;当Ti处理前钢中[O]含量在80×10−6以内时,随着[O]含量的增加,夹杂物尺寸未见明显变化;在Ti处理结束后加入Ca粒可对夹杂物进行改性处理,促使MnS在夹杂物上形核,从而有利于促进晶内针状铁素体的形成。Abstract: In this work, the influence of Ti treatment on inclusions in steel and the formation conditions and evolution process of Ti oxide inclusions were studied by a combination of simulation calculation and experiment. The results show that at 1 600 ℃, when the content of [O] in steel is greater than 22×10−6, Ti oxide inclusions will be formed. At the same time, since the presence of [Als] in the steel will inhibit the formation of Ti-containing oxide inclusions, it is required to avoid the use of metallic Al for deoxidation treatment as much as possible during the smelting process. When the [O] content in the steel before Ti treatment is less than 80×10−6, with the increase of [O] content, the size of the inclusions changes slightly. The addition of Ca particles after the Ti treatment can modify the inclusions and promote the nucleation of MnS on the inclusions, which is beneficial to promote the formation of intragranular acicular ferrite.
-
Key words:
- wear-resistant steel /
- Ti treatment /
- oxide metallurgy /
- inclusions /
- intragranular acicular ferrite
-
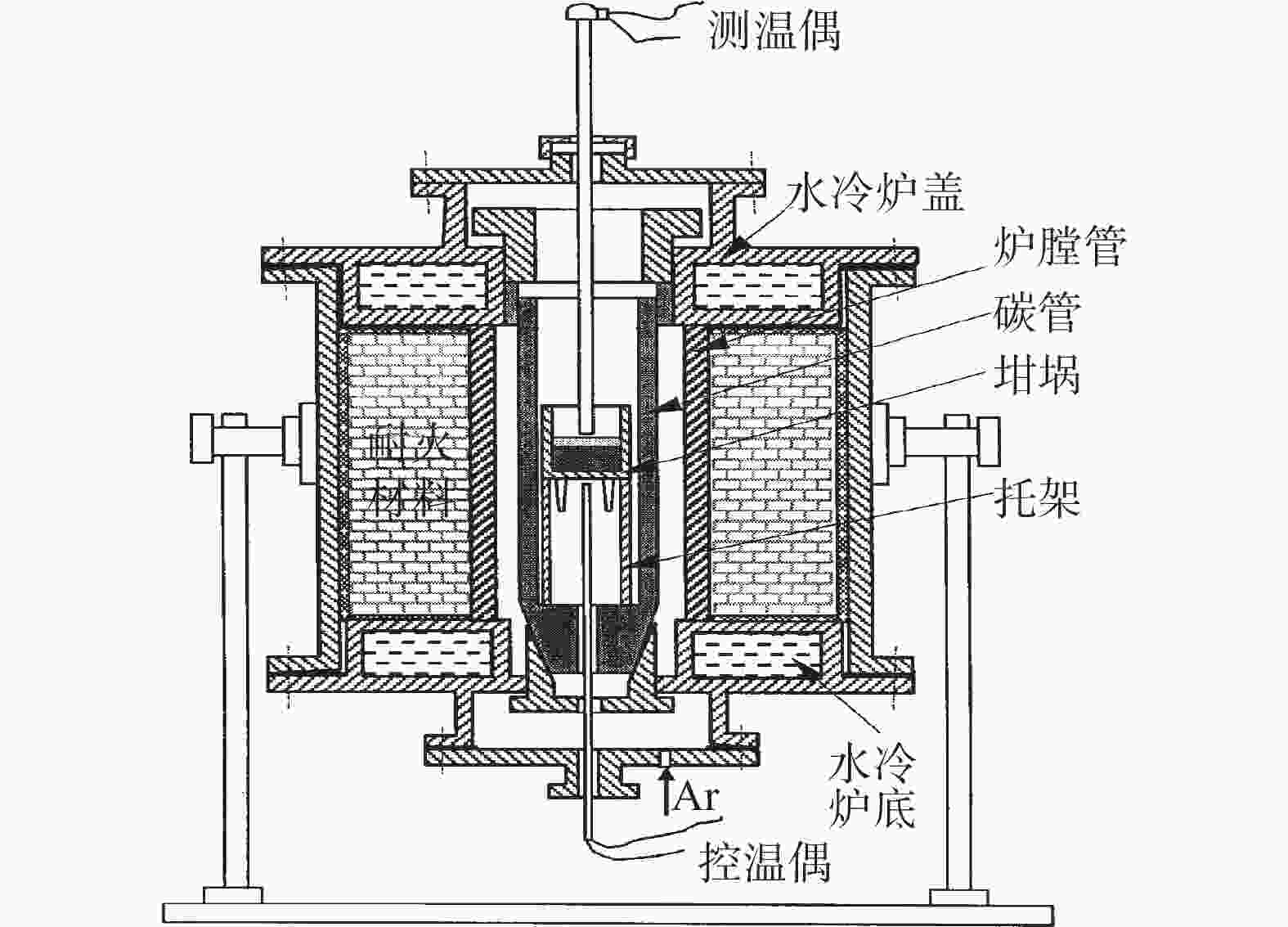
表 1 钛氧化物生成热力学计算钢水条件
Table 1. The chemical compositions of steel used for thermodynamic calculation
% C Si Mn P S Nb N 0.24 0.25 1.1 0.012 0.005 0.02 0.005 表 2 加Ti处理前后钢中[O]含量×106
Table 2. [O] content in steel before and after Ti treatment ×106
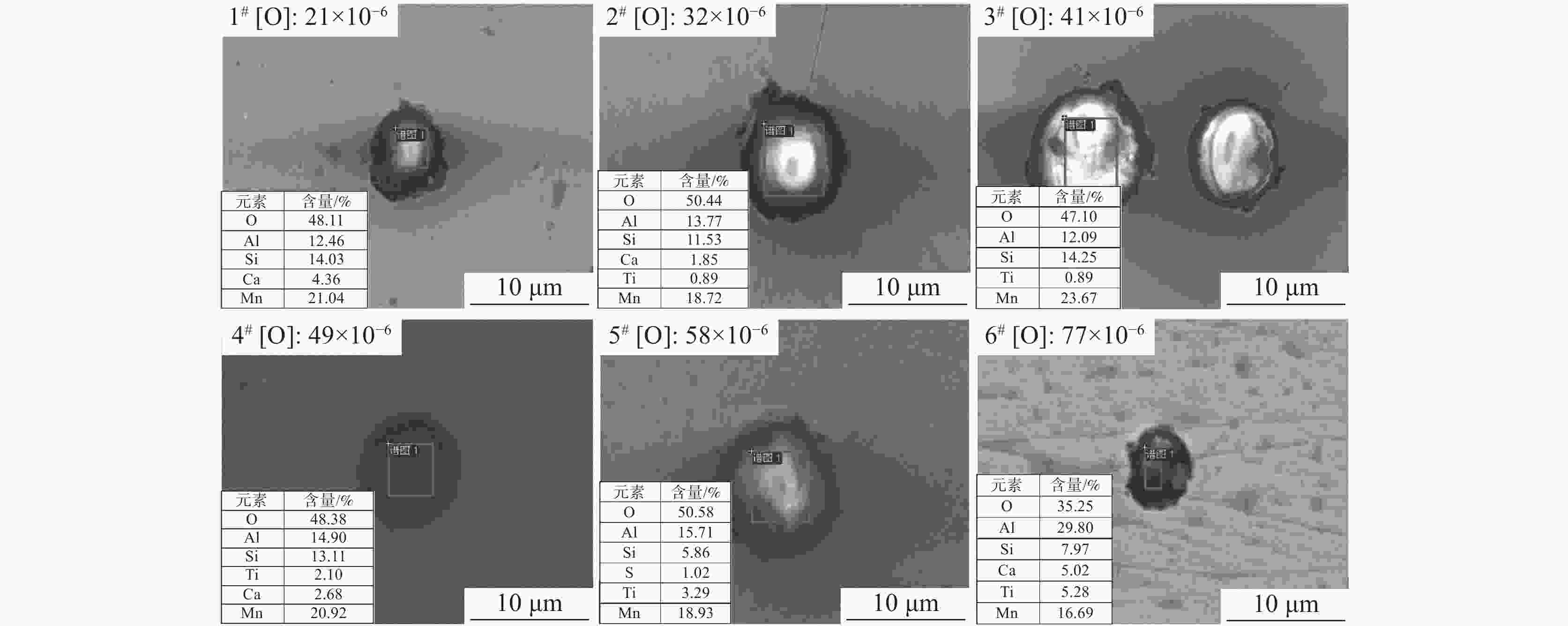
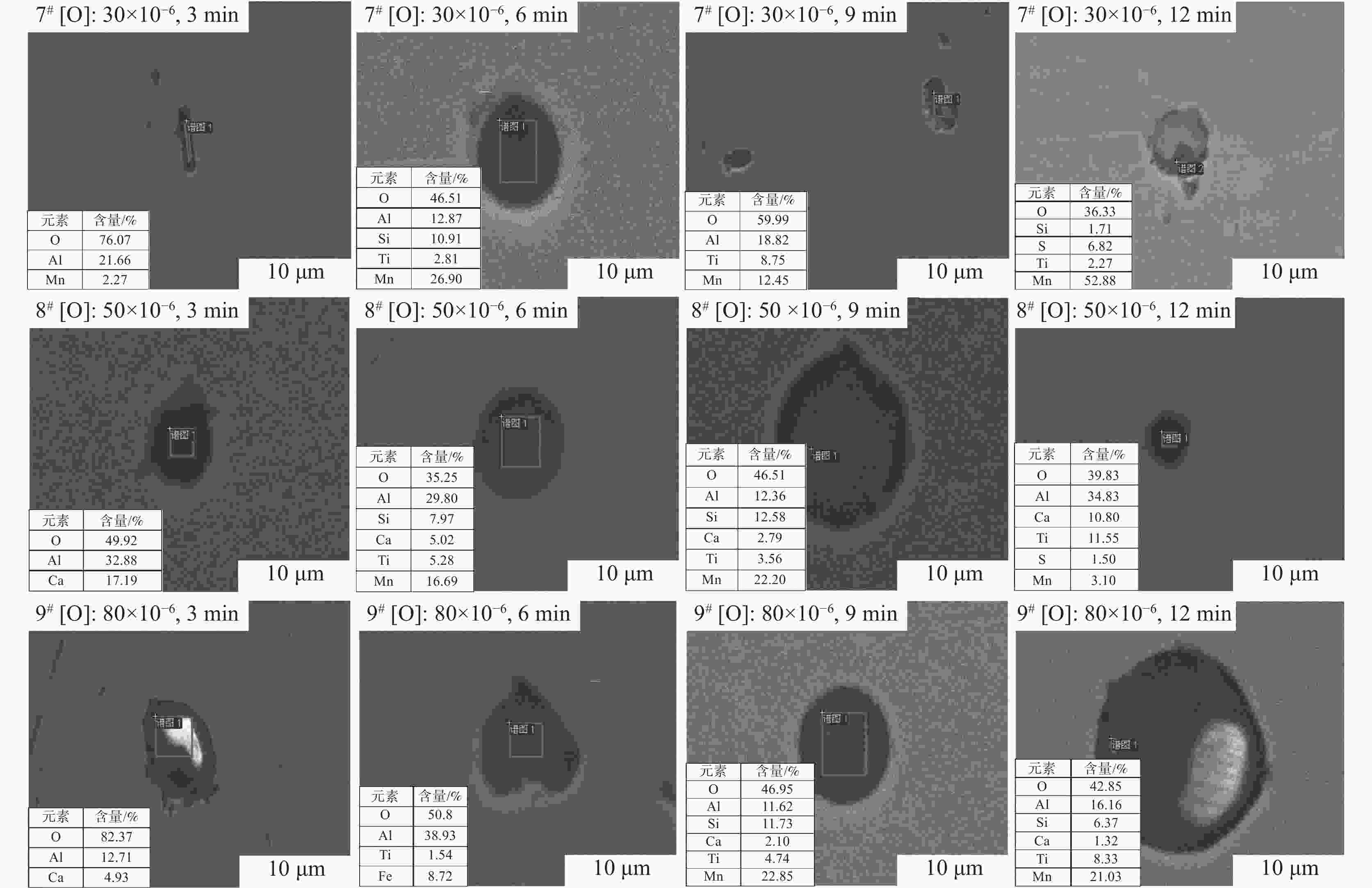
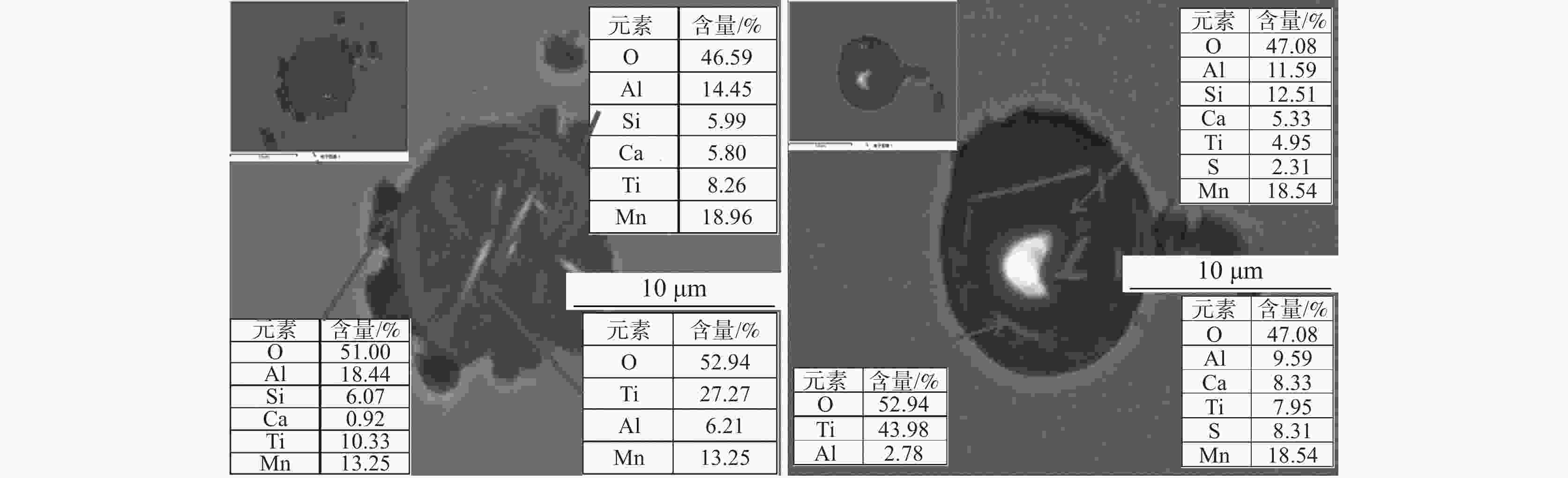
设计[O]含量 加Ti前[O]含量 加Ti后[O]含量 15 21 19 30 32 17 40 41 18 50 49 19 60 58 20 80 77 22 -
[1] Liu Liu. Key production-technology for high-quality special steels[J]. Iron & Steel, 2018,53(4):1−7. (刘浏. 高品质特殊钢关键生产技术[J]. 钢铁, 2018,53(4):1−7. [2] Wang Xindong, Tian Jinglei, Song Chengyuan. Innovative practice technology and outlook in large iron and steel enterprise green manufacturing[J]. Iron & Steel, 2018,53(2):1−9. (王新东, 田京雷, 宋程远. 大型钢铁企业绿色制造创新实践与展望[J]. 钢铁, 2018,53(2):1−9. [3] Wang Deyong, Qu Tianpeng. Development and prospect of Mg clean steel technology[J]. Steelmaking, 2020,36(5):1−13,20. (王德永, 屈天鹏. 镁洁净钢新技术发展与展望[J]. 炼钢, 2020,36(5):1−13,20. [4] Lu Bin, Chen Furong, Zhi Jianguo, et al. Enhanced welding properties of high strength steel via rare earth oxide metallurgy technology[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2020,56(9):1206−1216. (陆斌, 陈芙蓉, 智建国, 等. 应用稀土氧化物冶金技术改善高强钢焊接性能[J]. 金属学报, 2020,56(9):1206−1216. [5] Li Yang, Du Pengfei, Jiang Zhouhua, et al. Effects of TiC on the microstructure and formation of acicular ferrite in ferritic stainless steel[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2019,26(11):1385−1395. doi: 10.1007/s12613-019-1845-2 [6] Wang Bingxing, Zhu Fuxian, Wang Chao, et al. Application of oxide metallurgy in high heat input welding steels[J]. Iron & Steel, 2019,54(9):12−21. (王丙兴, 朱伏先, 王超, 等. 氧化物冶金在大线能量焊接用钢中的应用[J]. 钢铁, 2019,54(9):12−21. [7] Zhu Liguang, Sun Ligen. Application and prospect for shipbuilding steel development with oxide metallurgy technique[J]. Steelmaking, 2017,33(5):1−11. (朱立光, 孙立根. 氧化物冶金技术及其在船体钢开发中的应用及展望[J]. 炼钢, 2017,33(5):1−11. [8] Pan Xiulan, Li Zhen, Wang Yanhong, et al. Oxygen control in steel and oxide metallurgy[J]. Angang Technology, 2007,(1):10−13,20. (潘秀兰, 李震, 王艳红, 等. 钢中氧的控制及氧化物冶金[J]. 鞍钢技术, 2007,(1):10−13,20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4613.2007.01.003 [9] Tian Qianren, Li Jie, Wu Xiangyu, et al. Growth mechanism of MnS/Fe on TiN surface: First principle investigation[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020:844. [10] Zhu Liguang, Wang Yan, Wang Shuoming, et al. Research of microalloy elements to induce intragranular acicular ferrite in shipbuilding steel[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2019,46(6):499−507. [11] Sun Ligen, Li Huirong, Zhu Liguang, et al. Research on the evolution mechanism of pinned particles in welding HAZ of Mg treated shipbuilding steel[J]. Materials & Design, 2020,192:1−13. [12] Kong Hui, Zhou YaHui, Lin Hao, et al. The mechanism of intragranular acicular ferrite nucleation induced by Mg-Al-O inclusions[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2015,(6):1−6. [13] Lou Haonan, Wang Chao, Wang Bingxing, et al. Evolution of inclusions and associated microstructure in Ti–Mg oxide metallurgy steel[J]. ISIJ International, 2019,59(2):312−318. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2018-445 [14] Li Chao, Dong Tingliang, Kong Weiming, et al. Evolution of inclusions in high heat input welding steel with TiCa compound deoxygenation[J]. Iron & Steel, 2019,54(2):35−40. (李超, 董廷亮, 孔维明, 等. Ti-Ca复合脱氧大线能量焊接用钢中夹杂物的演变[J]. 钢铁, 2019,54(2):35−40. [15] Wang Bingxing, Wu Zhongzi, Lou Haonan, et al. Effect of oxide metallurgy on microstructure and properties of HAZ in EH36 steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2019,31(2):239−246. (王丙兴, 武仲子, 娄号南, 等. 氧化物冶金工艺对EH36钢HAZ组织性能的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2019,31(2):239−246. [16] Wan Xiangliang, Wu Kaiming, Wang Henghui, et al. Applications of oxide metallurgy technology on high heat input welding steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2015,25(6):6−12. (万响亮, 吴开明, 王恒辉, 等. 氧化物冶金技术在大线能量焊接用钢的应用[J]. 中国冶金, 2015,25(6):6−12. [17] 陈光勇. 氧化物冶金工艺对热轧EH40钢板大线能量焊接性能的影响[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2010.Chen Guangyong. Effect of oxidation metallurgical process on weldability with high heat input welding of hot rolling EH40 plate steel[D]. Shengyang: Northeastern University, 2010. [18] Li Minggang, Matsuura Hiroyuki, Tsukihashi Fumitaka. Time-dependent evolution of Ti-bearing oxide inclusions during isothermal holding at 1573 K (1300 ℃)[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2019,50(2):863−873. doi: 10.1007/s11661-018-5015-3 [19] 郑世伟. 氧化物冶金过程中晶内铁素体竞争优先析出机制的研究[D]. 唐山: 华北理工大学, 2019.Zheng Shiwei. Research on the preferential precipitation mechanism of intragranular ferrite in the process of oxide metallurgy[D]. Tangshan: North China University of Technology, 2019. [20] Xu Chen, Zhang Mingya, Li Jianli, et al. The effect of MgTiO3 adding on inclusion characteristics[J]. High Temperature Materials and Processes, 2019,38(2019):576−581. doi: 10.1515/htmp-2019-0004 [21] Wang Chao, Lou Haonan, Wang Bingxing, et al. Effect of alloying elements on microstructure and properties of high heat input welding steel[J]. Iron & Steel, 2018,53(6):85−91,97. (王超, 娄号南, 王丙兴, 等. 合金元素对大线能量焊接用钢组织性能的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2018,53(6):85−91,97. -




 下载:
下载: