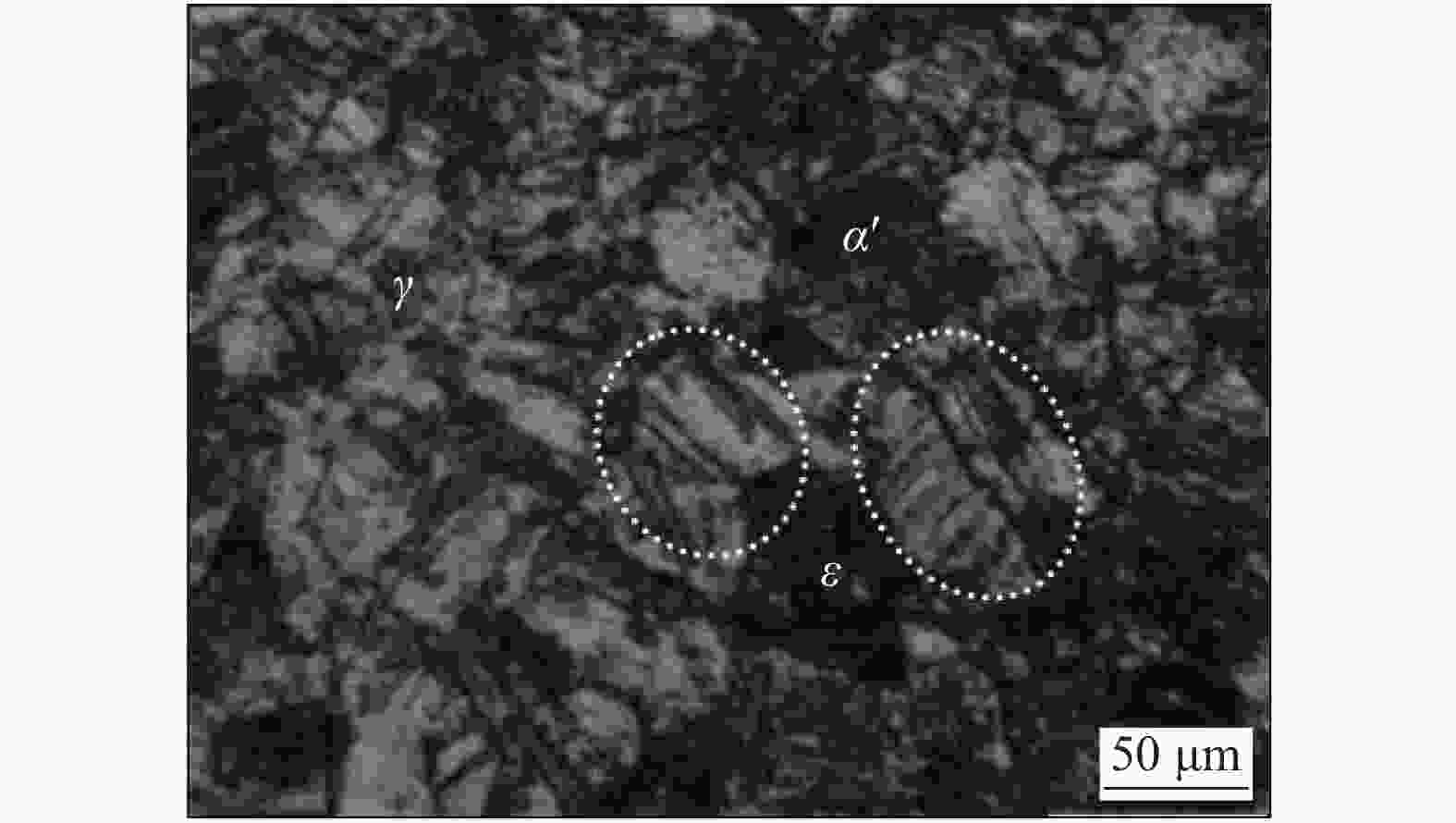
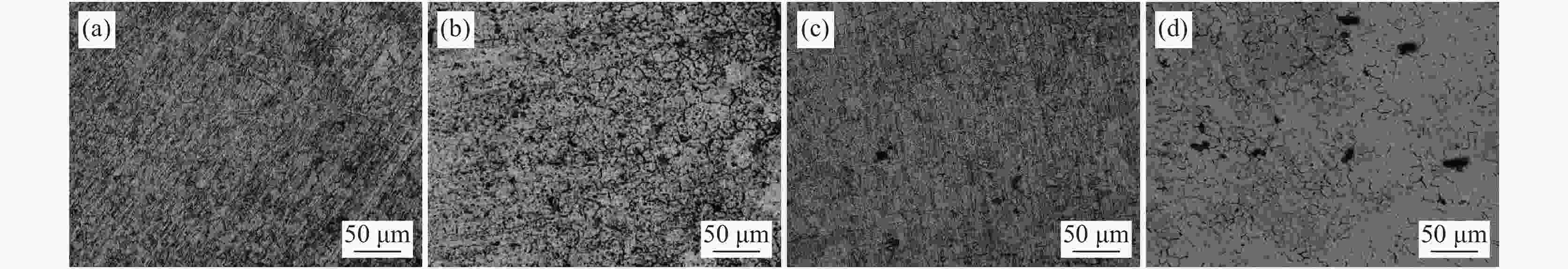
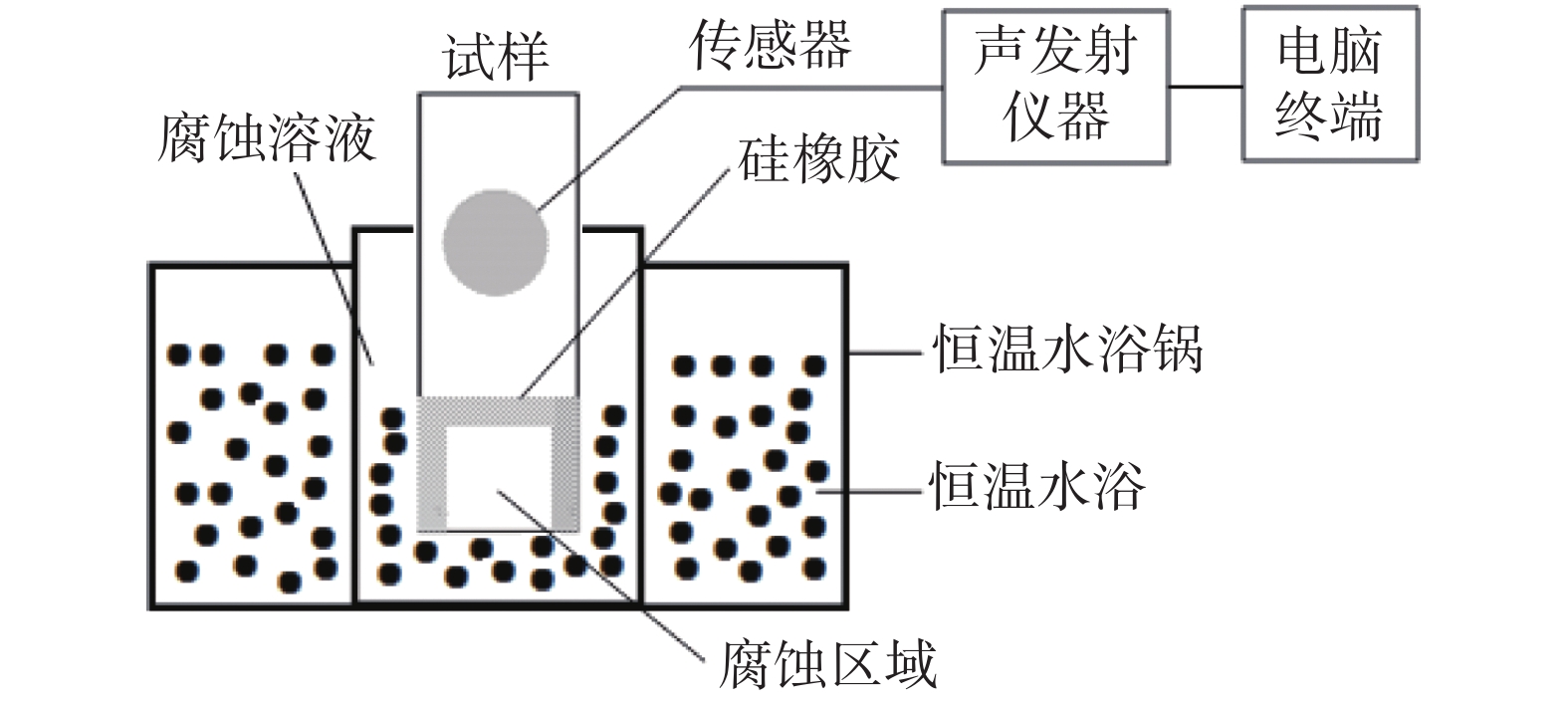
Effect of SO42− concentration on corrosion damage of 304 stainless steel in Cl− solution
-
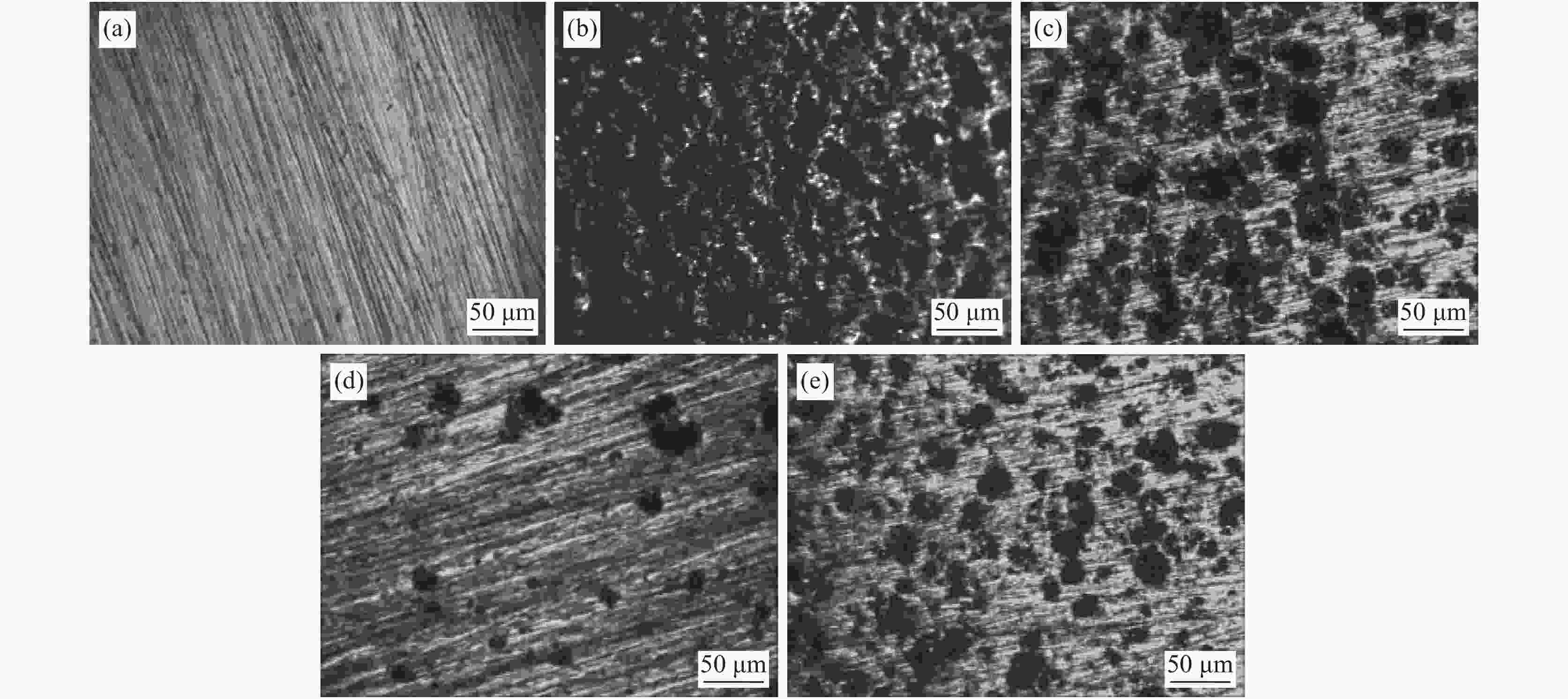
摘要: 为了研究SO42−对含有0.7 mol/L Cl−溶液中304不锈钢腐蚀损伤的影响,采用声发射技术与形貌观察技术分别测试试样腐蚀过程中产生的声信号和腐蚀前后试样表面形貌。结果表明:在Cl−/SO42−溶液中,随着SO42−浓度的增加,304不锈钢腐蚀过程产生的AE信号相对能量与幅度较大值、撞击累积数曲线斜率、持续时间等参数先减小后增加;腐蚀坑与龟裂块状的腐蚀产物数量先减少后增加,由龟裂腐蚀产物引起的表面疏松程度先紧密后疏松。试样腐蚀损伤发生的时间因SO42−离子浓度不同,0、0.10、0.25和0.40 mol/L时试样损伤发生的时间段分别为腐蚀的前中期、前期、后期以及全程时间段。腐蚀损伤程度由强到弱的顺序为0 mol/L> 0.40 mol/L> 0.10 mol/L > 0.25 mol/L。综合试样腐蚀形貌与声发射参数,在本试验范围内,对于含0.7 mol/L Cl−溶液中,为了减轻304不锈钢腐蚀发生,添加SO42−离子的适宜浓度为0.25 mol/L。Abstract: In order to investigate the effect of SO42− on the corrosion damage of 304 stainless steel in a solution containing 0.7 mol/L Cl−, acoustic emission technology and morphology observation technology were used to test the acoustic signal generated during the corrosion process and the surface morphology of the sample before and after corrosion, respectively. In the Cl−/SO42− solution, with the increase of SO42− concentration, the parameters such as relative energy and amplitude of AE signal generated during the corrosion process, the slope of cumulative number of impacts and duration time, as well as the number of corrosion pits and the number of cracked massive corrosion products firstly decrease and then increase. The degree of surface looseness caused by cracked corrosion products is firstly tight and then loose with the increase of SO42− concentration. The time period of sample corrosion damage is different due to the concentration of SO42− ions. The time periods for sample damage at 0, 0.10, 0.25, and 0.40 mol/L concentrations are the early and mid-term, early, late and full time periods of corrosion, respectively. The order of SO42− ion concentration influencing the degree of corrosion damage from heavy to light is 0 mol/L> 0.40 mol/L> 0.10 mol/L> 0.25 mol/L. In this study, after evaluating sample corrosion morphology and acoustic emission parameters, appropriate concentration of SO42− ions of 0.25 mol/L can effectively reduce the corrosion of 304 stainless steel in a 0.7 mol/L Cl− solution.
-
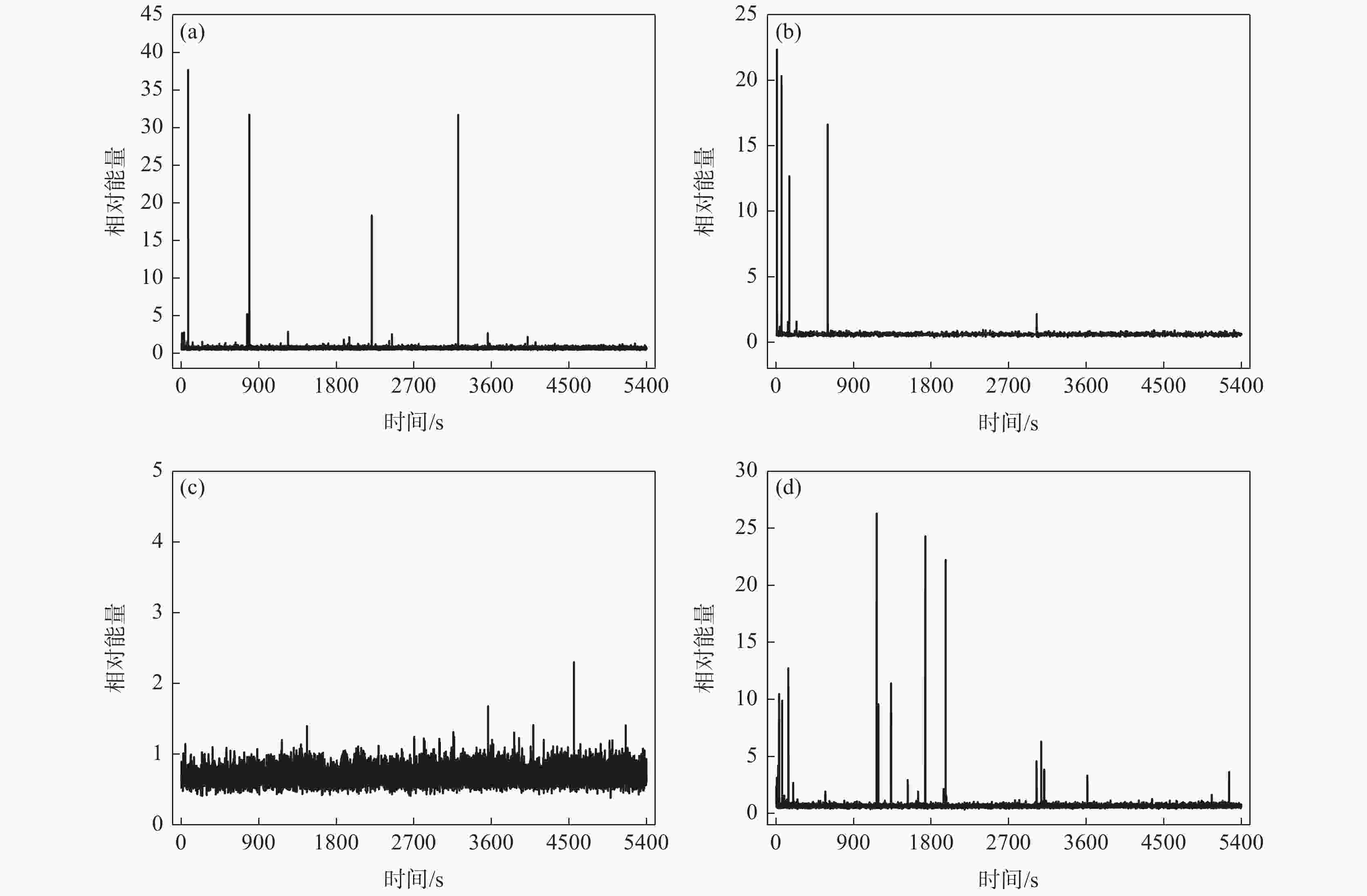
表 1 试样腐蚀过程中声发射信号数量及占比
Table 1. The number and proportion of acoustic emission signals during sample corrosion
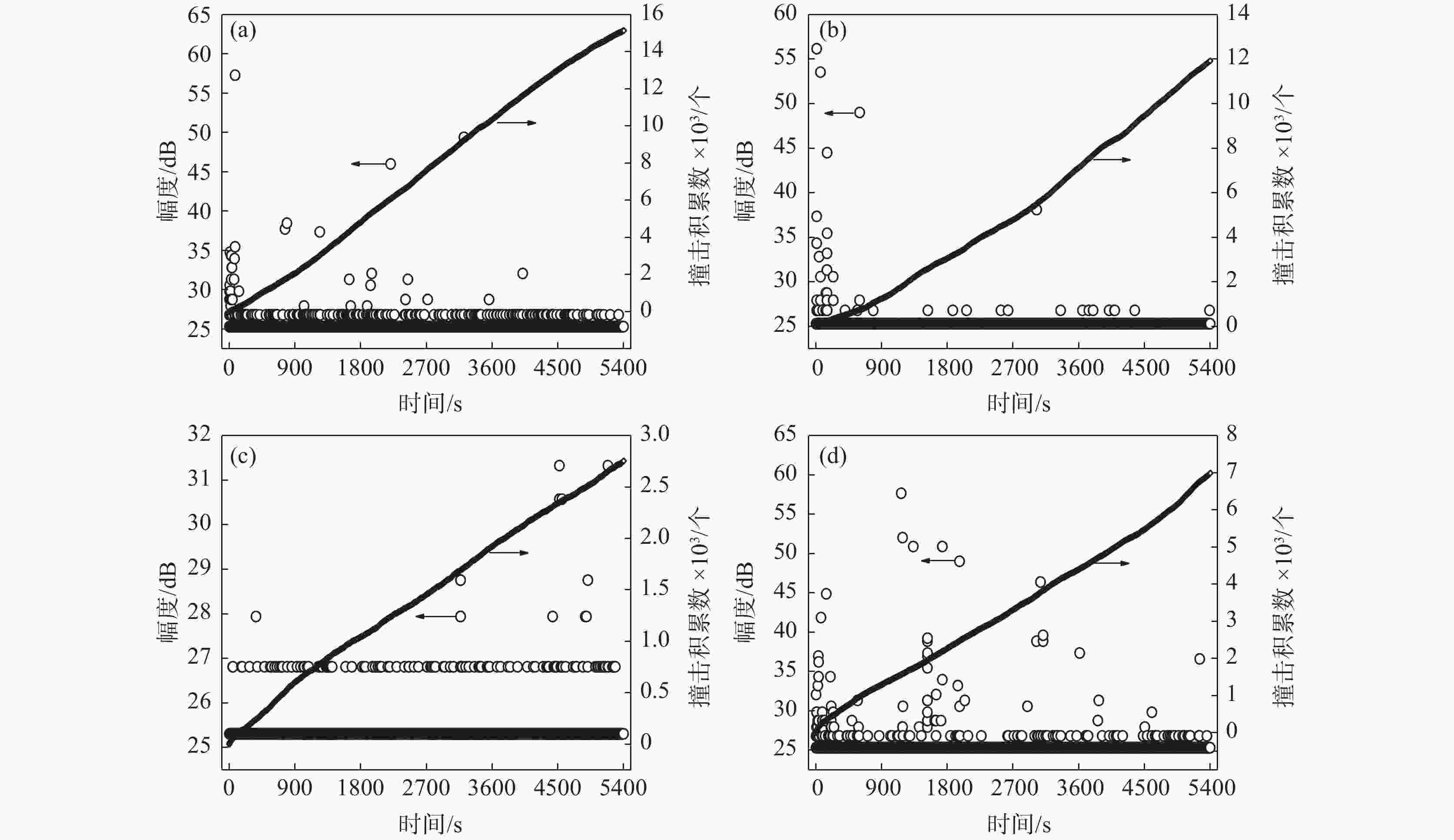
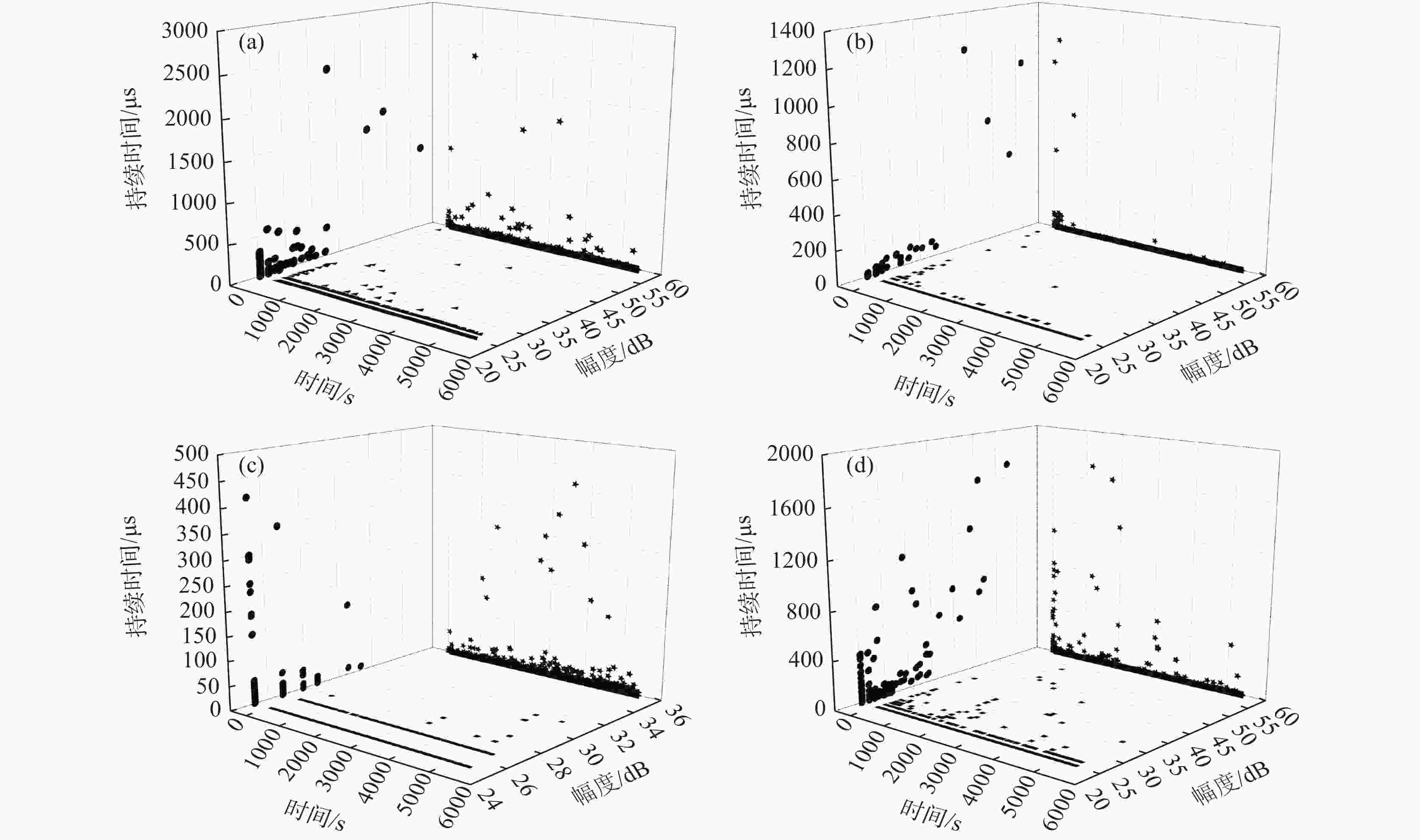
SO42− 浓度/(mol·L−1) 腐蚀时间/s AE 信号撞击积累数/个 AE 信号幅度/dB 信号相对能量占比/% < 2 2~10 >10 0 0~1800 15123 4794 99.833 0.125 0.042 1800~3600 5529 99.910 0.054 0.036 3600~5400 4800 99.958 0.042 0.1 0~1800 3015 1307 99.617 0.077 0.306 1800~3600 877 99.886 0.114 3600~5400 831 100.000 0.25 0~1800 11857 3008 100.000 1800~3600 4058 100.000 3600~5400 4791 99.979 0.021 0.40 0~1800 6959 2253 99.112 0.666 0.222 1800~3600 2130 99.718 0.235 0.047 3600~5400 2576 99.922 0.078 表 2 试样的AE信号幅度值和持续时间占比
Table 2. Proportion of AE signal amplitude and duration of the sample
SO42− 浓度/
(mol·L−1)腐蚀时间/s 信号幅度值占比 /% 持续时间占比 /% <30 dB 30~40 dB >40 dB <100 μs >100 μs 0 0~1800 99.708 0.271 0.021 99.791 0.209 1800~3600 99.910 0.054 0.036 99.801 0.199 3600~5400 99.979 0.021 99.896 0.104 0.10 0~1800 98.746 0.868 0.386 99.614 0.386 1800~3600 99.890 0.110 100.000 3600~5400 100.000 100.000 0.25 0~1800 100.000 99.100 0.100 1800~3600 100.000 99.877 0.123 3600~5400 99.958 0.042 99.937 0.063 0.40 0~1800 98.935 0.799 0.266 99.068 0.932 1800~3600 99.596 0.314 0.090 99.624 0.376 3600~5400 99.884 0.116 99.845 0.155 -
[1] Cheng C Q, Klinkenberg L I, Ise Y, et al. Pitting corrosion of sensitised type 304 stainless steel under wet–dry cycling condition[J]. Corrosion Science, 2017,118:217−226. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2017.02.010 [2] Naeem M, Javed I, Zakaullah M, et al. Enhanced wear and corrosion resistance of AISI-304 steel by duplex cathodic cage plasma treatment[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2019,375:34−45. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.07.012 [3] Wang X H, Yang Z L, Wang Z, et al. The influence of copper on the stress corrosion cracking of 304 stainless steel[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019,478:492−498. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.01.291 [4] Mukahiwa K, Bertali G, Burke M G, et al. The beneficial effect of surface carbon coating on stress corrosion cracking of type 304 austenitic stainless steels in high temperature water[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2019,158:77−82. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.08.033 [5] Peng Y W, Chen C M, Li X Y, et al. Effect of low-temperature surface carburization on stress corrosion cracking of AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2017,328:420−427. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.08.058 [6] Ju Yun, Zhu Weidong, Wang Pengcheng. Electrochemical corrosion behavior of 304 stainless steel dilute hydrochloric acid[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2014,43(6):53−55. (鞠云, 朱维东, 王鹏程. 304不锈钢在稀盐酸中的电化学腐蚀行为[J]. 热加工工艺, 2014,43(6):53−55. [7] Zhang Siqi, Du Nan, Wang Meifeng, et al. Effect of cathode area on stable pitting growth rate of 304 stainless steel in 3.5%NaCl solution[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2018,38(6):551−557. (张思齐, 杜楠, 王梅丰, 等. 阴极面积对3.5%NaCl溶液中304不锈钢稳态腐蚀生长速率的影响[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2018,38(6):551−557. doi: 10.11902/1005.4537.2017.187 [8] Zeng Qunfeng, Xu Yating, Lin Naiming. Tribocorrosion behaviors of 304 stainless steel in artificial seawater[J]. Surface Technology, 2020,49(1):194−202. (曾群锋, 许雅婷, 林乃明. 304 不锈钢在人工海水环境中的腐蚀磨损行为研究[J]. 表面技术, 2020,49(1):194−202. [9] 石慧英, 唐幸明, 左禹. PO43-对304不锈钢在氯离子水溶液中小孔腐蚀形核过程的影响[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2013, 33(1): 36-40.Shi Huiying, Tang Xingming, Zuo Yu. Effect of PO43- on pitting nucleation of 304 stainless steel in chloride solutions[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2013, 33(1): 36-40. [10] Wang Haitao, Zhao Jingmao, Zuo Yu, et al. The effects of some anions on metastable pitting of 316 L stainless steel[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2002,2(4):202−206. (王海涛, 赵景茂, 左禹, 等. 几种阴离子对316 L不锈钢亚稳态孔蚀行为的影响[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2002,2(4):202−206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4537.2002.04.003 [11] Zhang A, Wu X Q, Tan J B, et al. In-situ monitoring of stress corrosion cracking of 304 stainless steel in high-temperature water by analyzing acoustic emission waveform[J]. Corrosion Science, 2019,146:90−98. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2018.10.022 [12] Liu Jin, e, Duan Quan, Yang Xu. Acoustic emission testing of the pitting corrosion of 304 stainless steel[J]. Nondestructive Testing, 2017,39(3):60−63. (刘金娥, 段权, 杨旭. 304不锈钢点腐蚀的声发射检测[J]. 无损检测, 2017,39(3):60−63. doi: 10.11973/wsjc201703015 [13] Pang Yanrong, Dong Xiaoping, Chen Jiayi, et al. Characterization of acoustic emission in corrosion process of 304 stainless steel in NaCl solution[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2015,36(2):214−218. (庞艳荣, 董小平, 陈家熠, 等. NaCl 溶液中 304 不锈钢腐蚀过程的声发射特征[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2015,36(2):214−218. [14] Yang Liqing, Zhang Chao, Xiao Junsheng. Effect of NaCl solution concentration on acoustic emission feature during corrosion of 304 stainless steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2014,35(12):184−189. (杨立清, 张超, 肖俊生. NaCl 溶液浓度对304不锈钢腐蚀过程的声发射特征影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2014,35(12):184−189. [15] Yang Ruicheng, Bi Haijuan, Niu Shaorui, et al. Influence of temperature and mass fraction of Cl- on pitting corrosion resistance of 304 stainless steel[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 2010,36(5):5−9. (杨瑞成, 毕海娟, 牛绍蕊, 等. 温度和 Cl-质量分数对 304 不锈钢耐点蚀性能的影响[J]. 兰州理工大学学报, 2010,36(5):5−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5196.2010.05.002 [16] 杜楠, 田文明, 赵晴. 等. 304不锈钢在3.5%NaCl溶液中的点蚀动力学及机理[J]. 金属学报, 2012, 48(7): 807-814.Du Lan, Tian Wenming, Zhao Qing, et al. Pitting corrosion dynamics and mechanisms of 304 stainless steel in 3.5% NaCl solution[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2012, 48(7): 807-814. [17] 潘金生, 仝健民, 田民波. 材料科学基础(修订版)[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2012.Pan Jinsheng, Tong Jianmin, Tian Minbo. Fundamentals of materials science (Revised edition)[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2012. [18] Peng Wenshan, Hou Jian, Ding Kangkang. Corrosion behavior of 304 stainless steel in deep sea environment[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2019,39(2):145−150. (彭文山, 侯健, 丁康康. 深海环境中304不锈钢腐蚀行为研究[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2019,39(2):145−150. doi: 10.11902/1005.4537.2018.103 [19] Niu Libin, Nakada Kensuke. Effect of chloride and sulfate ions in simulated boiler water on pitting corrosion behavior of 13 Cr steel[J]. Corrosion Science, 2015,96:171−177. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2015.04.005 [20] Aouina N, Balbaud-Célérier F, Huet F, et al. Initiation and growth of a single pit on 316 L stainless steel: influence of SO42− and ClO4− anions[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013,104:274−281. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2013.04.109 -





 下载:
下载: