Study on microstructure and properties of new titanium bearing high strength building steel
-
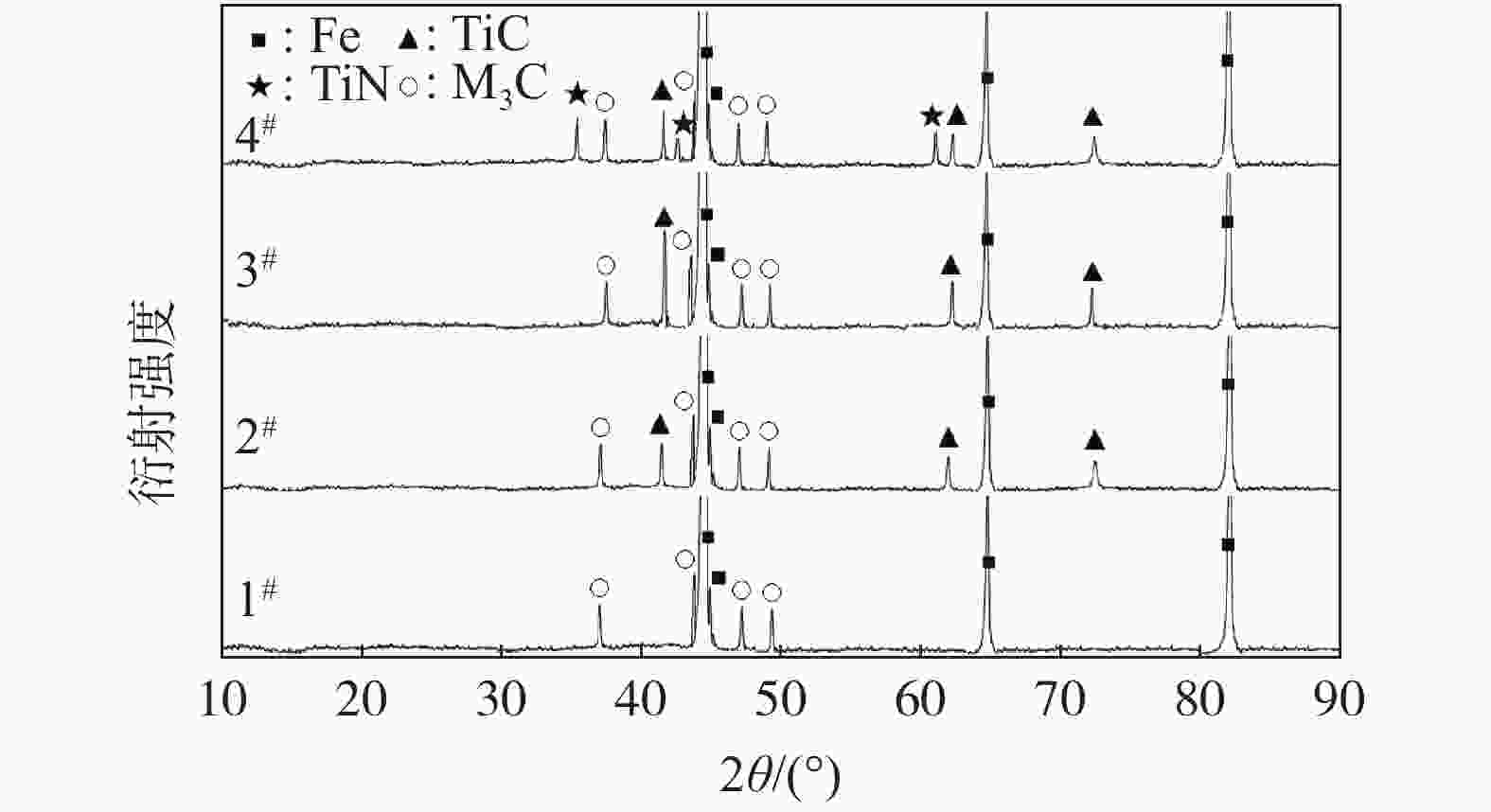
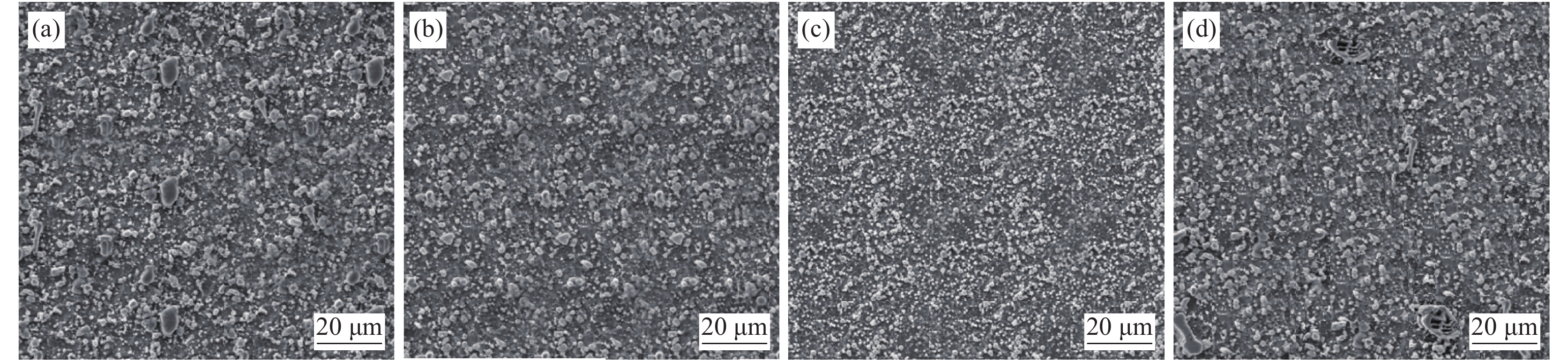
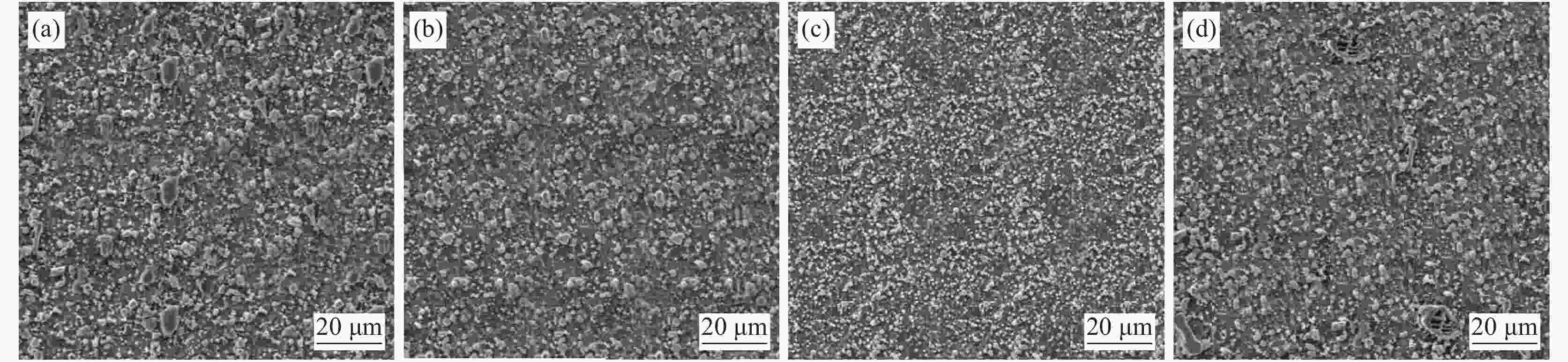
摘要: 进行了不同钛含量的Fe-Si-Mn-C-Ti系建筑高强钢显微组织,以及耐腐蚀性能和耐磨损性能的测试与分析。结果表明,添加合金元素钛,有助于细化试验钢的内部组织,提高耐腐蚀性能和耐磨损性能。随钢中钛含量从0逐步增至0.15%,试验钢的内部组织先细化后粗化,腐蚀电位先正移后负移,磨损体积先减小后增大,耐腐蚀性能和耐磨损性能先提高后下降。与不添加钛相比,添加0.06%钛含量时,试验钢的腐蚀电位正移91 mV,磨损体积减小9×10−3 mm3,耐腐蚀性能显著提高。不添加钛时,Fe-Si-Mn-C试验钢中由基体Fe和M3C碳化物组成;当合金元素钛含量0.02%~0.06%时,试验钢由基体Fe、TiC和M3C碳化物组成;当合金元素钛含量0.15%时,试验钢由基体Fe、TiC、TiN和M3C碳化物组成。Abstract: In this paper, the microstructure, corrosion resistance and wear resistance of Fe-Si-Mn-C-Ti high-strength building steel with different titanium content were tested and analyzed. The results show that the addition of alloy element titanium is helpful to refine the internal structure and improve the corrosion resistance of the steel. With the increase of Ti content from 0 to 0.15%, the internal structure of the test steel is refined firstly and then coarsened, the corrosion potential firstly shifts to positive and then negative, the wear volume firstly decreases and then increase, the corrosion resistance and wear resistance increases firstly and then decreases. When 0.06% Ti is added, the corrosion potential of the steel is shifted forward by 91 mV, the wear volume decreases by 9×10−3 mm3, and the corrosion resistance is significantly improved. Fe-Si-Mn-C steel without titanium consists of matrix Fe and M3C carbides. When the content of Ti is 0.02%–0.06%, the steel consists of matrix Fe, TiC and M3C carbides. When the content of Ti is 0.15%, the steel consists of matrix Fe, TiC, TiN and M3C carbides.
-
Key words:
- high-strength building steel /
- Ti /
- microstructure /
- corrosion resistance /
- wear resistance
-
表 1 试验钢化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of the tested steel
% 试样编号 C Si Mn P S N Ti Fe 1# 0.05 0.20 1.52 <0.005 <0.005 <0.005 0 Bal. 2# 0.05 0.20 1.52 <0.005 <0.005 <0.005 0.02 Bal. 3# 0.05 0.20 1.52 <0.005 <0.005 <0.005 0.06 Bal. 4# 0.05 0.20 1.52 <0.005 <0.005 <0.005 0.15 Bal. 表 2 试验钢电化学腐蚀试验结果
Table 2. Corrosion results of the tested steels
试样编号 合金元素钛含量/% 腐蚀电位/V 1# 0 -0.615 2# 0.02 -0.598 3# 0.06 -0.524 4# 0.15 -0.581 表 3 试验钢磨损试验结果
Table 3. Test results of the tested steels’ wear resistance
试样编号 合金元素钛含量/% 磨损体积/mm3 1# 0 34×10−3 2# 0.02 31×10−3 3# 0.06 25×10−3 4# 0.15 28×10−3 -
[1] Chen Shouguan, Wang Li, Li Xiaolin, et al. Effect of titanium strengthening on mechanical properties of 700 MPa grade high strength weathering steel and its improvement[J]. China Metallurgy, 2016,(3):17−21. (陈守关, 王莉, 李晓林, 等. 钛强化对700 MPa 高强耐候钢性能的影响及改进[J]. 中国冶金, 2016,(3):17−21. [2] Luo Xu, Yang Caishui, Kang Yonglin, et al. Effect of precipitates on the austenite grain growth of titanium microalloyed high performance steel[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2016,38(2):230−234. (罗许, 杨财水, 康永林, 等. 析出粒子对钛微合金化高强钢奥氏体晶粒长大的影响[J]. 工程科学学报, 2016,38(2):230−234. [3] Yang Yuebiao, Deng Shen, Fan Lei, et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties and strengthening mechanism of Ti microalloyed high strength steel[J]. Iron & Steel, 2019,54(10):72−79. (杨跃标, 邓深, 樊雷, 等. 钛微合金化高强钢的组织性能及强化机制[J]. 钢铁, 2019,54(10):72−79. [4] Li Liming, Feng Yunli, Yang Lina. Thermodynamic calculation of Ti-containing second phase in Ti microalloyed high strength steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019,40(1):118−122. (李立铭, 冯运莉, 杨丽娜. 钛微合金化高强钢含Ti第二相的热力学计算[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2019,40(1):118−122. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2019.01.021 [5] Huo Xiangdong, Xia Jinian, Li Liejun, et al. Research and development of titanium microalloyed high strength steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(4):105−112. (霍向东, 夏继年, 李烈军, 等. 钛微合金化高强钢的研究与发展[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(4):105−112. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.04.019 [6] Huo Xiangdong, Hou Liang, Li Liejun, et al. Recrystallization of titanium micro-alloyed high strength steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2017,38(4):119−125. (霍向东, 侯亮, 李烈军, 等. 钛微合金化高强钢的再结晶规律[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2017,38(4):119−125. [7] Tian Xing, Zhu Guoming, Kang Yonglin, et al. Precipitation behavior of Ti-microalloyed high-strength steel by CSP process[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2015,(1):42−49. (田星, 朱国明, 康永林, 等. CSP流程钛微合金化高强钢的第二相粒子析出行为[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2015,(1):42−49. [8] Zheng Wan, Qu Yong, Fu Xuehao, et al. Inclusion precipitation behaviors in Ti-containing high strength steel[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2017,40(3):161−166. (郑万, 瞿勇, 付学好, 等. 含钛高强钢中夹杂物析出行为研究[J]. 武汉科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2017,40(3):161−166. [9] Wu Jingrong. Discussion on phase transformation of high strength trace-Ti alloy steel in continuous cooling process[J]. Foundry Technology, 2016,37(3):427−429. (吴京戎. 连续冷却过程中高强度建筑用微钛合金钢相变问题探讨[J]. 铸造技术, 2016,37(3):427−429. -




 下载:
下载: