Molten salt assisted preparation of TiB2 powder from Ti-Si-Fe and B
-
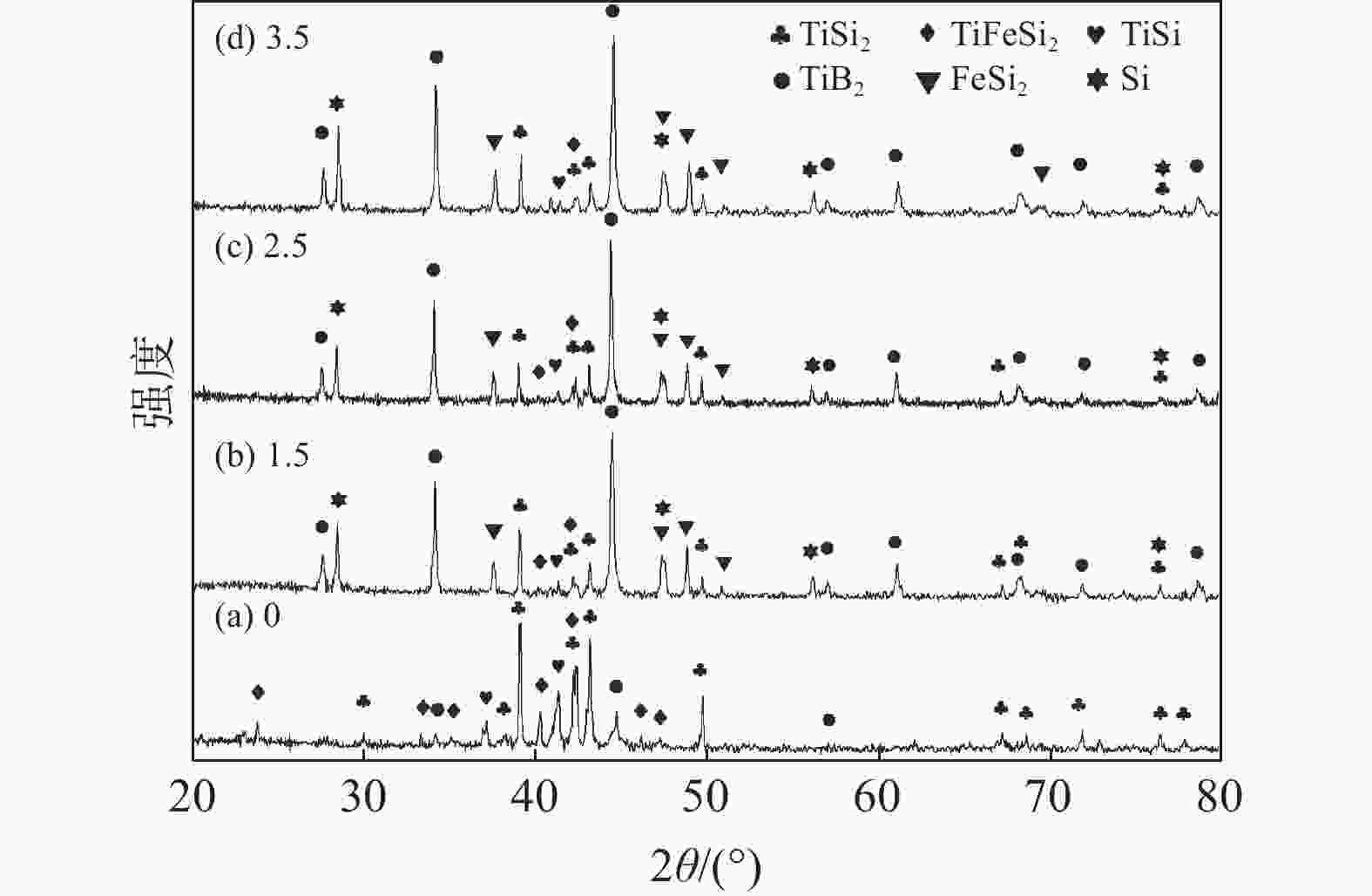
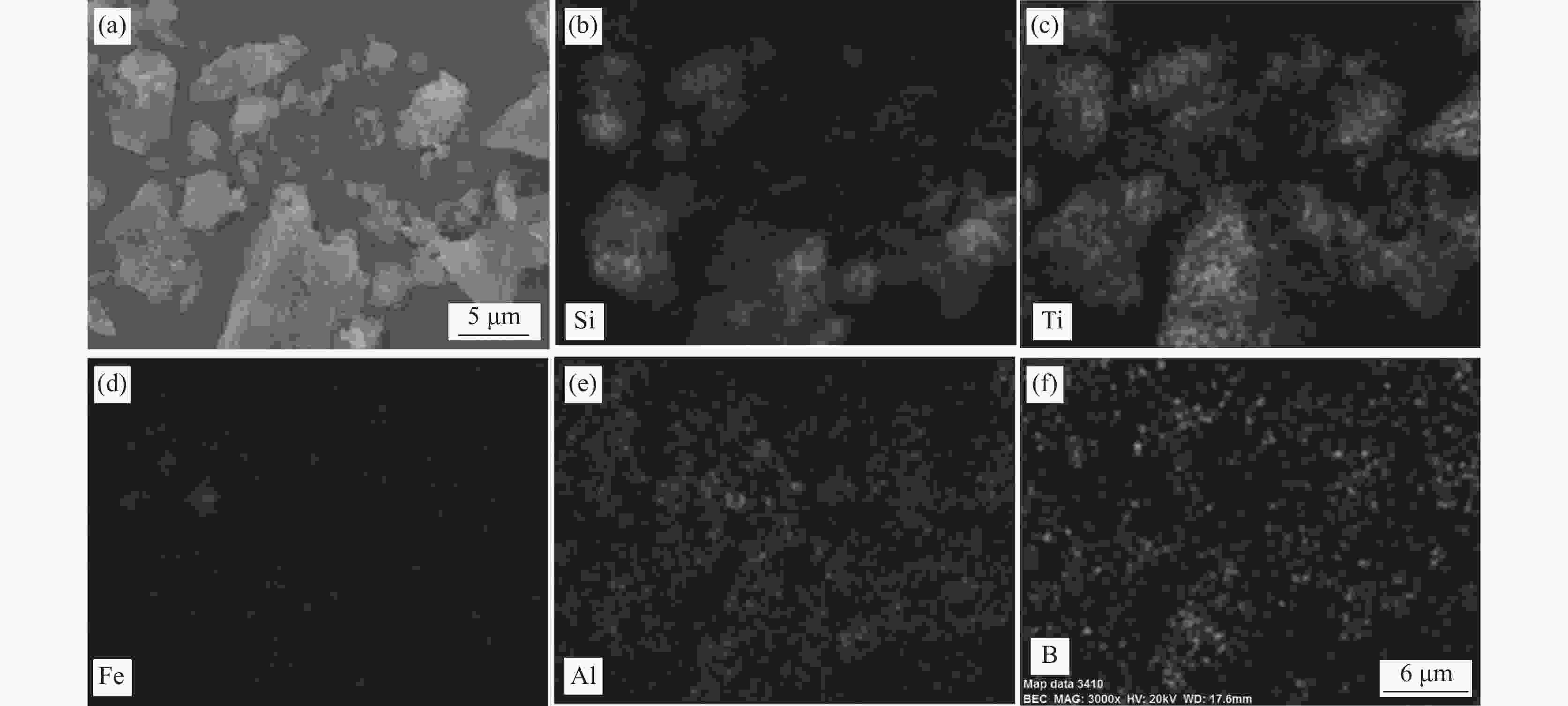
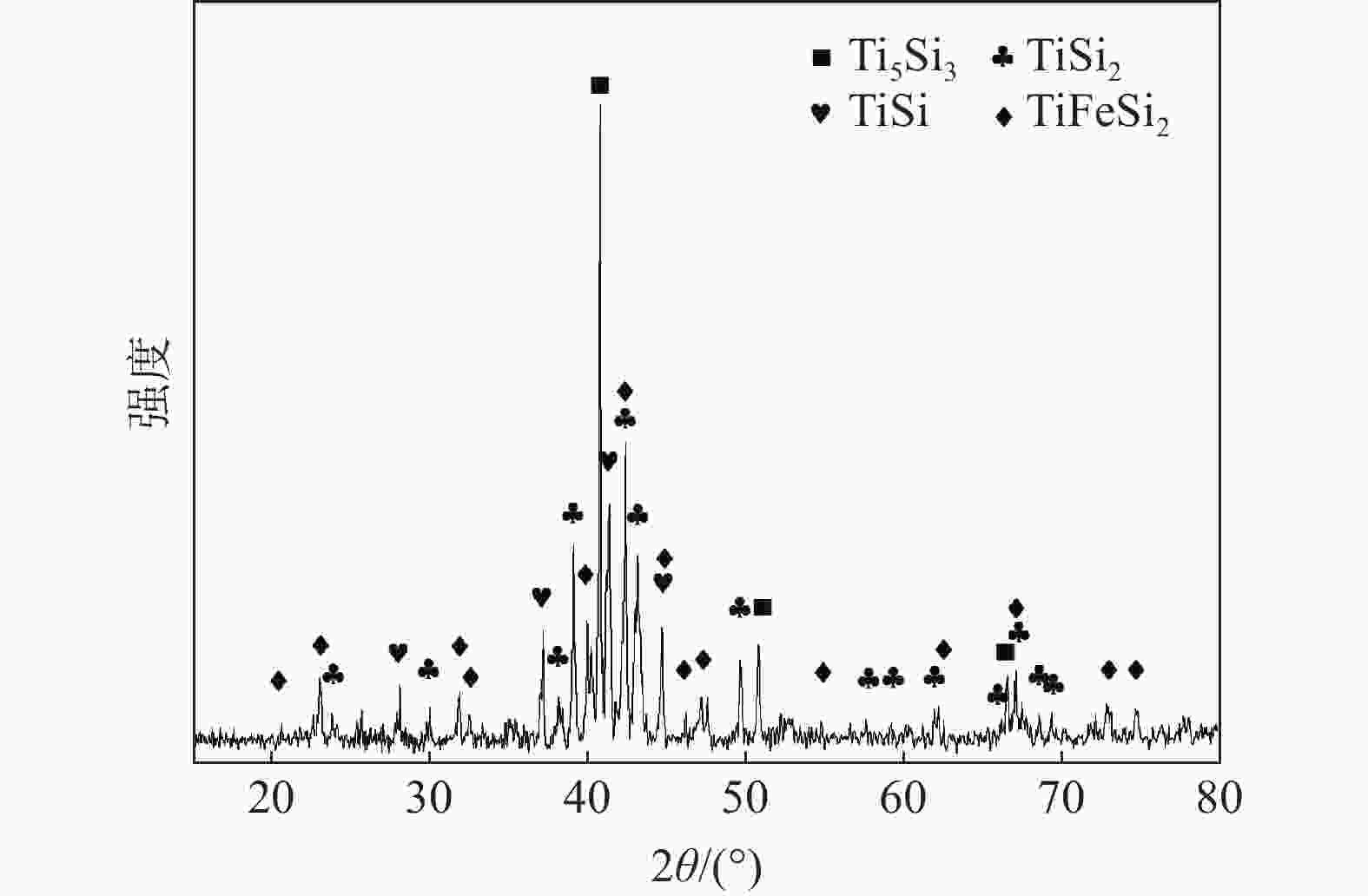
摘要: 以从高钛型高炉渣中提取的Ti-Si-Fe合金和无定形硼粉为原料,在NaCl-KCl熔盐中合成了TiB2粉体,研究了反应温度、保温时间、熔盐量、B/Ti摩尔比对反应进程的影响。结果表明:提高反应温度或延长保温时间均能促进反应进行,在850 ℃时开始有TiB2生成,1100 ℃时反应完全。熔盐有促进反应过程的作用。元素分布表明,含Fe的颗粒同时含Si,这与产物FeSi2相对应;大多数颗粒同时含有Si、Ti、B,说明在这些颗粒中产物TiB2和Si是伴生在一起的;少数颗粒只含有Ti、B,对应产物TiB2。产物颗粒形貌有两种,一种颗粒表面呈龟裂状,有裂缝或微米级孔洞与颗粒内部相连,这种颗粒同时含有TiB2、Si或FeSi2;另一种颗粒由片状TiB2组成。Ti-Si-Fe合金与B在熔盐中的反应机制为:在熔盐促进作用下,含钛物中的Ti与B反应生成TiB2,释放出Si及FeSi2,大部分TiB2以Si、FeSi2为骨架形核并长大,从而维持了颗粒原有形貌,少量TiB2在熔盐中形核并长大形成片状TiB2的聚集体。合金相与B反应完全的先后顺序依次为:Ti5Si3、TiSi、TiFeSi2和TiSi2。
-
关键词:
- 二硼化钛 /
- 熔盐法 /
- Ti-Si-Fe合金 /
- B粉 /
- 高钛型高炉渣
Abstract: TiB2 powders were synthesized in NaCl-KCl molten salt by amorphous boron and Ti-Si-Fe alloy extracted from high titanium blast furnace slag. The effects of reaction temperature, holding time, molten salt amount and mole ratio of B to Ti on the reaction process were investigated. The results show that increasing the reaction temperature or extending the holding time can promote the reaction process. TiB2 begins to form at 850 ℃ and the reaction completes at 1 100 ℃. Molten salt can facilitate the reaction process. The distribution of elements shows that the particles containing Fe also contain Si, corresponding to the product FeSi2. Most of the particles contain Si, Ti and B at the same time, indicating that TiB2 and Si are associated in these particles. A few particles contain only Ti and B, corresponding to TiB2. There are two kinds of particle morphology of the product. One kind of particle presents cracking appearance with cracks or micron holes connected to the interior, which contains TiB2, Si or FeSi2. The other particle is composed of flake TiB2. The reaction mechanism of Ti-Si-Fe alloy with B in molten salt is described below. First of all, titanium reacts with B to form TiB2 , then Si and FeSi2 are released. Most TiB2 nucleate and grow with Si and FeSi2 as the skeleton which maintain the original morphology of Ti-Si-Fe particles. A small amount of TiB2 nucleate and grow in molten salt to form flake TiB2 aggregates. The sequence of reaction between alloy phase and B is Ti5Si3, TiSi, TiFeSi2 and TiSi2.-
Key words:
- titanium diboride /
- molten salt method /
- Ti-Si-Fe alloy /
- B powder /
- high titanium blast furnace slag
-
表 1 Ti-Si-Fe合金粉的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of Ti-Si-Fe alloy powder
% Ti Si Fe Al 其他 43.80 41.26 10.55 3.1 1.29 表 2 试验参数
Table 2. Experimental parameters
试验目的 反应温度/℃ 保温时间/h B/Ti摩尔比 熔盐/反应物
质量比考察温度对反应的影响 800、850、950、1000、1050、1100 4.0 2.1 2.5 考察保温时间对反应的影响 950、1100 1.0、2.5、
4.0、5.52.1 2.5 考察熔盐/反应物
质量比对反应的影响950、1100 1.0、4.0 2.1 0、1.5、2.5、3.5 考察B/Ti摩尔比
对反应的影响1100 4.0 2.0、2.1、2.2、2.3 2.5 -
[1] Ma Junwei, Sui Zhitong, Chen Bingchen. The comprehensive utilization of the tirannium-containing blast slag of Panzhihua Iron & Steel Co.[J]. Metal Mine, 1999,10:42−45. (马俊伟, 隋智通, 陈炳辰. 攀钢含钛高炉渣的综合利用[J]. 金属矿山, 1999,10:42−45. [2] Xu Ying, Li Dandan, Yang Shanshan, et al. Research progress of comprehensive utilization of Ti-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021,(1):23−31. (许莹, 李单单, 杨姗姗, 等. 含钛高炉渣综合利用研究进展[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021,(1):23−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.01.004 [3] Peng Yi. Development of technologies for recovering titanium from pangang BF slag[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2005,22(3):44−49. (彭毅. 攀钢高炉渣提钛技术进展[J]. 钛工业进展, 2005,22(3):44−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2005.03.012 [4] 柯昌明, 李楠. 利用含钛炉渣制备钛及钛合金的方法: 中国, ZL200510019664.3[P]. 2005-10-26.Ke Changming, Li Nan. Method of preparing titanium and titanium alloy using titanium containing furnace clinker: China, ZL200510019664.3[P]. 2005-10-26. [5] 柯昌明, 韩兵强, 李楠. 一种铝酸盐水泥及其制备方法: 中国, ZL200910060792.0[P]. 2009-02-19.Ke Changming, Han Bingqiang, Li Nan. Aluminate cement and preparation thereof: China, ZL200910060792.0[P]. 2009-02-19. [6] 柯昌明, 韩兵强, 李楠, 等. 一种铁铝酸盐水泥及其制备方法: 中国, ZL201010150254.3[P]. 2010-04-14.Ke Changming, Han Bingqiang, Li Nan, et al. Aluminoferriate cement and preparation method thereof: China, ZL201010150254.3[P]. 2010-04-14. [7] 柯昌明, 吴海杰, 韩兵强, 等. 一种钒钛硅铁合金的制备方法: 中国, ZL201410132790.9[P]. 2014-02-03.Ke Changming, Wu Haijie, Han Bingqiang, et al. Preparation method for vanadium-titanium-silicon-iron alloy: China, ZL201410132790.9[P]. 2014-02-03. [8] Han Bingqing, Wang Peng, Ke Changming, et al. Hydration behavior of spinel containing high alumina cement from high titania blast furnace slag[J]. Cement & Concrete Research, 2016,79:257−264. [9] 柯昌明, 刘学新, 韩兵强, 等. 高钛型高炉渣环境友好资源化高效综合利用研究[C]//第十一届中国钢铁年会论文集. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2017: 1115−1123.Ke Changming, Liu Xuexin, Han Bingqiang, et al. Eco-efficient titanium-bearing blast furnace slag recycling[C]//Proceedings of the 11th CSM Steel Congress. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2017: 1115−1123. [10] Wang Jingran, Ke Changming, Zhang Jinhua. Effect of Ti-bearing blast furnace slag on hydration properties of portland cement[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2020,39(5):1511−1516. (王景然, 柯昌明, 张锦化. 提钛尾渣对硅酸盐水泥水化性能的影响[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2020,39(5):1511−1516. [11] 柯昌明, 李雪, 韩兵强. 以Ti-Si-Fe合金为原料的TiC材料及其制备方法: 中国, 201110089361.4[P]. 2011-04-11.Ke Changming, Li Xue, Han Bingqiang. TiC material with Ti-Si-Fe alloy as raw material and preparation method : China, 201110089361.4[P]. 2011-04-11. [12] Zhang Jinhua, Xiong Si, Ke Changming, et al. Synthesis and reaction mechanism of Ti3SiC2 by molten salt method from Ti-Si-Fe alloy[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2017,768:159−166. [13] Ma Li, Yu Jincheng, Guo Xue, et al. Preparation and sintering of ultrafine TiB2 powders[J]. Ceramics International, 2018,44:4491−4495. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.009 [14] Karthiselva N S, Murty B S, Bakshi Srinivasa R. Low temperature synthesis of dense TiB2 compacts by reaction spark plasma sintering[J]. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2015,48:201−210. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2014.09.015 [15] Rabiezadeh A, Hadian A M, Ataie A. Synthesis and sintering of TiB2 nanoparticles[J]. Ceramics International, 2014,40(10):15775−15782. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.07.102 [16] Tetsushi Matsuda. Synthesis and sintering of TiC-TiB2 composite powders[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2020,25:101457. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101457 [17] Marina Vlasova, Mykola Kakazey, Pedro Antonio Marquez Aguilar, et al. Processes connected with local laser heating of TiB2 armor ceramics[J]. Science of Sintering, 2019,51(2):125−134. doi: 10.2298/SOS1902125V [18] Alvar F Sajedi, Heydari M, Kazemzadeh A, et al. Al2O3-TiB2 nanocomposite coating deposition on titanium by air plasma spraying[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2018,5(7, Part 3):15739−15743. [19] Jerzy Smolik, Joanna Kacprzyn´ska-Gołacka, Sylwia Sowa. The analysis of resistance to brittle cracking of tungsten doped TiB2 coatings obtained by magnetron sputtering[J]. Coatings, 2020,10(9):1−10. [20] Huang Youguo, Wang Yi, Zhang Xiaohui, et al. Preparation of wettable TiB2-TiB/Ti cathode by electrolytic boronizing for aluminum electrolytic[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019,26(10):2681−2687. doi: 10.1007/s11771-019-4205-5 [21] Liu Yue, Huang Chuanzhen, Liu Hanlian, et al. The influence of TiB2 content on high temperature flexural strength and reliability of the developed titanium carbonitride based ceramic tool material[J]. Ceramics International, 2020,46(8):10356−10361. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.01.032 [22] Qin Bo, Zhou Houming, Zeng Guozhang, et al. Mechanical properties and friction and wear performance of TiB2/TiN/WC composite ceramic tool materials[J]. China Ceramics, 2019,55(5):7−13. (覃波, 周后明, 曾国章, 等. TiB2/TiN/WC复合陶瓷刀具材料力学性能及其摩擦磨损性能[J]. 中国陶瓷, 2019,55(5):7−13. [23] Fan Xiaowen, Wang Guozhen, Lu Fengxiang. Study on fabrication and tribological properties of TiB2-based cutting tools[J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering, 2019,39(6):62−68. (范晓文, 王国珍, 卢凤祥. TiB2基切削刀具的制备和摩擦学性能研究[J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程, 2019,39(6):62−68. [24] Wang Han, Zhang Haiming, Cui Zhenshan, et al. Compressive response and microstructural evolution of in-situ TiB2 particle-reinforced 7075 aluminum matrix composite[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2021,31(5):1235−1248. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65574-7 [25] Yu Changfu, Zhang Zhuhui, Yang Lu, et al. Effect of TiB2 reinforced particle content on properties of 6061 aluminum matrix composites[J]. Nonferrous Metals Processing, 2020,49(2):15−18. (于长富, 张祝珲, 杨路, 等. TiB2增强颗粒含量对6061铝基复合材料性能的影响[J]. 有色金属加工, 2020,49(2):15−18. [26] Lei Zhenglong, Bi Jiang, Chen Yanbin, et al. Effect of TiB2 content on microstructural features and hardness of TiB2/AA7075 composites manufactured by LMD[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020,53:283−292. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.02.036 [27] Radev D D, Marinov M. Properties of titanium and zirconium diborides obtained by self-propagated high-temperature synthesis[J]. J. Alloy. Compd., 1996,244:48−51. doi: 10.1016/S0925-8388(96)02406-1 [28] Oghenevweta J E, Wexler D, Calka A. Sequence of phase evolution during mechanically induced self-propagating reaction synthesis of TiB and TiB2 via magnetically controlled ball milling of titanium and boron powders[J]. J. Alloy. Compd., 2017,701:380−391. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.01.016 [29] Tang Wenming, Zheng Zhixiang, Wu Yuchen, et al. Synthesis of TiB2 nanocrystalline powder by mechanical alloying[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006,16(3):613−617. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(06)60108-8 [30] Sahar Nekahi, Mohammad Vajdi, Farhad Sadegh Moghanlou, et al. TiB2–SiC-based ceramics as alternative efficient micro heat exchangers[J]. Ceramics International, 2019,45(15):19060−19067. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.06.150 [31] Zhao Guolong, Huang Chuanzhen, He Ning, et al. Microstructural development and mechanical properties of reactive hot pressed nickel-aided TiB2-SiC ceramics[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2016,61:13−21. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2016.08.001 [32] Barin I, Platzki G. Thermochemical data of pure substances[M]. 3rd ed. VCH, Weinheim, 1995. -




 下载:
下载: