Preparation of graphene/TiO2 composites and study on degradation of methyl blue
-
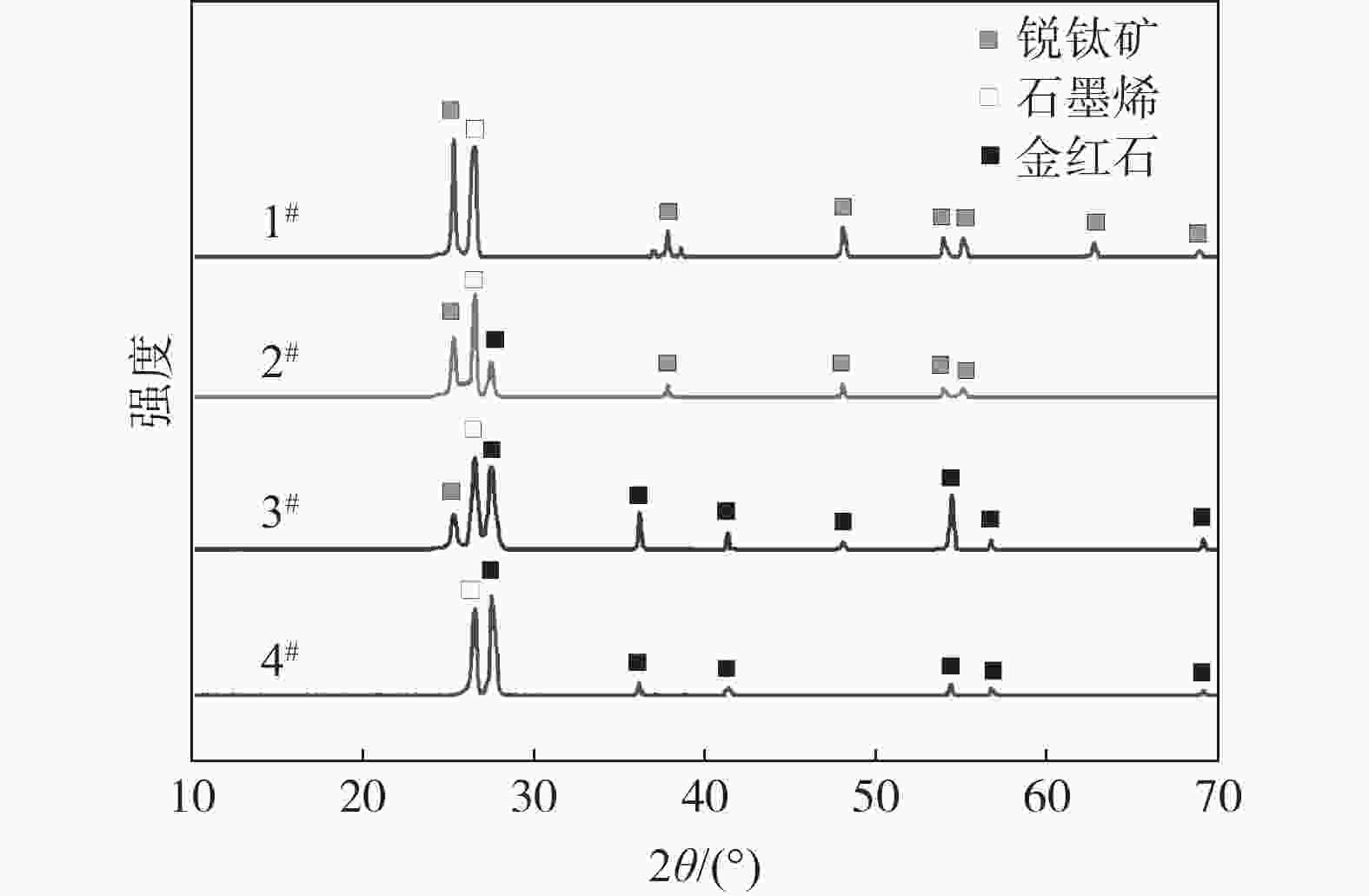
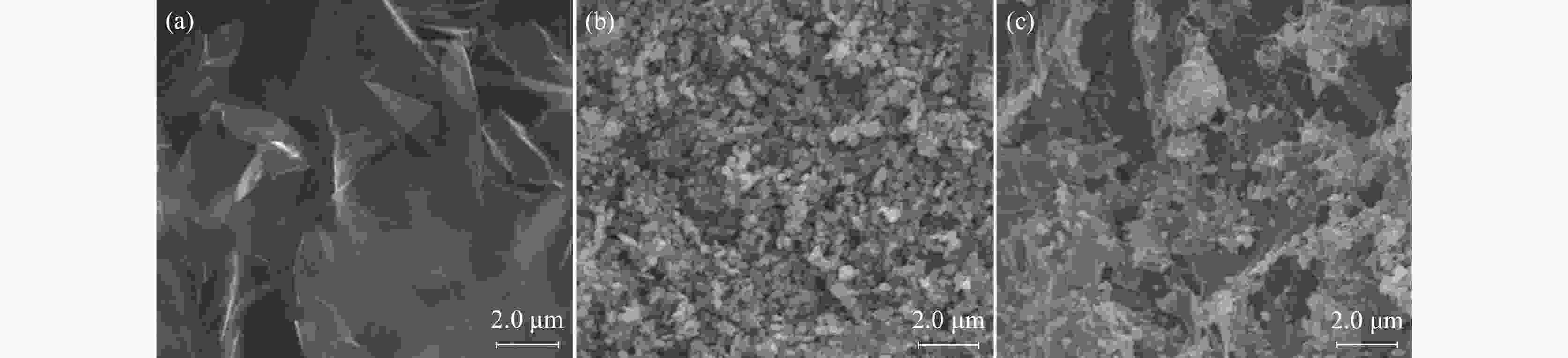
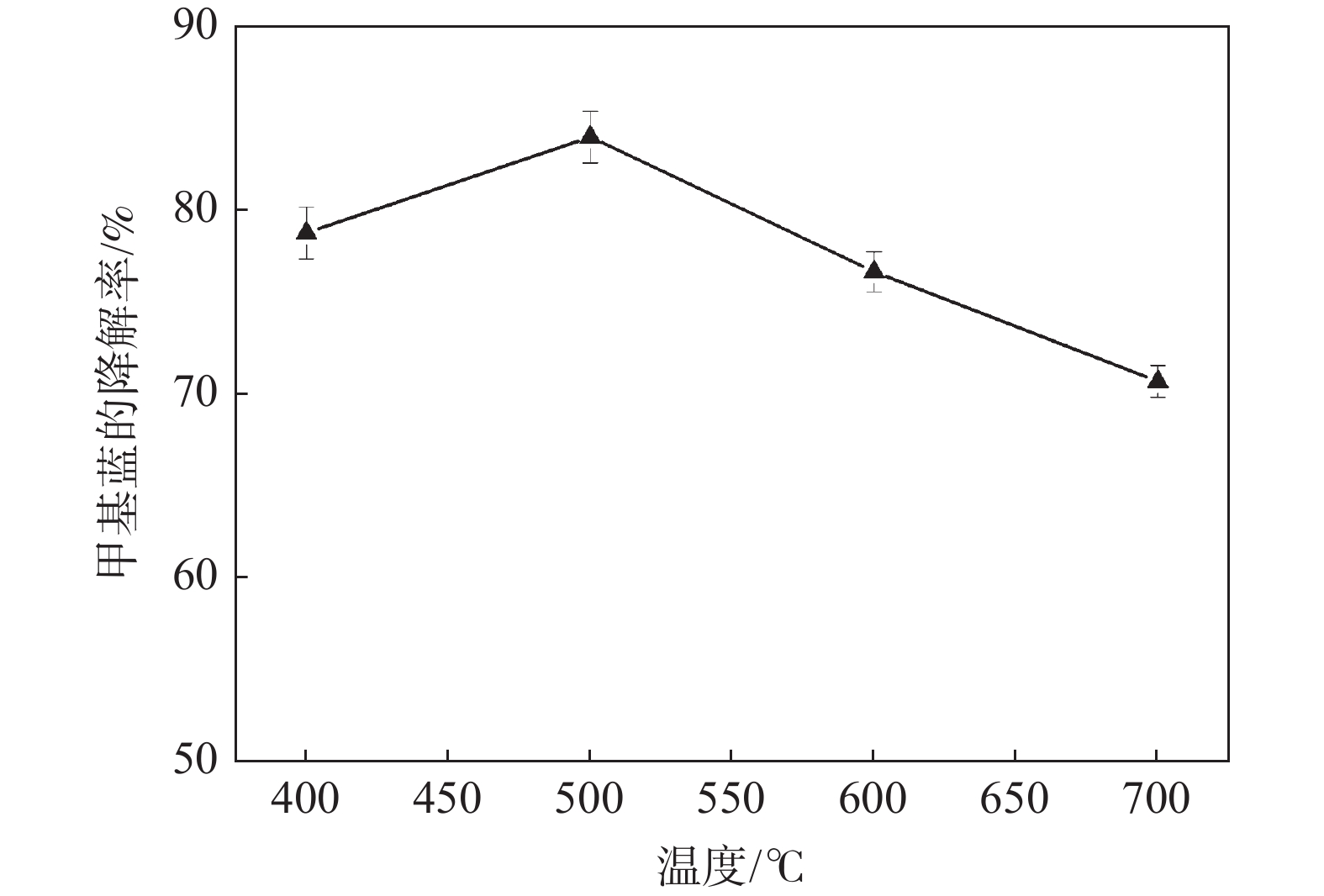
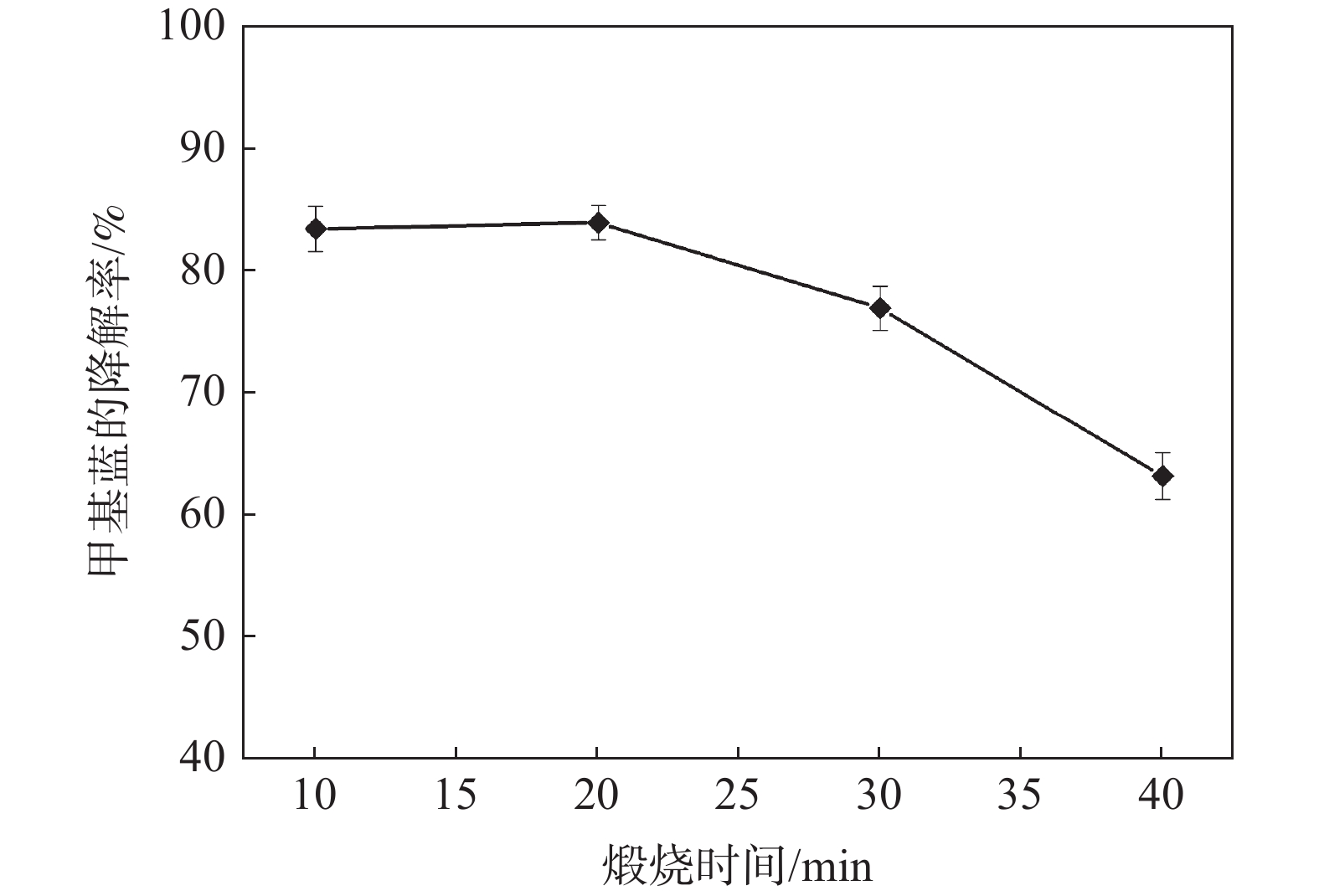
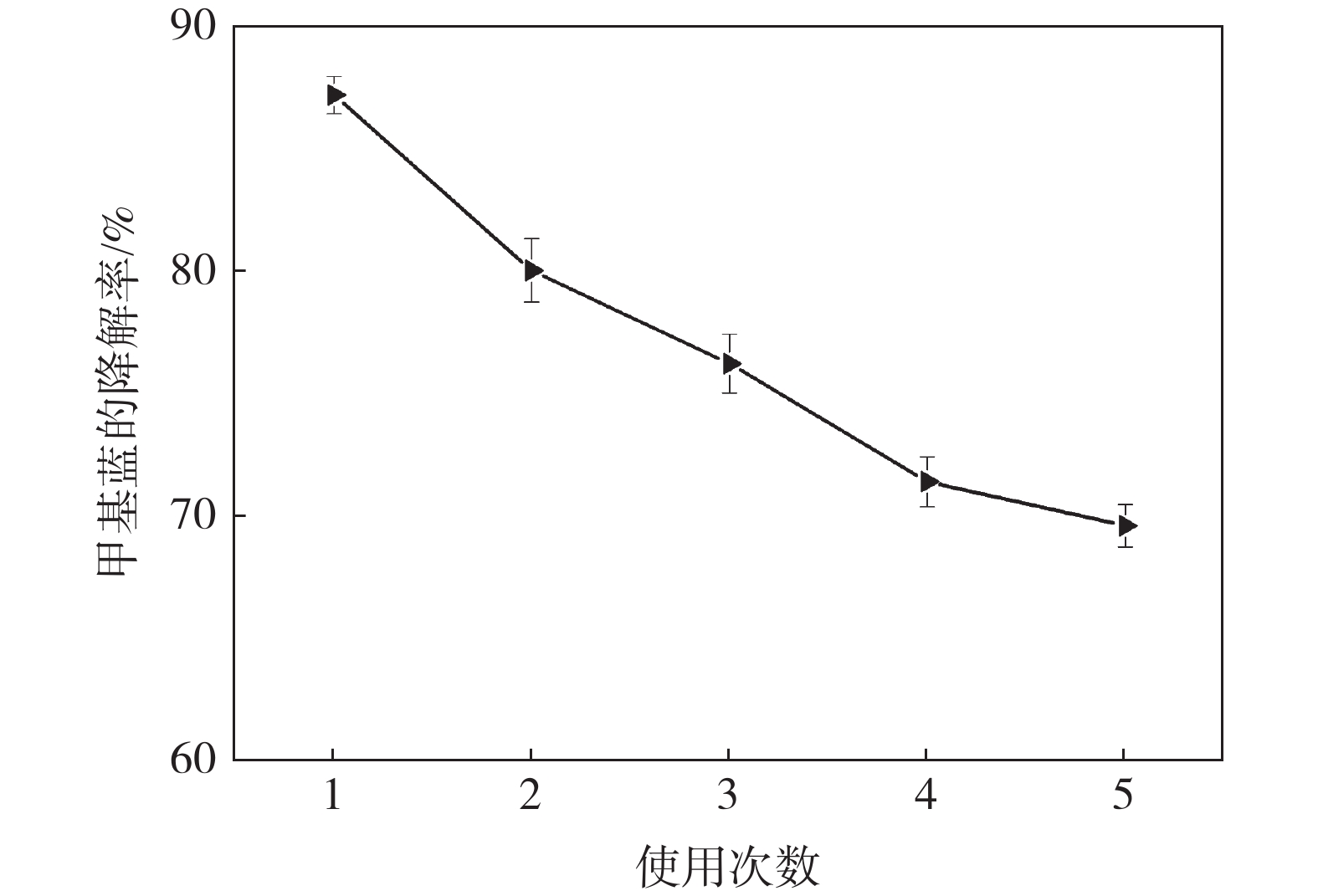
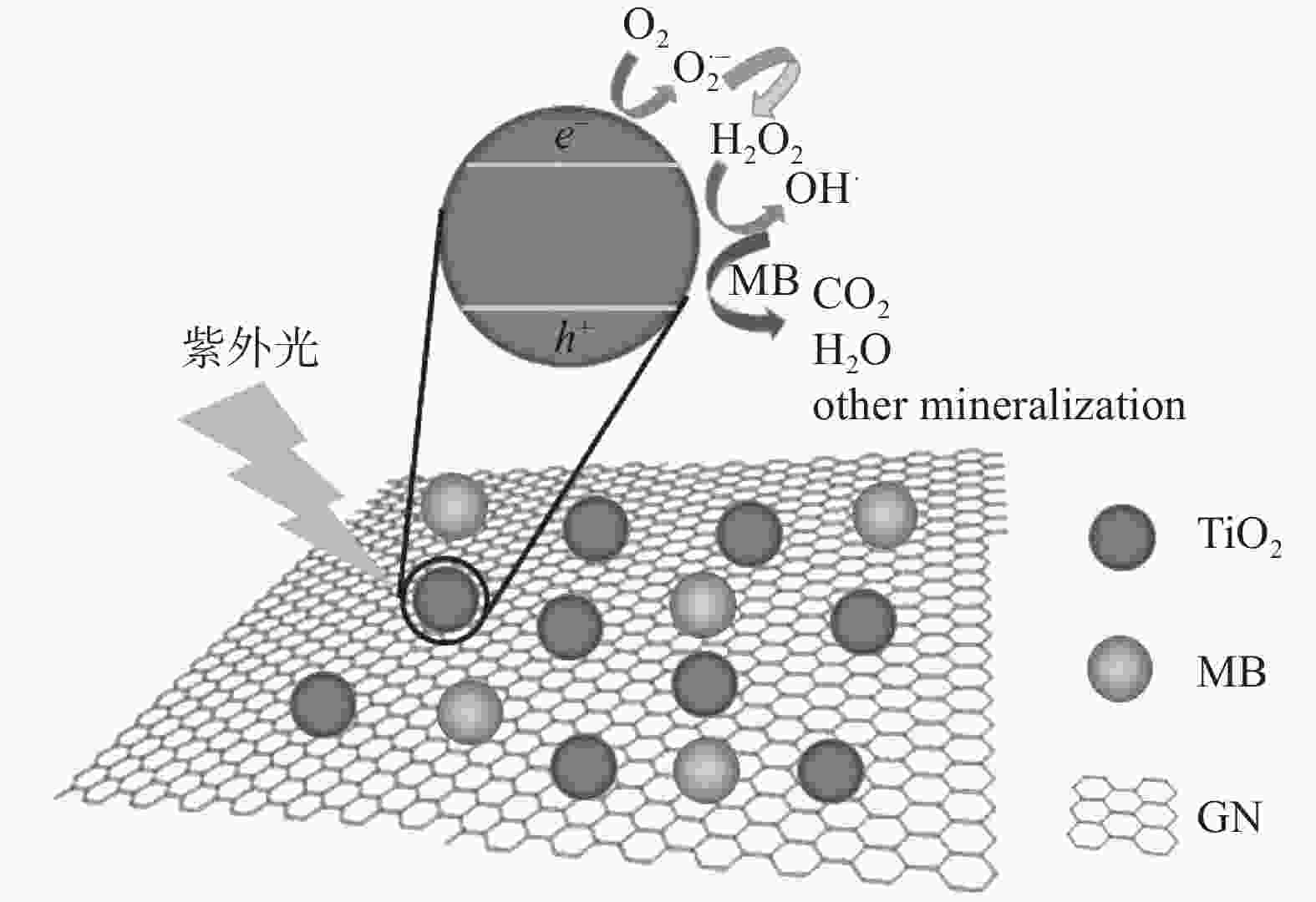
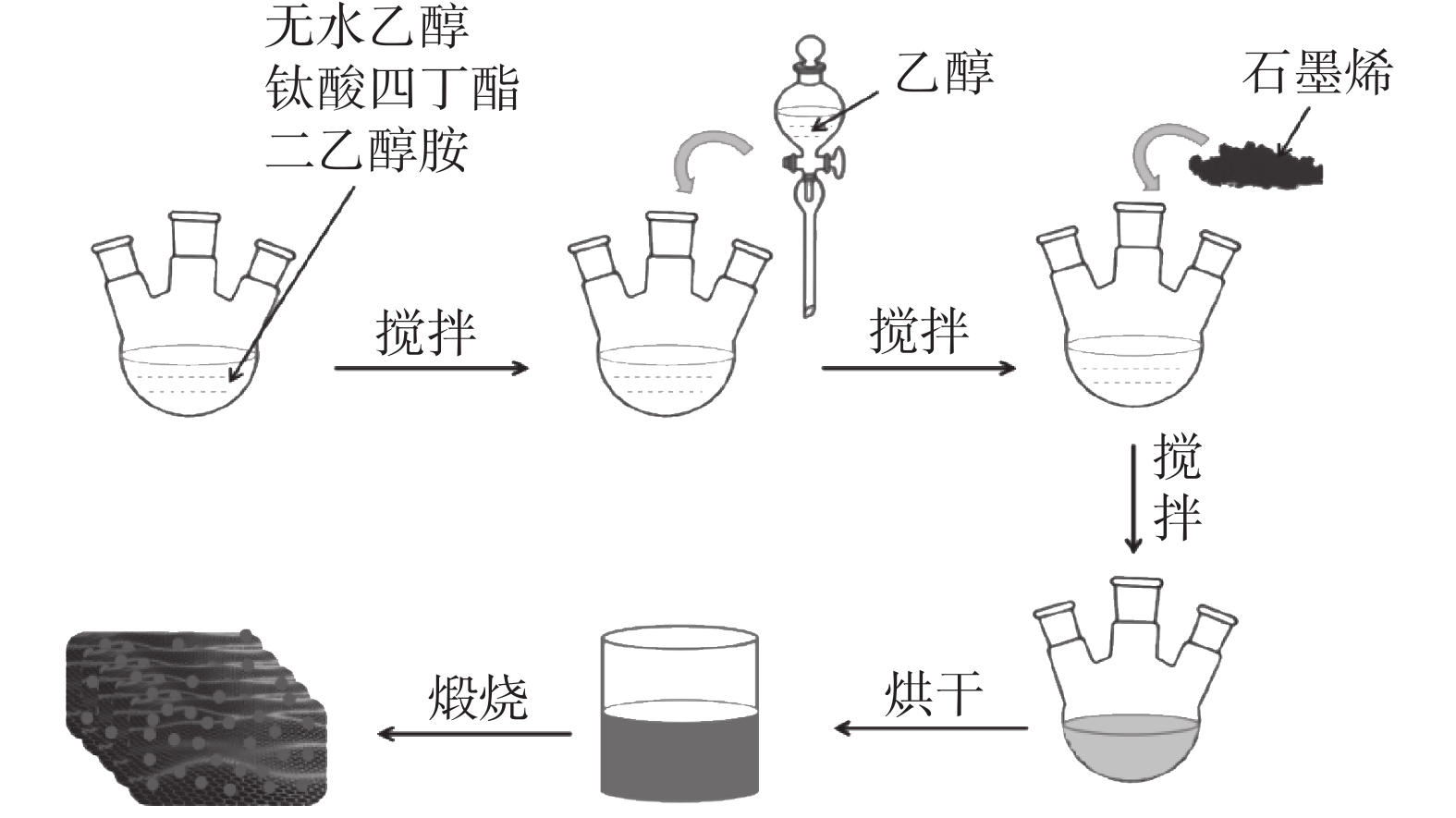
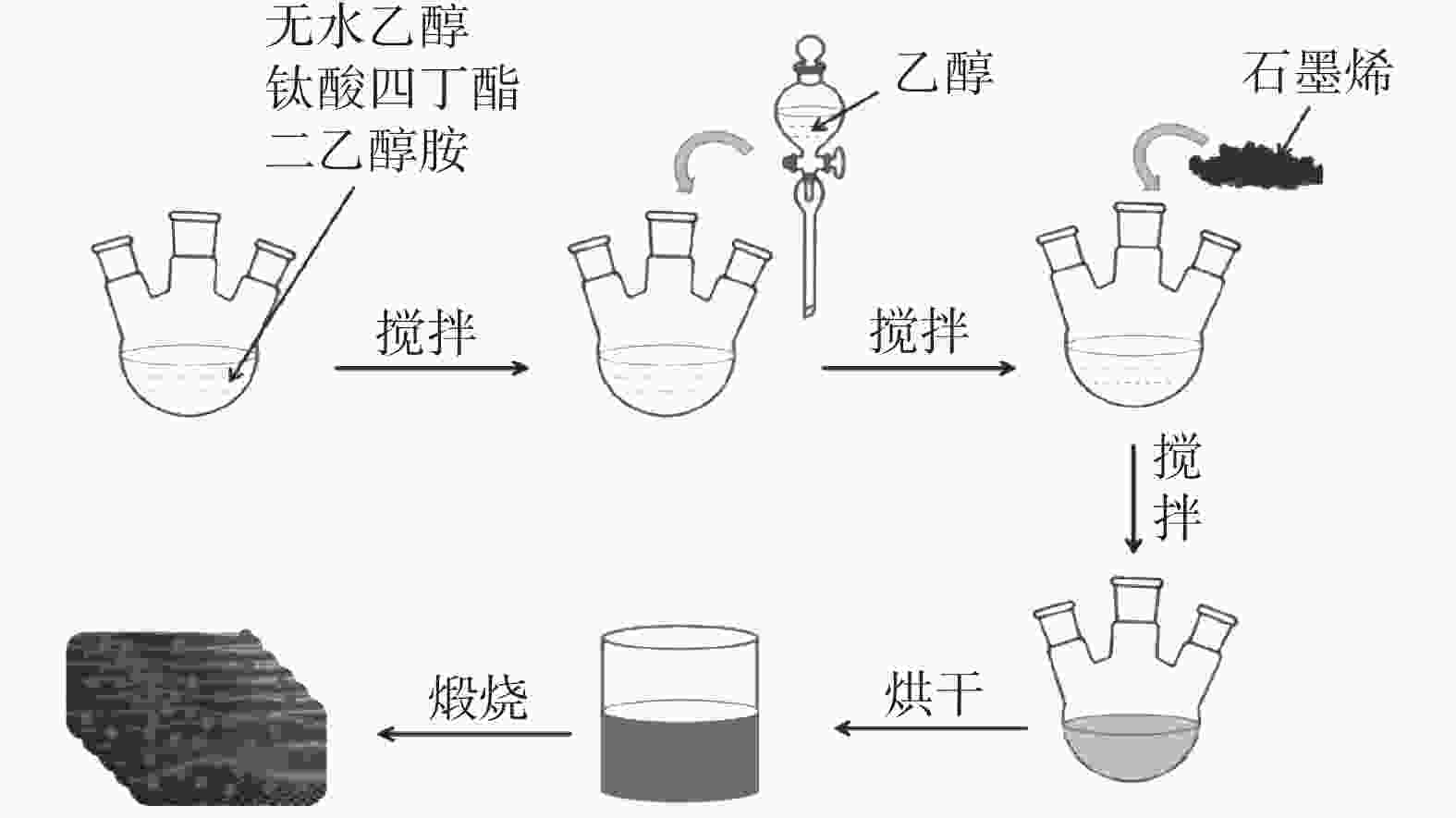
摘要: 光催化降解已成为污水处理领域发展最快的方法。为改善TiO2的光催化性能,采用溶胶-凝胶法制备石墨烯(GN)/TiO2复合材料,利用XRD、SEM对样品的微观结构进行表征,研究制备过程中煅烧温度、煅烧时间以及石墨烯含量对GN/TiO2复合材料光催化性能的影响。结果表明:所制备TiO2为球状形貌,粒径为70~200 nm,分布在石墨烯的片层和边缘。当煅烧温度为500 ℃,煅烧时间为20 min,石墨烯含量为5%时对甲基蓝(MB)的光催化降解率最高,为87.21%。此外,研究了GN/TiO2复合材料对甲基蓝光催化降解的重复利用率,并探讨了光催化机理,结果表明重复使用5次后,对甲基蓝的降解率降低了17.64个百分点。
-
关键词:
- 石墨烯/TiO2复合材料 /
- 溶胶-凝胶法 /
- 光催化 /
- 甲基蓝 /
- 降解率
Abstract: Photocatalytic degradation has become the fastest developing method in the field of wastewater treatment. GN/TiO2 composites were prepared by sol-gel method in order to improve the photocatalytic performance of TiO2 and the degradation effect of the composites on methyl blue was studied. The microstructure of the sample was characterized by XRD and SEM. The effects of calcination temperature, calcination time and the content of graphene on the photocatalytic performance of GN/TiO2 composites were investigated. The experimental results show that TiO2 is spherical with a size of 70~200 nm and distributing on the lamellar and edge of the graphene. When kept at 500 ℃ for 20 min and the concentration of graphene is 5%, the material has the best photocatalytic performance on the degradation rate of methyl blue with the value of 87.21%. Moreover, the reutilization rate and the mechanism of photocatalytic degradation of methyl blue by GN/TiO2 composites were studied, and the results show that the degradation rate of methyl blue is reduced by 17.64% after 5 times repeated.-
Key words:
- graphene/TiO2 composites /
- sol-gel method /
- photocatalytic /
- methylene blue /
- degradation rate
-
表 1 GN/TiO2复合材料的制备参数
Table 1. Process parameters of GN/TiO2 composite
序号 煅烧温度/℃ 煅烧时间/min 石墨烯含量/% 1# 400 20 3 2# 500 20 3 3# 600 20 3 4# 700 20 3 5# 500 10 3 6# 500 20 3 7# 500 30 3 8# 500 40 3 9# 500 20 0 10# 500 20 1 11# 500 20 3 12# 500 20 5 13# 500 20 7 14# 500 20 9 -
[1] Wang Min, Xia Lixin, Lin Qingxian. Hollow 3 D rGO/P-HC/TiO2 for photocatalytic degradation of ammonia nitrogen[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(6):45−51. (王敏, 夏立新, 林清娴. 中空三维rGO/P-HC/TiO2复合材料光催化降解氨氮[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(6):45−51. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.06.010 [2] You Jia, Jiang Huan, Han Yanlin, et al. Study on preparation of CdS/TiO2 composite by microemulsion and its photocatalytic properties[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(1):24−31. (尤佳, 江环, 韩炎霖, 等. 微乳液法制备CdS/TiO2复合材料及光催化性能研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(1):24−31. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.01.005 [3] Assadi A A, Loganathan S, Tri P N, et al. Pilot scale degradation of mono and multi volatile organic compounds by surface discharge plasma/TiO2 reactor: investigation of competition and synergism[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2018,357:305−313. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.06.007 [4] Xu H, Han F, Xia C, et al. Correction to: wafer-scale fabrication of sub-10 nm TiO2-Ga2O3 n-p Hetero junctions with efficient photocatalytic activity by atomic layer deposition[J]. Nanoscale Res Lett, 2019,14:173. doi: 10.1186/s11671-019-3028-5 [5] Andronic L, Enesca A, Cazan C, et al. TiO2-active carbon composites for wastewater photocatalysis[J]. J Sol-Gel Sci Techn, 2014,71(3):396−405. doi: 10.1007/s10971-014-3393-6 [6] El-Sayed B A, Mohamed W A, Galal H R, et al. Photocatalytic study of some synthesized MWCNTs/TiO2 nanocomposites used in the treatment of industrial hazard materials[J]. Egypt J Pet, 2019,28(2):247−252. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpe.2019.05.002 [7] Qi K, Selvaraj R, Fahdi T A, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of anatase-TiO2 nanoparticles by fullerene modification: A theoretical and experimental study[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2016,387:750−758. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.06.134 [8] Khalaghi M, Atapour M, Momeni M M, et al. Photocatalytic activity and photo-electrochemical performance of trimetallic (Cu-Ni-Zn)/TiO2 coating on AISI 316 L stainless steel for water treatment[J]. Applied Physics A, 2020,126:352. doi: 10.1007/s00339-020-03550-1 [9] Sheshmani S, Nayebi M. Modification of TiO2 with graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide; enhancing photocatalytic activity of TiO2 for removal of remazol Black B[J]. Polym Compos, 2019,40(1):210−216. doi: 10.1002/pc.24630 [10] Yu Lan, Wang Juanjuan, Wang Zhangzhi, et al. Preparation of TiO2 microspheres/zeolite and its degradation on ofloxacin[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2021,41(1):88−92. (俞岚, 王娟娟, 王长智, 等. 微球TiO2/沸石催化剂的制备及其对氟氧沙星的降解[J]. 工业水处理, 2021,41(1):88−92. [11] Miranda S M, Romanos G E, Likodimos V, et al. Pore structure, interface properties and photocatalytic efficiency of hydration/dehydration derived TiO2/CNT composites[J]. Appl Catal B, 2014,147:65−81. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.08.013 [12] Katsumata K I, Matsushita N, Okada K. Preparation of TiO2-fullerene composites and their photocatalytic activity under visible light[J]. Int J Photoenergy, 2011,2012:1302−1312. [13] Ibrahim Q, Akbarzadeh R. A photocatalytic TiO2/graphene bilayer membrane design for water desalination: a molecular dynamic simulation[J]. J Mol Model, 2020,26:165. doi: 10.1007/s00894-020-04422-4 [14] Liu Y, Zhang D. Effects of structural differences of graphene and the preparation strategies on the photocatalytic activity of graphene–TiO2 composite film[J]. J Mater Sci Mater Electron, 2017,28:4965−4973. doi: 10.1007/s10854-016-6150-5 [15] Thaweechai T, Siriaksoontorn W, Poo-arporn Y, et al. Transparent graphene quantum dot/amorphous TiO2 nanocomposite sol as homogeneous-like photocatalyst[J]. J Nanopart Res, 2021,23:225. doi: 10.1007/s11051-021-05338-7 [16] Gao Wei, Zhao Zhifeng, Zhou Changhai. Preparation and electrochemical properties of polypyrrole/graphene composites[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang University of Science and Technology, 2018,28(2):204−208. (高微, 赵志凤, 周长海. 聚吡咯/石墨烯复合材料的制备及电化学性能[J]. 黑龙江科技大学学报, 2018,28(2):204−208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-7262.2018.02.016 [17] Sun Aihua, Guo Pengju, Li Yong, et al. Preparation of titania nano-particles by self-born seed-hydrolysis of TiCl4[J]. China Powder Science and Technology, 2008,14(6):44−48. (孙爱华, 郭鹏举, 李勇, 等. TiCl4自生晶种水解法制备纳米二氧化钛[J]. 中国粉体技术, 2008,14(6):44−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5548.2008.06.012 [18] Huang Mianfeng, Zheng Zhixiang, Xu Guanqing, et al. Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity of exfoliated graphite supported titanium dioxide photocatalyst[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2008,38(3):325−329. (黄绵峰, 郑治祥, 徐光青, 等. 膨胀石墨负载纳米二氧化钛光催化剂的制备、表征与其光催化性能[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2008,38(3):325−329. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2008.03.012 [19] Zuo R, Du G, Zhang W, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue using TiO2 impregnated diatomite[J]. Adv Mater Sci Eng, 2014,2014:1−7. [20] Balarak D, Mengelizadeh N, Rajiv P, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin from aqueous solutions by titanium dioxide nanoparticles loaded on graphene oxide[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 2021,28:49743−49754. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-13525-1 -




 下载:
下载: