Study on phase and chemical composition of V-Ti sinter during softening, melting and dripping process
-
摘要: 钒钛磁铁精矿的入炉方式是攀钢优化高炉炉料结构的重要内容,对V和Ti在软熔滴落过程中的迁移以及Ti(C,N)的生成有重要影响。目前钒钛烧结矿是攀钢高炉的主要炉料,约一半的钒钛磁铁精矿通过烧结矿进入高炉。通过对钒钛烧结矿在软熔滴落过程中的物相组成和化学成分的变化规律进行研究发现,在烧结矿的软熔滴落过程中,Ti、V、Si、Mg、Al等元素逐渐从钛赤铁矿、钛磁铁矿、铁酸钙等物相迁移到渣相中,同时炉渣吸收焦炭的硫分和灰分。金属铁中Ti、Si、S和C的质量分数已达到甚至超过正常生产时的水平,V的质量分数虽远低于正常生产时的水平,但在金属铁中的收得率远高于Ti、Si、S。烧结矿炉渣冷却后形成的主要物相是黄长石,其次是钙钛矿和辉石。Ti和V主要赋存于钙钛矿中,其次是黄长石和辉石中。在软熔过程中,生成的碳氮化钛很少;在重熔滴落过程中,渣中碳氮化钛显著增加。Abstract: The charging mode of vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite concentrate is an important matter for optimizing the burden structure of blast furnace in Pangang, which also has an important influence on the migration of V and Ti in the process of softening and melting process and the formation of Ti(C,N). At present, vanadium-titanium sinter is the main burden of blast furnace in Pangang, and about half of vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite concentrate enters the blast furnace through sinter. Therefore, the change of phase and chemical composition of vanadium-titanium sinter in the process of softening and melting process was studied. In the softening and dripping process of sinter, Ti, V, Si, Mg, and Al gradually migrate from the phases of titanohematite, titanomagnetite, calcium ferrite to the slag phase, and the slag absorbs the sulfur and ash of coke. The mass fraction of Ti, Si, S and C in hot metal has reached or even exceeded that of normal production. Although the mass fraction of V is much lower than that in normal production, the yield in metallic iron is much higher than that of Ti, Si and S. The main phase of slag after cooling is melilite, followed by perovskite and pyroxene. Ti and V mainly exist in perovskite, followed by melilite and pyroxene. In the process of softening, little titanium carbonitride is produced. However, in the process of melting, the content of titanium carbonitride in slag increases significantly.
-
表 1 钒钛烧结矿的主要化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of vanadium-titanium sinter
化学成分/% RO TFe FeO CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 TiO2 V2O5 S 50.77 7.99 10.97 5.58 2.72 3.00 5.59 0.388 0.025 1.97 表 2 焦炭的化学成分
Table 2. Chemical compositions of coke
% Fcad Mt St Vdaf Ad K2O Na2O CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 Fe2O3 合计 85.88 0.23 0.63 1.09 0.08 0.10 0.49 7.24 0.13 3.73 1.03 12.80 表 3 烧结矿重熔后的渣铁质量
Table 3. Weight of slag and metallic iron after sinter remelting
g 未滴落炉渣 未滴落金属铁 滴落炉渣 滴落金属铁 合计 41.0 70.0 13.1 25.8 149.9 表 4 不同炉渣的化学成分
Table 4. Chemical compositions of different slags
样品名称 化学成分/% TFe FeO CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 TiO2 V2O5 S TiC TiN 软熔液泛渣 6.00 2.25 38.47 22.42 5.14 10.14 14.64 0.695 0.18 <0.1 <0.1 软熔未滴渣 4.25 3.09 29.72 15.83 8.56 8.14 15.31 0.701 0.14 <0.1 <0.1 软熔滴落渣 14.00 3.92 37.34 21.23 7.74 10.41 16.56 0.720 0.16 <0.1 <0.1 重熔未滴渣 11.75 3.41 30.52 21.23 7.91 8.79 13.45 0.232 0.53 1.13 0.34 重熔滴落渣 19.88 2.08 29.95 18.68 7.77 8.25 12.77 0.145 0.41 <0.1 0.247 表 5 主要造渣组份的相对质量分数
Table 5. Relative content of main slagging components in different slags
样品名称 相对质量分数/% R2 CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 TiO2 V2O5 S 软熔液泛渣 41.96 24.45 5.61 11.06 15.97 0.76 0.20 1.72 软熔未滴渣 37.91 20.19 10.92 10.38 19.53 0.89 0.18 1.88 软熔滴落渣 39.66 22.55 8.22 11.06 17.59 0.76 0.17 1.76 重熔未滴渣 36.92 25.68 9.57 10.63 16.27 0.28 0.64 1.44 重熔滴落渣 38.41 23.96 9.96 10.58 16.38 0.19 0.53 1.60 烧结矿渣相 38.80 19.74 9.62 10.61 19.77 1.37 0.09 1.97 表 6 不同金属铁的化学成分
Table 6. Chemical compositions of different metallic irons
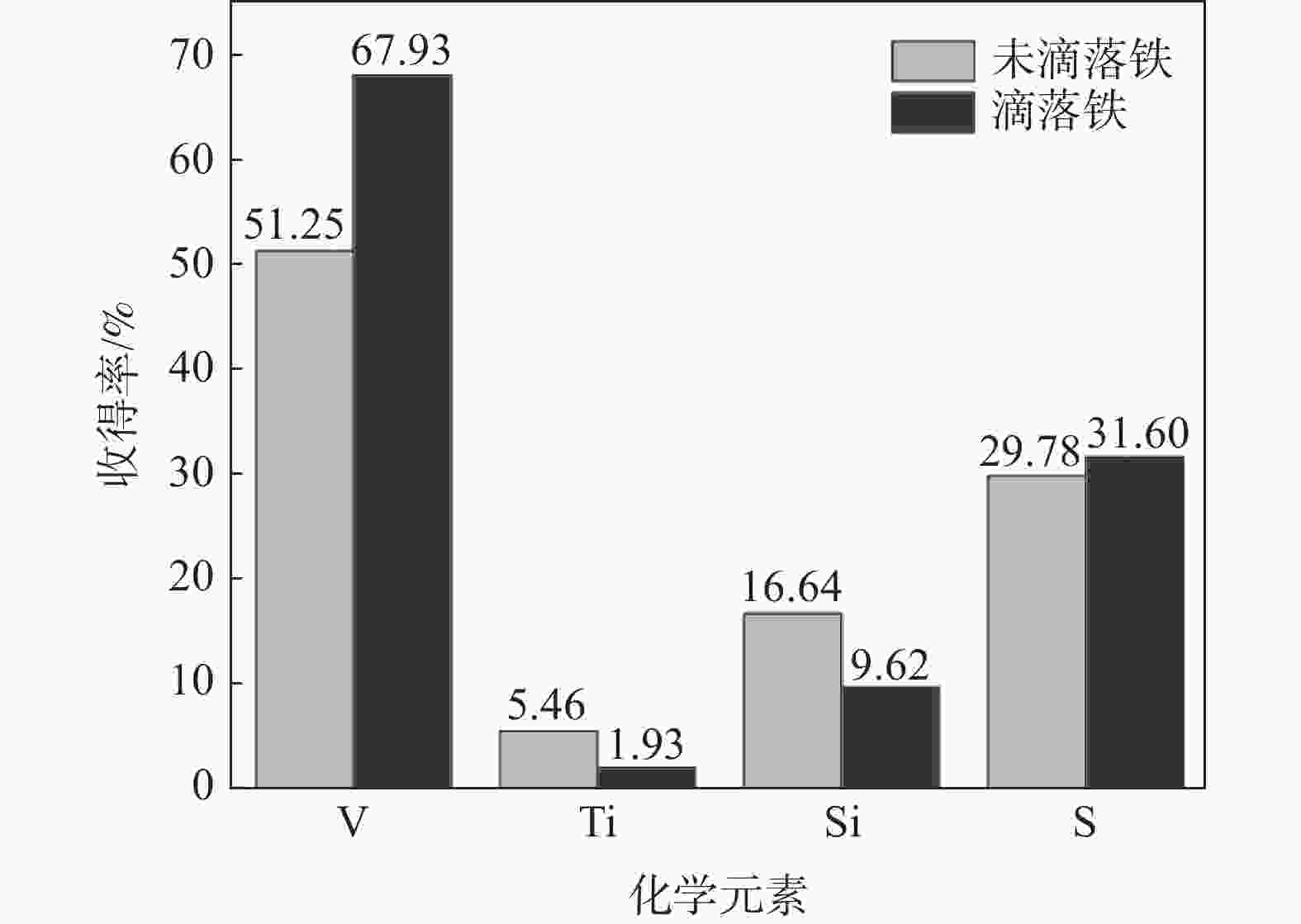
样品名称 化学成分/% C S V Ti Si 软熔未滴铁 4.83 0.055 0.102 0.114 0.135 软熔滴落铁 3.40 0.080 0.029 0.207 0.193 重熔未滴铁 4.53 0.125 0.076 0.259 1.100 重熔滴落铁 4.76 0.088 0.080 0.070 0.431 生产铁样 4.42 0.087 0.333 表 7 烧结矿软熔液泛渣的物相组成和元素分布
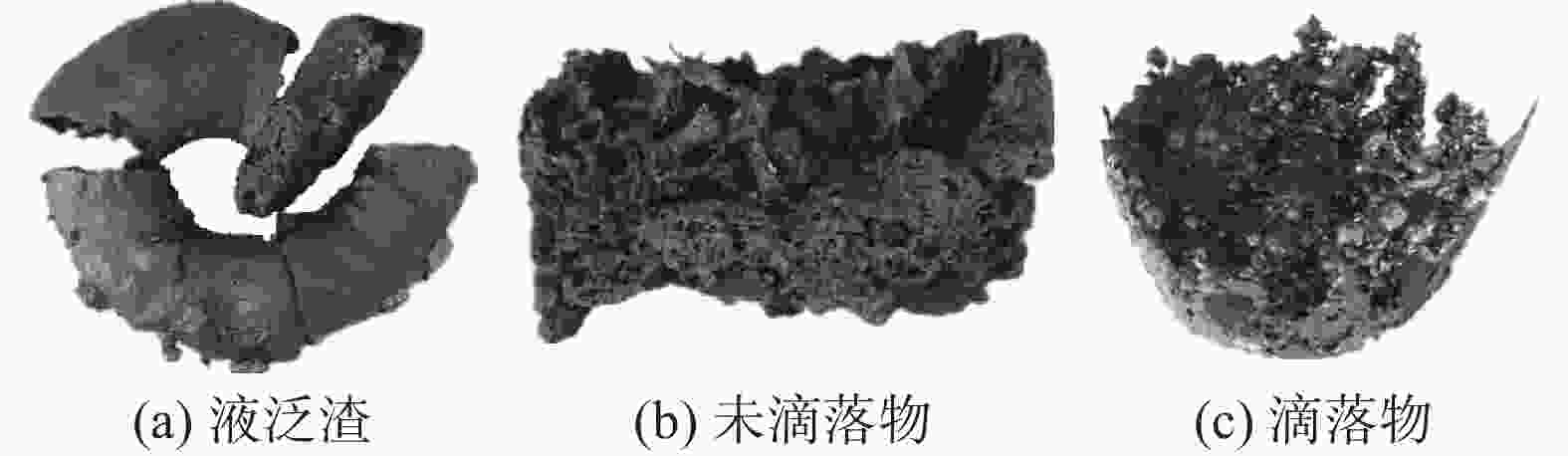
Table 7. Phase and element distribution of flooding slag on graphite pusher during softening
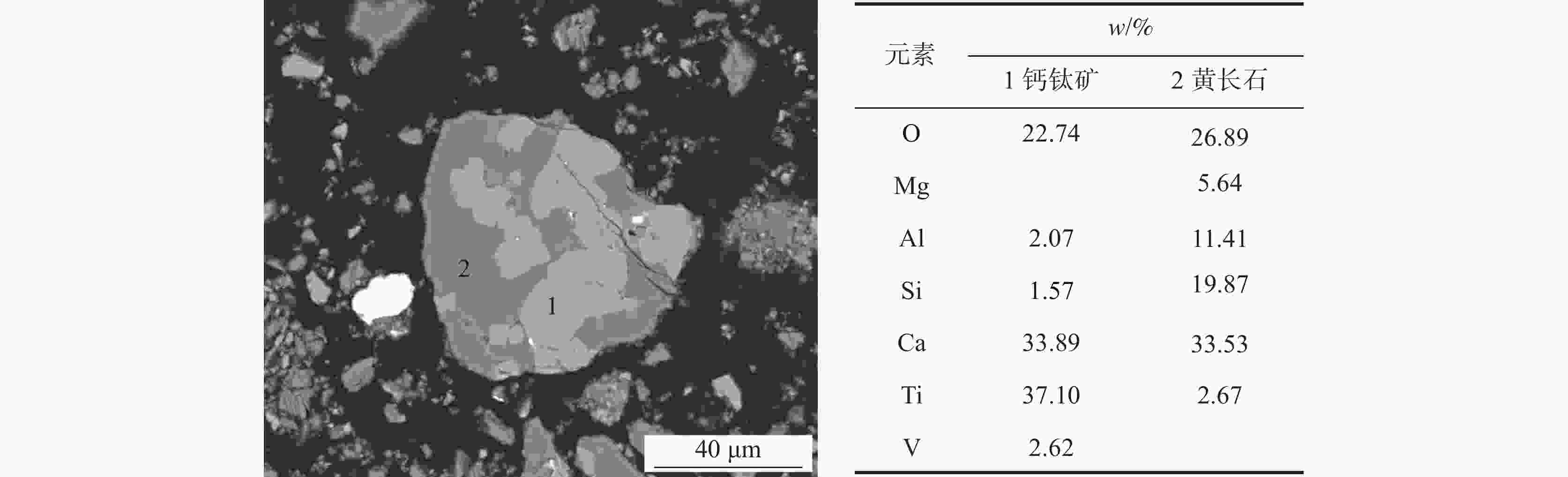
矿物名称 w/% 化学成分/% Fe O Ti V Si Ca Mg Al 黄长石 68.54 3.71 74.00 23.39 39.00 90.19 72.93 84.19 88.65 钙钛矿 21.84 2.21 21.40 73.70 56.03 4.34 23.16 5.86 7.15 金属铁 4.71 81.52 0.09 0.28 1.55 0.24 0.17 0.59 0.32 辉石 1.21 0.04 1.33 1.01 0.10 1.30 0.91 3.45 1.72 透辉石 0.80 0.23 0.91 0.20 0.54 1.12 0.63 2.58 0.38 铁酸钙 1.15 8.70 0.62 0.94 1.33 0.67 0.59 1.54 0.64 玻璃质 0.04 0.00 0.05 0.01 0.05 0.07 0.01 0.11 0.06 其它 1.71 3.61 1.60 0.47 1.42 2.07 1.58 1.69 1.08 表 8 烧结矿软熔未滴落渣的物相组成和元素分布
Table 8. Phase and element distribution of residual slag in graphite crucible during softening
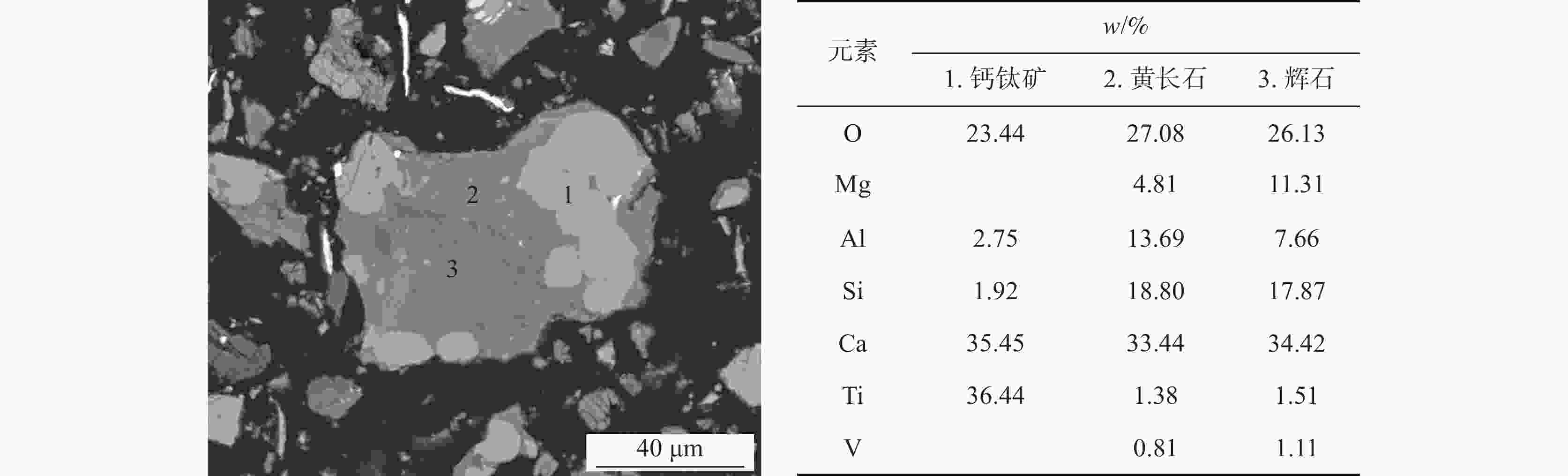
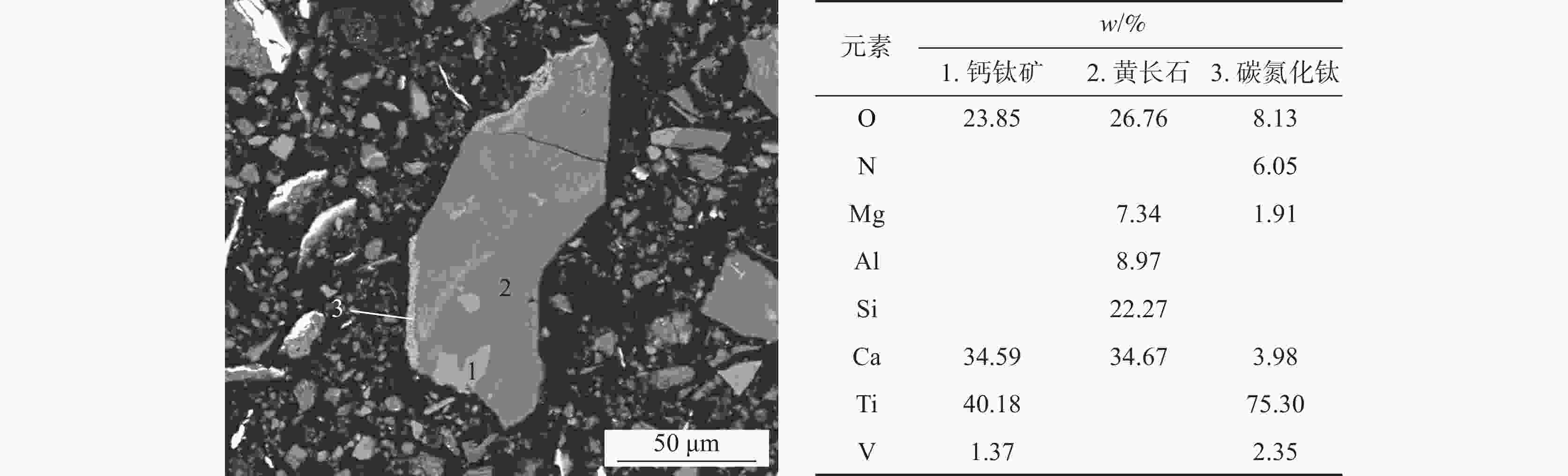
矿物名称 w/% 化学成分/% Fe O N Ti V Si Ca Mg Al 黄长石 35.73 0.26 47.26 0 7.40 13.83 69.45 51.82 35.88 56.82 钙钛矿 22.76 0.49 27.03 0 84.13 58.82 3.91 31.48 3.68 8.61 金属铁 22.15 93.21 0.50 0 1.10 7.28 1.24 0.82 1.89 1.59 辉石 7.03 0.07 9.91 0 2.89 4.78 9.66 7.22 16.04 16.93 透辉石 6.03 0.19 8.36 0 1.45 4.89 12.01 6.46 17.50 2.60 镁铝尖晶石 1.90 0.05 2.90 0 0.99 4.47 0.55 0.38 6.21 11.28 MgO 1.26 0.03 1.76 0 0.14 2.68 0.04 0.07 14.57 0 铁酸钙 2.09 4.67 1.14 0 1.46 2.00 1.41 1.19 1.85 1.28 玻璃质 0.03 0 0.05 0 0.01 0.03 0.09 0.01 0.05 0.07 碳氧化钛 0.01 0 0.01 0 0.03 0.02 0 0 0 0 碳氮化钛 0 0 0 100.00 0.05 0.01 0 0 0 0 其它 1.00 1.03 1.09 0 0.37 1.20 1.64 0.55 2.33 0.82 *注:碳氮化钛为0.005225%,碳氮化钛物相0.006066%。 表 9 烧结矿软熔滴落渣的物相组成和元素分布
Table 9. Phase and element distribution of dripping slag during softening
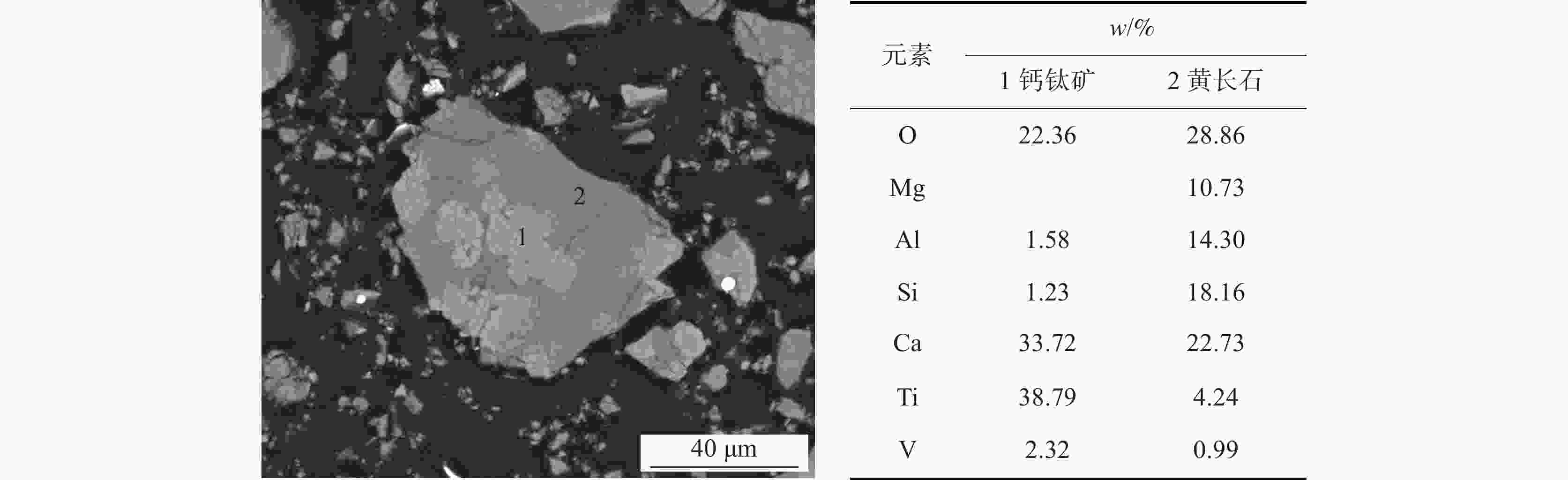
矿物名称 w/% 化学成分/% Fe O N Ti V Si Ca Mg Al 黄长石 57.84 8.98 59.91 0 41.28 62.71 71.22 63.54 53.06 61.51 钙钛矿 16.33 2.12 15.87 0 45.05 32.97 3.45 18.32 3.22 5.47 金属铁 3.50 79.48 0.04 0 0.10 0.34 0.11 0.08 0.18 0.15 辉石 20.94 0.01 23.04 0 12.93 2.88 23.96 17.24 41.61 31.88 透辉石 0.28 0.06 0.35 0 0.08 0.16 0.40 0.24 0.57 0.21 镁铝尖晶石 0.01 0 0.01 0 0 0.01 0 0 0.02 0.04 铁酸钙 0.57 5.37 0.32 0 0.39 0.56 0.36 0.32 0.55 0.35 碳氮化钛 0.454* 0 0 100.00 0 0 0 0 0 0 其它 0.54 3.98 0.46 0 0.17 0.38 0.51 0.27 0.79 0.41 *注:碳氮化钛为0.000454%。 表 10 烧结矿重熔未滴落渣的物相组成和元素分布
Table 10. Phase and element distribution of residual slag in graphite crucible during remelting
矿物 w/% 化学成分/% Fe O N Ti V Si Ca Mg Al 黄长石 53.16 1.78 59.29 0.00 17.99 29.30 72.54 64.68 50.79 69.71 钙钛矿 16.92 0.57 17.38 0.00 65.59 47.47 1.91 19.99 2.54 5.18 金属铁 9.61 90.43 0.31 0.00 1.02 3.58 0.83 0.63 1.39 1.16 辉石 5.32 0.24 6.15 0.00 5.37 2.50 5.73 3.87 11.27 9.26 透辉石 8.87 0.44 10.51 0.00 2.06 6.96 12.93 8.31 23.37 2.96 钙铁辉石 2.48 5.66 2.24 0.00 0.84 2.80 2.91 1.72 3.20 2.57 镁铝尖晶石 1.61 0.14 2.05 0.00 1.51 3.62 0.20 0.20 5.31 7.64 碳氮化钛 0.31 0.01 0.01 100.00 2.43 0.43 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.00 碳氧化钛 0.39 0.00 0.34 0.00 1.97 1.34 0.21 0.19 0.34 0.27 其它 1.32 0.74 1.72 0.00 1.22 2.01 2.69 0.36 1.74 1.25 表 11 不同炉渣主要物相组成对比
Table 11. Main phase composition of different slags
% 样品名称 黄长石 钙钛矿 辉石 其它 软熔液泛渣 71.93 22.92 2.11 3.04 软熔未滴落渣 45.90 29.24 16.78 8.08 软熔滴落渣 59.93 16.92 21.99 1.16 重熔未滴落渣 58.82 18.72 18.44 4.02 表 12 生产高炉渣的化学成分
Table 12. Chemical composition of blast furnace slag during production
% CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 TiO2 V2O5 S R2 27.03 24.72 8.11 13.09 21.85 0.24 0.50 1.09 -
[1] 攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿选矿烧结高炉冶炼试验资料汇编[R]. 北京. 1978: 167−498.Data compilation of beneficiation, sintering and blast furnace smelting test of Panzhihua vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite[R]. Beijing. 1978:167−498. [2] Xu Caidong, Lin Rong. Important physicochemical problems in high temperature reduction of Panzhihua vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1980,2(2):1−10. (徐采栋, 林蓉. 攀枝花钒铁磁铁矿高温还原中的重要物理化学问题[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1980,2(2):1−10. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.1987.04.001 [3] Bai Chenguang, Pei Henian, Zhao Shijin, et al. An investigation of the relationship between the particle size of titanium carbonitride and the viscosity of blast furnace slag bearing high titania[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1995,16(3):6−9. (白晨光, 裴鹤年, 赵诗金, 等. 碳氮化钛粒度与熔渣粘度关系的研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1995,16(3):6−9. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.1995.03.002 [4] Xie Dongsheng, Mao Yuwen, Guo Zhaoxin, et al. Viscosity of TiO2-containing blast furnace slags under neutral condition[J]. Iron and Steel, 1986,21(1):7−11. (谢冬生, 毛裕文, 郭昭信, 等. 中性条件下高炉钛渣粘度的研究[J]. 钢铁, 1986,21(1):7−11. [5] Liao J L, Li J, Wang X D, et al. Influence of TiO2 and basicity on viscosity of Ti bearing slag[J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2012,39(2):133−139. doi: 10.1179/1743281211Y.0000000064 [6] Xie Hong’en, Qin Xingguo, Zheng Kui, et al. Analysis of effect factors of smelting temperature of high-titanium-type blast furnace slag[J]. China Metallurgy, 2017,27(9):13−19. (谢洪恩, 秦兴国, 郑魁, 等. 高钛型高炉渣熔化性温度影响因素分析[J]. 中国冶金, 2017,27(9):13−19. [7] Lin Y H, Zhang L Q, Huang X L. Influence of CaF2 on the apparent viscosity of CaO-SiO2-MgO-Al2O3-TiO2 slags[J]. Metallurgical Research and Technology, 2017,114(6):606−610. doi: 10.1051/metal/2017067 [8] Qu Yanping, Du Hegui. Determination of surface viscosity and bulk viscosity of blast furnace type titanium slag containing MnO[J]. Metallurgy of Sichuan, 1997,19(1):22−24, 32. (曲彦平, 杜鹤桂. 含MnO高炉型钛渣表面粘度和体相粘度的测定[J]. 四川冶金, 1997,19(1):22−24, 32. [9] Qi C L, Zhang J L, Shao J G, et al. Study of boronizing mechanism of high-alumina Slag[J]. Steel Research International, 2011,82(11):1319−1324. doi: 10.1002/srin.201100118 [10] Song Guocai, Yuan Tianyu, Chen Xiaowu. Study on phase composition of the cohesive dropping zone in BF during smelting V-bearing titaniferrous maganetite sinter[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1996,17(2):25−27. (宋国才, 苑天宇, 陈小武. 高炉冶炼钒钛烧结矿软熔滴落带物相组成研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1996,17(2):25−27. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.1996.02.005 [11] Yang Guangqing, Yang Wenkang, Li Xiaosong, et al. Comparative study of microstructure changes in vanadium titanium sinter and ordinary sinter during reduction process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018,39(2):102−109. (杨广庆, 杨文康, 李小松, 等. 钒钛烧结矿与普通烧结矿还原过程中微观结构变化对比研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2018,39(2):102−109. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2018.02.017 [12] Gan Qin, He Qun, Wen Yongcai. Study on influence of MgO on mineral composition and metallurgical properties of V-bearing titaniferous magnetite sinter[J]. Iron and Steel, 2008,43(8):7−11. (甘勤, 何群, 文永才. MgO对钒钛烧结矿矿物组成及冶金性能影响的研究[J]. 钢铁, 2008,43(8):7−11. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2008.08.002 [13] Bai Dongdong, Han Xiuli, Li Changcun, et al. Influence of mineral structure of vanadium-titanium sinter on its metallurgical properties[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018,39(5):111−115. (白冬冬, 韩秀丽, 李昌存, 等. 钒钛烧结矿矿相结构对其冶金性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2018,39(5):111−115. [14] Zhang Jianliang, Yang Guangqing, Guo Hongwei, et al. Microstructure change of V-Ti magnetite concentrate pellets during reduction[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2013,35(1):42−48. (张建良, 杨广庆, 国宏伟, 等. 含钒钛铁矿球团还原过程中微观结构变化[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2013,35(1):42−48. [15] 程功金. 块状带高铬型钒钛磁铁矿还原动力学及有价组元迁移行为的研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2013.Cheng Gongjin. Study on kinetics of high chromia vanadium-titanium magnetite reduction and migration behavior of valuable elements in lumpy zone[D]. Shenyang: Northeatern University, 2013 [16] 刘建兴. 软熔滴落带高铬型钒钛磁铁矿有价组元迁移机理[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2013.Liu Jianxing. The migration mechanism of valuable components for high chromia vanadium-titanium magnetite in cohesive zone[D]. Shenyang: Northeatern University, 2013. [17] Zhan Xing. Anatomical study on smelting vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite in small blast furnace[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1984,5(2):3−15. (詹星. 小高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿解剖研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1984,5(2):3−15. [18] 黄希祜. 钢铁冶金原理[M]. 北京, 冶金工业出版社, 2013.Huang Xigu. Principles of iron and steel metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013. [19] 王筱留. 钢铁冶金学(炼铁部分)[M]. 北京, 冶金工业出版社, 2018.Wang Xiaoliu. Iron and steel metallurgy (ironmaking)[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2018. [20] Du Hegui, Zhang Ziping. The function of V2O5 in Ti-containing slag of blast furnace type to inhibit TiO2 reduction[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1994,15(4):1−3, 27. (杜鹤桂, 张子平. 高炉型钛渣中V2O5对TiO2还原的抑制[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1994,15(4):1−3, 27. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.1994.04.001 [21] 杜鹤桂. 高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996.Du Hegui. Principle of smelting vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite in blast furnace[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996. [22] 曾广策. 晶体光学及光性矿物学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2017.Zeng Guangce. Crystal optics and optical mineralogy[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2017. [23] Fu Weiguo, Diao Risheng, Li Jianming, et al. Characteristics analysis of furnace hearth sediment at No. 1 blast furnace at PZH steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2003,24(3):37−41. (付卫国, 刁日升, 黎建明, 等. 攀钢1号高炉炉底沉积物特点分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2003,24(3):37−41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7638.2003.03.008 -




 下载:
下载: