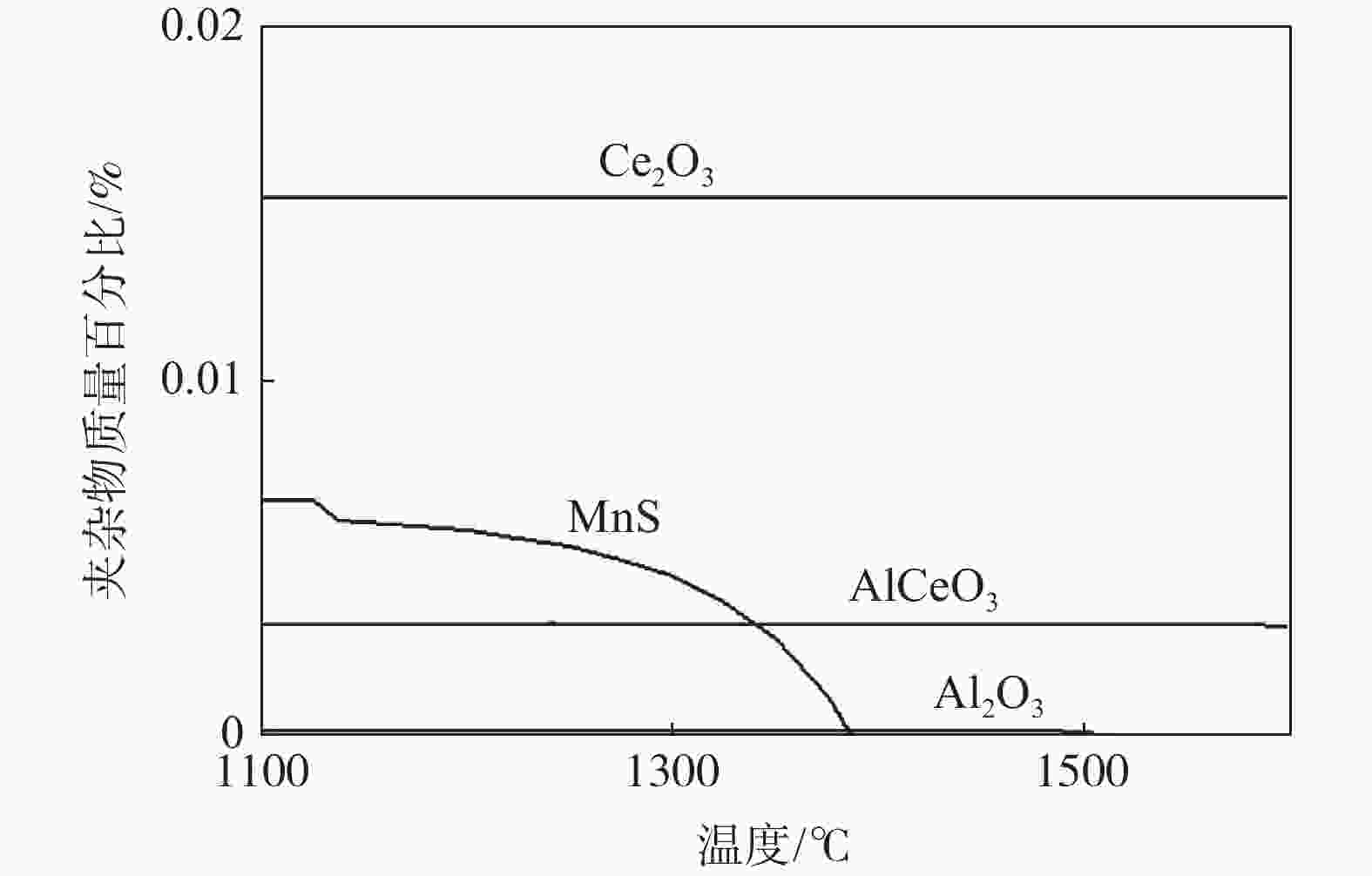
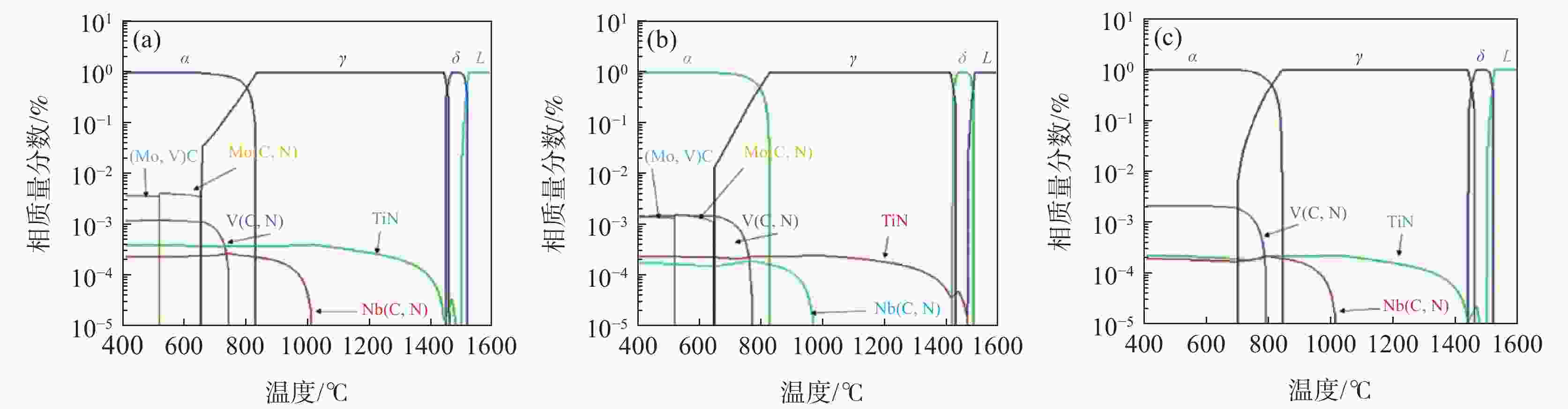
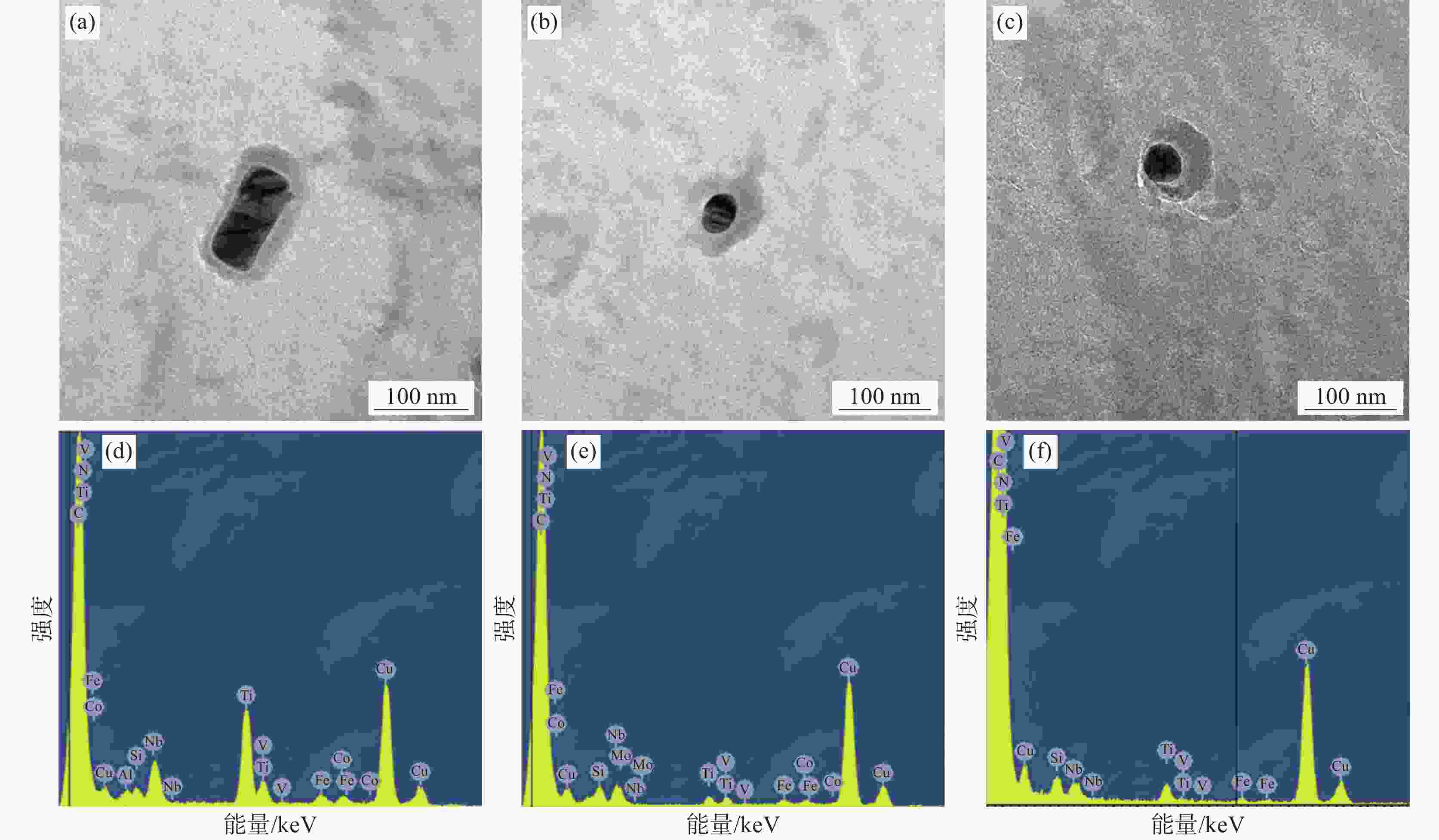
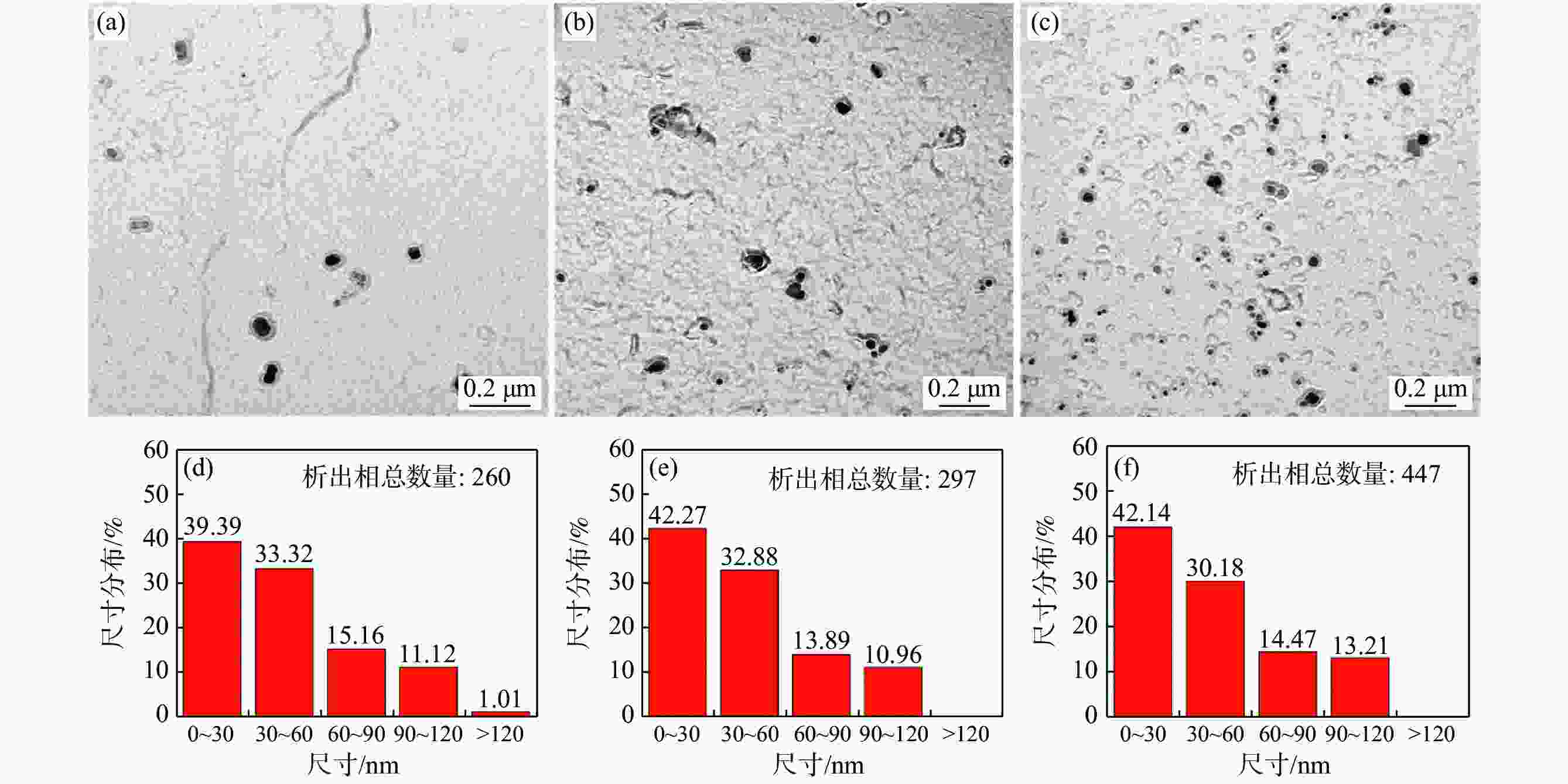
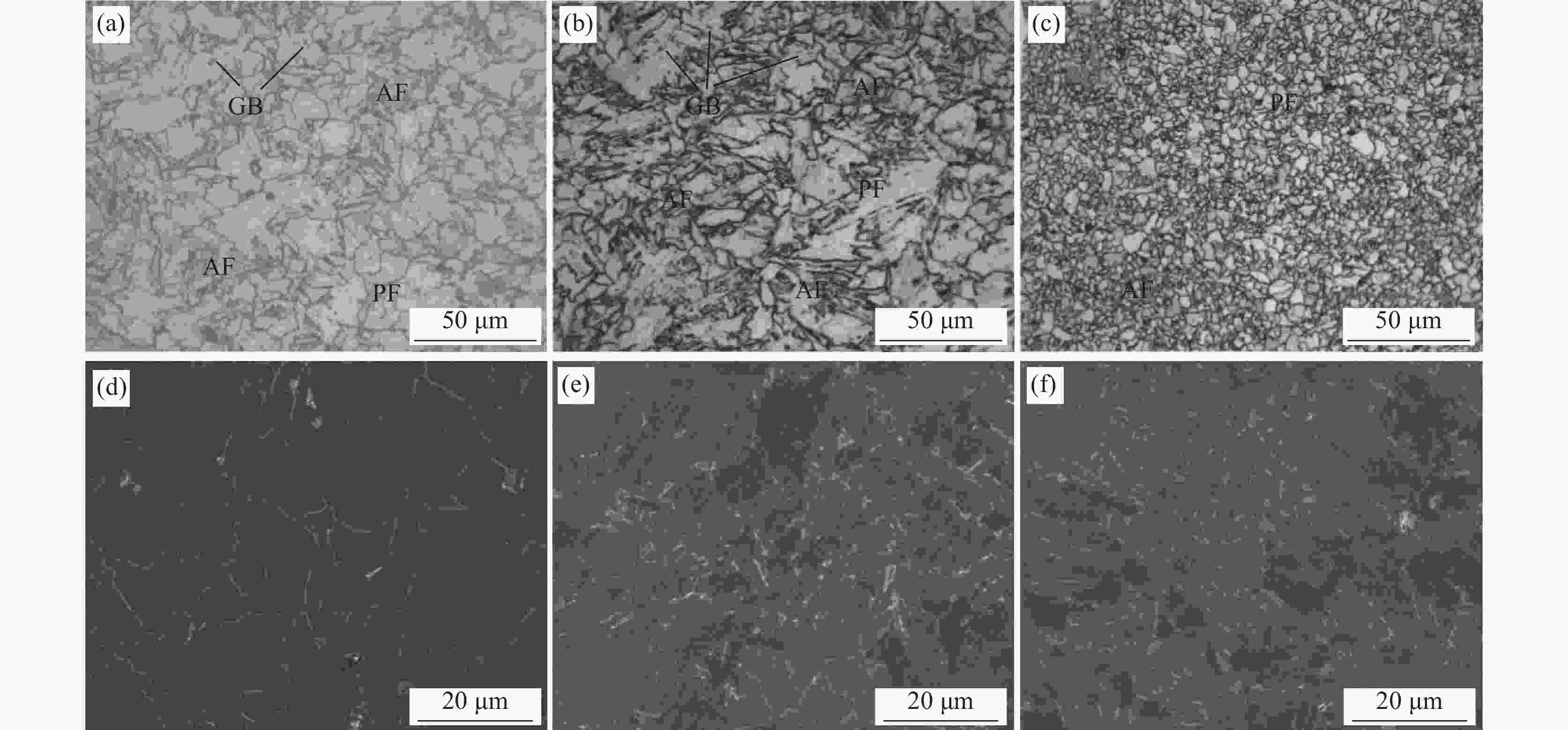
Effect of vanadium content on microstructure and precipitation of rare earth treated X80 linepipe steels
-
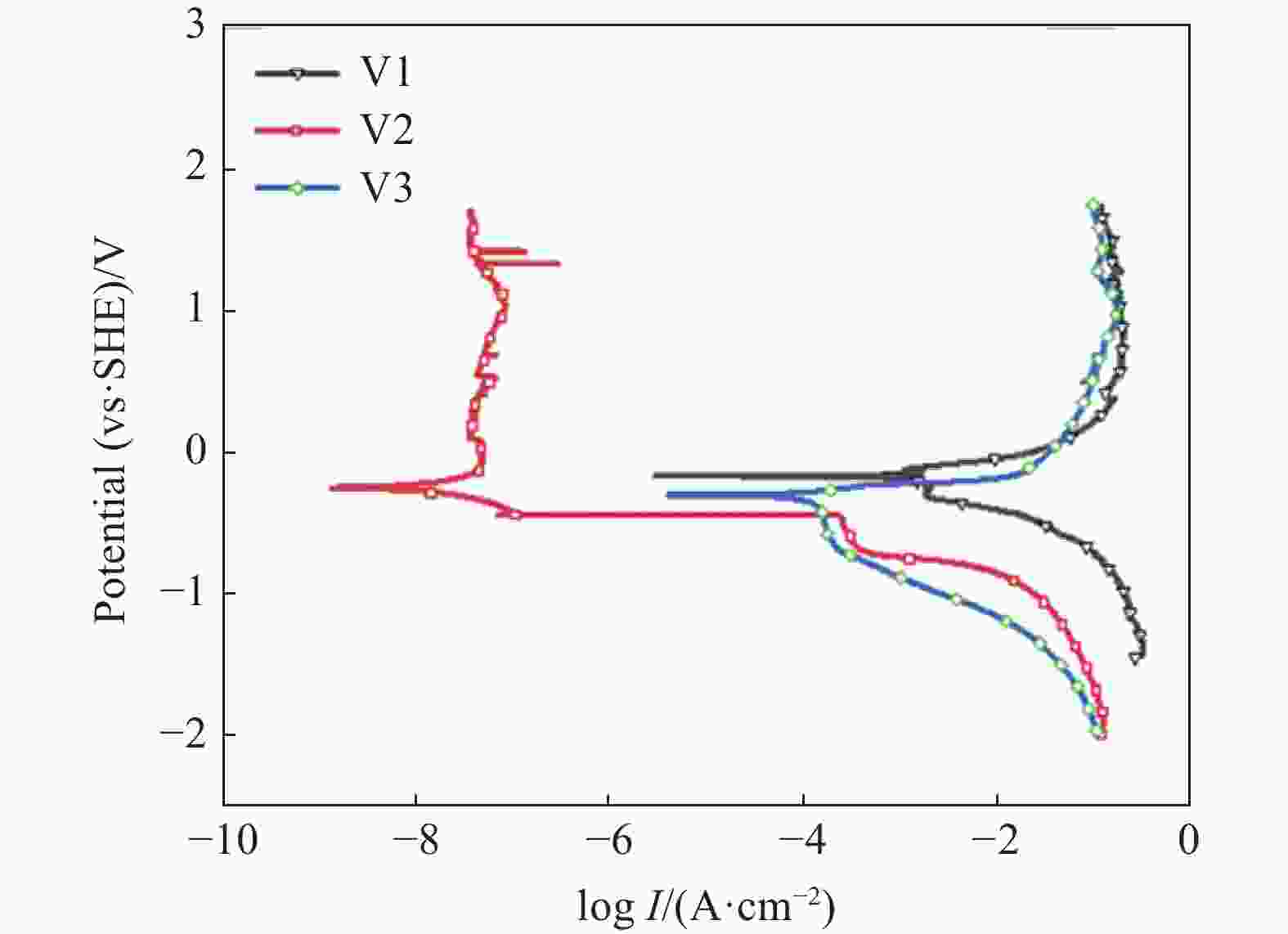
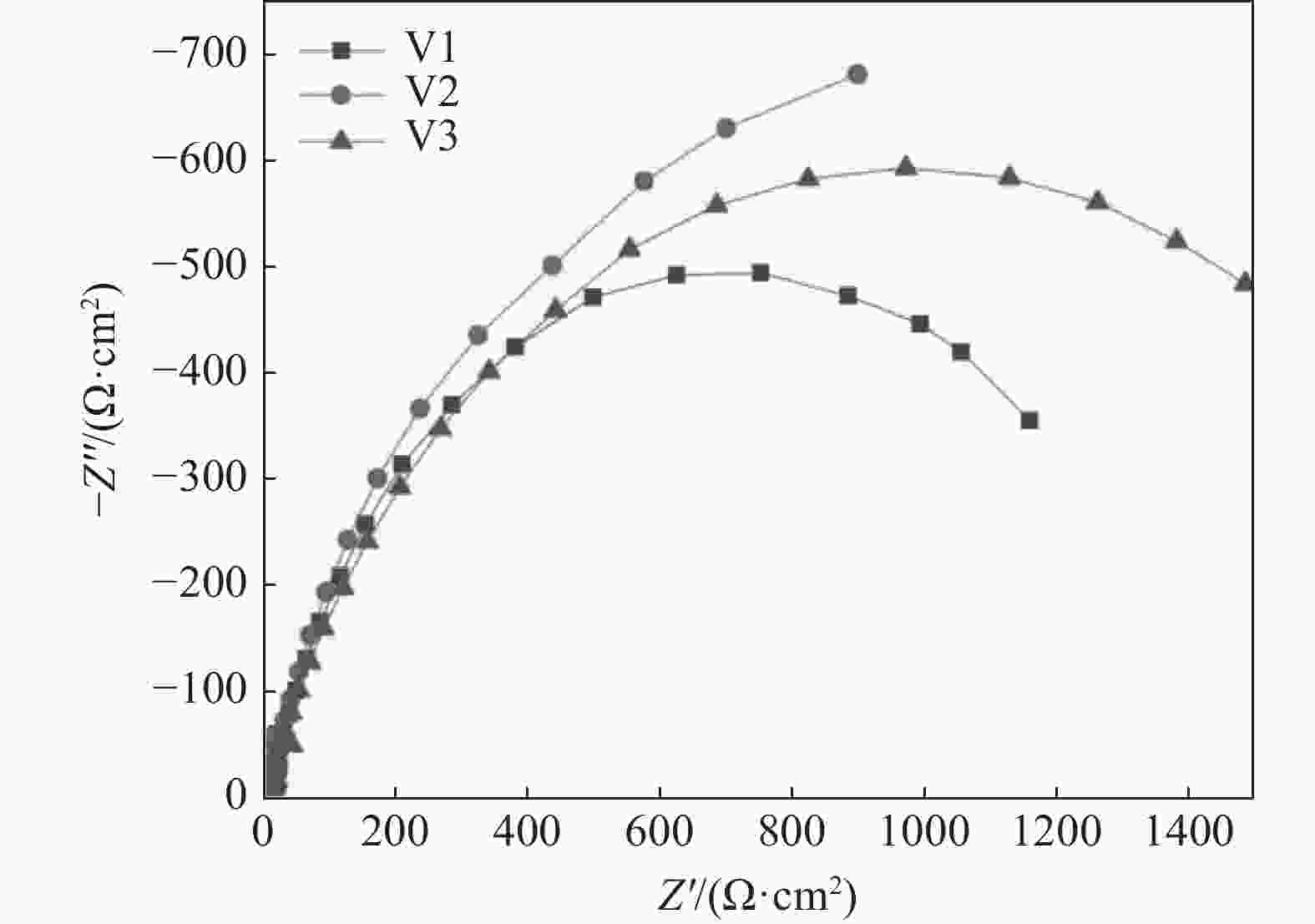
摘要: 针对国内某X80管线钢的抗腐蚀问题,在加入稀土(0.02%)处理后,设计三种不同钒含量(0.05%、0.10%、0.15%)的试验钢,通过光学显微镜(OM)、扫描电镜(SEM)、Thermo-Calc热力学软件、Fatesage7.0热力学软件、透射电子显微镜-能谱仪(TEM-EDS)等试验仪器对钢中组织和夹杂物的观察分析,论述了稀土在钢中对针状铁素体的生成机理。通过热力学计算,研究不同钒含量梯度对试验钢微观组织和析出相的影响。通过电化学技术检测了不同钒含量试验钢在(3.5%)NaCl溶液中抗腐蚀性能。结果表明:稀土可以变质夹杂物,诱导针状铁素体的形成。钒可以细化晶粒,从而起到细晶强化的作用。通过透射电镜观察,析出相的数量和平均尺寸都随着钒含量的增加而增加,有效起到钉扎作用,从而提高钢的强度。通过极化曲线和交流阻抗曲线看出,试验钢的抗腐蚀性能随着钒含量的增加先增强后减弱。钒促进铁素体的形成,晶粒过细反而导致抗腐蚀性能减弱。Abstract: In order to improve the corrosion resistance of X80 linepipe steel, different vanadium content (0.05%, 0.10% and 0.15%) was added into a rare earth (0.02%) treated X80 linepipe steel. Optical microscope (OM), cold field emission scanning electron microscope, thermodynamic software Thermo-CalC, transmission electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectrometer (TEM-EDS) had been used to investigate the structure and inclusions in steel to reveal formation mechanism of acicular ferrite in rare earth treated steel. Besides, the effects of different vanadium content gradients on the microstructure and precipitation of the experimental steels had been studied by thermodynamic calculations. Moreover, the corrosion resistance of experimental steels with different vanadium content in NaCl (3.5%) solution was tested by electrochemical technology. The results indicate that rare earth can bring inclusion modification and facilitate the formation of acicular ferrite. Vanadium can achieve grain refinement. The transmission electron microscope shows a positive correlation between the number and average size of precipitates and vanadium content, which causes a pinning effect and improves the strength of steel. The polarization curve and the AC impedance curve suggest that the corrosion resistance of the experimental steel is initially increased and then decreased with the increase of vanadium content. Vanadium can accelerate the formation of ferrite, which in turn lead to lower corrosion resistance ability due to refine grains.
-
表 1 三种试验钢的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of the three experimental steels
% 编号 C Si Mn S Mo Nb Ti Mo Ce V V1 0.04 0.14 1.67 0.0034 0.094 0.013 0.0084 0.094 0.0168 0.045 V2 0.04 0.14 1.67 0.0038 0.094 0.014 0.0084 0.094 0.0171 0.092 V3 0.04 0.14 1.67 0.0039 0.095 0.014 0.0085 0.095 0.0165 0.134 表 2 三种试验钢中V(C,N)平衡相的析出温度以及最大析出摩尔分数
Table 2. Precipitation temperature and maximum precipitation mole fraction of the V(C,N)in the three experimental steels
钢种 析出温度/℃ 最大析出摩尔分数 V1 743 6.92×10−4 V2 778 1.52×10−3 V3 790 2.1×10−3 表 3 试验钢腐蚀极化曲线的拟合参数
Table 3. Fitting parameters of corrosion polarization curve of experimental steel
钢种 腐蚀电位/mV 腐蚀电流密度/(μA·cm−2) V1 −397.070 834.122 V2 −491.586 0.07 V3 −554.455 60.204 -
[1] Joakim Andersson, Stefan Gronkvist. Large-scale storage of hydrogen[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019,44:11901−11919. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.03.063 [2] Liu Z Y, Wang X Z, Du C W, et al. Effect of hydrogen-induced plasticity on the stress corrosion cracking of X70 pipeline steel in simulated soil environments[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2016,658:348−354. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2016.02.019 [3] Yang Z X, Kan B, Li J X, et al. Hydrostatic pressure effects on stress corrosion cracking of X70 pipeline steel in a simulated deep-sea environment[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017,42(44):27446−27457. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.09.061 [4] Loidl M, Kolk O, Veith S, et al. Characterization of hydrogen embrittlement in automotive advanced high strength steels[J]. Materials Science & Engineering Technology, 2011,42(12):1105−1110. doi: 10.1002/mawe.201100917 [5] Zhao Mingchun, Shan Yiyin, Li Yuhai, et al. Effect of microstructure on stress corrosion cracking of sulphide in pipeline steel[J]. Journal of Metal, 2001,37(10):1087−1092. (赵明纯, 单以银, 李玉海, 等. 显微组织对管线钢硫化物应力腐蚀开裂的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2001,37(10):1087−1092. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2001.10.018 [6] Wang C, Wang X, Kang J, et al. Effect of austenitization conditions on the transformation behavior of low carbon steel containing Ti–Ca oxide particles[J]. Materials, 2019,12:1070. doi: 10.3390/ma12071070 [7] Park G T, Koh S U, Jung H G, et al. Effect of microstructure on the hydrogen trapping efficiency and hydrogen induced cracking of linepipe steel[J]. Corrosion Science, 2008,50(7):1865−1871. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2008.09.014 [8] Zhang Xiaofeng, Tang Jianping, Han Chunpeng, et al. The role of rare earth in steel and the status of industrial production[J]. Rare Earth, 2021,42(4):117−130. (张晓峰, 唐建平, 韩春鹏, 等. 稀土在钢中作用及工业化生产现状浅析[J]. 稀土, 2021,42(4):117−130. doi: 10.16533/j.cnki.15-1099/tf.20210034 [9] Yang Quanhai, Yang Jichun, Ding Haifeng, et al. Thermodynamic analysis and experimental study of inclusions in rare earth pipeline steel[J]. Rare Earth, 2018,39(2):96−101. (杨全海, 杨吉春, 丁海峰, 等. 稀土管线钢中夹杂物热力学分析及实验研究[J]. 稀土, 2018,39(2):96−101. doi: 10.16533/J.CNKI.15-1099/TF.201802013 [10] Song M M, Song B, Xin W, et al. Effects of rare earth addition on microstructure of C-Mn steel[J]. Ironmak. Steelmak, 2015,42:594−599. doi: 10.1179/1743281215Y.0000000006 [11] Lin Qin, Song Bo, Guo Xingmin, et al. Microalloying of rare earth in steel and its application prospect[J]. Rare Earth, 2001,22(4):31−36. (林勤, 宋波, 郭兴敏, 等. 钢中稀土微合金化作用与应用前景[J]. 稀土, 2001,22(4):31−36. doi: 10.16533/j.cnki.15-1099/tf.2001.04.004 [12] Lin Qin, Wang Huaibin, Tang Li, et al. Study on the recombination of rare earth vanadium in microalloyed steel[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Earth, 2001,19(2):146−149. (林勤, 王怀斌, 唐历, 等. 微合金钢中稀土钒复合作用的研究[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2001,19(2):146−149. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4343.2001.02.012 [13] Xu Feng, Li Liwei, Xu Jinqiao, et al. Development status and development trend of high-grade acid resistant pipeline steel[J]. Iron and Steel Research, 2014,42(4):58−61. (徐锋, 李利巍, 徐进桥, 等. 高级别耐酸管线钢的开发现状及发展趋势[J]. 钢铁研究, 2014,42(4):58−61. [14] Cui Q Q, Wu J S, Xie D H, et al. Effect of nanosized NbC precipitates on hydrogen diffusion in X80 pipeline steel[J]. Materials, 2017,10(7):721. doi: 10.3390/ma10070721 [15] Li L F, Song B, Cheng J, et al. Effects of vanadium precipitates on hydrogen trapping efficiency and hydrogen induced cracking resistance in X80 pipeline steel[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018,43(36):17353−17363. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.07.110 [16] Liu Shuai, Liu Jing, Huang Feng, et al. Control of submicron inclusion in pipeline steel and its influence on anti-HIC performance[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2019,48(4):52−56. (刘帅, 刘静, 黄峰, 等. 管线钢亚微米级夹杂物的控制及对抗HIC性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2019,48(4):52−56. doi: 10.14158/j.cnki.1001-3814.2019.04.012 [17] Turk A, MartínSan D, Rivera-Díaz-del-CastilloPEJ, et al. Correlation between vanadium carbide size and hydrogen trapping in ferritic steel[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2018,152:112−116. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.04.013 [18] Beidokhti B, Koukabi A H, Dolati A. Effect of titanium addition on the microstructure and inclusion formation in submerged arc welded HSLA pipeline steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009,209:4027−4035. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.09.021 [19] Depover T, Verbeken K. Evaluation of the effect of V4C3 precipitates on the hydrogen induced mechanical degradation in Fe-C-V alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2016,675:299−313. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2016.08.053 [20] Takahashi J, Kawakami K, Kobayashi Y. Origin of hydrogen trapping site in vanadium carbide precipitation strengthening steel[J]. Acta Mater, 2018,153:193−204. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2018.05.003135 [21] Cheng X B, Cheng X Y, Jiang C W, et al. Hydrogen diffusion and trapping in V-microalloyed mooring chain steels[J]. Mater. Lett, 2018,213:118−121. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2017.11.029 [22] Zhang Zhengyan, Sun Xinjun, Yong Qilong, et al. Strengthening mechanism and precipitation behavior of nanoscale carbides in Nb-Mo microalloy high strength steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016,52(4):410−418. (张正延, 孙新军, 雍岐龙, 等. Nb-Mo微合金高强钢强化机理及其纳米级碳化物析出行为[J]. 金属学报, 2016,52(4):410−418. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2015.00482 [23] Chen Y S, Haley D, Gerstls S A, et al. Direct observation of individual hydrogen atoms at trapping sites in a ferritic steel[J]. Science, 2017,355:1196−1199. doi: 10.1126/science.aal2418 [24] Kimura T, Kawabata F, Amano K, et al. The third-generation TMCP combined with fine inclusion metallurgy and development of heavy gauge H-shapes with excellent seismic-resistance for building structure[J]. Materia Japan, 1999,38(2):160−162. doi: 10.2320/materia.38.160 [25] Liu Jian, Wang Huakun, Song Liqiu, et al. Research and application of vanadium nitrogen microalloying high strength steel[J]. Sichuan Metallurgy, 2006,28(1):24−27. (刘建, 王华昆, 宋立秋, 等. 钒氮微合金化高强度钢的研究及应用[J]. 四川冶金, 2006,28(1):24−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2006.02.012 [26] Kang Y, Jeong S, Kang J H, et al. Factors affecting the inclusion potency for acicular ferrite nucleation in high-strength steel welds[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2016,47A(6):2842−2854. [27] Yang Jichun, Yang Quanhai, Zhao Wei. Effect of yttrium on corrosion resistance of X100 pipeline steel[J]. Rare Earth, 2018,39(3):101−107. (杨吉春, 杨全海, 赵伟. 钇对 X100 管线钢抗腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 稀土, 2018,39(3):101−107. doi: 10.16533/J.CNKI.15-1099/TF.201803014 -




 下载:
下载: