Research on IAF nucleation behavior induced by Ce/Ce-Zr inclusion in high strength steel plate for shipbuilding
-
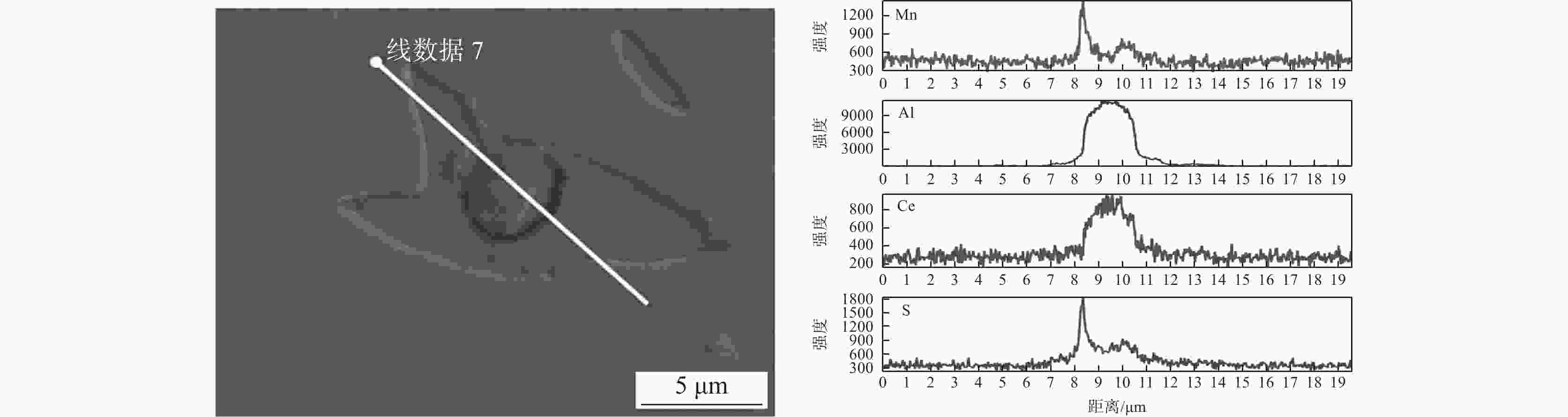
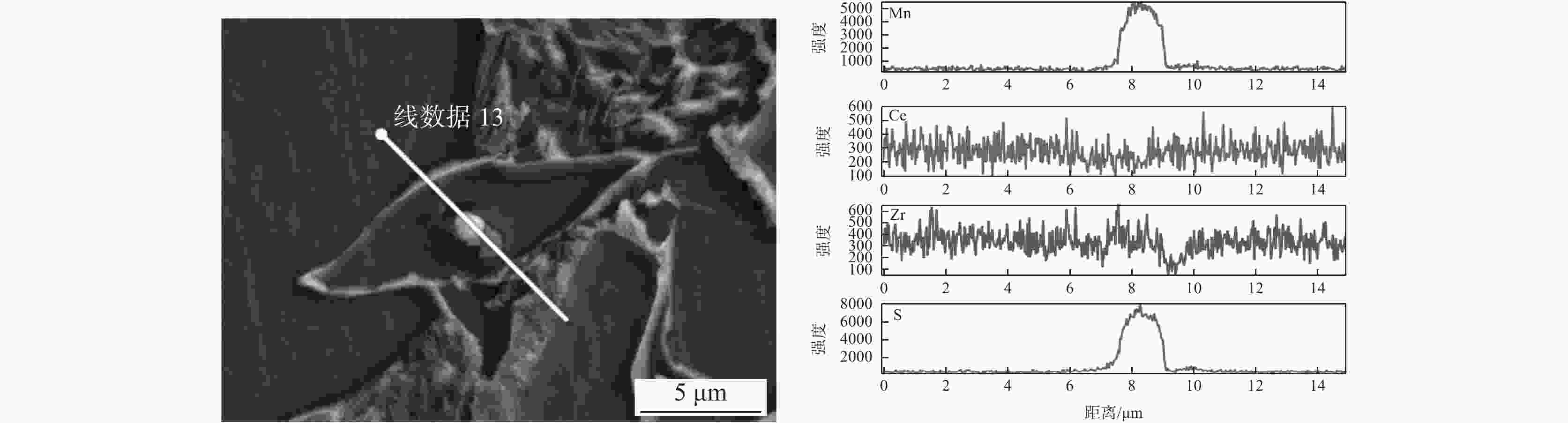
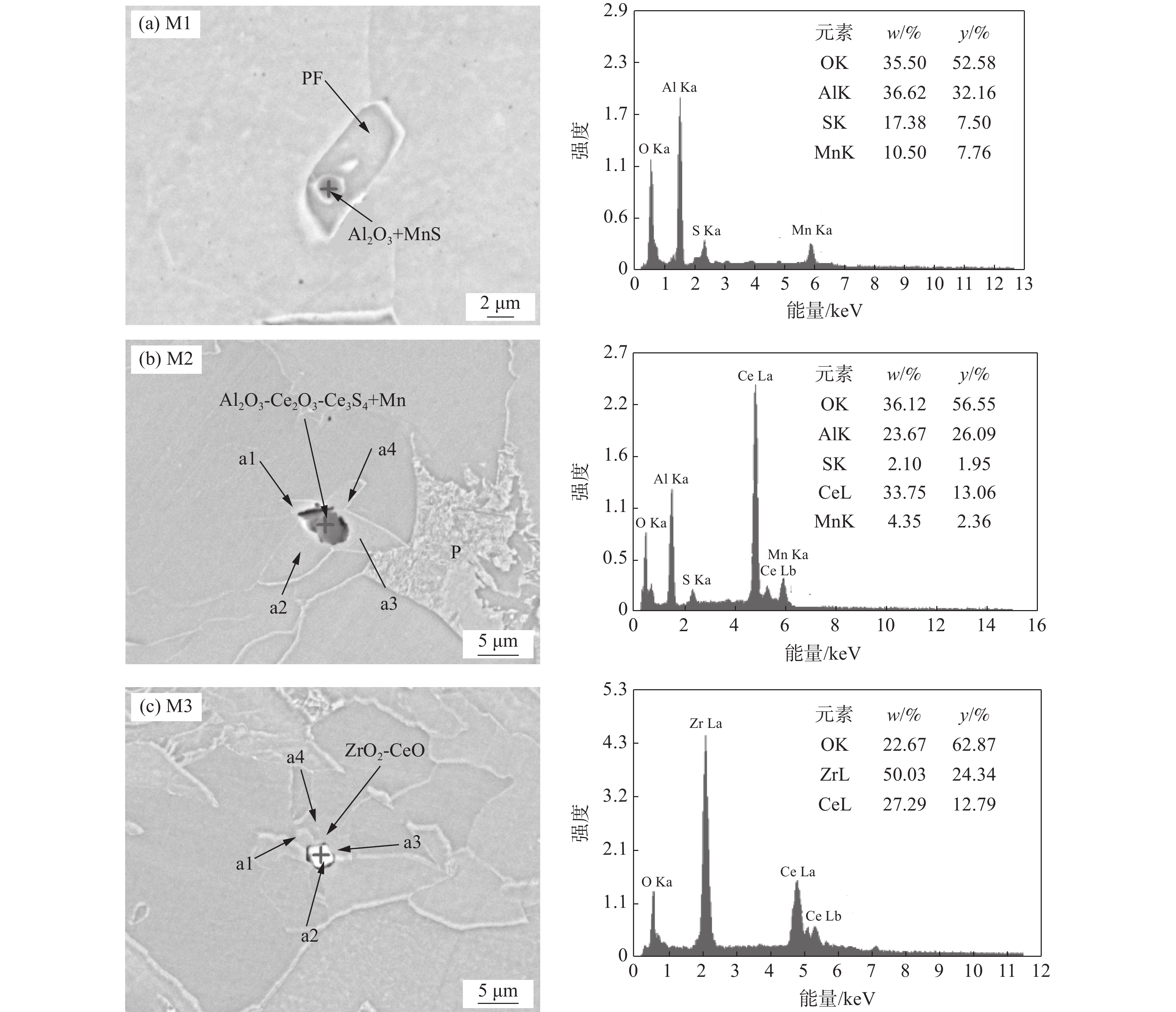
摘要: 研究了FH40高强船板钢经稀土合金化处理后夹杂物诱发铁素体的变化行为,利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和能量衍射谱(EDS)等手段观察分析了钢中稀土夹杂物的形貌特征以及诱发形成IAF的行为机制。研究结果表明:经Ce或Ce-Zr复合处理后,稀土复合夹杂物形状得到球化,且均能诱发针状铁素体形成;单独Ce处理形成的Al-Ce-O+MnS夹杂物诱导针状铁素体行为可用贫Mn区机制和惰性基底机理解释,而Ce-Zr复合处理形成的Ce-Zr-O+MnS夹杂物诱导针状铁素体行为只能用贫锰区机制解释。Abstract: In this paper, the evolution behavior of ferrite induced by inclusions in FH40 ship plate steel after rare earth alloying was studied. The morphology characteristics of rare earth inclusions formed in steel and the mechanism of IAF formation were observed and analyzed by means of scanning electron microscope (SEM) and energy diffraction spectrum (EDS). The results show that the shape of the rare earth composite inclusions is spheroidized after Ce or Ce-Zr composite treatment, and both inclusions can induce the formation of IAF. Al-Ce-O+MnS inclusions formed by Ce can be explained by Mn-poor zone mechanism and inert substrate mechanism, while Ce-Zr-O+MnS inclusions formed by Ce-Zr combined treatment can only be explained by Mn-poor zone mechanism.
-
Key words:
- FH40 ship plate steel /
- rare earth treatment /
- inclusion /
- nucleation mechanism /
- intra-granular ferrite
-
表 1 试验钢实际化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of experimental steels
% 试样 C Si Mn P S Ni Nb Ti Al N Ce Zr M1 0.063 0.251 1.59 0.0096 0.0058 0.303 0.0395 0.0127 0.034 0.0078 M2 0.069 0.245 1.57 0.0097 0.0055 0.296 0.0401 0.0132 0.034 0.0059 0.0580 M3 0.065 0.247 1.58 0.0093 0.0056 0.298 0.0395 0.0129 0.031 0.0069 0.0576 0.0054 表 2 夹杂物的热膨胀系数(α)值(273~1273 K)
Table 2. Thermal expansion coefficient (α) values of inclusions(273~1 273 K)
物质 热膨胀系数×106 物质 热膨胀系数×106 γ-Fe 20.0~23.0 Ce2S3 12.7 TiN 10 Ce3S4 12.5 SiO2 0.5 La2O3 13.6 Ti2O3 ≤10 CeO2 13.2 MnO·Al2O3 8 Ce2O3 13.6 2 MnO·2 Al2O3·5 SiO2 2.0 LaS 11.5 莫来石Al2O3·SiO2 5.3 Ce2O2S 12.0 La2S3 10.4 La2O2S 12.0 La3S4 11.4 CeAlO3 10.0 CeS 12.3 LaAlO3 10.0 -
[1] Jiang M Z, Yu Y C, Li H, et al. Effect of rare earth cerium addition on microstructures and mechanical properties of low carbon high manganese steels[J]. High Temperature Materials and Processes, 2017,36(2):145−153. doi: 10.1515/htmp-2015-0183 [2] Milyutsa V G, Tsukanova V V, Malykhinab O Y, et al. Effect of complex inoculation of a high-strength shipbuilding steel on the composition and morphology of nonmetallic inclusions[J]. Inorganic Materials:Applied Research, 2014,5(6):554−561. doi: 10.1134/S2075113314060070 [3] Yang Jialin, Jiang Mingzhen, Cui Zilong, et al. Effect of Ce addition on microstructures and properties of 65Mn steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2015,36(6):141−149. (杨佳林, 姜名贞, 崔子龙, 等. 微量Ce对65Mn钢微观组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2015,36(6):141−149. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2015.06.026 [4] Yang Jichun, Yu Haicun, Gao Jianjun. Effects of Ce on the microstructure and mechanical mroperties of A36 ship plate steel[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2015,36(5):43−48. (杨吉春, 余海存, 高建军. Ce对A36船板钢显微组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 稀土, 2015,36(5):43−48. [5] Meng Xianghai, Wang Zhe, Bi Sheng, et al. Research progress on microstructure and properties of high strength ship plate steel treated by rare earth Ce[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2021,50,(1):1−5. (孟祥海, 王哲, 毕胜, 等. 稀土Ce处理的高强船板钢的组织与性能研究进展[J]. 热加工工艺, 2021,50,(1):1−5. [6] Byun J S, Shim J H, Cho Y W, et al. Non-metallic inclusion and intra-granular nucleation of ferrite in Ti-killed C-Mn steel[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003,51(6):1593−1606. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(02)00560-8 [7] Madariaga I, Gutierrez I, Andres C G, et al. Acicular ferriteformation in a medium carbon steel with a two stage continuous cooling[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1999,41(3):229−235. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6462(99)00149-9 [8] Kivio M, Holppa L, Iung T. Addition of dispersoid titanium oxide inclusions in steel and their influence on grain refinement[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2010,41(6):1194−1204. doi: 10.1007/s11663-010-9416-y [9] Sarma D S, Karasev A V, Jonsson P G. On the role of non-metallic inclusions in the nucleation of acicular ferrite in steels[J]. ISIJ International, 2009,49(7):1063−1074. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.49.1063 [10] Liu Y Q, Wang L J, Chou K C. Effect of cerium on the cleanliness of spring steel used in fastener of high-speed railway[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2014,32(8):759. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(14)60137-X [11] Grong Q, Kolbeinsen L, Casper Van Der Eijk, et al. Microstructure control of steels through dispersoid metallurgy using novel grain refining alloys[J]. ISIJ International, 2006,46(6):824−831. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.46.824 [12] Thewlis G. Effect of cerium sulphide particle dispersions on acicular ferrite microstructure development in steels[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2006,22(2):153−166. doi: 10.1179/026708306X81432 [13] Wakoh M, Sawai T, Mizoguchi S. Effect of content on the MnS precipitation in steel with oxide nuclei[J]. ISIJ International, 1996,36(8):1014−1021. [14] Lee J L, Pan Y T. Effect of sulfur content on the microstructure and toughness of simulated heat-affected zone in Ti-killed steels[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1993,24(6):1399−1408. doi: 10.1007/BF02668208 [15] Tomita Y, Saito N, Tsuzuki T, et al. Improvement in HAZ toughness of steel by TiN-MnS addition[J]. ISIJ International, 1994,34(10):829−835. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.34.829 [16] Deng X X, Jiang M, Wang X H. Mechanisms of inclusion evolution and intra-granular acicularferrite formation in steels containing rare earth elements[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica(English Letters), 2012,25(3):241−248. [17] Song M M, Song B, Hu C L, et al. Formation of acicular ferrite in Mg treated Ti-bearing C-Mn steel[J]. ISIJ International, 2015,55(7):1468−1473. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.55.1468 [18] Ohashi T, Hiromoto T, Fujii H, et al. Effect of oxides on nucleation behaviour in supercooled iron[J]. Tetsu-to-Haganne, 1976,62(6):614−623. doi: 10.2355/tetsutohagane1955.62.6_614 [19] Huang Cheng, Song Bo, Mao Jinghong, et al. Study on the mathematical model of inhomogeneous nucleation wetting angle[J]. Science In China-Ser. Engineering & Materials Science, 2004,34(7):737−742. (黄诚, 宋波, 毛境红, 等. 非均质形核润湿角数学模型研究[J]. 中国科学:E辑, 2004,34(7):737−742. [20] Jiao X Y, Fu W T, Shao W, et al. First-principles calculation on β-Fe/La2O3 interface properties and austenite refinement mechanism by La2O3[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2021,259:124194. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.124194 -





 下载:
下载: