Effect of different amounts of oil on electrochemical corrosion behavior of DC06 automobile steel
-
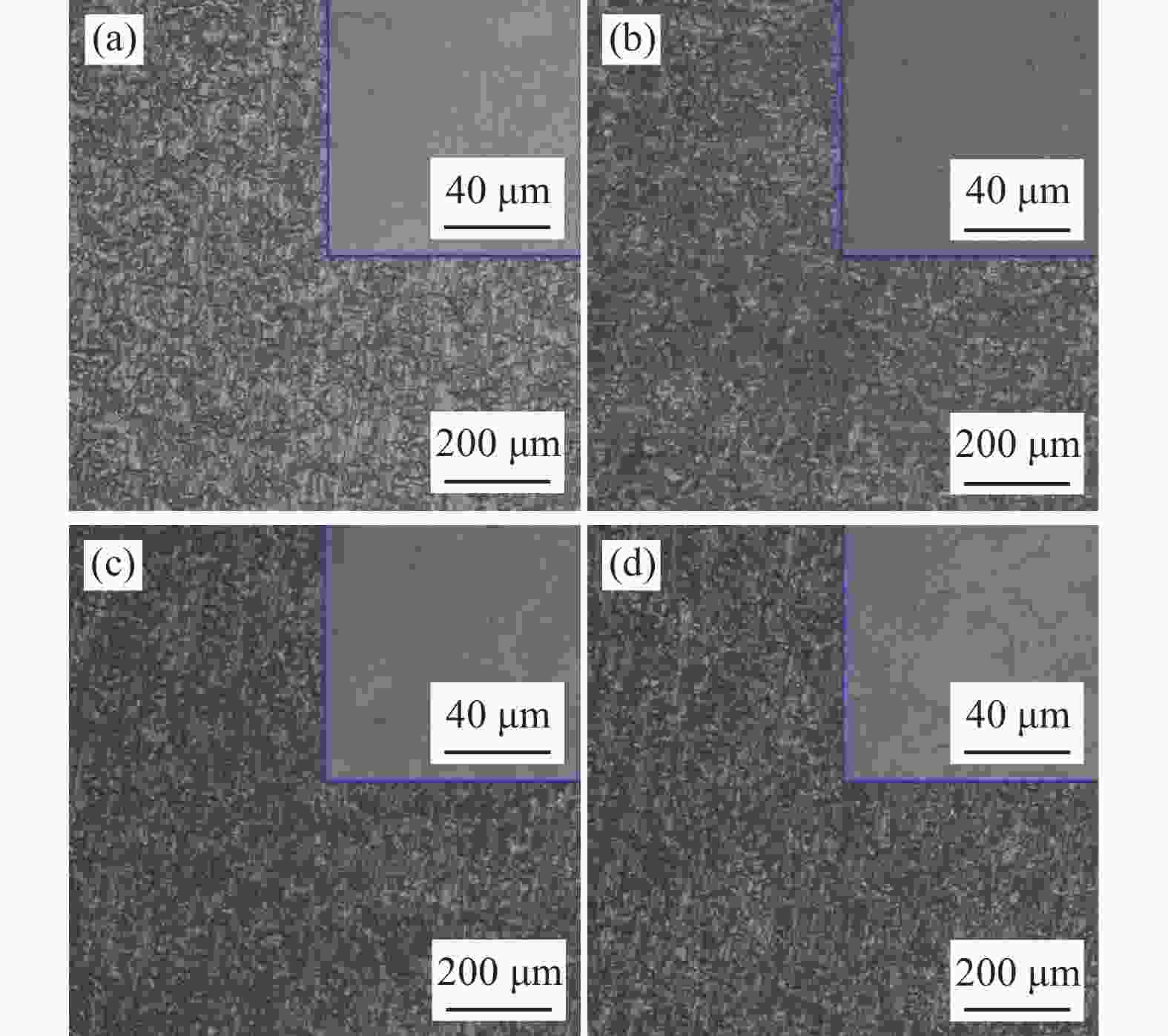
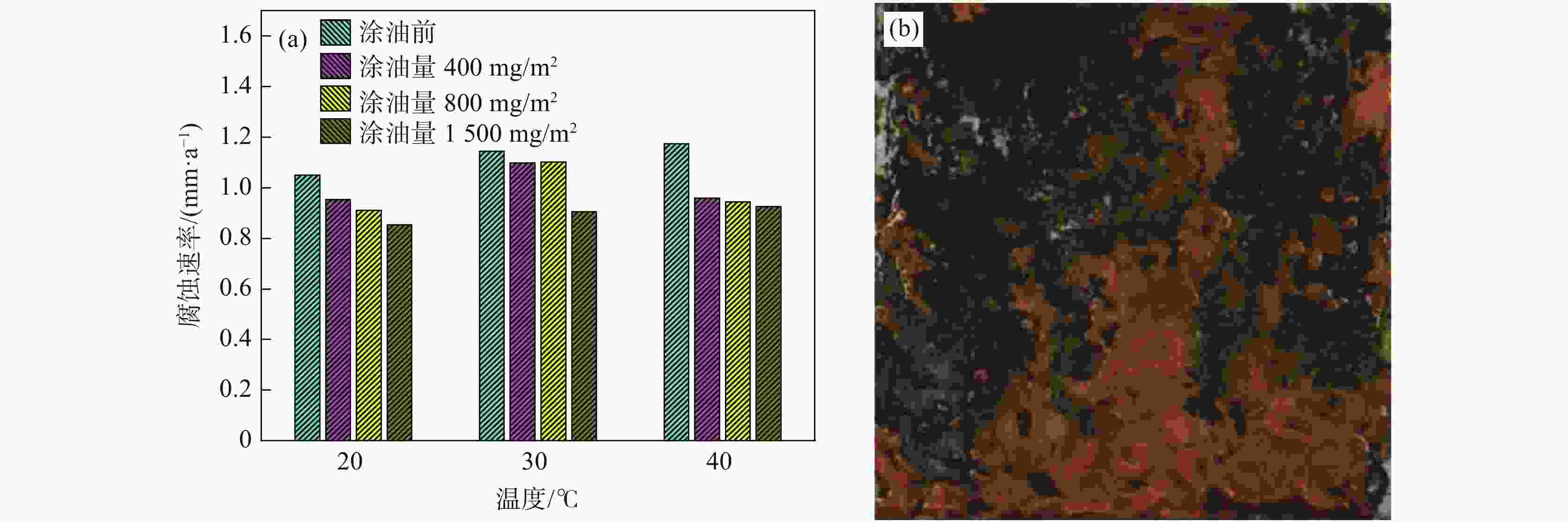
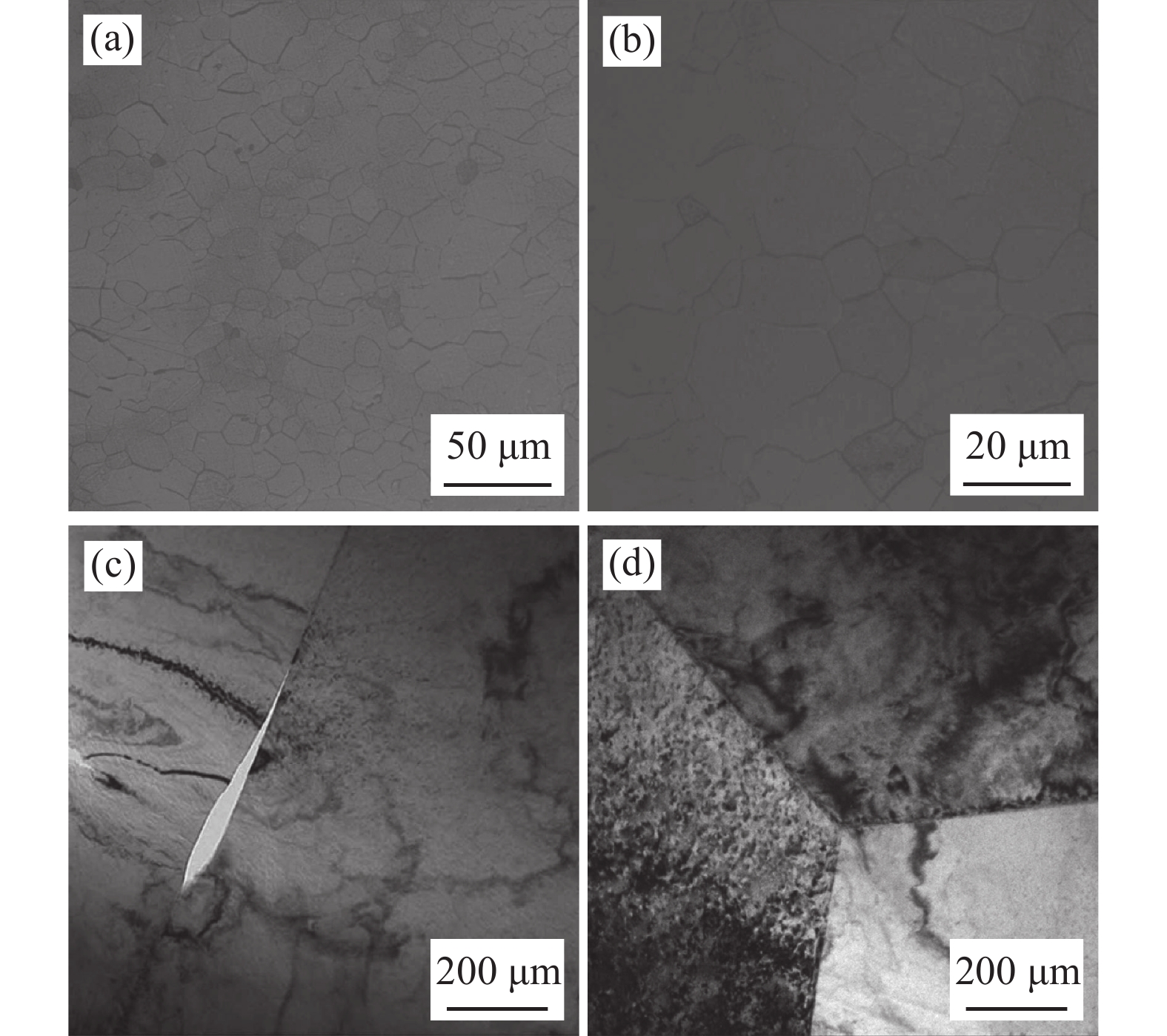
摘要: 利用恒温恒湿试验、电化学极化曲线测试及微区电化学阻抗测试试验对不同涂油量的DC06钢板在不同温度条件下的腐蚀规律进行了研究。结果表明:DC06钢板的腐蚀速率随温度增加而逐步提高,且当温度为40 ℃时,发生了严重的点蚀现象,随温度增加,腐蚀加快的程度越高。随着涂油量增加至1500 mg/m2,钢板的腐蚀速率下降了20%左右;DC06钢板在粗糙度为1.2 μm时具有最佳的耐腐蚀性能;DC06钢板腐蚀产物的活性溶解程度随温度的增加而加大,防锈油无法在高温条件下形成稳定的保护膜层,钢板表面存在不均匀的微区阻抗特性,共同导致高温条件下DC06钢板耐蚀能力的下降。Abstract: The electrochemical corrosion behavior of DC06 steel plate under different temperatures and oil content was studied by constant temperature and humidity, electrochemical polarization curve and local electrochemical impedance tests. The experimental results showed that the corrosion rate of the DC06 steel plate increased with the increase in temperature under different temperature conditions, and severe pitting corrosion occurred when the temperature was 40 °C. With the increase of oil content to 1500 mg/m2, the corrosion rate of steel plate decreased by about 20%, and with the increase in temperature, the corrosion performance improved; DC06 steel plate with a roughness of 1.2 μm can be obtained the optimum corrosion resistance. Moreover, the active dissolution degree of corrosion products of DC06 steel plate increased with the increase in temperature. The corrosion resistance of DC06 steel at high temperature was reduced due to the failure of antirust oil to form a stable protection film at high temperature and the uneven impedance characteristics of the micro area.
-
Key words:
- automobile steel /
- DC06 /
- potentiodynamic polarization curves /
- amount of oil
-
表 1 试验钢的主要合金成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of the tested steel
% 钢种 C Si Mn Al P S Cr Cu Ti Co DC06 0.001 0.003 0.05 0.028 0.004 0.007 0.011 0.043 0.072 0.024 -
[1] 李光瀛, 马鸣图. 我国汽车板生产现状及展望[J]. 轧钢, 2014, 31(4): 22.Li Guangying, Ma Mingtu. The present situation and prospect of automobile plate production in China[J]. Roll Steel, 2014, 31(4): 22. [2] 康永林, 朱国明. 中国汽车发展趋势及汽车用钢面临的机遇与挑战[J]. 钢铁, 2014, 49(12): 1.Kang Yonglin, Zhu Guoming. The development trend of Chinese automobiles and the opportunities and challenges faced by automobile steels[J]. Steel, 2014, 49(12): 1. [3] 李光瀛, 唐荻, 王先进. 汽车板深加工技术的发展[J]. 轧钢, 2013, 30(1): 1.Li Guangying, Tang Di, Wang Xianjin. The development of automobile plate deep processing technology[J]. Roll Steel, 2013, 30(1): 1. [4] 李麟, 何燕霖, 张梅,等. 先进高强度汽车钢板的研制[J]. 上海大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 17: 480.Li Lin, He Yanlin, Zhang Mei, et al. Research and development of advanced high strength automobile steel plate[J]. Journal of Shanghai University (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 17: 480. [5] Zhong Qingdong, Rohwerder Michael, Zhang Zhao. Study of lubricants and their effect on the anti-corrosion performance as temporarily protective oil coatings[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2004,185(2/3):234−239. [6] Bhagavathi L R, Chaudhari G P, Nath S K. Mechanical and corrosion behavior of plain low carbon dual-phase steels[J]. Materials & Design, 2011,32:433. [7] Chen Heng, Lu Lin, Huang Yunhua, et al. Insight into TiN inclusion induced pit corrosion of interstitial free steel exposed to aerated NaCl solution[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2021,13:13−24. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.04.046 [8] Yilmaz A, Traka K, Pletincx S, et al. Effect of microstructural defects on passive layer properties of interstitial free (IF) ferritic steels in alkaline environment[J]. Corrosion Science, 2021,182:109271. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2021.109271 -





 下载:
下载: