Effect of heating rate on austenitization of as-cast 60Si2Mn steel
-
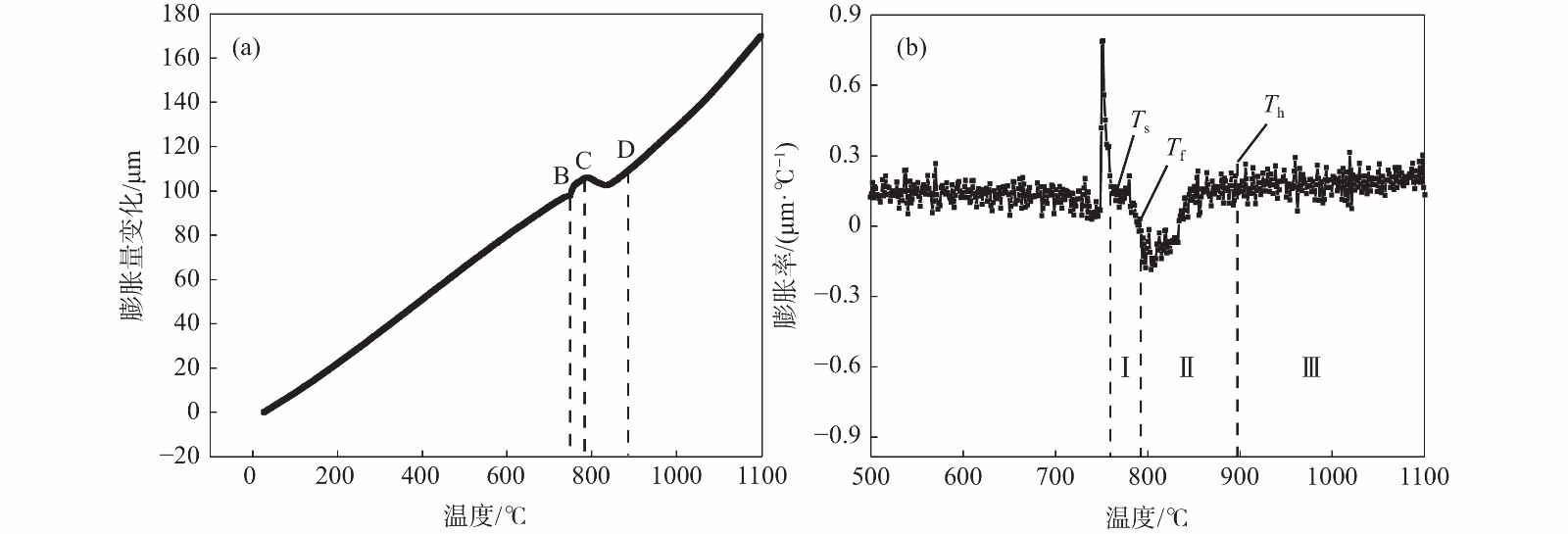
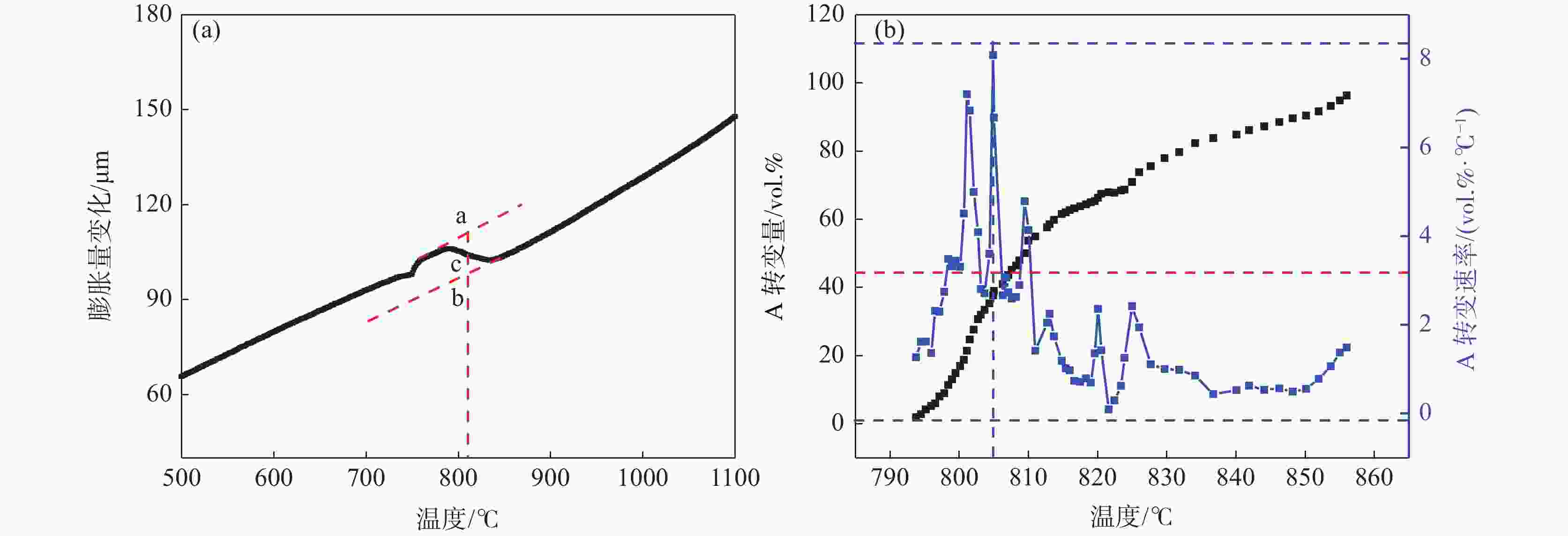
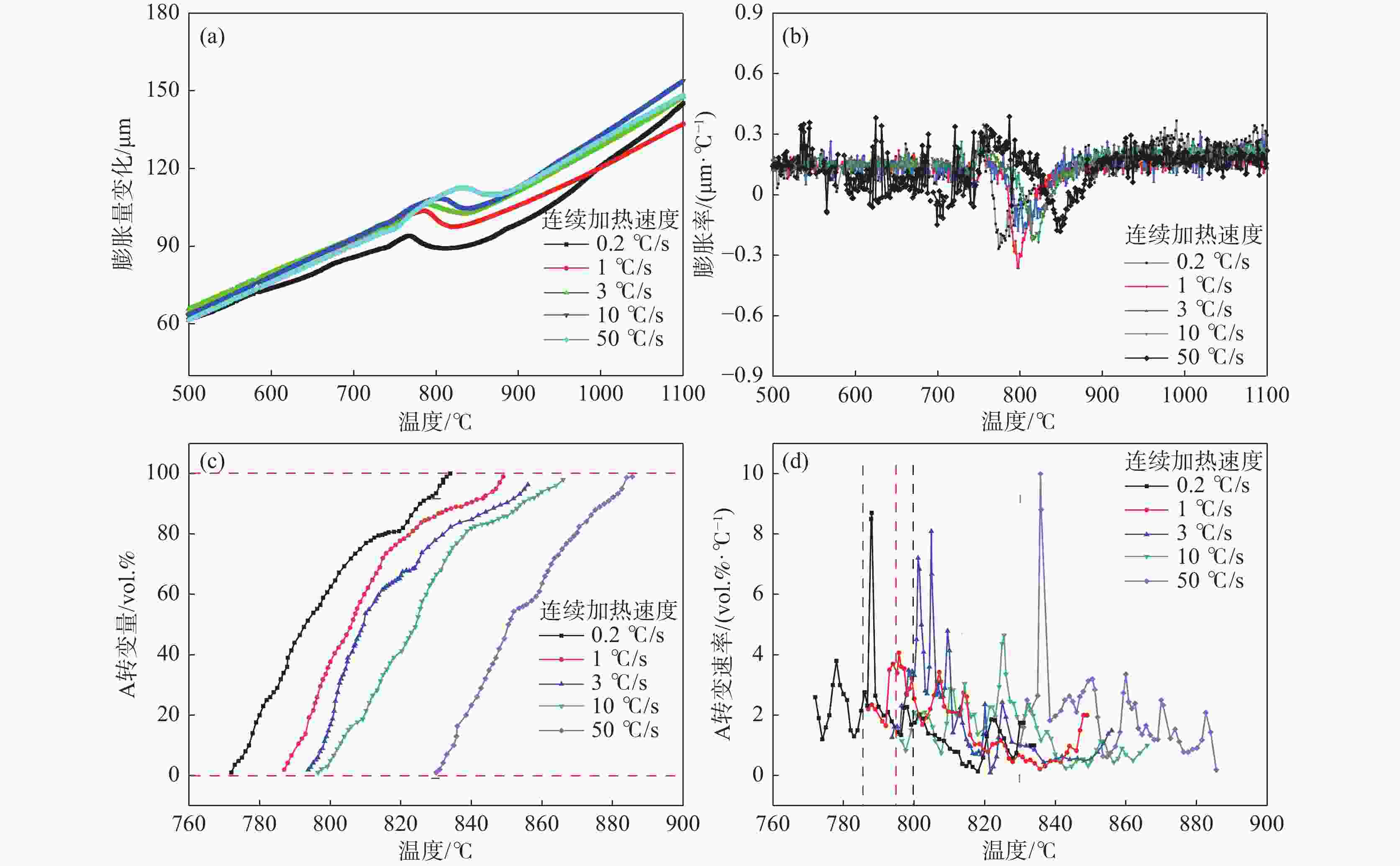
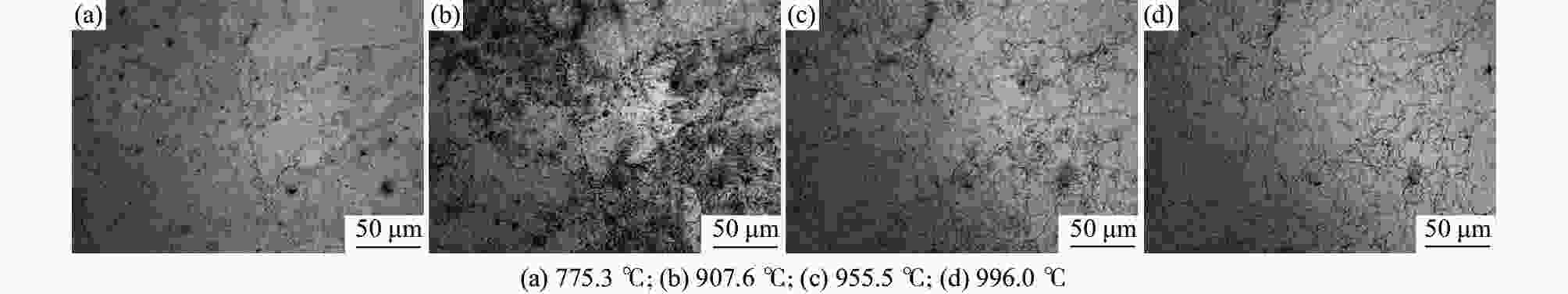
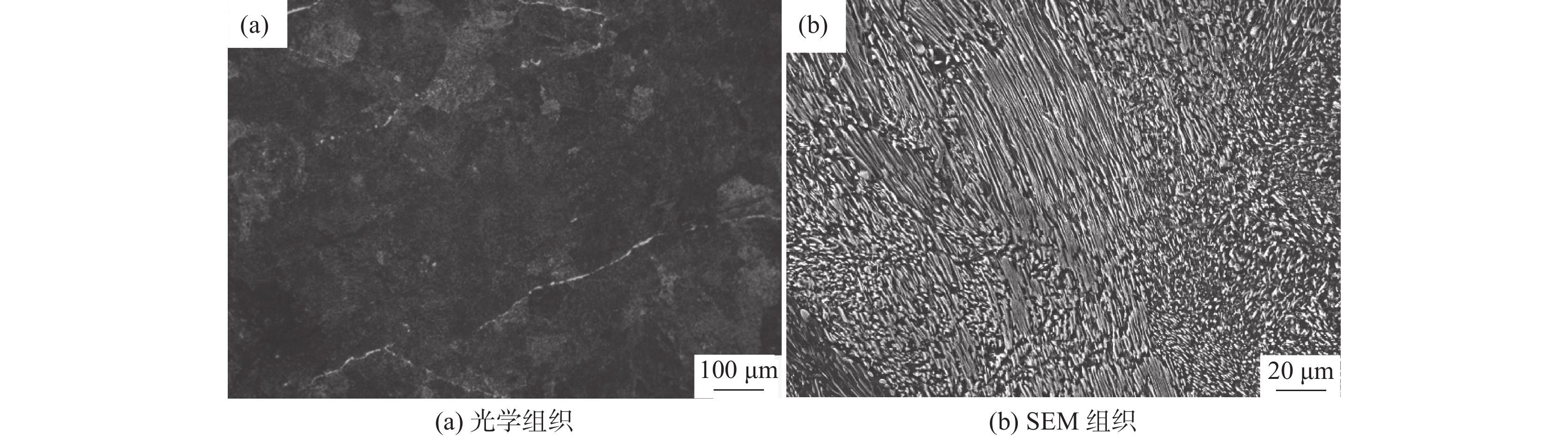
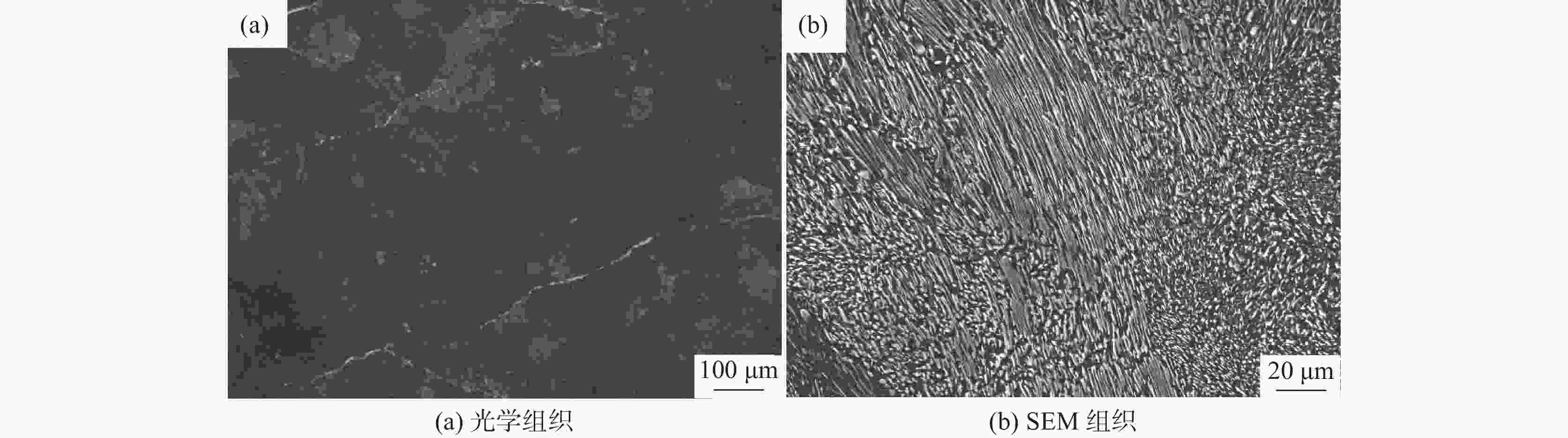
摘要: 利用DIL805A热膨胀仪记录了铸态60Si2Mn钢在不同的加热速率下(0.2、1、3、10、50 ℃/s)的线膨胀系数,获得了各自的热膨胀曲线和奥氏体体积转变分数曲线,研究了加热速率对奥氏体化的影响。采用高温金相显微镜对该钢在连续加热过程中的奥氏体转变过程进行了观察分析。结果表明:60Si2Mn钢在连续加热过程中的奥氏体转变可分为三个阶段:珠光体向奥氏体的转变、(Mn,Fe)3C向奥氏体中的溶解和奥氏体的成分均匀化。随着加热速率提高,相变临界温度提高,相变速率提高。通过高温金相可以观察到,在连续加热过程中,铸态60Si2Mn钢的A转变是一个形核和长大交替进行的过程,并且由于Si元素含量的不同,导致这个过程是不连续的。Abstract: The linear expansion coefficient of as-cast 60Si2Mn steel at different heating rates (0.2, 1, 3, 10, 50 ℃/s) was recorded using the thermal dilatometer DIL805A. The corresponding thermal expansion curves and volume transformation fraction curves (austenite) were obtained to study the effect of heating rate on austenitization. A high-temperature metallurgical microscope was used to observe and analyze the austenite transformation process of the steel during continuous heating. Studies have shown that the austenite transformation of 60Si2Mn steel during continuous heating can be divided into three stages: the transformation of pearlite to austenite, the dissolution of (Mn,Fe)3C into austenite and the composition of austenite homogenizing. And as the heating rate increases, the critical temperature of phase transition increases, and the rate of phase transition increases. In addition, high-temperature metallography shows that the A transformation of the as-cast 60Si2Mn steel during the continuous heating process is an alternate nucleation and growth process. This process is discontinuous due to the difference in Si element content.
-
表 1 60Si2Mn主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of 60Si2Mn steel
% C Si Mn P S Cr Ni Cu 0.56~0.64 1.6~2.0 0.7~1.0 ≤0.025 ≤0.025 ≤0.35 ≤0.35 ≤0.25 -
[1] Wang Xiaodong. Development status and trend analysis of high strength spring steel[J]. China’s Manganese Industry, 2017,35(4):104−106. (王筱冬. 高强度弹簧钢的发展现状和趋势分析[J]. 中国锰业, 2017,35(4):104−106. [2] Huo Dongmei, Xiao Bangguo. Production status and development prospect of spring steel in China[J]. Metallurgical Economics and Management, 2015,(5):8−11. (霍咚梅, 肖邦国. 我国弹簧钢生产现状及发展展望[J]. 冶金经济与管理, 2015,(5):8−11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1779.2015.05.003 [3] Geng Zhijiang, Yue Xinsheng, Ren Xiangyang, et al. The heat treatment technology comprehensive evaluation of spring steel 60Si2Mn[J]. New Technology, New Process, 2003,(1):30−31. (耿志江, 岳新生, 任向阳, 等. 60Si2Mn弹簧钢热处理工艺综述[J]. 新技术新工艺, 2003,(1):30−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5311.2003.01.013 [4] Wang Guitang, Lin Jinxuan. Optimization of heat treatment process on 60Si2Mn vehicle plate springs[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2005,(7):34−36. (王桂棠, 林金萱. 60Si2Mn钢汽车板簧热处理工艺优化研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2005,(7):34−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3814.2005.07.014 [5] Zhang Xingyuan, Xu Hongxing, Li Zhichao. Comparison of strengthening and toughing craft of 60Si2Mn cold-punched mould steel[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2005,(3):40−41. (张兴元, 徐宏兴, 李智超. 60Si2Mn冷冲模具钢强韧化工艺对比研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2005,(3):40−41. [6] Ling Wendan, Wang Hairui, Li Xiaofei. Effect of intercritical hardening on microstructure and strength and toughness of quenched 60Si2Mn steel[J]. Heat Treatment Technology and Equipment, 2010,31(4):13−16. (凌文丹, 王海瑞, 李小飞. 亚温淬火对淬火态60Si2Mn钢组织与强韧性的影响[J]. 热处理技术与装备, 2010,31(4):13−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4971.2010.04.003 [7] Liu Juan, Chen Yulai, Jiang Haitao. Thermal deformation resistance of 60Si2Mn spring steel and its mathematical model[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2011,35(11):44−46. (刘娟, 陈雨来, 江海涛. 60Si2Mn弹簧钢的热变形抗力及其数学模型[J]. 机械工程材料, 2011,35(11):44−46. [8] Wang Xiaoxi, Wang Bao, Zhou Jian,an, et al. Effect of boron on continuous cooling transformation behavior of 60Si2Mn spring steel[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2019,48(10):181−184. (王晓茜, 王宝, 周建安, 等. 硼对60Si2Mn弹簧钢连续冷却相变行为的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2019,48(10):181−184. [9] Sun Wei, Zhang Weixing, Zhang Huixing, et al. Study on control of continuous cooling structure of 60Si2Mn spring steel[J]. China Measurement & Test, 2020,46(2):137−142. (孙伟, 张炜星, 张慧星, 等. 60Si2Mn弹簧钢连续冷却组织调控研究[J]. 中国测试, 2020,46(2):137−142. [10] Duan Baoyu, Liu Zongchang, Bai Yaqiong, et al. Undercooled austenite isothermal transformation diagram and microstructure of P92 steel[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2016,40(12):16−20. (段宝玉, 刘宗昌, 白雅琼, 等. P92钢的过冷奥氏体等温转变曲线及显微组织[J]. 机械工程材料, 2016,40(12):16−20. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl201612005 [11] Pan Hui, Liu Yazheng, Cui Juan, et al. Study on controlled rolling and cooling process parameters of high-quality spring steel 60Si2Mn for automobile[J]. Steel Rolling, 2006,(5):20−23. (潘辉, 刘雅政, 崔娟, 等. 汽车用优质60Si2Mn弹簧钢控轧控冷工艺研究[J]. 轧钢, 2006,(5):20−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9996.2006.05.007 [12] Wen Ming, Ma Xiaoli, Gu Nanju, et al. Study on heating phase transition of 60Si2Mn steel[J]. Material Science & Technology, 1994,(3):55−60. (温鸣, 马晓莉, 谷南驹, 等. 60Si2Mn钢加热相变研究[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 1994,(3):55−60. [13] Eggbauer A, Lukas M, Ressel G, et al. In situ analysis of the effect of high heating rates and initial microstructure on the formation and homogeneity of austenite[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2019,54(12):9197−9212. doi: 10.1007/s10853-019-03527-3 [14] Ågren J, Vassilev G P. Computer simulations of cementite dissolution in austenite[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1984,64(1):95−103. doi: 10.1016/0025-5416(84)90076-4 [15] Li Junjie, Godfrey Andrew, Liu Wei, et al. Investigation of austenitization during continuous heating process in hypereutectoid steels[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2014,50(10):1179−1188. (李俊杰, Godfrey Andrew, 刘伟, 等. 连续加热条件下过共析钢奥氏体化研究[J]. 金属学报, 2014,50(10):1179−1188. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2014.00078 [16] Wen Ming, Ma Xiaoli, Meng Xianling, et al. Research on heating transformation of some die steels[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 1989,(10):12−19. (温鸣, 马晓莉, 孟宪玲, 等. 几种模具钢加热相变的研究[J]. 金属热处理, 1989,(10):12−19. -




 下载:
下载: