Study on effect of Al-Zn composite salt treatment on the quality of rutile TiO2
-
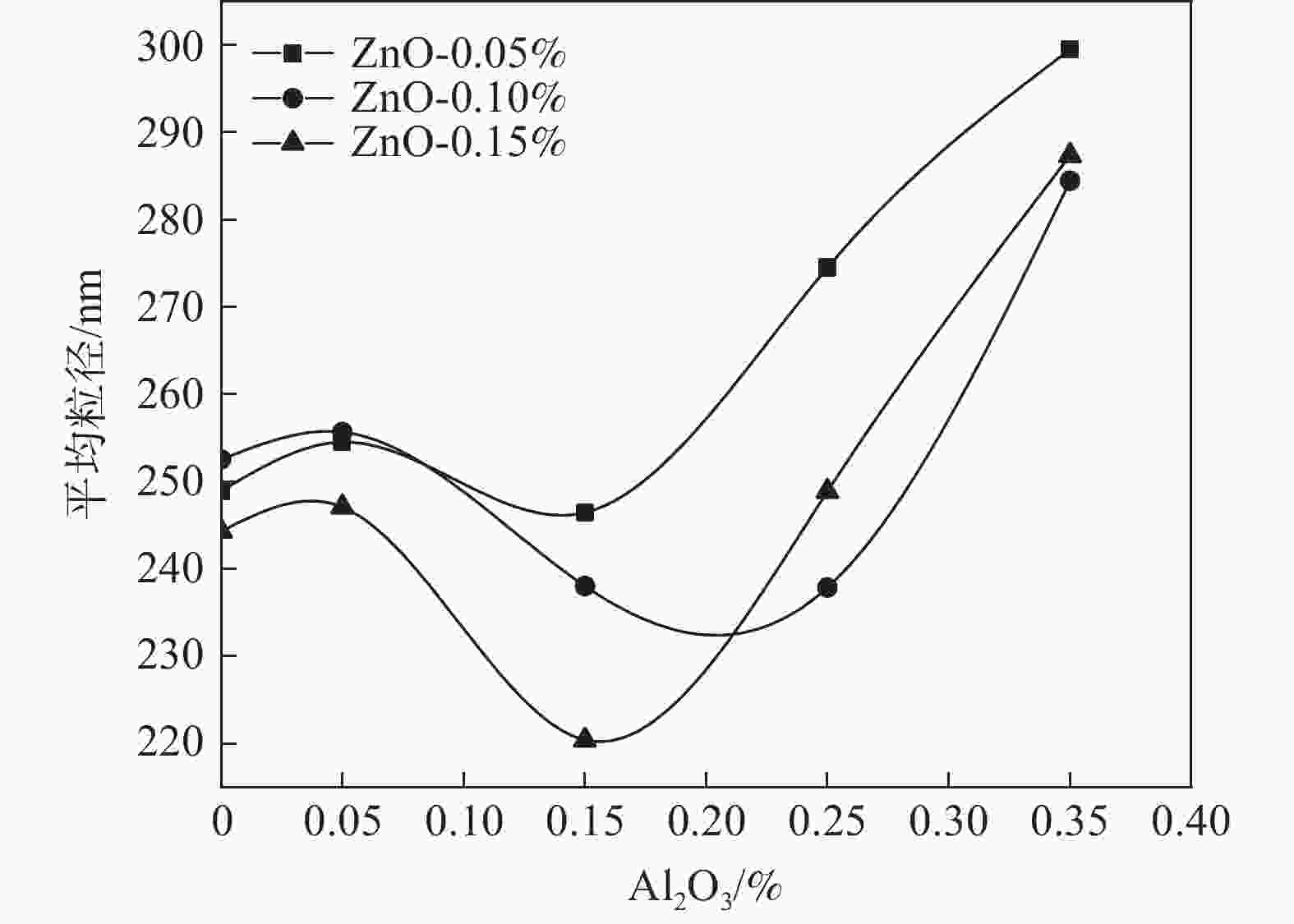
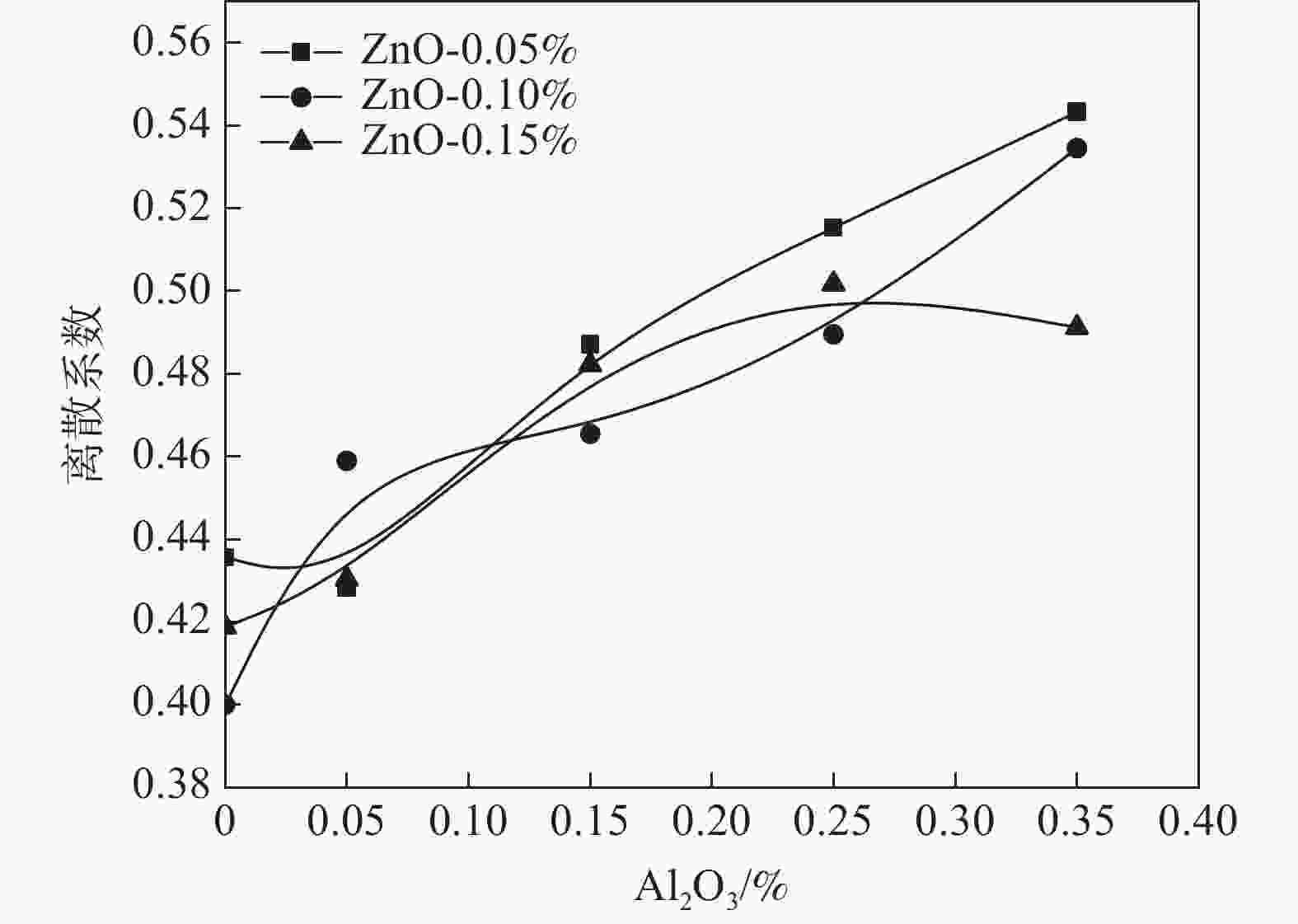
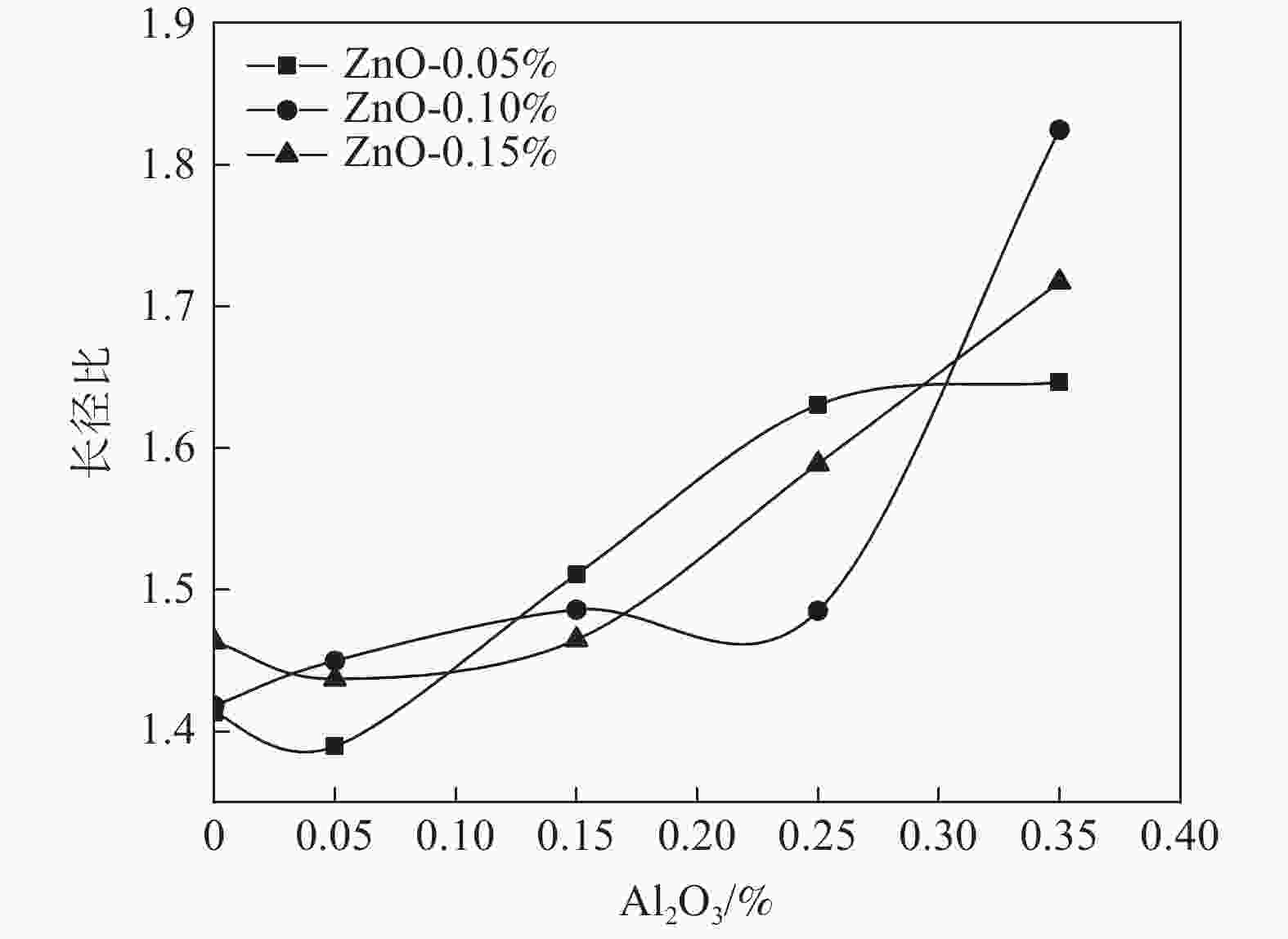
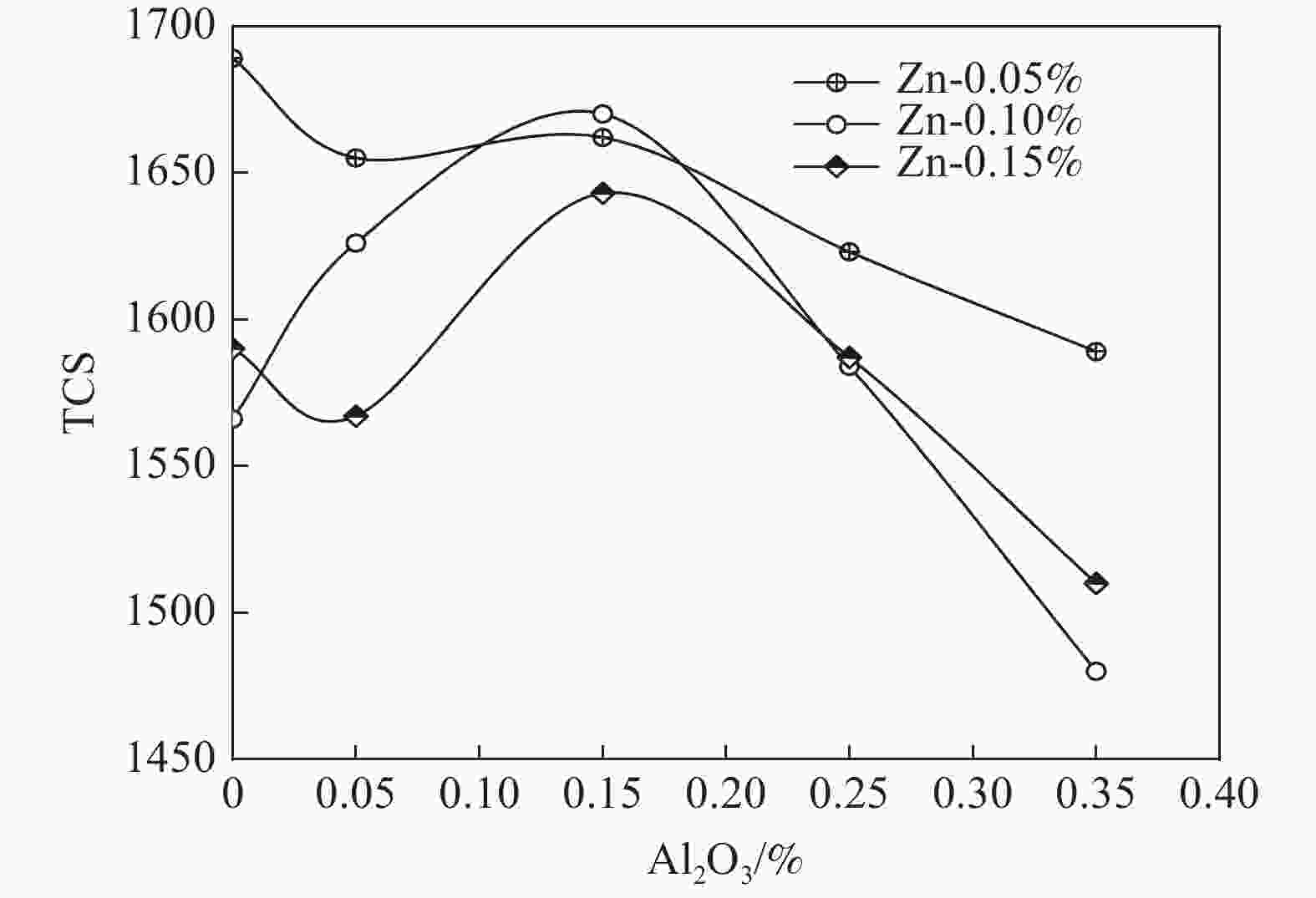
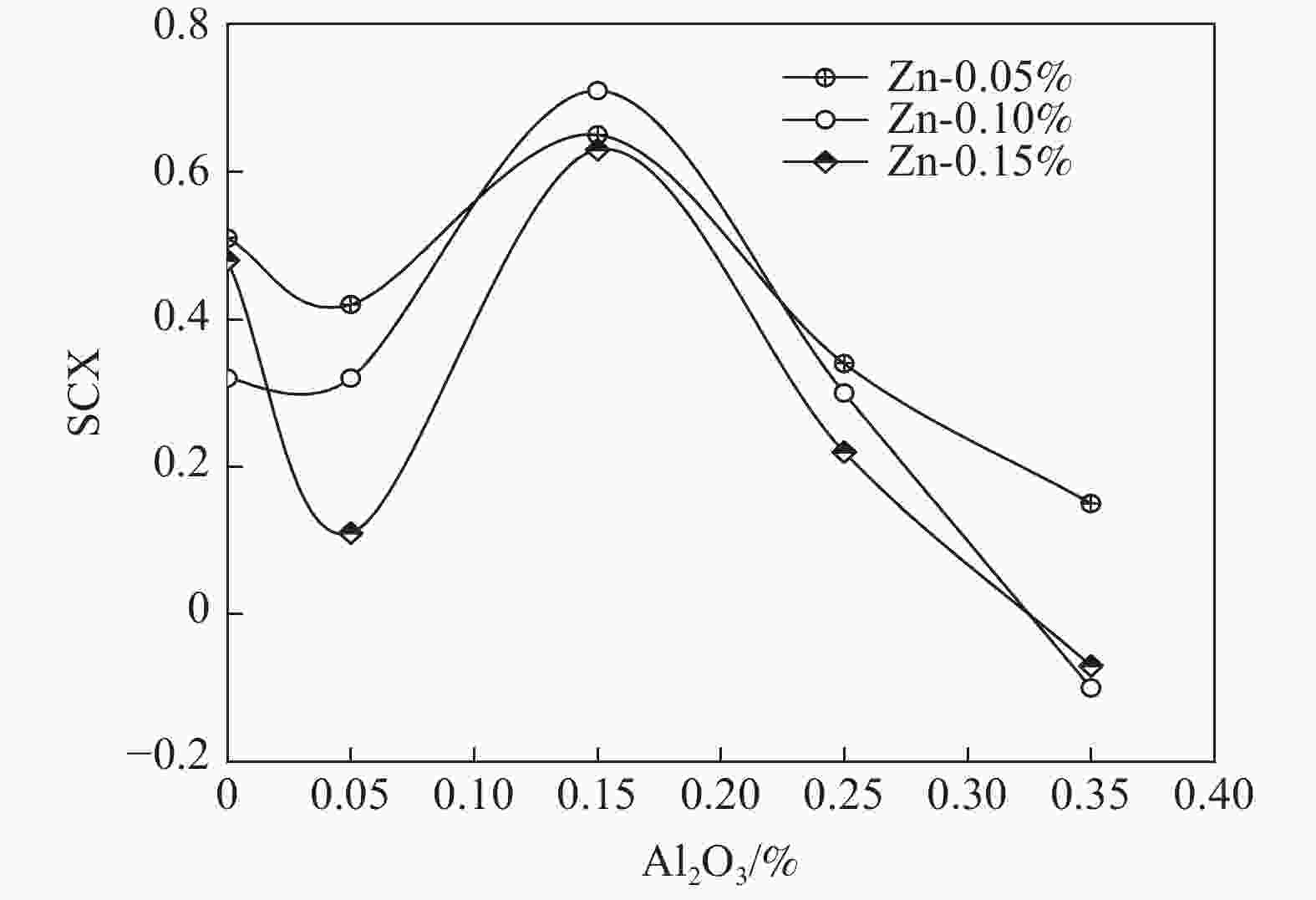
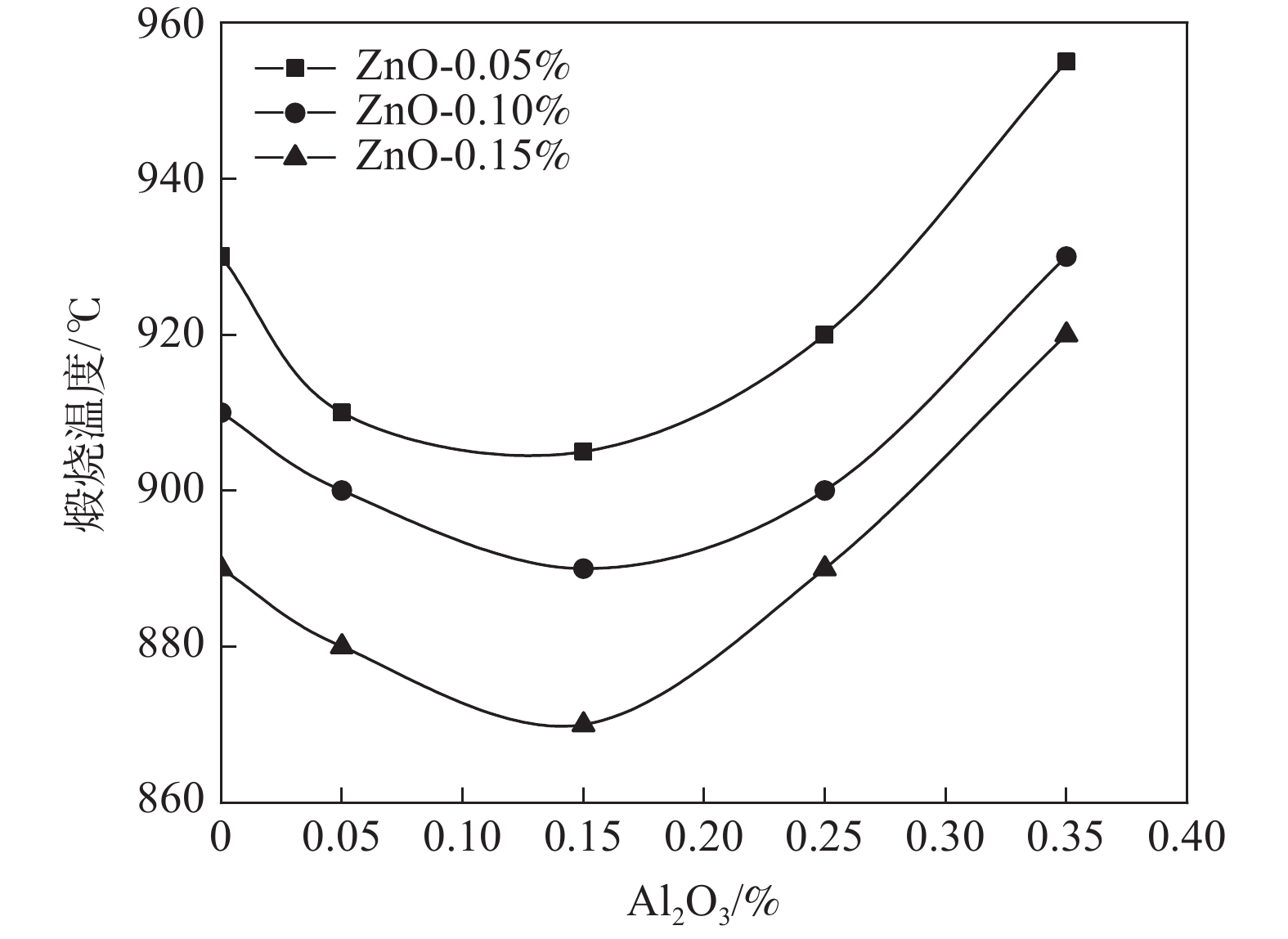
摘要: 以水解偏钛酸为原料,开展铝锌复合盐处理对金红石型二氧化钛质量的影响研究。通过调整煅烧温度制备金红石转化率合格的二氧化钛样品,考察Al2O3和ZnO加量对金红石合格所需煅烧温度的影响。然后对金红石合格的二氧化钛样品的粒度分布和形貌以及颜料性能进行分析。结果表明:在铝锌复合盐处理体系中,Al2O3加量较低时促进金红石转化,Al2O3加量较高时抑制金红石转化;ZnO促进金红石转化。随着Al2O3加量的增加,样品的TCS和SCX先增加后降低、平均粒径先降低后增加、离散系数变大、长径比增加、粒子逐渐由椭球形长成长条形;Al2O3加量0.15%时样品TCS和SCX最好、平均粒径最小。随着ZnO加量的增加,样品的TCS和SCX、平均粒径、离散系数、长径比均无明显变化规律;Al2O3加量0.15%时随ZnO加量的增加,样品平均粒径减小,长径比减小,粒子逐渐由长条形长成椭球形。Abstract: Using hydrolyzed metatitanic acid as raw materials, the effect of Al-Zn composite salt treatment on the quality of rutile TiO2 was studied. Rutile TiO2 samples were prepared by adjusting the calcination temperature. The effects of the addition of Al2O3 and ZnO on the calcination temperature required for rutile qualification were investigated. The pigment properties, particle size distribution and morphology of the rutile TiO2 were then analyzed. The results show that for the Al-Zn composite salt treatment system, the low addition of Al2O3 promotes the rutile transformation, and the high addition of Al2O3 inhibits the rutile transformation; ZnO promotes rutile transformation. With the increase of Al2O3 dosage, TCS and SCX first increase and then decrease, the mean diameter first decreases and then increases, the coefficient of variation increases, the length-diameter ratio increases, and the particles gradually grow from ellipsoid to strip. When the dosage of Al2O3 is 0.15%, the TCS and SCX of the sample are the best and the average particle size is the smallest. With the increase of ZnO dosage, the TCS and SCX, average particle size, dispersion coefficient and aspect ratio have no obvious variation rules. When the addition of Al2O3 is 0.15%, with the increase of ZnO addition, the mean diameter decreases, the length-diameter ratio decreases, and the particles gradually grow from long strip to ellipsoid.
-
Key words:
- titanium dioxide /
- metatitanic acid /
- salt treatment /
- mean diameter /
- coefficient of variation /
- length-diameter ratio
-
表 1 试验所用主要设备
Table 1. Main experimental facilities for sample preparation
名 称 型号 生产商 用 途 马弗炉 TM3010P 北京盛安科技有限公司 煅 烧 三头研磨机 RK/XPM-Ø120*3 武汉洛克粉磨设备制造有限公司 样品研磨 色差仪 Ci6X American X-rite Pantone 颜料性能检测 拉曼光谱仪 DXR532 ThermoFisher 金红石含量检测 扫描电镜 JSM-7001F 日本电子株式会社 形貌和粒度检测 X-ray衍射仪 X'Pert Pro 帕纳科 晶型分析 表 2 盐处理方案
Table 2. Scheme of salt treatment
% 编号 K2O P2O5 ZnO Al2O3 煅烧晶种 ZnO-0.05%系列 0.37 0.03 0.05 0 5.5 0.37 0.03 0.05 0.05 5.5 0.37 0.03 0.05 0.15 5.5 0.37 0.03 0.05 0.25 5.5 0.37 0.03 0.05 0.35 5.5 ZnO-0.10%系列 0.37 0.03 0.10 0 5.5 0.37 0.03 0.10 0.05 5.5 0.37 0.03 0.10 0.15 5.5 0.37 0.03 0.10 0.25 5.5 0.37 0.03 0.10 0.35 5.5 ZnO-0.15%系列 0.37 0.03 0.15 0 5.5 0.37 0.03 0.15 0.05 5.5 0.37 0.03 0.15 0.15 5.5 0.37 0.03 0.15 0.25 5.5 0.37 0.03 0.15 0.35 5.5 -
[1] 陈朝华, 刘长河. 钛白粉生产及应用技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007.Chen Chaohua, Liu Changhe. Production and application technology of titanium dioxide[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2007. [2] Tioxide Group Limited. Manufacture and general properties of titanium dioxide pigments[M]. London: Tioxide Ltd., 1992. [3] Lin Zhihua. Characteristics and application of titanium dioxide in China[J]. Shanghai Dyestuffs, 2020,48:56−59. (林治华. 国内钛白粉的特性和用途[J]. 上海染料, 2020,48:56−59.Lin Zhihua. Characteristics and application of titanium dioxide in China[J] . Shanghai Dyestuffs , 2020, 48: 56-59. [4] Wu You. Analysis and forecast of supply and demand in global titanium dioxide market[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2017,34(5):7−11. (吴优. 全球钛白市场供需现状分析及预测[J]. 钛工业进展, 2017,34(5):7−11.Wu You. Analysis and forecast of supply and demand in global titanium dioxide market[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2017, 34(5): 7-11. [5] Piccolo L, Paolinelli A, Pellizzon T. Process for the hydrolysis of titanium sulphate solutions, US: 4014977[P]. 1977-03-29. [6] Tian C, Huang S, Yang Y. Anatase TiO2 white pigment production from unenriched industrial titanyl sulfate solution via short sulfate process[J]. Dyes and Pigments, 2013,96:609−613. doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2012.09.016 [7] Wang Z, Chen K, Zhu J, et al. Formation mechanism of rutile in sulfate process[J]. Materials Science and Engineering(IOP Conference Series), 2019,562:012002. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/562/1/012002 [8] 陈俊. 钛白粉生产过程关键工艺条件优化研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2011.Chen Jun. Study on optimization of key process conditions in titanium dioxide production process[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2011. [9] Gesenhues U, Rentschler T. Crystal growth and defect structure of Al3+-doped rutile[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1999,143(2):210−218. doi: 10.1006/jssc.1998.8088 [10] Hidalgo-Jimenez J, Wang Q, Edalati K, et al. Phase transformations, vacancy formation and variations of optical and photocatalytic properties in TiO2-ZnO composites by highpressure torsion[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2020,124:170−185. doi: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2019.08.010 [11] Ma J S, Wen M C, Lu C H. Reaction mechanism and kinetics analysis of the phase transformation of TiO2 from the anatase phase to the rutile phase[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics, 2013,24:2506−2512. doi: 10.1007/s10854-013-1125-2 [12] Rodríguez-Talavera R, Vargas S, Arroyo-Murillo R, et al. Modification of the phase transition temperatures in titania doped with various cations[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 1997,12:439−443. doi: 10.1557/JMR.1997.0065 [13] Anitha B, Abdul Khadar M. Anatase-rutile phase transformation and photocatalysis in peroxide gel route prepared TiO2 nanocrystals: Role of defect states[J]. Solid State Sciences, 2020,108:106392. doi: 10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2020.106392 [14] Jiang Guimin, Yan Jikang, Yang Gang, et al. Influencing factors of crystal phase transformation (A→R) of TiO2[J]. Materials Review (A):Summarize, 2016,30(10):95−100. (姜贵民, 严继康, 杨钢, 等. TiO2晶型转变(A→R)的影响因素[J]. 材料导报(A):综述篇, 2016,30(10):95−100.Jiang Guimin, Yan Jikang, Yang Gang, et al. Influencing factors of crystal phase transformation (A→R) of TiO2[J]. Materials Review (A): Summarize, 2016 , 30 (10): 95-100. [15] Wu Jianchun, Lu Ruifang, Ma Weiping. Analysis of difference between zinc salt and aluminum salt treated titanium dioxide[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(2):29−32. (吴健春, 路瑞芳, 马维平. 锌系与铝系盐处理钛白差异分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(2):29−32.Wu Jianchun, Lu Ruifang, Ma Weiping. Analysis of difference between zinc salt and aluminum salt treated titanium dioxide[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020, 41(2): 29-32. -




 下载:
下载: