Effect of biomass drying titanium concentrate on its acid hydrolysis performance
-
摘要: 针对生物质烘干钛精矿时出现酸解性能下降现象,通过对比不同烘干方式钛精矿酸解性能差异,查找了其对酸解性能的影响,并开展了酸解性能提升探索试验。试验结果表明:生物质直接烘干的钛精矿中混入生物质及其燃烧残渣后,其相对煤气直接烘干的钛精矿,酸解性能中酸解率及钛液抽速下降,且混入量越大,酸解率及钛液抽速下降越大;当生物质直接烘干的钛精矿C含量为煤气直接烘干钛精矿C含量的4倍时,在反应酸矿比增加0.02,反应酸浓度增加2%,熟化温度增加10 ℃,熟化时间增加1 h的条件下,其酸解率93.00%大于煤气直接烘干钛精矿酸解率90.91%,但其钛液100 mL抽速615 s低于煤气直接烘干钛精矿钛液100 mL抽速122 s,且随着酸解率的提升,钛液抽速降低,通过将生物质直接烘干的钛精矿与煤气直接烘干的钛精矿按照质量比5:95混合后进行酸解,其酸解率、钛液抽速与煤气直接烘干钛精矿的酸解率、钛液抽速基本一致。Abstract: In view of the decline of acid hydrolysis performance of titanium concentrate directly dried by biomass, the influence of different drying methods on acid hydrolysis performance of titanium concentrate were found by comparing the difference of acid hydrolysis performance of titanium concentrate, and the exploration test of improving acid hydrolysis performance was carried out. The results show that after a small amount of biomass fuel and its combustion residues mixed into the titanium concentrate directly dried by biomass fuel, the acid hydrolysis rate and the filtration rate of titanium liquid in the titanium concentrate are lower than that of the titanium concentrate directly dried by coal gas. The larger the mixed amount, the greater the drop in the acid hydrolysis rate and the filtration rate of titanium liquid. When the C content of direct-drying titanium concentrate with biomass is 4 times that of the direct-drying titanium concentrate with coal gas and keep the conditions of reaction acid-ore ratio increasing 0.02, reaction acid concentration increasing 2%, ripening temperature increasing 10 °C and ripening time increasing 1 h, the acid hydrolysis rate of titanium concentrate dried by biomass fuel is 93.00%, which is higher than 90.91% of titanium concentrate dried by coal gas. But the extraction rate of 100 mL titanium liquid is 615 s lower than 122 s of the latter. With the increase of acid hydrolysis rate, the pumping speed of titanium liquid decreases. The titanium concentrate directly dried by biomass fuel and coal gas are mixed according to the mass ratio of 5:95, the acid hydrolysis rate of titanium concentrate and the filtration rate of titanium liquid are almost the same as those of gas-drying titanium concentrate.
-
Key words:
- titanium concentrate /
- acid hydrolysis performance /
- drying /
- biomass /
- coal gas /
- acid hydrolysis rate /
- extraction rate
-
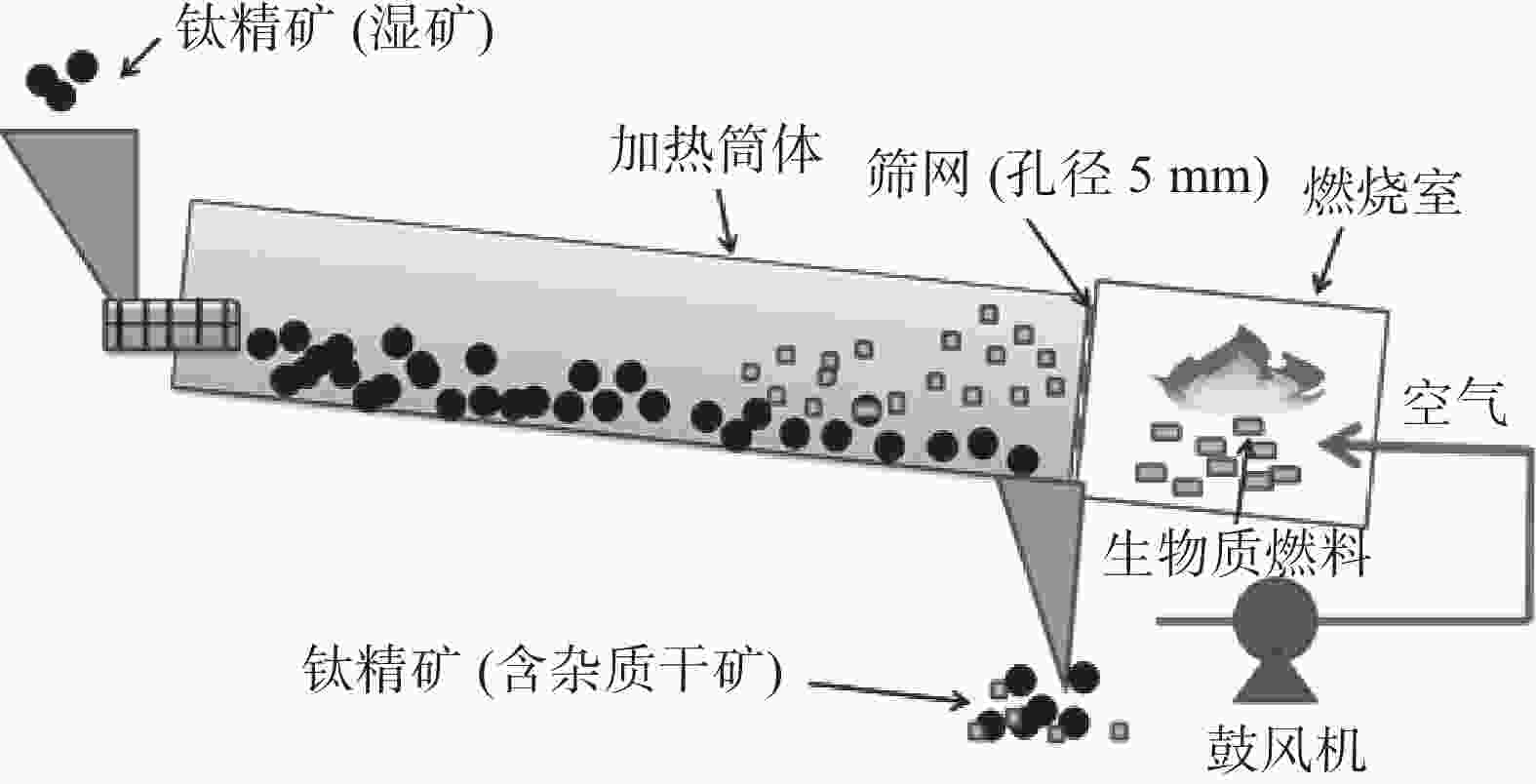
表 1 不同烘干方式的钛精矿主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical components of titanium concentrate with different drying methods
% 编号 C FeO MgO MnO TFe SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 烘干燃料 1 0.080 35.70 4.89 0.66 31.88 2.46 47.29 0.94 煤气 2 0.160 35.86 4.99 0.70 32.00 2.39 47.19 1.06 生物质 3 0.320 35.54 5.01 0.68 32.00 2.53 47.25 1.05 生物质 表 2 不同烘干方式钛精矿酸解试验结果
Table 2. Acid hydrolysis results of titanium concentrate with different drying methods
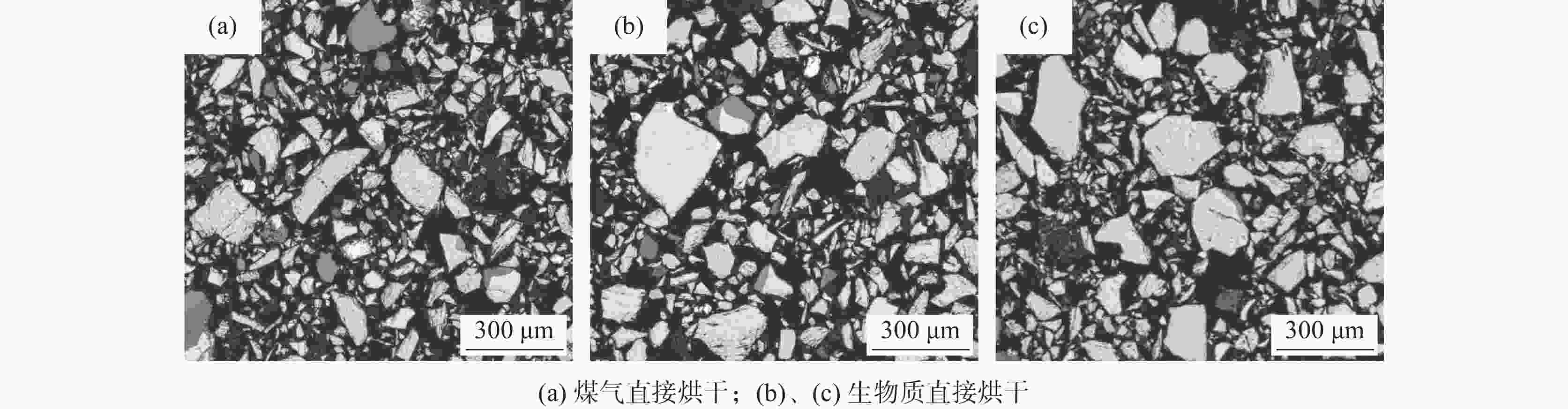
编号 100 mL抽速/s 酸解率/% 主反应体积膨胀/mL 上清液高度/mL 试验现象 1 120 90.74 500 400 沉降钛液上清液较多,
过滤后滤纸上基本无黑色残渣122 90.12 510 410 2 437 87.70 600 150 沉降钛液上清液较少,
过滤后滤纸上有黑色残渣435 87.60 590 143 3 450 78.72 1000 100 沉降钛液上清液较少,
过滤后滤纸上有黑色残渣448 78.07 1050 104 表 3 不同烘干方式的钛精矿粒度
Table 3. Particle sizes of titanium concentrate with different drying methods
钛精矿编号 研磨状态 D10 /μm D50 /μm D90/ μm 径距 烘干燃料 1 磨前 47.30 110.00 213.00 1.51 煤气 2 33.30 94.80 276.00 2.56 生物质 3 22.20 85.90 297.00 2.98 生物质 1-1 磨后 3.32 38.50 110.00 2.78 煤气 2-1 2.53 26.40 97.00 3.37 生物质 3-1 1.57 15.00 68.70 4.47 生物质 表 4 不同烘干方式钛精矿主要物相组成
Table 4. Main phase compositions of titanium concentrate with different drying methods
% 编号 钛铁矿 辉石 镁橄榄石 磁铁矿 透辉石 铁铝榴石 绿泥石 磁黄铁矿 铁板钛矿 金红石 榍石 斜长石 1 90.03 3.01 0.45 0.86 1.38 0.11 0.87 0.32 0.25 0.01 0.24 0.69 2 90.11 3.37 0.77 0.80 1.19 0.25 0.92 0.47 0.21 0.07 0.25 0.99 3 90.53 2.93 0.38 0.82 0.94 0.21 0.77 0.32 0.52 0.01 0.36 0.54 表 5 验证及优化试验
Table 5. Results of validation and optimization experiments
编号 矿-1∶矿-3 酸浓度/% 酸矿比 熟化温度/℃ 熟化时间/h 酸解率/% 100 mL抽速/s 备注 1 100∶0 83 1.58 155 2 90.91 122 空白 2 0∶100 83 1.58 155 2 78.56 448 3 0∶100 85 1.60 155 2 88.28 514 酸解工
艺优化4 0∶100 85 1.60 165 3 93.00 615 5 90∶10 83 1.58 155 2 87.06 186 互配
酸解6 95∶5 83 1.58 155 2 91.02 132 -
[1] Karimia L, Yazdanshenas M E, Khajavi R, et al. Optimizing the photocatalytic properties and the synergistic effects of graphene and nano titanium dioxide immobilized on cotton fabric[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015,332:665−673. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.01.184 [2] Romanovska N I, Manoryk P A, Ermokhina N I, et al. Effect of structural and dimensional characteristics of TiO2 and its photocatalytic activity in the oxidation of tetracycline[J]. Theoretical and Experimental Chemistry, 2019,55(5):345−353. doi: 10.1007/s11237-019-09627-0 [3] Sobczyk-guzenda Anna, Szymanski Witold, Jedrzejczak Anna, et al. Bactericidal and photowetting effects of titanium dioxide coatings doped with iron and copper/fluorine deposited on stainless steel substrates[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2018,347:66−75. [4] Matsukura A, Onoda H. Influences of additives on phosphoric acid treatment of titanium dioxide as a novel white pigment[J]. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2015,4(3):211−216. doi: 10.1007/s40145-015-0151-3 [5] Kang J, Okabe T H. Removal of iron from titanium ore by selective chlorination using TiCl4 under oxygen content atmosphere[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2016,149:111−118. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2016.02.014 [6] Bi Sheng. Status of titanium dioxide industry in China and the development prospect[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021,42(2):1−4. (毕胜. 近年中国钛白粉行业基本状况及发展展望[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2021,42(2):1−4. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2021.02.001Bi Sheng. In recent years, the basic situation and development prospect of titanium dioxide industry in China [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021, 42 (2): 1-4. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2021.02.001 [7] Sneha, Samal. Synthesis and characterization of titanium slag from ilmenite by thermal plasma processing[J]. Journal of Metals, 2016,68(9):1−10. [8] Hu Kai, Zhang Run, Li Shengping, et al. Conductivity and melt structure of TiO2-FeO-X ( SiO2, CaO, MgO ) ternary high titanium slag[J]. China Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2019,29(1):167−175. (胡凯, 张润, 李生平, 等. TiO2-FeO-X(SiO2, CaO, MgO)三元高钛渣导电特性及其熔体结构[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2019,29(1):167−175.Hu Kai, Zhang Run, Li Shengping, et al. Conductivity and melt structure of TiO2-FeO-X ( SiO2, CaO, MgO ) ternary high titanium slag [J]. China Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 29 (1) : 167-175. [9] Lu Changyuan, Zou Xingli, Lu Xionggang, et al. Hydrogen reduction kinetics of Panzhihua ilmenite[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016,26(12):3266−3273. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64460-6 [10] Wu Ling, Chen Jiabin, Zhong Shengkui, et al. Effect of mechanical activation-hydrochloric acid atmospheric leaching of ilmenite[J]. China Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015,25(1):211−219. (伍凌, 陈嘉彬, 钟胜奎, 等. 机械活化-盐酸常压浸出钛铁矿的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015,25(1):211−219. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63598-1Wu Ling, Chen Jiabin, Zhong Shengkui, et al. Effect of mechanical activation-hydrochloric acid atmospheric leaching of ilmenite [J]. China Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(1): 211-219. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63598-1 [11] Li Yu, Lei Ying, Zhang Libo, et al. Microwave drying characteristics and kinetics of titanium concentrate[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011,21(1):202−207. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60700-0 [12] Cai Ning, Chen Chaochun, Wang Yafu, et al. Heat transfer characteristics of vibrating fluidized bed for fine titanium concentrate[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2001,22(2):33−36. (蔡宁, 陈朝春, 王亚夫, 等. 微细粒级钛精矿振动流化床的传热特性[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2001,22(2):33−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7638.2001.02.006Cai Ning, Chen Chaochun, Wang Yafu, et al. Heat transfer characteristics of vibrating fluidized bed for fine titanium concentrate [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium , 2001 , 22(2): 33-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7638.2001.02.006 [13] Sun Yu, Meng Changfang. Study on NO emission characteristics of biomass/bituminous coal powder fuel under air staged combustion[J]. Energy and Environmental Protection, 2021,43(10):1−6. (孙禹, 孟长芳. 生物质/烟煤粉体燃料在空气分级燃烧下NO排放特性研究[J]. 能源与环保, 2021,43(10):1−6.Sun Yu, Meng Changfang. Study on NO emission characteristics of biomass/bituminous coal powder fuel under air staged combustion [J]. Energy and Environmental Protection, 2021, 43 (10): 1-6. [14] Li Xian, Han Kuihua, Wang Xi, et al. Research progress of biomass briquette fuel additives[J]. Renewable Energy, 2021,39(12):1563−1569. (李贤, 韩奎华, 王茜, 等. 生物质成型燃料添加剂的研究进展[J]. 可再生能源, 2021,39(12):1563−1569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5292.2021.12.001Li Xian, Han Kuihua, Wang Xi, et al. Research progress of biomass briquette fuel additives [J]. Renewable Energy, 2021, 39 (12): 1563-1569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5292.2021.12.001 [15] Liu Yufei, Tang Jie, Chen Xiaohui, et al. Estimation of thermodynamic properties of complex fuels[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2021,42(11):2775−2779. (刘宇飞, 唐洁, 陈小辉, 等. 复杂燃料热力学性质的估算研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2021,42(11):2775−2779.Liu Yufei, Tang Jie, Chen Xiaohui, et al. Estimation of thermodynamic properties of complex fuels [J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2021, 42 (11) : 2775-2779. [16] Richard G Haverkamp, Desiderius Kruger, Ranjeeth Rajashekar. The digestion of New Zealand ilmenite by hydrochloric acid[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2016,163:198−203. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2016.04.015 [17] Jonglertjunya, Woranart, Rattanaphan, et al. Kinetics of the dissolution of ilmenite in oxalic and sulfuric acid solutions[J]. Asia-Pacific Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2014,9(1):24−30. doi: 10.1002/apj.1742 [18] Parapari, ParisaSemsari, Irannajad, et al. Modification of ilmenite surface properties by superficial dissolution method[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2016,9(2):160−167. [19] Wang Haibo, Wu Xiaoping, Gao Jian, et al. Kinetics of sulfuric acid leaching of ilmenite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(6):6−10. (王海波, 吴小平, 高健, 等. 硫酸浸取钛铁矿动力学研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(6):6−10. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.06.002Wang Haibo, Wu Xiaoping, Gao Jian, et al. Kinetics of sulfuric acid leaching of ilmenite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium , 2020, 41 (6): 6-10. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.06.002 -




 下载:
下载: