Research and industrial practice on improving quality and reducing impurities of Baima vanadium-titanium magnetite
-
摘要: 为进一步提高钒钛铁精矿品位,实现高炉精料方针,针对攀西白马矿区某选矿厂生产的钒钛磁铁精矿开展了工艺矿物学研究,认为钛磁铁矿中客晶矿物的存在影响了铁精矿的理论品位,是钒钛铁精矿品位难以提高的主要原因。通过实验室试验和工业试验,提出采用提高磨矿细度进行深度选别技术路线可以有效降低铁精矿中SiO2、MgO、Al2O3等元素含量,从而进一步提高其铁精矿品位。研究成果在白马矿区某选矿厂进行了工业应用,将钒钛铁精矿品位由55%提高至57%以上,有效地提高了冶炼系统高品位钒钛铁精矿的保供能力,提升钢铁全产线的经济效益,为攀西地区钒钛磁铁矿精矿品位的提高提供了技术路线。Abstract: In order to further improve the grade of vanadium-titanium-iron concentrate and realize the policy of blast furnace concentrate, the process mineralogy of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate produced by a concentrator in Baima mining area of Panxi was studied. It is pointed out that the presence of guest minerals in titanomagnetite affects the theoretical grade of iron concentrate, which is the main reason why it is difficult to improve the grade of vanadium titanomagnetite concentrate. Through laboratory and industrial tests, it is proposed that the content of SiO2, MgO and Al2O3 in iron concentrate can be effectively reduced by increasing the grinding fineness for deep separation, and the grade of iron concentrate can be further improved. The research results have been applied to a concentrator in Baima mining area and the grade of V-Ti-Fe concentrate has been increased from 55% to over 57%, thus effectively increasing the supply and maintenance capacity of high-grade V-Ti-Fe concentrate in smelting system, improving the economic benefit of the whole steel production line, which provides a technical route for improving the grade of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate in Panxi area.
-
表 1 钒钛铁精矿化学元素分析结果
Table 1. Results of chemical element analysis of V-Ti-Fe concentrate
原料粒级/mm w/% TFe TiO2 V2O5 S SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO +0.25 47.04 9.10 0.56 0.51 11.28 5.43 1.49 6.84 −0.25~+0.15 50.69 10.09 0.62 0.46 7.80 4.77 1.04 5.58 −0.15~+0.10 52.88 10.38 0.67 0.45 5.78 4.12 0.75 4.50 −0.10~+0.075 55.44 10.65 0.72 0.50 4.55 3.92 0.59 3.94 −0.075~+0.045 56.22 10.67 0.73 0.53 3.60 3.62 0.54 3.38 −0.045~+0.034 57.54 10.80 0.75 0.61 3.36 3.55 0.43 3.20 −0.034~+0.028 57.57 10.67 0.74 0.56 3.05 3.44 0.37 2.91 −0.028 57.62 9.98 0.74 0.59 3.44 3.47 0.47 2.85 回算品位 55.81 10.29 0.71 0.54 4.35 3.77 0.59 3.57 化验品位 55.79 10.40 0.69 0.51 4.30 3.63 0.56 3.51 表 2 钒钛铁精矿全粒级矿物含量
Table 2. Full grain mineral content of V-Ti-Fe concentrate
% 钛磁铁矿 钛铁矿类 钛铁矿 硫化物 脉石 辉石 斜长石 橄榄石 86.59 2.53 2.90 1.13 2.16 1.92 2.77 表 3 钒钛铁精矿主要矿物单体解离度
Table 3. Dissociation degree of main mineral monomers of V-Ti-Fe concentrate
% 类别 单体 连生体 钛磁铁矿 钛铁矿类 硫化物 总脉石 钛磁铁矿 92.00 2.00 6.00 钛铁矿类 5.00 90.00 2.00 3.00 钛铁矿 37.63 42.37 6.00 14.00 硫化物 51.98 43.98 8.00 总脉石 39.88 34.88 2.00 3.00 表 4 钒钛铁精矿铁钛金属量平衡
Table 4. Metal balance of iron and titanium of V-Ti-Fe concentrate
% 矿物名称 矿物含量 TFe品位 TiO2品位 铁金属量 钛金属量 分布率 TFe TiO2 钛磁铁矿 86.59 62.27 8.97 53.92 7.77 95.26 75.22 钛铁矿类 2.53 30.00 40.00 0.76 1.01 1.34 9.80 钛铁矿 2.90 33.00 51.00 0.96 1.48 1.70 14.32 硫化物 1.13 55.00 0.62 1.10 总脉石 6.85 5.00 1.00 0.34 0.07 0.60 0.66 化学品位 55.79 10.40 56.60 10.33 100 100 表 5 钒钛铁精矿粒度筛析结果
Table 5. Particle size sieve analysis results of V-Ti-Fe concentrate
% 粒级/mm 产率 负累计
产率品位 分布率 TFe TiO2 TFe TiO2 +0.25 3.40 100.00 47.04 9.10 2.86 3.00 −0.25~+0.15 7.40 96.60 50.69 10.09 6.72 7.25 −0.15~+0.10 9.42 89.20 52.88 10.38 8.92 9.50 −0.10~+0.075 11.01 79.78 55.44 10.65 10.94 11.39 −0.075~+0.045 17.36 68.77 56.22 10.67 17.49 18.00 −0.045~+0.034 3.24 51.41 57.54 10.80 3.34 3.40 −0.034~+0.028 11.33 48.18 57.57 10.67 11.69 11.75 −0.028 36.84 36.84 57.62 9.98 38.04 35.72 A 100.00 55.81 10.29 100.00 100.00 表 6 钒钛铁精矿细磨深选试验结果
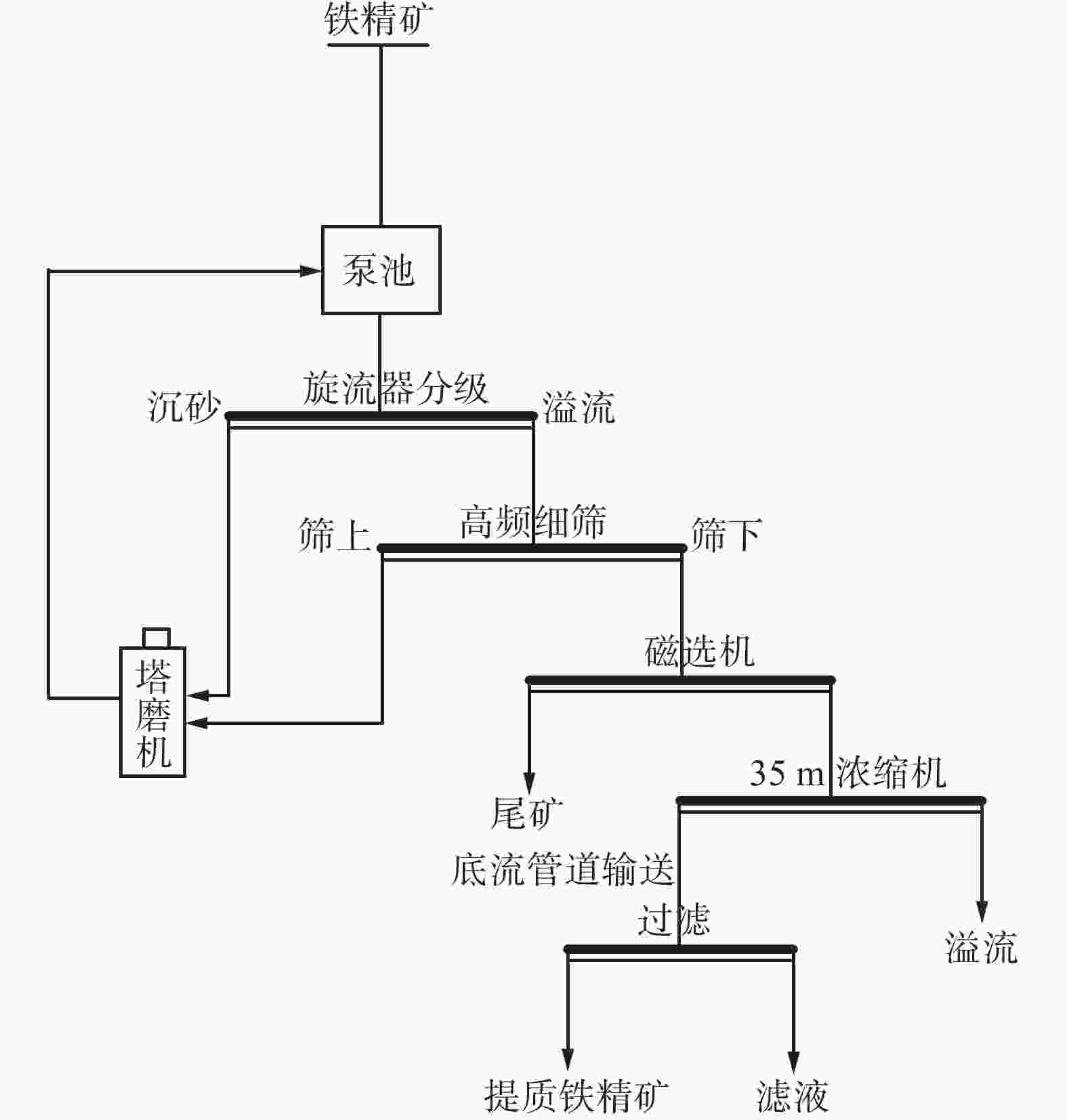
Table 6. Test results of fine grinding and deep dressing of V-Ti-Fe concentrate
% 磨矿细度(−74 μm占比) 产品 产率 TFe品位 TFe回收率 68.77 铁精矿 98.02 56.51 98.99 尾矿 1.98 28.35 1.01 给料 100.00 55.95 100.00 95.42 铁精矿 93.98 58.32 98.02 尾矿 6.02 18.42 1.98 给料 100.00 55.92 100.00 99.42 铁精矿 93.21 58.59 97.72 尾矿 6.79 18.81 2.28 给料 100.00 55.89 100.00 99.90 铁精矿 91.58 59.24 97.06 尾矿 8.42 19.55 2.94 给料 100.00 55.90 100.00 表 7 钒钛铁精矿粗细分别分选试验结果
Table 7. Experimental results of separation of coarse and fine V-Ti-Fe concentrate
产品 产率/% TFe品位/% TFe回收率/% 粗粒铁精矿 31.06 59.14 32.61 粗料尾矿 4.70 19.51 1.63 细粒铁精矿 61.82 58.83 64.56 细粒尾矿 2.42 28.07 1.21 总精矿 92.88 58.93 97.17 总尾矿 7.12 22.42 2.83 合计 100.00 56.33 100.00 表 8 钒钛铁精矿单一浮选试验结果
Table 8. Results of single flotation test for V-Ti-Fe concentrate
% 产品 产率 品位 回收率 TFe S TFe S 浮选铁精矿 86.40 56.64 0.12 87.25 23.51 浮选尾矿 13.60 52.56 2.48 12.75 76.49 合计 100.00 56.09 0.44 100.00 100.00 表 9 钒钛铁精矿浮选—磁选工艺试验结果
Table 9. Experimental results of floatation-magnetic process for V-Ti-Fe concentrate
% 产品 产率 品位 回收率 TFe S TFe S 铁精矿 81.10 58.97 0.11 85.28 20.46 磁选尾矿 5.30 20.95 0.18 1.98 2.19 浮选尾矿 13.60 52.56 2.48 12.75 77.35 总尾矿 18.90 43.70 1.84 14.72 79.54 合计 100.00 56.08 0.44 100.00 100.00 表 10 钒钛铁精矿磁—浮工艺试验结果
Table 10. Test results of magnetic floatation process for V-Ti-Fe concentrate
% 产品 产率 品位 回收率 TFe S TFe S 铁精矿 89.28 58.71 0.12 93.48 31.77 浮选尾矿 4.75 53.38 3.05 4.52 42.87 磁选尾矿 5.98 18.74 1.43 2.00 25.36 总尾矿 10.72 34.07 2.14 6.52 68.23 合计 100.00 56.07 0.34 100.00 100.00 表 11 不同提质铁精矿品位与处理量的关系
Table 11. Relationship between grade and treatment capacity of iron concentrate with different quality improvement
塔磨机处理量/(t·h−1) 铁精矿品位/% 395 57.12 329 57.63 298 57.74 228 58.57 186 58.61 123 58.94 表 12 不同提质铁精矿品位与铁精矿粒度的关系
Table 12. Relationship between grade and particle size of iron concentrate
% 铁精矿品位 −325目(45 μm)含量 −400目(37 μm)含量 57.12 77.79 66.82 57.63 82.69 76.42 57.74 86.23 76.65 58.57 94.53 91.44 58.61 96.30 93.43 58.94 96.59 93.81 表 13 提质前后铁精矿多元素对比分析结果
Table 13. Comparative analysis of multi-elements of iron concentrate before and after upgrading
% TFe TiO2 V2O5 CaO MgO Al2O3 SiO2 S 提质前含量 55.74 9.29 0.722 0.55 3.56 3.56 4.18 0.424 提质后含量 59.03 9.37 0.792 0.22 2.37 2.37 2.00 0.332 差值 3.29 0.08 0.07 −0.33 −1.19 −1.19 −2.18 −0.092 -
[1] 中国地调局成都矿产综合利用研究所, 国土资源部钒钛磁铁矿综合利用重点实验室. 攀西钒钛磁铁矿资源及综合利用技术[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2015: 1−12.Chengdu Institute of Comprehensive Utilization of Minerals, China Geological Survey Bureau, Key Laboratory of Comprehensive Utilization of Vanadium Titanium Magnetite, Ministry of Land and Resources. Panxi vanadium titanium magnetite resources and comprehensive utilization technology [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2015: 1−12. [2] Wen Xiaolian, Guo Mingbin, Ran Dingwei. Present situation, problems and countermeasures of titanium resources utilization in Panzhihua region[J]. Metal Mine, 2008,(10):5−8. (文孝廉, 郭明彬, 冉定伟. 攀枝花地区钛资源利用现状、存在问题及对策[J]. 金属矿山, 2008,(10):5−8. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1250.2008.10.002Wen Xiaolian, Guo Mingbin, Ran Dingwei. Present situation, problems and countermeasures of titanium resources utilization in Panzhihua region [J]. Metal Mine, 2008(10): 5-8. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1250.2008.10.002 [3] Yu Yongfu, Duan Qifu. Significance of silicon reduction and iron extraction to the development of China's iron and steel industry[J]. Mining and Metallurgy Engineering, 2002,(3):1−6. (余永富, 段其褔. 降硅提铁对我国钢铁工业发展的重要意义[J]. 矿冶工程, 2002,(3):1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2002.03.001Yu Yongfu, Duan Qifu. Significance of silicon reduction and iron extraction to the development of China's iron and steel industry [J]. Mining and Metallurgy Engineering, 2002 (3): 1-6 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2002.03.001 [4] Wang Hongbin. Optimization and transformation of fine titanium concentrate production line in Panzhihua Midi titanium concentrator[J]. Mining and Metallurgy Engineering, 2012,(4):56−58. (王洪彬. 攀枝花密地选钛厂细粒钛精矿生产线优化改造[J]. 矿冶工程, 2012,(4):56−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2012.04.015Wang Hongbin. Optimization and transformation of fine titanium concentrate production line in Panzhihua Midi titanium concentrator [J]. Mining and Metallurgy Engineering, 2012 (4): 56-58 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2012.04.015 [5] Xie Meifang, Wen Shuming, Zheng Hailei, et al. Experimental study on iron extraction and sulfur reduction process of vanadium titanium magnetite concentrate[J]. Metal Mine, 2010,(7):44−46. (谢美芳, 文书明, 郑海雷, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿精矿提铁降硫工艺试验研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2010,(7):44−46.Xie Meifang, Wen Shuming, Zheng Hailei, et al. Experimental study on iron extraction and sulfur reduction process of vanadium titanium magnetite concentrate[J]. Metal Mine, 2010 (7): 44-46 [6] Wu Xuehong. Experimental study on improving the grade of iron concentrate in Midi concentrator[J]. Mining and Metallurgy Engineering, 2013,(6):38−41. (吴雪红. 提高密地选矿厂铁精矿品位的试验研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2013,(6):38−41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2013.06.011Wu Xuehong. Experimental study on improving the grade of iron concentrate in Midi concentrator [J]. Mining and Metallurgy Engineering, 2013 (6): 38-41 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2013.06.011 [7] Wang Hongbin. Processing technology optimization for efficient recovery of ilmenite from tallings of iron ore dressing in Baima mine of Panzhihua[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2014,34(6):18. (王洪彬. 高效回收攀枝花白马矿区选铁尾矿中钛铁矿技术研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2014,34(6):18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2014.06.005Wang Hongbin. Processing technology optimization for efficient recovery of ilmenite from tallings of iron ore dressing in Baima mine of Panzhihua[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2014, 34(6): 18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2014.06.005 [8] Xiao Liangchu, Wang Yong. Panzhihua Baima low grade ilmenite separation difficulty analysis[J]. Modern Mining, 2016,3:58−62. (肖良初, 王勇. 攀枝花白马低品位钛铁矿选别难点分析[J]. 现代矿业, 2016,3:58−62.Xiao Liangchu, Wang Yong. Panzhihua Baima low grade ilmenite separation difficulty analysis [J]. Modern Mining, 2016 (3): 58-62. -




 下载:
下载: