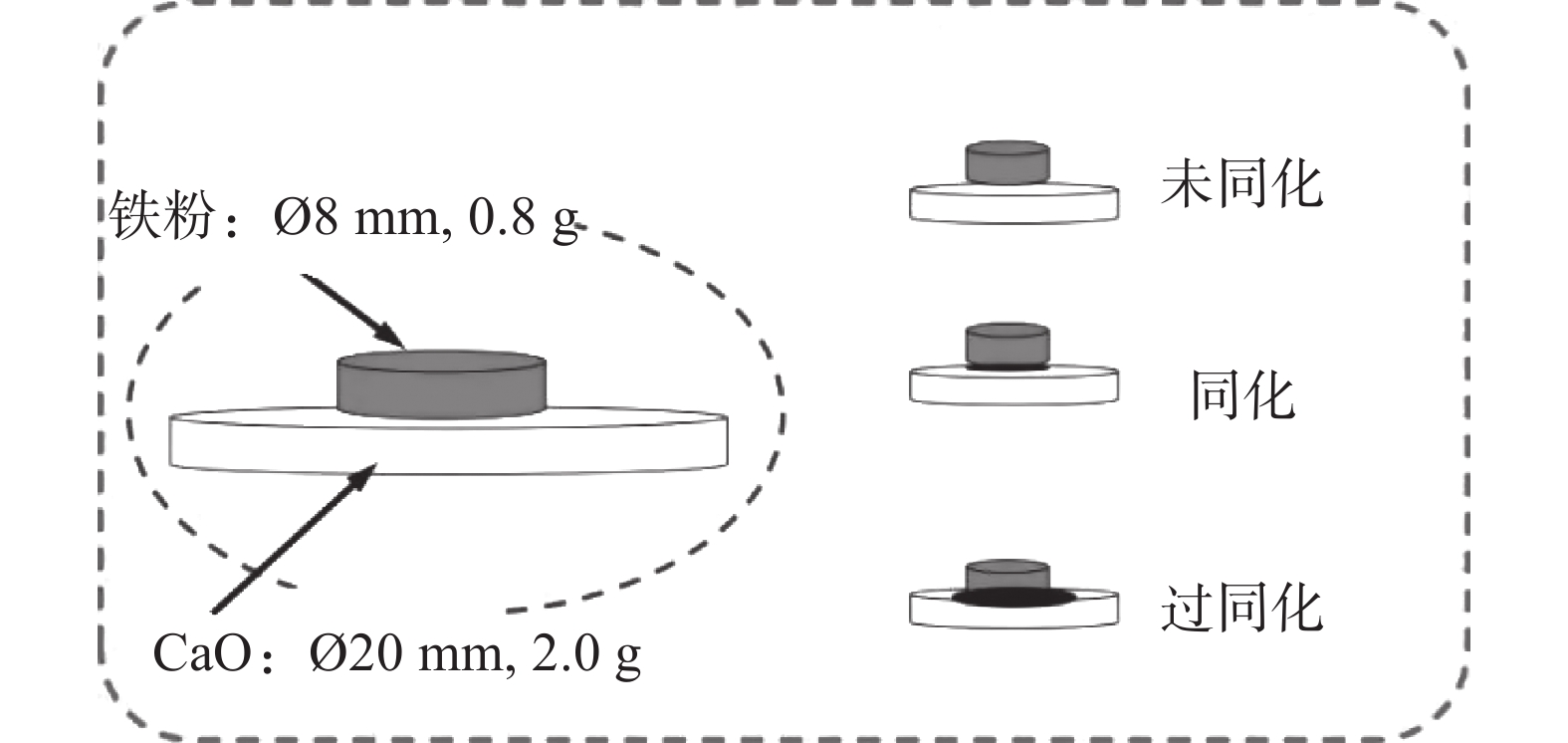
Study on high temperature properties and optimal ore blending of Pangang iron ore powder
-
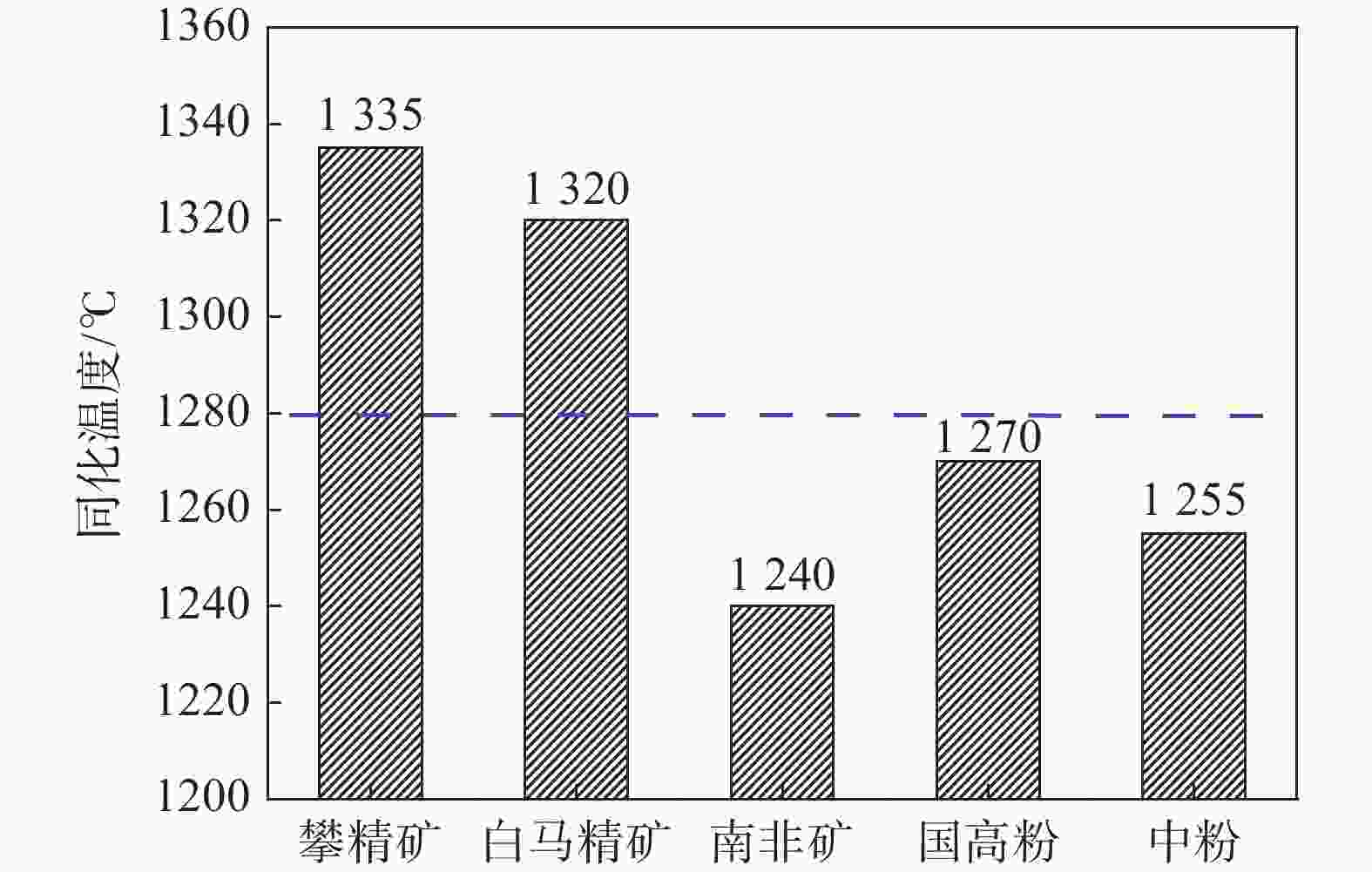
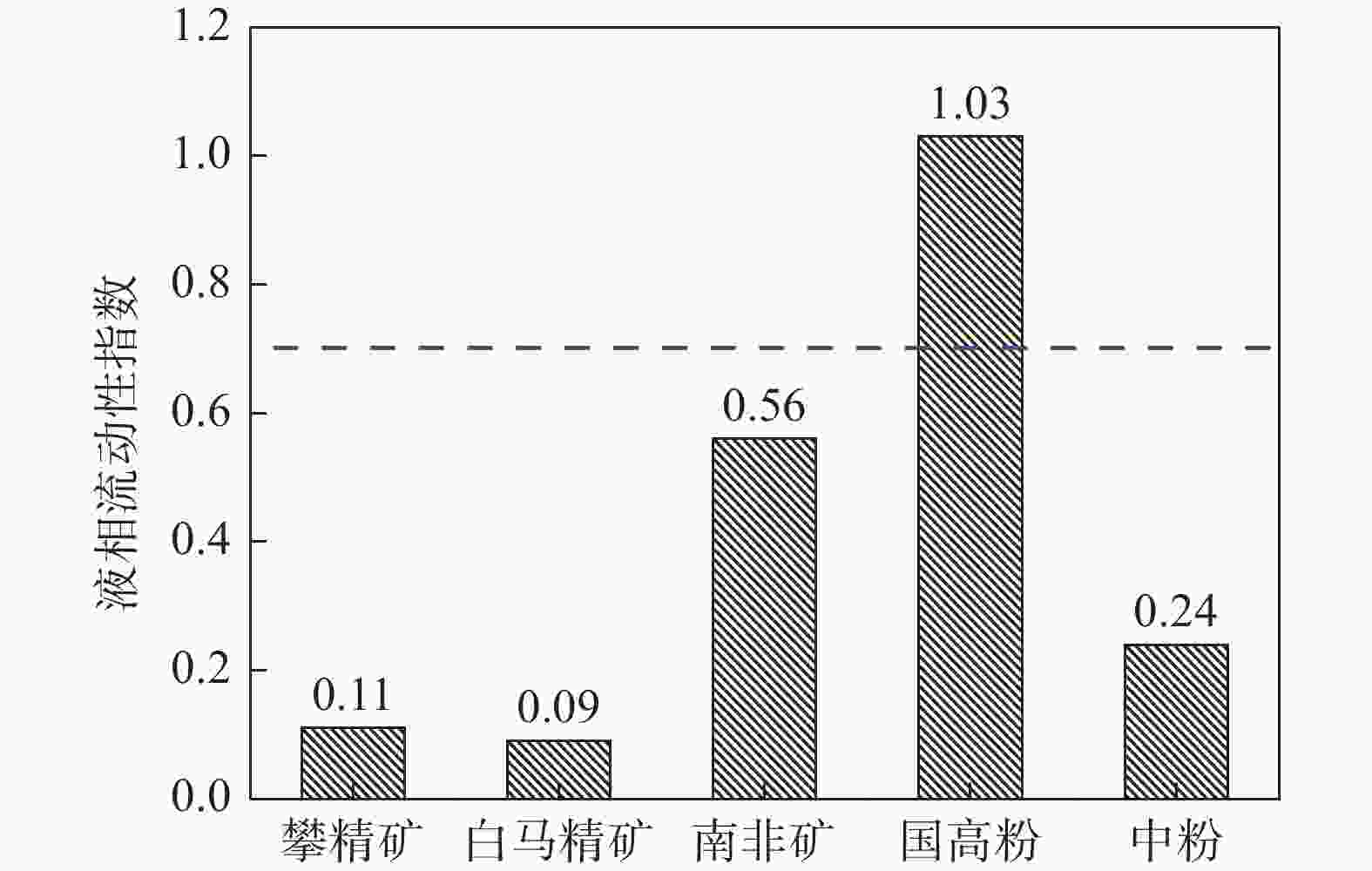
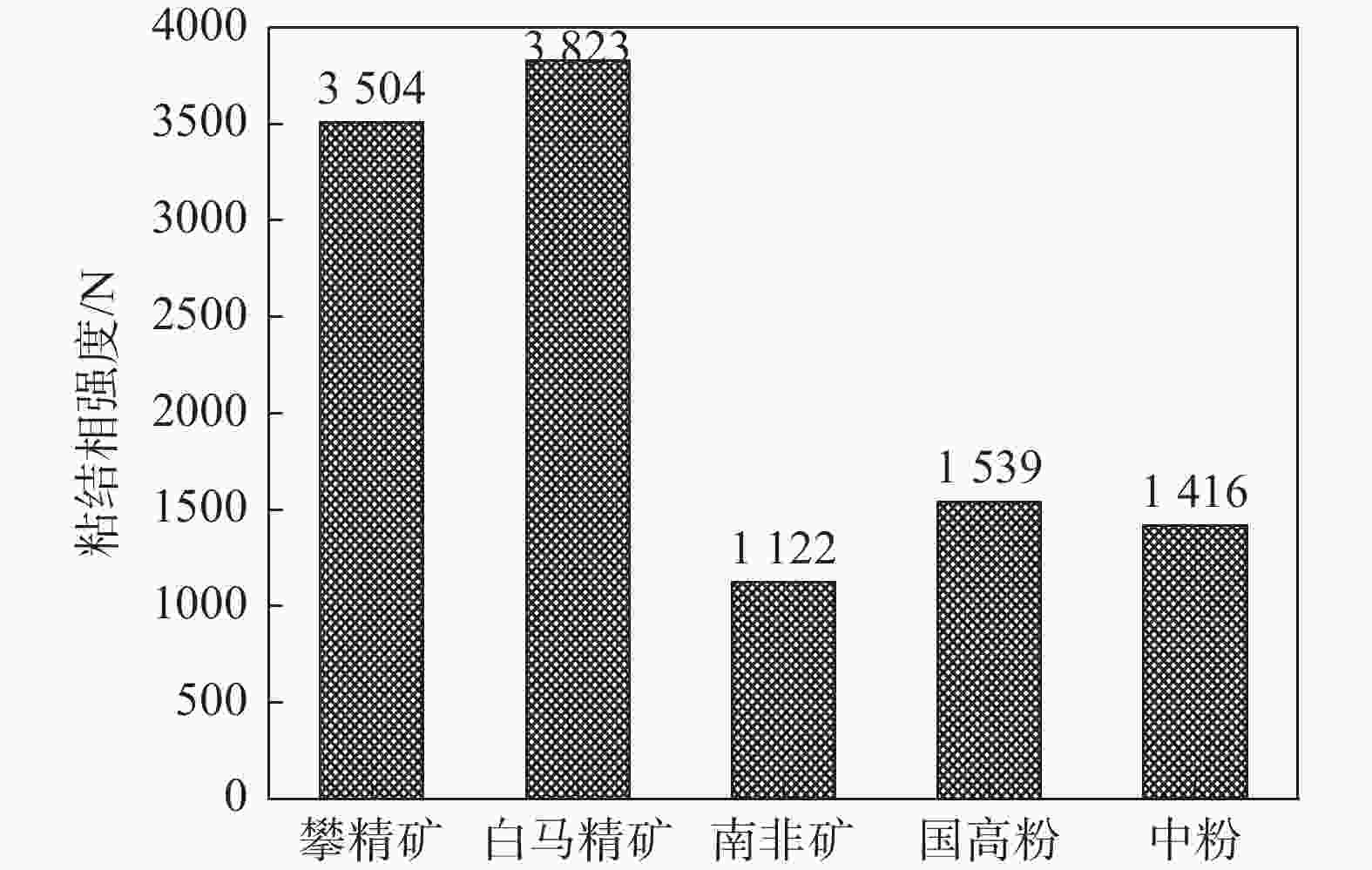
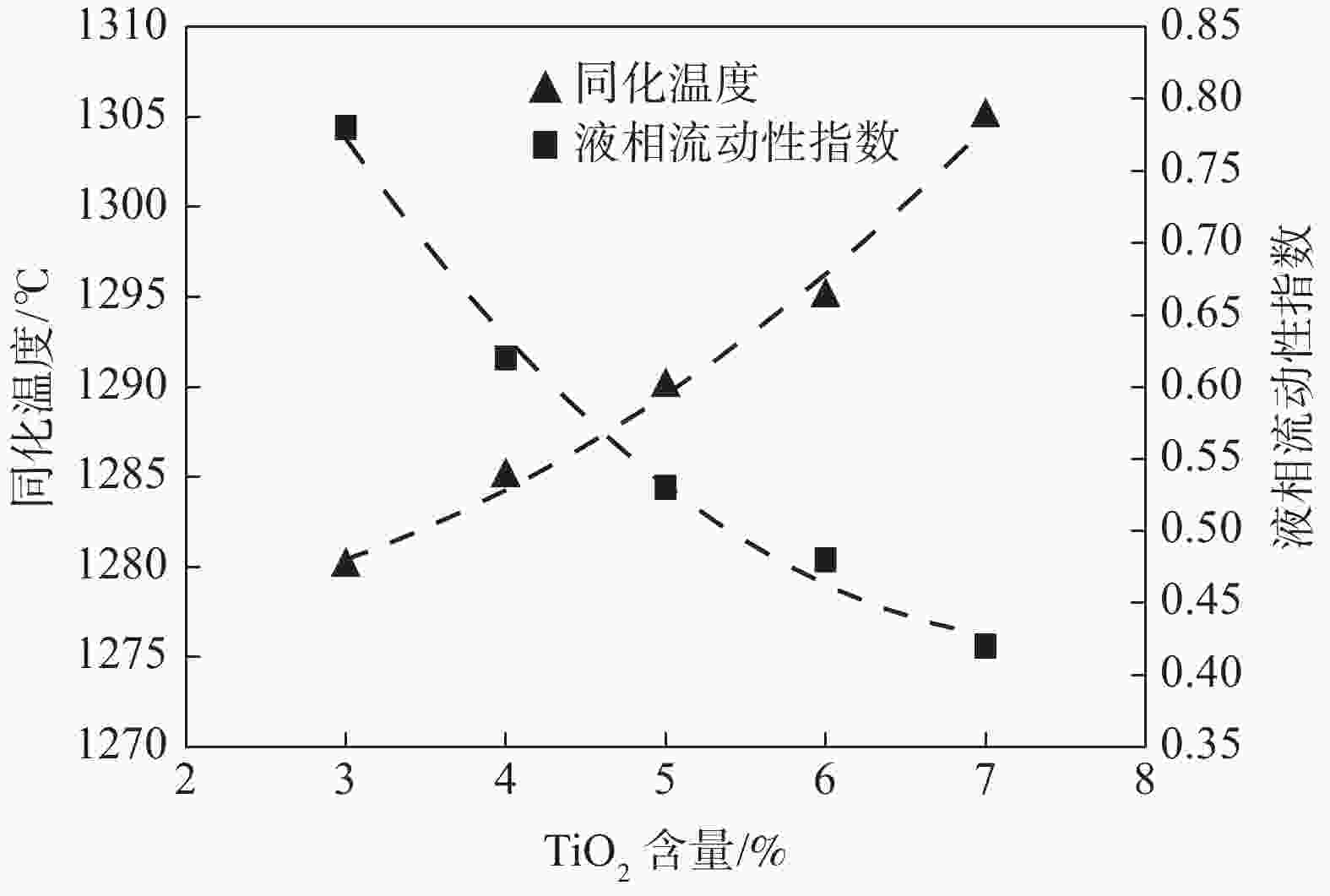
摘要: 通过微型烧结试验对攀钢铁矿粉高温性能进行了检测,结果表明攀钢所用高钛型钒钛磁铁矿同化温度达到1320 ℃以上,液相流动性指数仅0.1,粘结相强度大于3 500 N,需要通过优化配矿来改善烧结混匀矿性能。因此,根据高温性能进行了优化配矿,并开展了高温性能和烧结杯验证试验,结果表明:TiO2含量对铁矿粉烧结高温性能影响较大。随着TiO2含量从7.0%降低至3.0%时,混匀矿的同化温度从1305 ℃降低至1280 ℃,液相流动性指数从0.42提高至0.78,粘结相强度则从2 640 N降低至1 915 N,烧结矿成品率、转鼓强度和中低温性能显著提高,且烧结过程中TiO2与CaO反应生成的结构致密、熔点较高的钙钛矿物相减少,铁酸钙物相增加。Abstract: The results from micro sintering test on high temperature properties of Pangang iron ore power show that the assimilation temperature of high V-Ti magnetite used in Pangang exceeds 1 320 ℃, while the liquid phase fluidity index is only 0.1 and the bonding phase strength is greater than 3 500 N. It is necessary to improve the performance of sinter blending by optimizing ore blending. Therefore, the ore blending was optimized based on high temperature performance, and the sintering verification tests had been conducted. It is found out that the content of TiO2 has a great influence on the high temperature sintering properties of iron ore powder. When TiO2 content decreases from 7.0% down to 3.0%, the assimilation temperature of mixed ore decreases from 1 305 ℃ to 1 280 ℃, the liquid phase fluidity index is increased from 0.42 to 0.78, and the bonding phase strength decreases from 2 640 N to 1 915 N. The sinter yield, drum strength, and medium and low temperature properties are significantly improved. During the sintering process, the calcium titanium mineral phase with dense structure and high melting point formed by the reaction of TiO2 and CaO decreases, and the calcium ferrite phase increases.
-
Key words:
- vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite /
- sinter /
- ore blending /
- high temperature properties
-
表 1 试验用原料化学成份和烧损
Table 1. Chemical compositions and burning loss of raw iron ore for test
矿粉名称 化学成分/% Ig/% TFe FeO CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 TiO2 V2O5 攀精矿 53.90 32.55 0.40 3.80 2.80 3.80 12.25 0.56 −1.36 白马精矿 56.36 27.30 0.37 3.79 3.36 3.28 10.51 0.71 −1.50 南非矿 62.21 0.72 0.27 6.22 0.05 1.91 2.00 国高粉 59.61 17.69 2.42 4.36 3.80 0.86 0.50 3.00 中粉 44.03 2.64 2.29 20.82 1.62 5.33 0.30 0.04 4.32 表 2 铁矿粉配矿试验方案
Table 2. Iron ore powder blending test scheme
配矿方案 矿粉比例/% 攀精矿 南非矿 国内高粉 国内中粉 JZ 56 10 23 11 S1 47.5 10 32 10.5 S2 39 10 40.5 10.5 S3 30.5 10 49.5 10 S4 22 10 58.5 9.5 表 3 混匀矿化学成分检测结果
Table 3. Chemical compositions of mixed ore
配矿方案 化学成分/% TFe SiO2 CaO MgO Al2O3 V2O5 TiO2 JZ 54.96 6.04 1.06 2.63 3.10 0.32 7.00 S1 55.52 6.01 1.23 2.72 2.83 0.27 6.01 S2 56.01 6.06 1.40 2.81 2.58 0.22 5.01 S3 56.57 6.02 1.58 2.90 2.31 0.17 4.01 S4 57.13 5.99 1.75 3.00 2.04 0.13 3.00 表 4 烧结矿性能检测结果
Table 4. Sinter performance test results
配矿方案 成品率/% 转鼓强度/% 利用系数/[t·(m2·h)−1] RDI(+3.15 mm)/% RI/% JZ 70.75 52.60 1.442 54.37 86.77 S1 75.91 56.27 1.437 55.92 87.15 S2 79.35 58.27 1.360 57.39 87.72 S3 85.78 61.53 1.391 61.80 88.50 S4 85.43 63.13 1.622 62.80 90.87 表 5 典型烧结矿物相体积分数组成
Table 5. Volume fractions of typical sintered mineral phases
矿物方案 矿物组成/% 钛赤铁矿 钛磁铁矿 铁酸钙 钙钛矿 镁铝尖晶石 硅酸盐 JZ 18~22 23~27 19~23 7~11 0~2 22~26 S2 18~21 24~27 25~30 5~9 0-2 20~23 S4 16~20 24~28 28~32 2~6 0~2 16~20 -
[1] Wu Shengli, Liu Yu, Du Jianxin, et al. A new concept of basic sintering characteristics of iron ore[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2005,24(3):254−257. (吴胜利, 刘宇, 杜建新, 等. 铁矿石的烧结基础特性之新概论[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2005,24(3):254−257.Wu Shengli, Li Yu, Du Jianxin et al. A new concept of basic sintering characteristics of iron ore[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2005, 24(3): 254-257. [2] Hu Peng, Rao Jiating, Fu Weiguo, et al. Effect of SiO2 and CaO content on the high-titanium V-Ti sinters performance[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2017,42(3):16−20. (胡鹏, 饶家庭, 付卫国, 等. 高钛型钒钛烧结矿不同硅钙水平研究[J]. 烧结球团, 2017,42(3):16−20.Hu Peng, Rao Jiating, Fu Weiguo, et al. Effect of SiO2 and CaO content on the high-titanium V-Ti sinters performance[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2017, 42(3): 16-20. [3] Yan Bingji, Zhang Jianliang, Yao Zhaoquan, et al. Ore-blending optimization model based on liquid phase formation characteristics of iron ore fines[J]. Iron and Steel, 2015,50(6):40−45. (闫炳基, 张建良, 姚朝权, 等. 基于铁矿粉液相生成特性互补优化配料模型[J]. 钢铁, 2015,50(6):40−45.Yan Bingji, Zhang Jianliang YaoZhaoquan, et al. Ore-blending optimization model based on liquid phase formation characteristics of iron ore fines[J]. Iron and Steel, 2015, 50(6): 40-45. [4] Liu Song, Li Fumin, Lv Qing. Basic sintering characteristics of low titanium mixed iron ore[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2015,36(50):74−78. (刘颂, 李福民, 吕庆. 低钛性混匀矿的烧结基础特性[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2015,36(50):74−78.Liu Song, Li Fumin, Lv Qing. Basic sintering characteristics of low titanium mixed iron ore[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium TiTanium, 2015, 36(50): 74-78. [5] Wang Wenshan, Ren Gang, Lv Qing, et al. Study on optimization of Chengde vanadium-titanium magnetite sintering process[J]. Hebei Metallurcy, 2009,174:3−5. (王文山, 任刚, 吕庆, 等. 承钢钒钛粉的烧结基础性能研究[J]. 河北冶金, 2009,174:3−5.Wang Wenshan, Ren Gang, Lv Qing et al. Study on optimization of Chengde vanadium-titanium magnetite sintering process[J], Hebei Metallurcy, 2009, 174: 3-5. [6] Wu Shengli, Du Jianxin, Ma Hongbin, et al. Fluidity of liquid phase in iron ores during sintering[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2005,27(3):291−293. (吴胜利, 杜建新, 马洪斌, 等. 铁矿粉烧结液相流动特性[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2005,27(3):291−293. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-053X.2005.03.009Wu Shengli, Ma Jianxin, Ma Hongbin et al. Fluidity of liquid phase in iron ores during sintering[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2005, 27(3): 291-293. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-053X.2005.03.009 [7] Lv Qing, Zhang Xusheng, Liu Xiaojie, et al. Influence of titanium on the basic characteristics of sinter[J]. Iron and Steel, 2015,50(5):13−18. (吕庆, 张旭升, 刘小杰, 等. 钛对烧结矿基础性能的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2015,50(5):13−18.Lv Qing, Zhang Xusheng, Liu Xiaojie, La Xiaoshuai. Influence of titanium on the basic characteristics of sinter[J]. Iron and Steel, 2015, 50(5): 13-18. [8] Liu Zimin, Wu Shengli, Jin Jun, et al. Study on optimizing the sintering proportioning in Masteel[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2012,37(2):13−18. (刘自民, 吴胜利, 金俊, 等. 马钢烧结优化配矿技术的研究[J]. 烧结球团, 2012,37(2):13−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8764.2012.02.004Liu Zhimin, Wu Shengli, Jin Jun et al. Study on optimizing the sintering proportioning in Masteel[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2012, 37(2): 13-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8764.2012.02.004 [9] Wang Zhe, Zhang Jianliang, Zuo Haibin, et al. Study on sintering proportioning optimization based on basic high temperature properties of iron ore fines[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2013,38(3):1−4. (王喆, 张建良, 左海滨, 等. 基于铁矿粉高温基础性能的烧结配料优化研究[J]. 烧结球团, 2013,38(3):1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8764.2013.03.001Wang Zhe, Zhang Jianliang, Zuo Haibin et al. Study on sintering proportioning optimization based on basic high temperature properties of iron ore fines[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2013, 38(3): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8764.2013.03.001 [10] Lin Wengkang, Hu Peng. Influence of TiO2 content and basicity level on the metallogenic regularity of V-Ti sinter[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(2):94−100. (林文康, 胡鹏. TiO2含量和碱度水平对钒钛烧结矿成矿规律的影响研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(2):94−100. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.02.018Lin Wengkang, Hu Peng. Influence of TiO2 content and basicity level on the metallogenic regularity of V-Ti sinter[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020, 41(2): 94-100. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.02.018 -




 下载:
下载: