Microstructure and hardenability of vanadium microalloyed high temperature carburized SCM420H gear steel
-
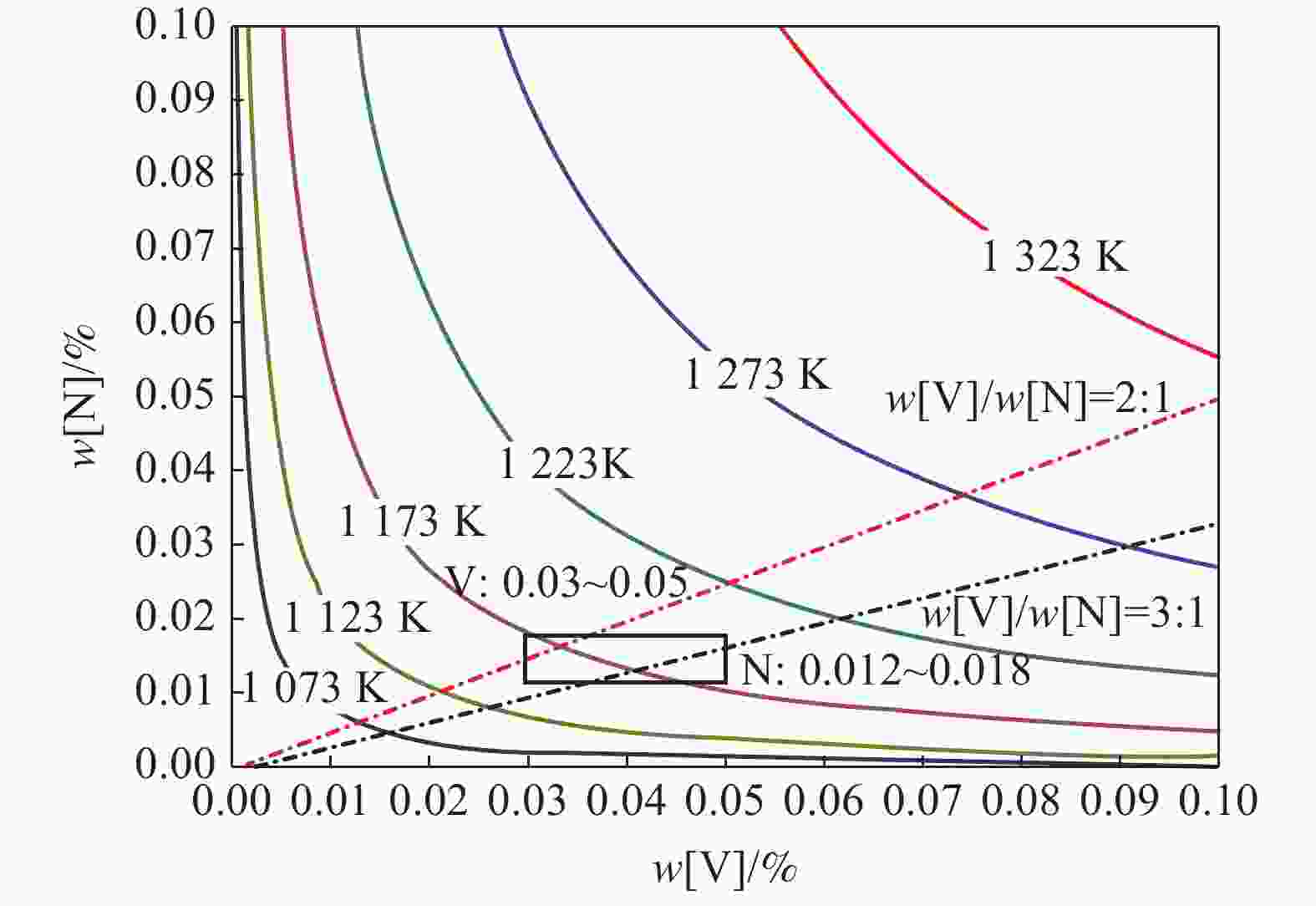
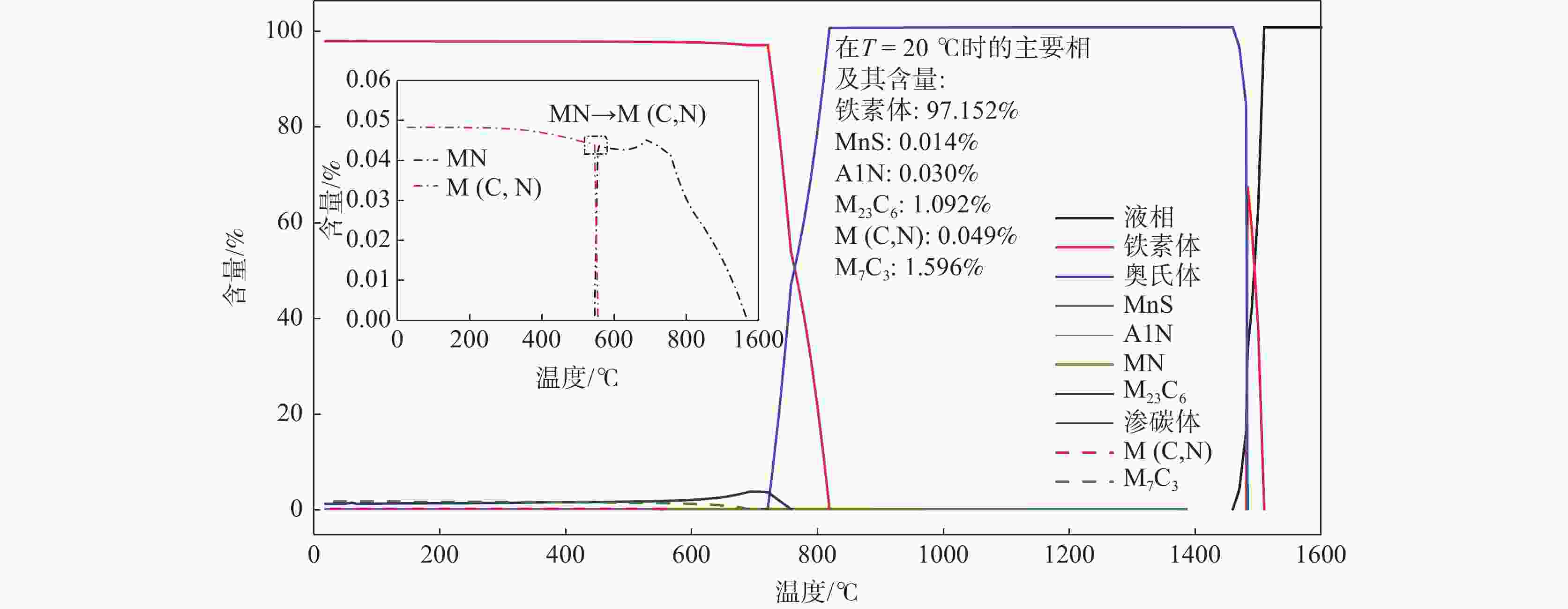
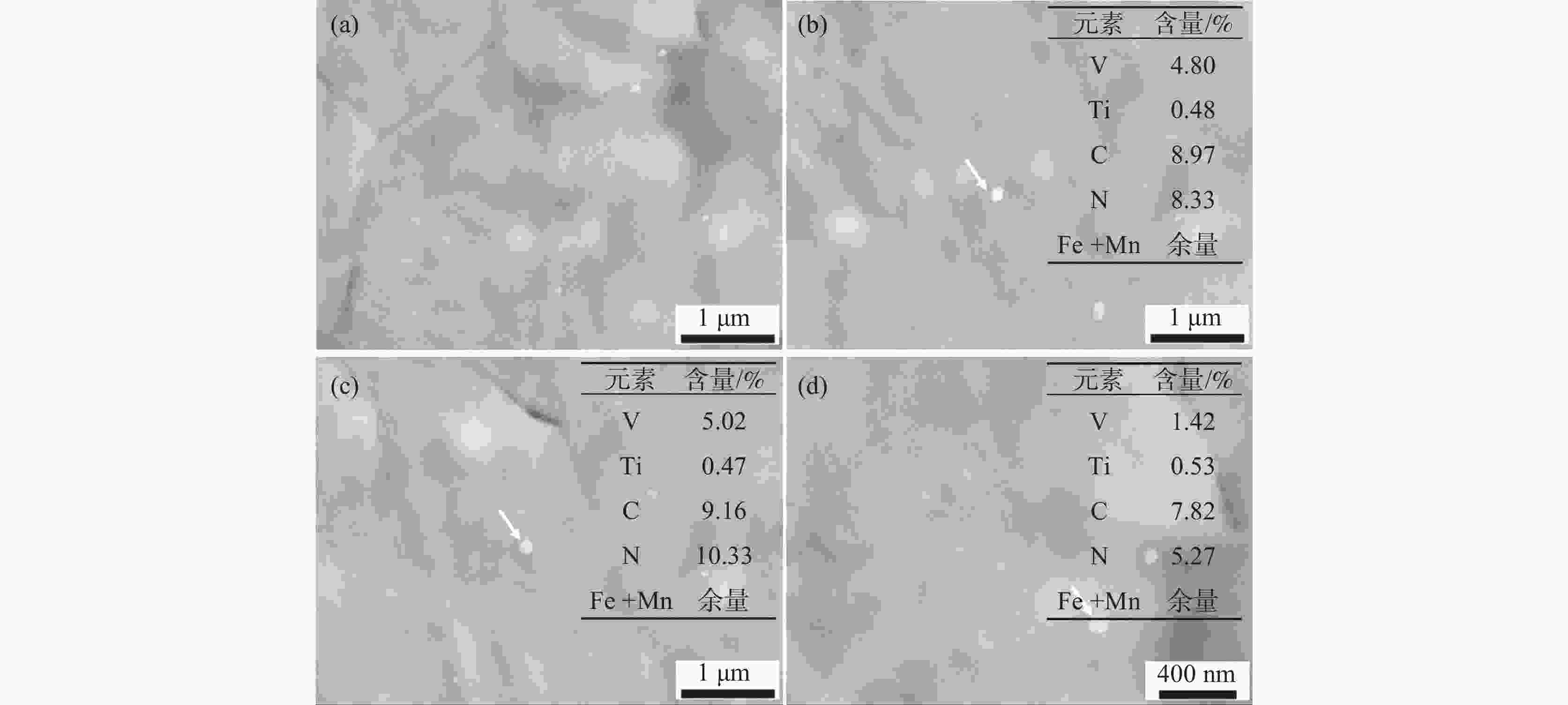
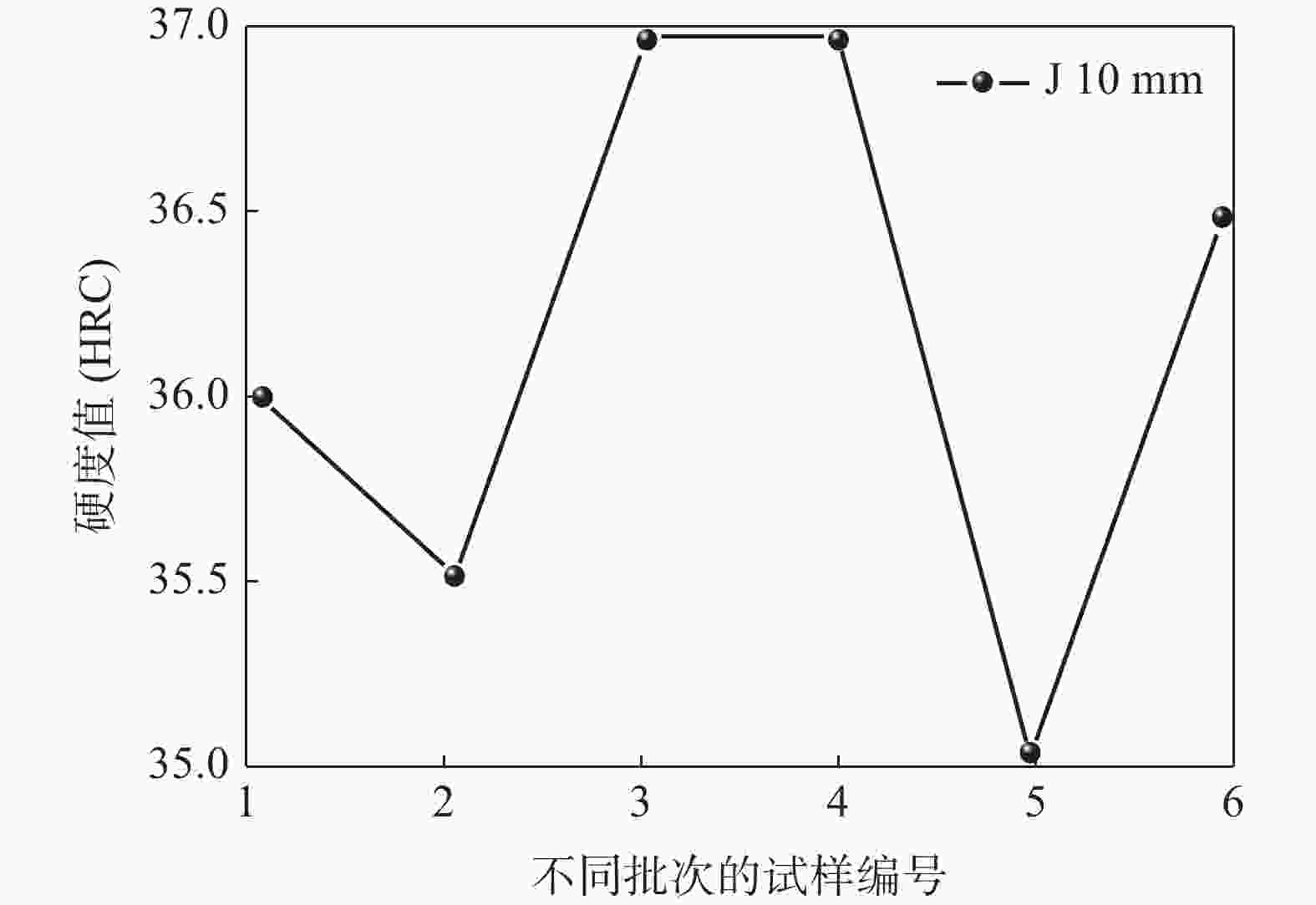
摘要: 对高温渗碳SCM420H齿轮钢进行了钒微合金化处理,并对钢中组织及淬透性进行了研究。结果表明:SCM420H齿轮钢中V含量和N含量应控制范围分别在0.03%~0.05%和0.012%~0.018%。MN(M=Ti,V)在966 ℃时析出并在559 ℃时向M(C,N)发生转化,常温时的M(C,N)质量百分数约为0.049%。将加热温度控制在1200 ℃±20 ℃,在预热段(室温升至850 ℃左右)加热时间控制在120 min内,在940~980 ℃高温渗碳保温6 h后,圆钢的带状组织控制在1.5~2级,奥氏体晶粒稳定在7.5~8级,M(C,N)主要为能起到钉扎晶界、细化奥氏体晶粒的纳米级球状V(C,N)。将连铸结晶器电磁搅拌强度参数调整为150 A,2.5 Hz,铸坯拉速为0.85 m/min,浇铸过热度为15~30 ℃,碳含量偏差值可控制在0.01%,碳含量的均匀化有利于淬透性的窄带化控制,钒微合金化后,试样的淬透性硬度值(HRC)最高为37,最低为35,淬透性带宽硬度值(HRC)≤3。Abstract: The high-temperature carburized SCM420H gear steel was modified with vanadium microalloying, and the structure and hardenability of the steel were studied. The results show that the V and N contents in SCM420H gear steel should be controlled within the range of 0.03%~0.05% and 0.012%~0.018%, respectively. MN (M=Ti,V) precipitates at 966 ℃ and transforms into M(C,N) at 559 ℃. The mass percentage of M(C,N) approximates 0.049%. The heating temperature is controlled at 1200 ℃±20 ℃, and the heating time is controlled within 120 minutes in the preheating section (from room temperature to about 850 ℃). After high temperature carburizing and holding at 940~980℃ for 6 hours, the banded structure of bar steel is controlled at 1.5 to 2 level, and the austenite grain size is at ASTM 7.5 to 8. M (C,N) is mainly nano-seized spherical V (C,N) which can pin grain boundaries and refine austenite grains. Under the following casting parameters: the electromagnetic stirring intensity parameters of the continuous casting mold are adjusted to 150 A, 2.5 Hz, the casting speed is at 0.85 m/min, the casting superheat is 15 to 30 ℃, the deviation value of carbon content can be controlled at 0.01% which is beneficial to narrowing control of hardenability. After vanadium microalloying, the maximum hardenability value(HRC) of the sample is 37, the minimum is 35, and the hardenability bandwidth(HRC)is not greater than 3.
-
Key words:
- gear steel /
- SCM420H /
- vanadium microalloying /
- high-temperature carburizing /
- hardenability
-
表 1 SCM420H齿轮钢化学成分要求及设计范围
Table 1. Chemical compositions requirements and design range for SCM420H gear steel
% 元素 C Si Mn P S Cr V Al Mo B N 技术
要求0.17
~
0.230.15
~
0.350.60
~
0.90≤ 0.025 ≤0.025 1.00
~
1.250.015
~
0.0400.15
~
0.300.010
~
0.020内控
范围0.19
~
0.210.20
~
0.300.82
~
0.88≤ 0.020 ≤0.015 1.12
~
1.160.03
~
0.050.015
~
0.0350.24
~
0.26≤0.0003 0.012
~
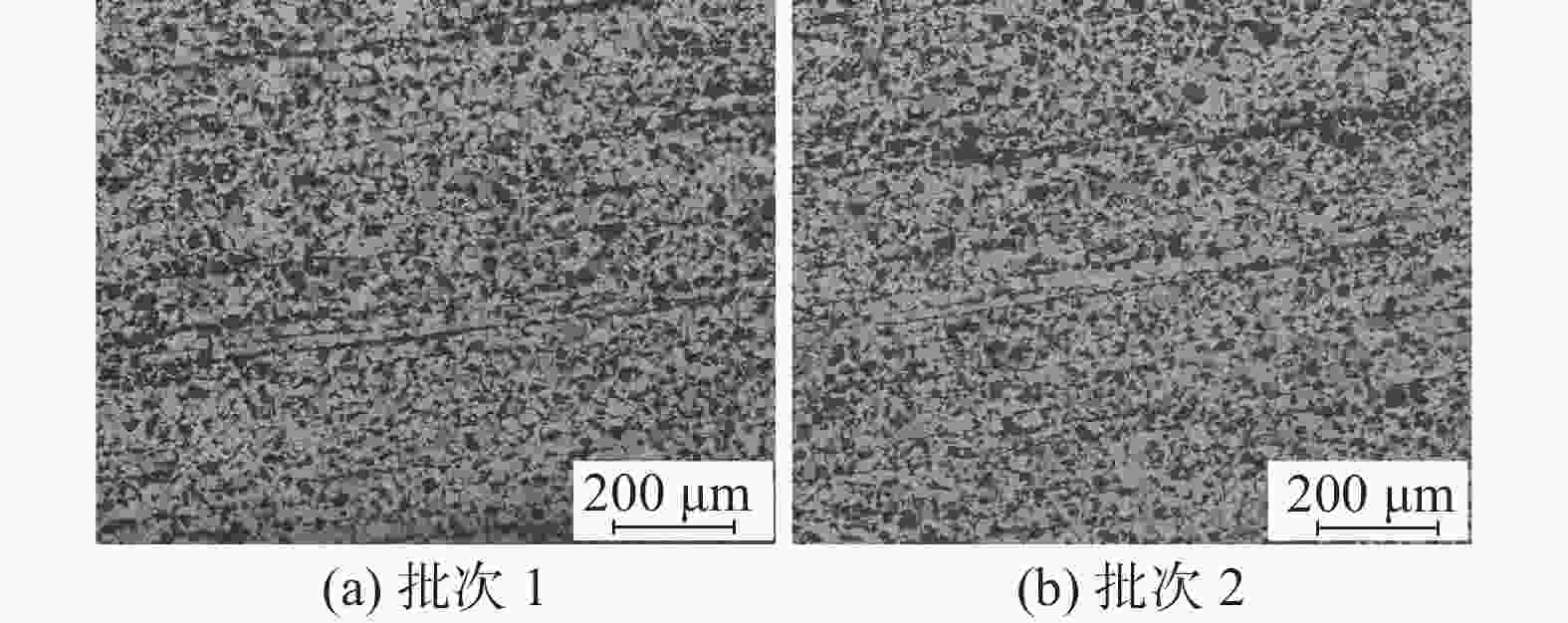
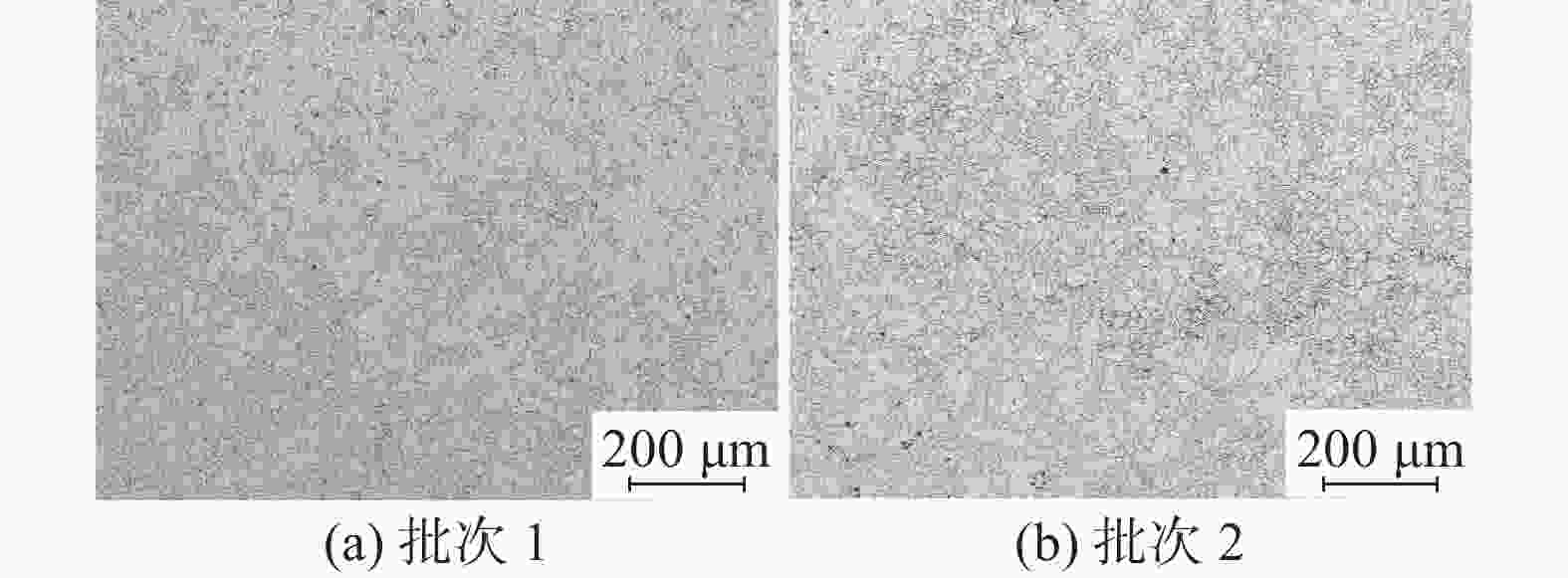
0.018批次1 0.20 0.24 0.84 0.011 0.005 1.13 0.037 0.018 0.24 0.0001 0.0145 批次2 0.20 0.25 0.85 0.013 0.004 1.14 0.041 0.022 0.25 0.0002 0.0161 表 2 圆钢显微组织情况
Table 2. Microstructures rating of steels
圆钢 带状组织/级 不同保温温度下的晶粒度/级 940 ℃ 960 ℃ 980 ℃ 批次1 2.0 8.0 8.0 7.5 批次2 1.5 8.0 8.0 8.0 -
[1] Zhang Guoqiang, He Xiaofei, Wei Wenchao, et al. Grain coarsening behavior of high temperature carburizing gear steels[J]. Iron & Steel, 2019,54(5):68−72,77. (张国强, 何肖飞, 尉文超, 等. 高温渗碳齿轮钢的晶粒粗化行为[J]. 钢铁, 2019,54(5):68−72,77.Zhang Guoqiang, He Xiaofei, Wei Wenchao, et al. Grain coarsening behavior of high temperature carburizing gear steels[J]. Steel, 2019, 54(5): 68-72+77. [2] Yang Yanhui, Wang Maoqiu, Chen Jingchao, et al. Research progress in gear steels for high temperature carburization[J]. Special Steel, 2013,34(1):22−24. (杨延辉, 王毛球, 陈敬超, 等. 高温渗碳齿轮钢的研究进展[J]. 特殊钢, 2013,34(1):22−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2013.01.006Yang Yanhui, Wang Maoqiu, Chen Jingchao, et al. Research progress in gear steels for high temperature carburization[J]. Special Steel, 2013, 34(1): 22-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2013.01.006 [3] Zhang Huawei. Development and application of high temperature carburizing gear steel[J]. Nisco Technology and Management, 2015,(3):1−5,27. (张华伟. 高温渗碳齿轮钢研制与应用[J]. 南钢科技与管理, 2015,(3):1−5,27.Zhang hua wei. Development and application of high temperature carburizing gear steel. Nisco Technology And Management, 2015(3): 1-5+27. [4] Yang Yanhui, Wang Maoqiu, Chen Jingchao, et al. Fatigue properties of gear steels after high temperature carburizing[J]. Iron & Steel, 2013,48(7):53−57,83. (杨延辉, 王毛球, 陈敬超, 等. 齿轮钢高温渗碳后的疲劳性能[J]. 钢铁, 2013,48(7):53−57,83.Yang Yanhui, Wang Maoqiu, Chen Jingchao, et al. Fatigue properties of gear steels after high temperature carburizing[J]. Steel, 2013, 48(7): 53-57+83. [5] 刘连骞. 高温临界区渗碳细化晶粒20CrMn(Ti)-Al齿轮钢组织与性能研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2015.Liu Lianqian. Study on microstructures and properties of 20CrMn(Ti)-A1gear steel: high temperature intercritical carburization grain refinement[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2015. [6] 刘年富, 岳峰, 包锋. 一种高温渗碳齿轮钢: 中国, ZL201810994814. X[P]. 2020-08-28.Liu Nianfu, Yue Feng, Bao Feng. High temperature carburized gear steel: China, ZL201810994814. X[P]. 2020-08-28. [7] Li Jiawang, Liu Fangce, Wang Qi, et al. Effect of oxide particles containing Ti on microstructure and mechanical properties of high-temperature hot-rolled low-carbon steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2021,42(6):82−90. (李家旺, 刘方策, 王琪, 等. 含Ti 氧化物对低碳钢高温热轧组织及力学性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2021,42(6):82−90.Li Jiawang, Liu Fangce, Wang Qi, et al. Effect of oxide particles containing Ti on microstructure and mechanical properties of high-temperature hot-rolled low-carbon steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2021, 42(6): 82-90. [8] Miao Huajun, Zhao Xiaogang, Wang Zhixiang. The development of the high grade gear steel SCM420H[J]. Heavy Castings and Forgings, 2004,(2):12−14. (苗华军, 赵晓刚, 王之香. 高等级齿轮钢SCM420H的开发研制[J]. 大型铸锻件, 2004,(2):12−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5635.2004.02.005Miao Huajun, Zhao Xiaogang, Wang Zhixiang. The development of the high grade gear steel SCM420 H[J]. Heavy Castings and Forgings, 2004(2): 12-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5635.2004.02.005 [9] 郑桂芸, 亓显玲, 王志明, 等. SCM420H高级汽车齿轮钢研制[J]. 山东冶金, 2008(4): 14-15.Zheng Guiyun, Qi Xianling, Wang Zhiming, et al. Development of high grade gear steel SCM420H for automobile[J]. Shandong Metallurgy, 2008(4): 14-15. [10] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. GB/T 13298—2015《金属显微组织检验方法》[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015: 2.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 13298-2015《Inspection methods of microstructure for metals》[S]. Beijing: China Standards Publishing House, 2015: 2. [11] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. GB/T 6394—2017《金属平均晶粒度测定方法》[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017: 5.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 6394—2017《Determination of estimating the average grain size of metal》[S]. Beijing: China Standards Publishing House, 2017: 5. [12] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. GB/T 225—2006《钢淬透性的末端淬火试验方法(Jominy试验)》[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006: 2.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 225-2006《SteeI hardenability test by end quenching(Jominy test)》[S]. Beijing: China Standards Publishing House, 2006: 2. [13] Yong Qilong, Zheng Lu. Solid solubility formula and stoichiometry on the composition design of microalloy steels[J]. Iron & Steel, 1988,23(7):47−51. (雍岐龙, 郑鲁. 固溶度积公式、理想化学配比值与微合金钢化学成分设计[J]. 钢铁, 1988,23(7):47−51.Yong Qilong, Zheng Lu. Solid solubility formula and stoichiometry on the composition design of microalloy steels[J]. Steel, 1988, 23(7): 47-51. [14] Liu Nianfu. Development of gear steel 20CrMnTiH with narrow hardenability band[J]. Special Steel, 2018,39(1):45−47. (刘年富. 窄淬透性带20CrMnTiH齿轮钢的开发[J]. 特殊钢, 2018,39(1):45−47.Liu Nianfu. Development of gear steel 20 CrCrMnTiH with narrow hardenability band[J]. Special Steel, 2018, 39 (1): 45-47. [15] Yan Huicheng. Effect of electromagnetic stirring on hardenability of gearing steel[J]. Metal Materials and Metallurgy Engineering, 2015,43(5):34−37. (颜慧成. 结晶器电磁搅拌对齿轮钢端淬检验值的影响[J]. 金属材料与冶金工程, 2015,43(5):34−37.Yan Huichen. Effect of electromagnetic stirring on hardenability of gearing steel[J]. Metal Materials and Metallurgy Engineering, 2015, 43(5): 34-37. [16] Gu Tie, Zhou Yuelin. Effect of thermal deformation on banded structure of SCM420H gear steel[J]. Modern Metallurgy, 2017,45(6):4−7. (顾铁, 周月林. 热变形对SCM420H齿轮钢带状组织的影响[J]. 现代冶金, 2017,45(6):4−7.Gu Tie, Zhou Yuelin. Effect of thermal deformation on banded structure of SCM420 H gear steel[J]. Modern Metallurgy, 2017, 45(6): 4-7. -




 下载:
下载: