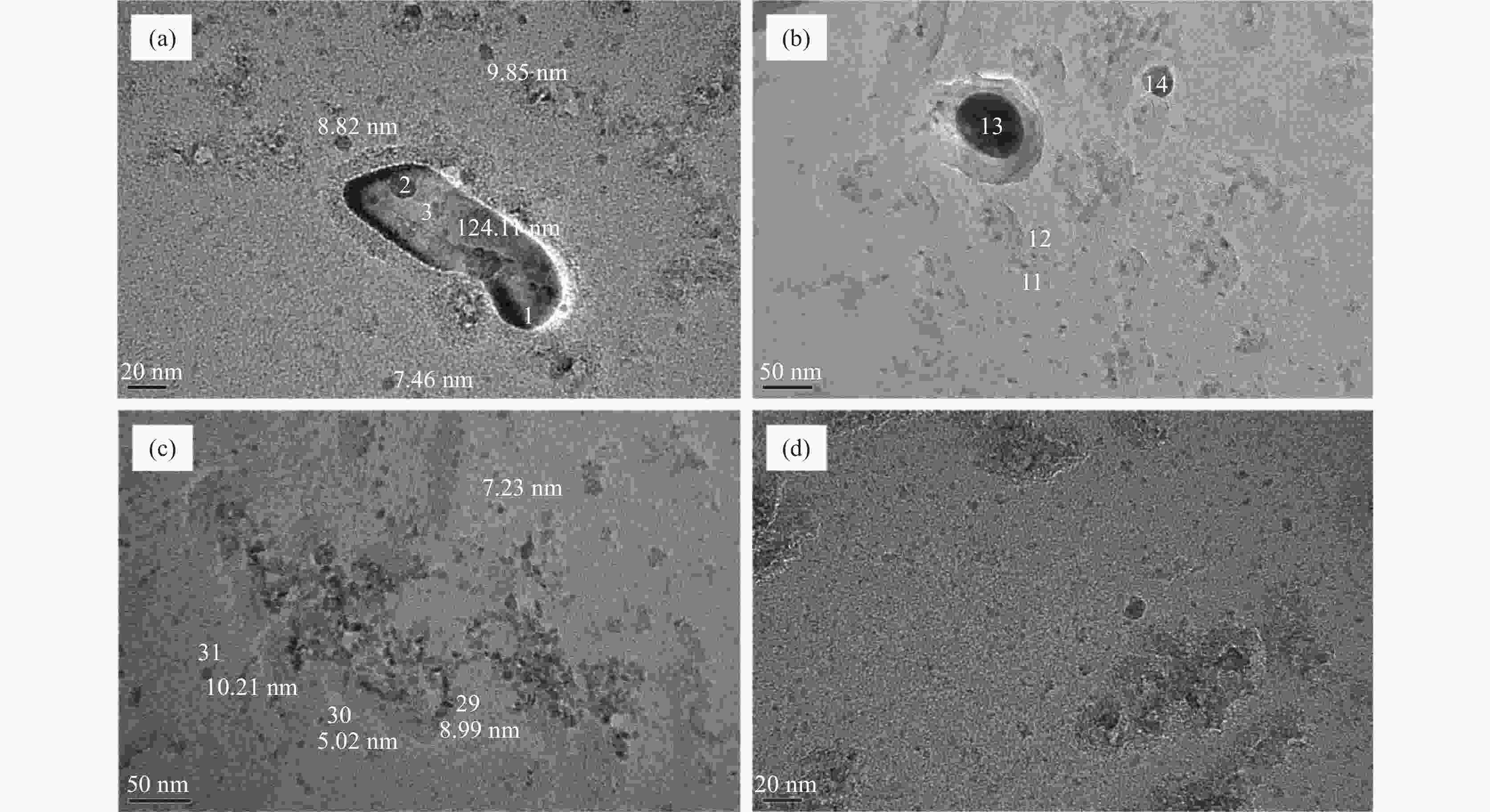
Effect of titanium content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 0.17C-0.30Si-1.40Mn steel
-
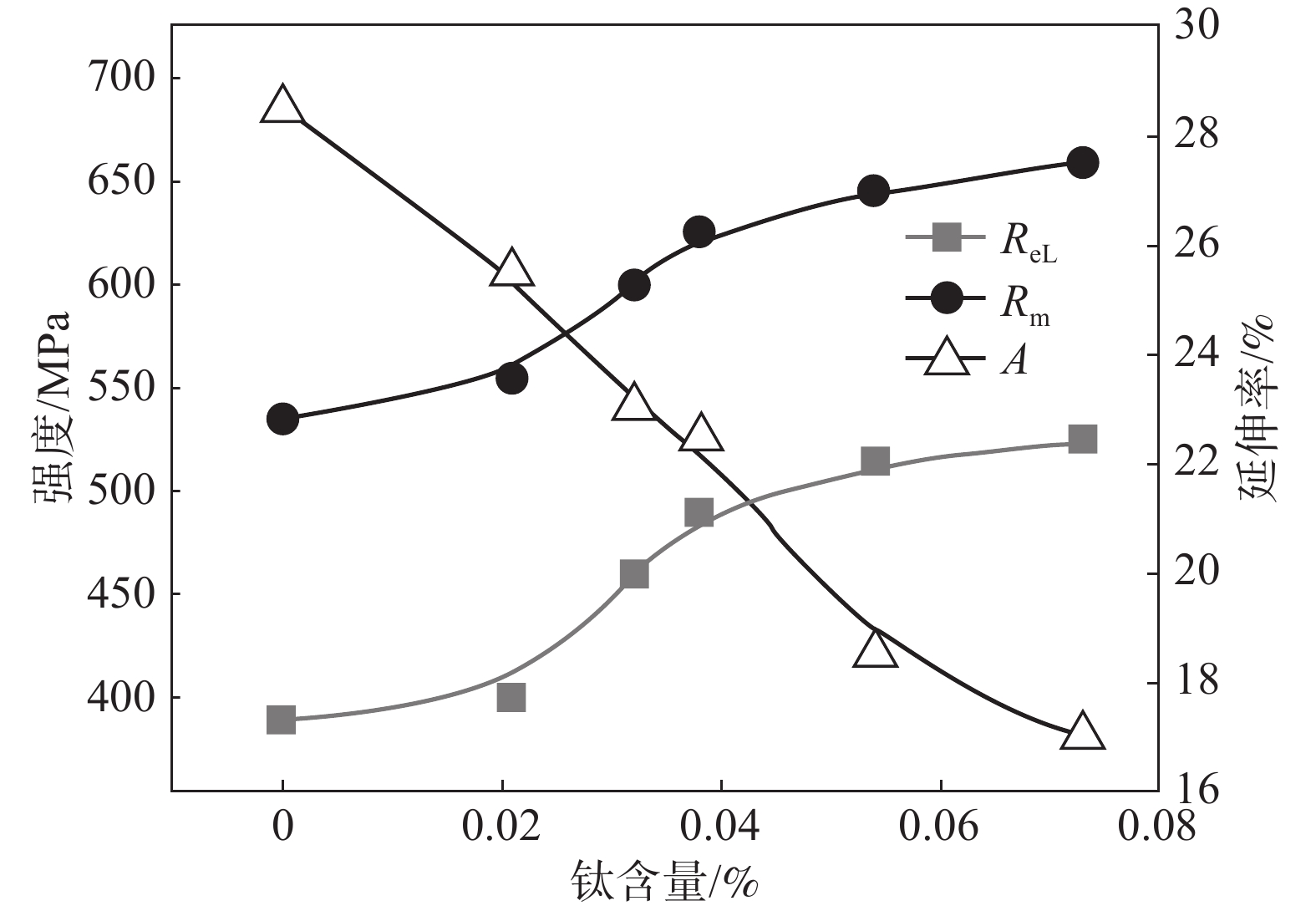
摘要: 在某钢厂冶炼的0.17C-0.30Si-1.40Mn钢中添加不同含量的微合金化元素钛,热连轧成板卷后逐卷取样进行力学性能测试和金相组织检验,并采用碳复型萃取方法制作薄膜样品进行透射电镜观察,研究了钛含量对0.17C-0.30Si-1.40Mn钢组织和力学性能的影响。结果表明:随钢中钛含量由0增加至0.073%,当Ti含量≤0.020%时,强度缓慢提高;当Ti含量为0.021%~0.038%时,强度显著提高;当Ti含量>0.038%时,强度增加趋缓。钛加入0.17C-0.30Si-1.40Mn钢越多,钢的延伸率和冲击功下降就越多。钛对0.17C-0.30Si-1.40Mn钢的显微组织影响不大,仅能使其晶粒尺寸略微减小。钛在0.17C-0.30Si-1.40Mn钢中只能沉淀析出少量尺寸较大的Ti(N,C)和Ti4C2S2颗粒,起到微弱的细晶强化作用,但是钛在钢中能够沉淀析出大量细微的TiC颗粒,产生强烈的沉淀强化作用。此外,研究发现钛含量对低碳锰钢力学性能的影响还与钢中碳含量有关,钢中碳含量不同,强度随钛含量转变曲线上的2个拐点也不相同。Abstract: 0.17C-0.30Si-1.40Mn steels with different titanium contents were prepared by smelting process. After hot rolling into hot-rolled coils, samples were taken for mechanical property test and metallographic structure inspection. Thin-film samples were made by the carbon replica extraction method for transmission electron microscope observation. The effect of titanium content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 0.17C-0.30Si-1.40Mn steel was studied. The results show that the strength evolution corresponds to the Ti content (from 0 to 0.073%). The strength increases slowly when the Ti content is less than 0.020%, subsequently the strength increases significantly when the Ti content is 0.021%-0.038%, finally, the strength increases slowly again when the Ti content is more than 0.038%. The more titanium is added into 0.17C-0.30Si-1.40Mn steel, the more the elongation and impact energy decrease. Titanium has little effect on the microstructure of 0.17C-0.30Si-1.40Mn steel and can only slightly reduce its grain size. A small amount of Ti(N, C) and Ti4C2S2 particles of large size can be precipitated in 0.17C-0.30Si-1.40Mn steel, which weakly plays a fine-grain strengthening; however, a large number of fine TiC particles can be precipitated in the steel, resulting in strong precipitation strengthening effect. It is found that the influence of titanium content on the mechanical properties of low carbon manganese steel is also related to the carbon content in the steel. The two inflection points of the curve about strength transformation with titanium content also vary with different carbon content in the steel. Thereby restraining martensitic phase transformation.
-
表 1 6炉试验钢的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of 6 heats of test steel
% 编号 C Si Mn P S Alt Als Ti O N 1 0.16 0.35 1.40 0.015 0.008 0.017 0.016 0 0.0018 0.0025 2 0.17 0.30 1.38 0.015 0.005 0.026 0.025 0.021 0.0017 0.0023 3 0.17 0.32 1.40 0.017 0.008 0.029 0.028 0.032 0.0019 0.0024 4 0.16 0.31 1.38 0.014 0.008 0.027 0.025 0.038 0.0017 0.0031 5 0.17 0.27 1.39 0.012 0.006 0.022 0.021 0.054 0.0023 0.0026 6 0.17 0.31 1.38 0.011 0.005 0.031 0.029 0.073 0.0016 0.0021 -
[1] Xu Fengyun, Bai Bingzhe, Fang Hongsheng. Development of titanium micro-alloying in high strength low alloy steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2007,32(12):29−34. (许峰云, 白秉哲, 方鸿生. 低合金高强度钢钛微合金化进展[J]. 金属热处理, 2007,32(12):29−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6051.2007.12.006Xu Fengyun, Bai Bingzhe, Fang Hongsheng. Development of titanium micro-alloying in high strength low alloy steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2007, 32(12): 29-34. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6051.2007.12.006. [2] Cai Zhen, Han Bin, Tan Wen, et al. Development status of titanium micro-alloying technology[J]. China Metallurgy, 2015,25(2):1−5. (蔡珍, 韩斌, 谭文, 等. 钛微合金化技术发展现状[J]. 中国冶金, 2015,25(2):1−5. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20140086Cai Zhen, Han Bin, Tan Wen, et al. Development status of titanium micro-alloying technology[J]. China Metallurgy, 2015, 25(2): 1-5. DOI: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20140086. [3] Mao Xinping, Chen Qilin, Zhu Dayan. Recent development of microalloying technology in thin slab casting and rolling process[J]. Iron and Steel, 2008,43(4):1−9. (毛新平, 陈麒琳, 朱达炎. 薄板坯连铸连轧微合金化技术发展现状[J]. 钢铁, 2008,43(4):1−9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2008.04.001MaoXinping, Chen Qilin, Zhu Dayan. Recent development of microalloying technology in thin slab casting and rolling process[J]. Iron and Steel, 2008, 43(4): 1-9. . DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0449-749 X.2008.04.001. [4] Liu W J, Jonas J J. Nucleation kinetics of Ti carbonitride in microalloyed austenite[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1989,20A:689−697. doi: 10.1007/BF02667586 [5] Turkdogan E T. Causes and effects of nitride and carbonitride precipitation in HSLA steels in relation with continuous casting[J]. Steelmaking Conference Proceedings(AIME), 1987,70:399−416. [6] Saikaly W, Bano X, Issartel C, et al. The effects of thermomechanical processing on the precipitation in a industrial dualphase steel microalloyed with titanium[J]. Metallurgical and Materials TransactionsA, 2001,32A(8):1939−1947. doi: 10.1007/s11661-001-0006-0 [7] Soto R, Saikaly W, Bano X, et al. Statistical and theoretical analysis of precipitates in dual-phase steels microalloyed with titanium and their effect on mechanical properties[J]. Acta Material, 1999,47(12):3475−3481. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(99)00190-1 [8] Huo Xiangdong, Mao Xinpin, Chen Kangmin, et al. Influence of titanium content on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot rolled strips[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2009,30(1):23−28. (霍向东, 毛新平, 陈康敏, 等. Ti含量对热轧带钢组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2009,30(1):23−28. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2009.01.005Huo Xiangdong, Mao Xinpin, Chen Kangmin, et al. Influence of titanium content on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot rolled strips[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2009, 30(1): 23-28. DOI:CNKI:SUN:GTFT.0.2009-01-010. [9] Wang Jianfeng, Deng Shen, Rao Jiangping, et al. Experimental study on the Ti microalloyed Q345E steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2010,31(2):20−25. (王建锋, 邓深, 饶江平, 等. 钛微合金化Q345E钢的试验研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2010,31(2):20−25.Wang Jianfeng, Deng Shen, Rao Jiangping, et al. Experimental study on the Ti microalloyed Q345 E steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2010, 31(2): 20-25. [10] Zhao Xiaoting, Song Guobin, Li Hongbin. Effect of Ti content on mechanical properties of C-Mn steel in heavy plate[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2012,41(14):77−79. (赵小婷, 宋国斌, 李红斌. Ti含量对碳锰钢厚板力学性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2012,41(14):77−79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3814.2012.14.021Zhao Xiaoting, Song Guobin, Li Hongbin. Effect of Ti content on mechanical properties of C-Mn steel in heavy plate[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2012, 41(14): 77-79. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3814.2012.14.021. [11] Mao Xinping, Sun Xinjun, Kang Yonglin, et al. Physical metallurgy for the titanium microailoyed strip produced by thin slab casting and rolling process[J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica, 2006,42(10):1091−1095. (毛新平, 孙新军, 康永林, 等. 薄板坯连铸连轧Ti微合金化钢的物理冶金学特征[J]. 金属学报, 2006,42(10):1091−1095. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2006.10.018Mao Xinping, Sun Xinjun, Kang Yonglin, et al. Physical metallurgy for the titanium microailoyed strip produced by thin slab casting and rolling process[J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica , 2006, 42(10): 1091-1095. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2006.10.018. [12] Petch N J. The cleavage strength of polycrystals[J]. Journal of the Iron and Steel Institute, 1953,174:25−28. doi: 10.1016/0001-6160(53)90043-1 [13] Gladman T, Pickering F B. Grain-coarsening of austenite[J]. Journal of the Iron and Steel Institute, 1967,205(6):653−664. [14] Gladman T, Mcivor I D, Pickering F B. Effect of carbide and nitride particles on the recrystallization of ferrite[J]. Journal of the Iron and Steel Institute, 1971,(5):380−390. -





 下载:
下载: