Study of carbide evolution in a 6Cr13Mo stainless steel
-
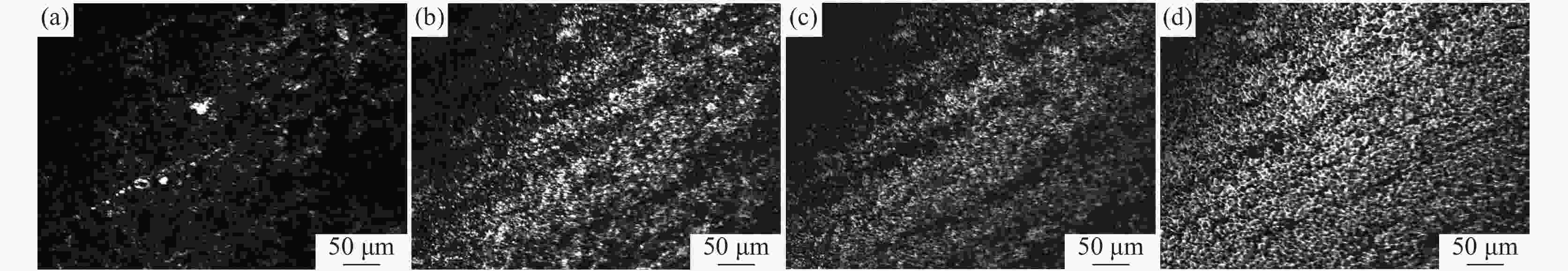
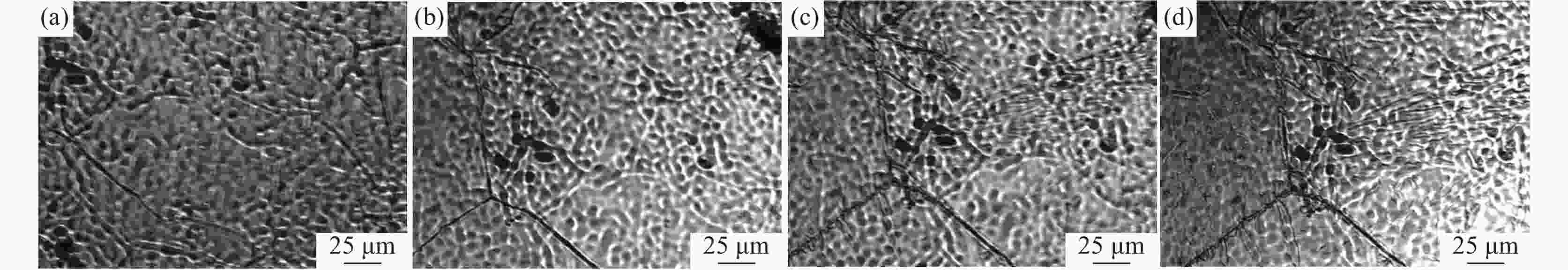
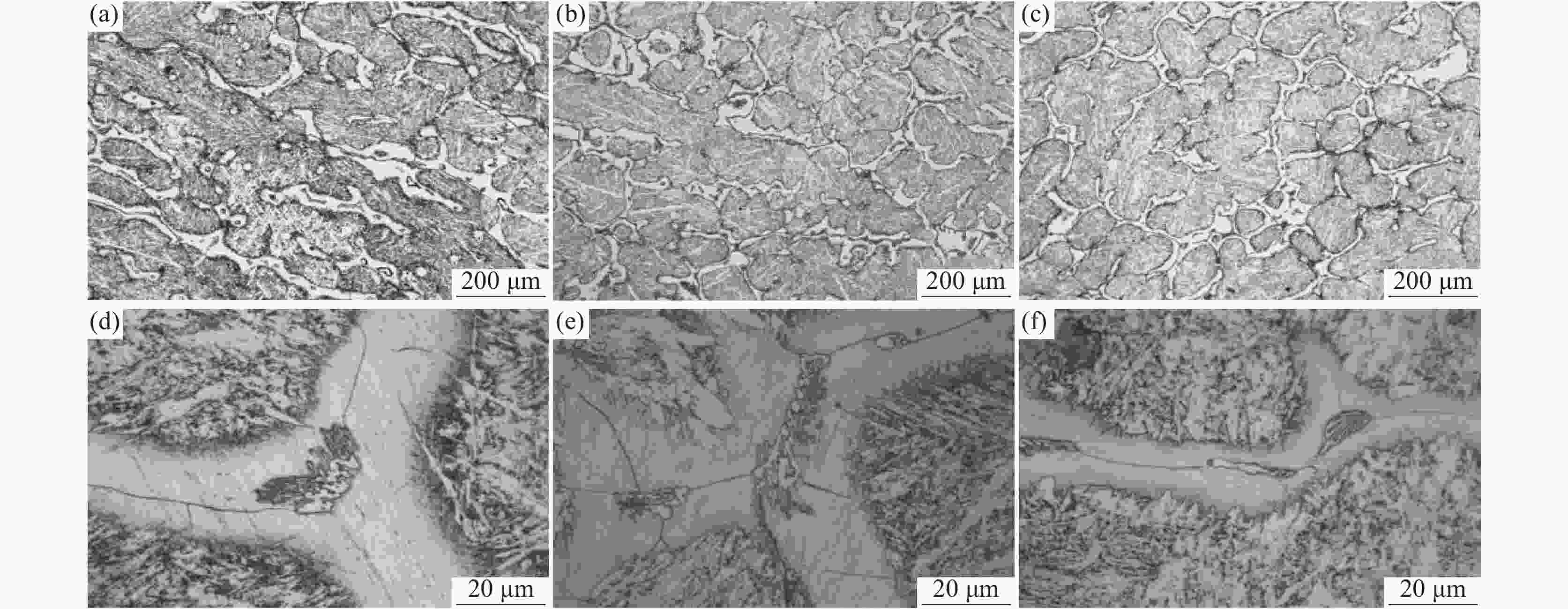
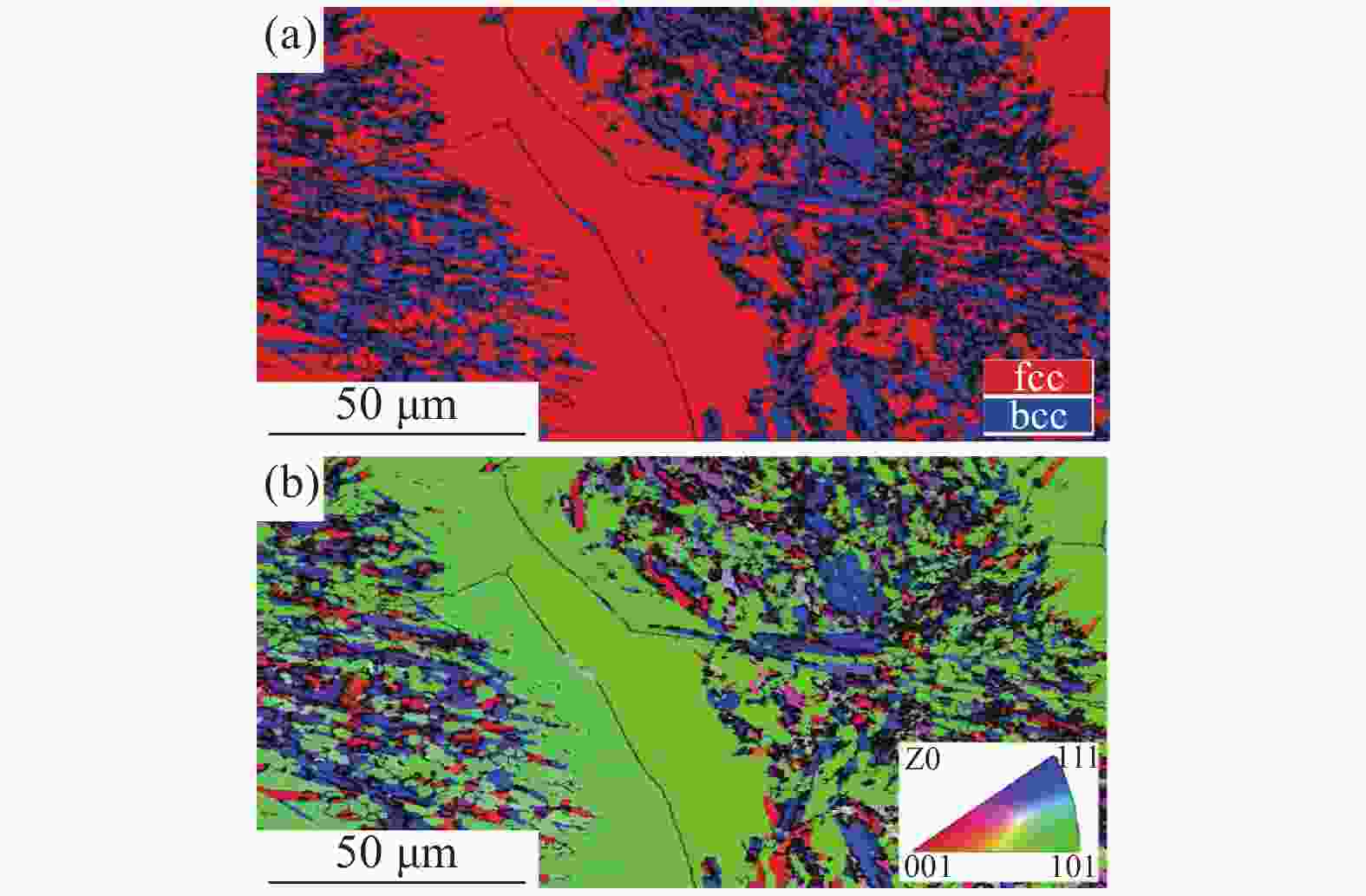
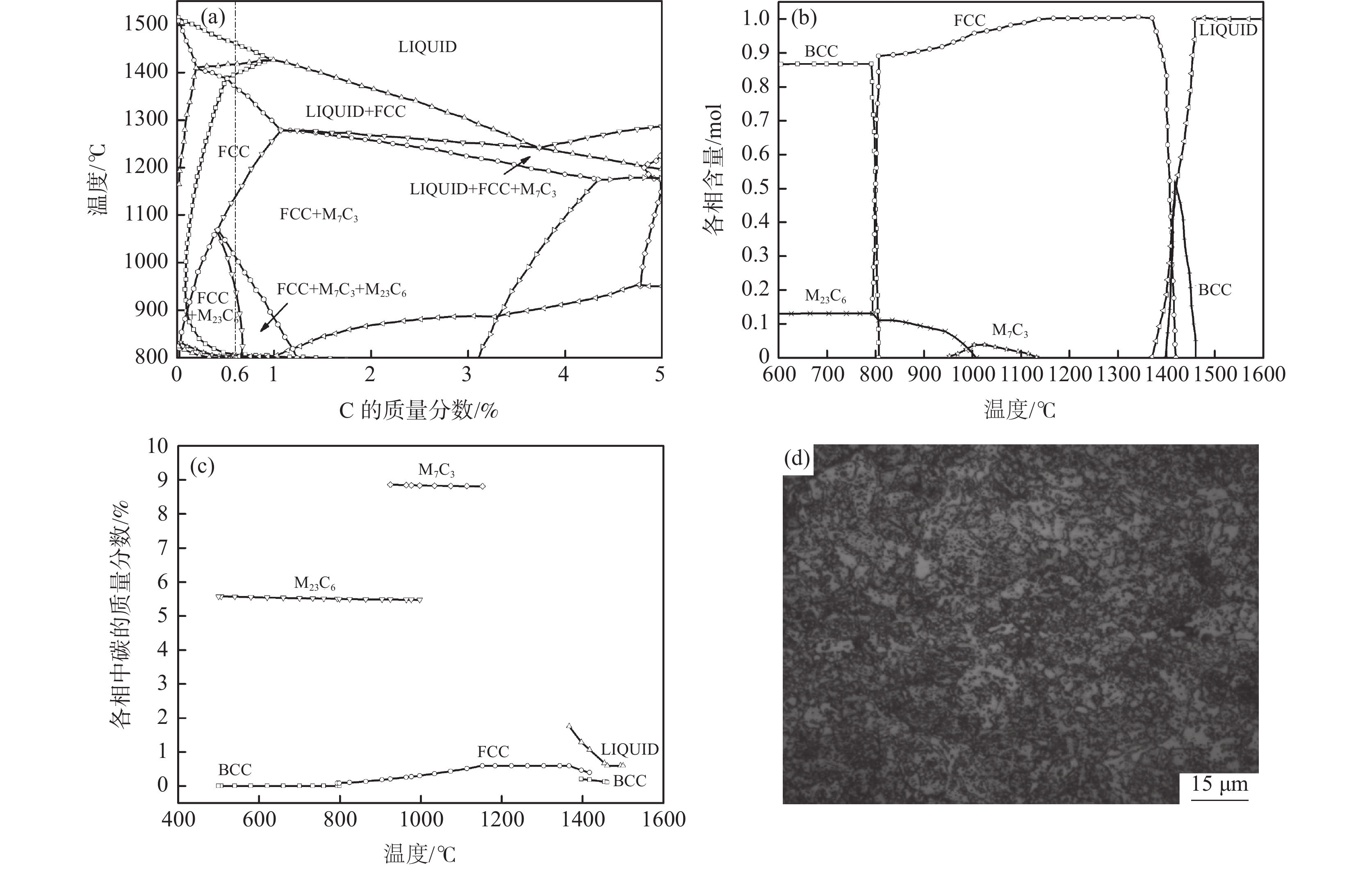
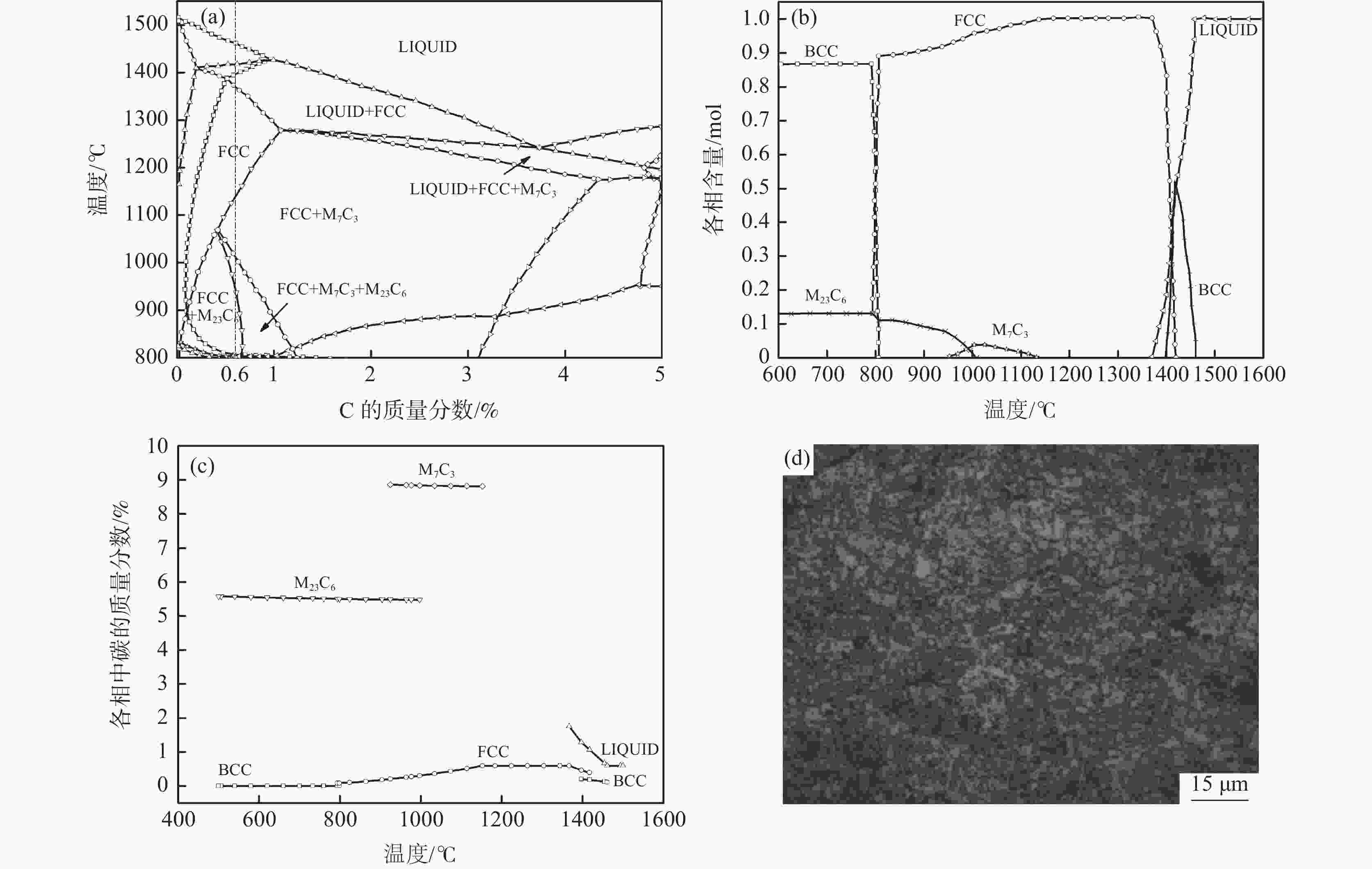
摘要: 采用Thermo-Calc热力学软件对6Cr13Mo不锈钢进行了相图计算,利用超高温共聚焦显微镜模拟了6Cr13Mo不锈钢加热、冷却及凝固过程,观察分析了碳化物的演变规律。结果表明:相图计算的6Cr13Mo不锈钢平衡室温组织为铁素体和M23C6类型碳化物;凝固过程中成分发生凝固偏析,当液相中C含量达到约为1%时,成分体系变为亚共晶钢体系,在析出奥氏体的同时,液相中直接析出M7C3类型的碳化物;加热过程中,随着温度升高,碳化物呈先增加后减少趋势;降温过程中,随着温度降低,碳化物逐渐增多,且在800 ℃时达到峰值;凝固过程中,随着凝固速率的提高,M7C3数量减少且形态改变。
-
关键词:
- 6Cr13Mo不锈钢 /
- 凝固;偏析 /
- M23C6碳化物 /
- M7C3碳化物 /
- 凝固速率
Abstract: Thermo-Calc thermodynamic software was used to calculate the phase diagram of 6Cr13Mo stainless steel. The heating, cooling, and solidification processes of 6Cr13Mo stainless steel were simulated via an ultra-high temperature confocal microscope, and the evolution of carbide was observed and analyzed. The results show that the room temperature microstructure of 6Cr13Mo stainless steel calculated by phase diagram is ferrite and M23C6 type carbides. During the solidification process, the components undergo solidification segregation. The composition system changes into the hypoeutectic steel system when the content of C in the liquid phase reaches about 1%, and M7C3 type carbides precipitate directly from the liquid phase while austenite precipitates. During the heating process, the carbide first increases and then decreases with the increase in temperature. During the cooling process, the carbide gradually increases with the decrease of temperature and reaches a peak at 800 ℃. During the solidification process, the number of M7C3 decreases, and the morphology changes with the increase in the solidification rate. -
表 1 6Cr13Mo不锈钢主要合金成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of 6Cr13Mo stainless steel
% C Mn Si Cr Mo Ni 0.58~0.65 0.20~0.48 0.25~0.50 13~14 0.25~−0.32 ≤0.60 -
[1] Verhoeven J D, Pendray A H, Clark H F. Wear tests of steel knifeblades[J]. Wear, 2008,265(7/8):1093−1099. [2] Mesa D H, Toro A, Sinatora A, et al. The effect of testing temperatureon corrosion-erosion resistance of martensitic stainless steels[J]. Wear, 2003,255(S1/6):139−145. [3] Zhang Lixiang, Zhi Huaifeng, Zheng Fengmei, et al. Effect of cold rolling reduction on mechanical property and microstructure of 6Cr13Mo steel[J]. Metal Products, 2015,41(5):35−38. (张理想, 支怀峰, 郑风美, 等. 冷轧压下量对6Cr13Mo 钢力学性能及组织的影响[J]. 金属制品, 2015,41(5):35−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4226.2015.05.008Zhang Lixiang, Zhi Huaifeng, Zheng Fengmei, et al. Effect of cold rolling reduction on mechanical property and microstructure of 6 Cr13 Mo steel[J]. Metal Products, 2015, 41(5): 35-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4226.2015.05.008 [4] Liu Wenbo. A summary of engine piston ring materials[J]. Tropical Agricultural Engineering, 2008,32(2):16−19. (刘文波. 发动机活塞环材料综述[J]. 热带农业工程, 2008,32(2):16−19.Liu Wenbo. A summary of engine piston ring materials[J]. Tropical Agricultural Engineering, 2008, 32(2): 16-19. [5] 陆世英 著. 不锈钢概论[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 2007: 21-33.Lu Shiying. Introduction to stainless steel[M]. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press, 2007: 21-33. [6] (美)John C, Lippold Damian J, Kotecki. 不锈钢焊接冶金学及焊接性[M]. 陈剑虹, 译. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2008: 18-21.John C, Lippold Damian J, Kotecki. Welding metallurgy and weldability of stainless steels[M]. Chen Jianhong, Trans. Beijing: Machinery Industry Press, 2008: 18-21. [7] 袁兆静. 热处理对G95Cr18和G102Cr18Mo钢的组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 上海金属. 2018, 40(2): 59-63.Yuan Zhaojing. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of G95Cr18 and G102Cr18Mo steels[J]. Shanghai Metals. 2018, 40(2): 59-63. [8] Yu Wentao, Li Jing, Shi Chengbin, et al. Microstructure and carbides of as-cast high carbon martensitic stainless steel 8Cr13MoV[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2016,38(9):1264−1269. (于文涛, 李晶, 史成斌, 等. 高碳马氏体不锈钢8Cr13MoV 钢铸态组织及碳化物[J]. 工程科学学报, 2016,38(9):1264−1269.Yu Wentao, Li Jing, Shi Chengbin, et al. Microstructure and carbides of as-cast high carbon martensitic stainless steel 8 Cr13 MoV[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2016, 38(9): 1264-1269. [9] Yu Wentao, Li Jing, Shi Chengbin, et al. Evolution of carbides in high carbon martensite stainless steel 8Cr13MoV during spheroidizing annealing process[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2016,41(9):30−36. (于文涛, 李晶, 史成斌, 等. 高碳马氏体不锈钢8Cr13MoV球化退火过程中碳化物的演变[J]. 金属热处理, 2016,41(9):30−36.Yu Wentao, Li Jing, Shi Chengbin, et al. Evolution of carbides in high carbon martensite stainless steel 8 Cr13 MoV during spheroidizing annealing process[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2016, 41(9): 25-3. [10] 崔忠圻, 覃耀春. 金属学与热处理[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2013: 270.Cui Zhongqi, Qin Yaochun. Metallography and heat treatment[M]. Beijing: Machinery Industry Press, 2013: 270. [11] 陆世英. 不锈钢[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 1995: 15.Lu Shiying. Stainless steel[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 1995: 15. [12] 肖纪美. 不锈钢的金属学问题[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2006: 41.Xiao Jimei. Metal problems of stainless steel[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006: 41. -




 下载:
下载: