Evolution of inclusions in IF steel during continuous casting process
-
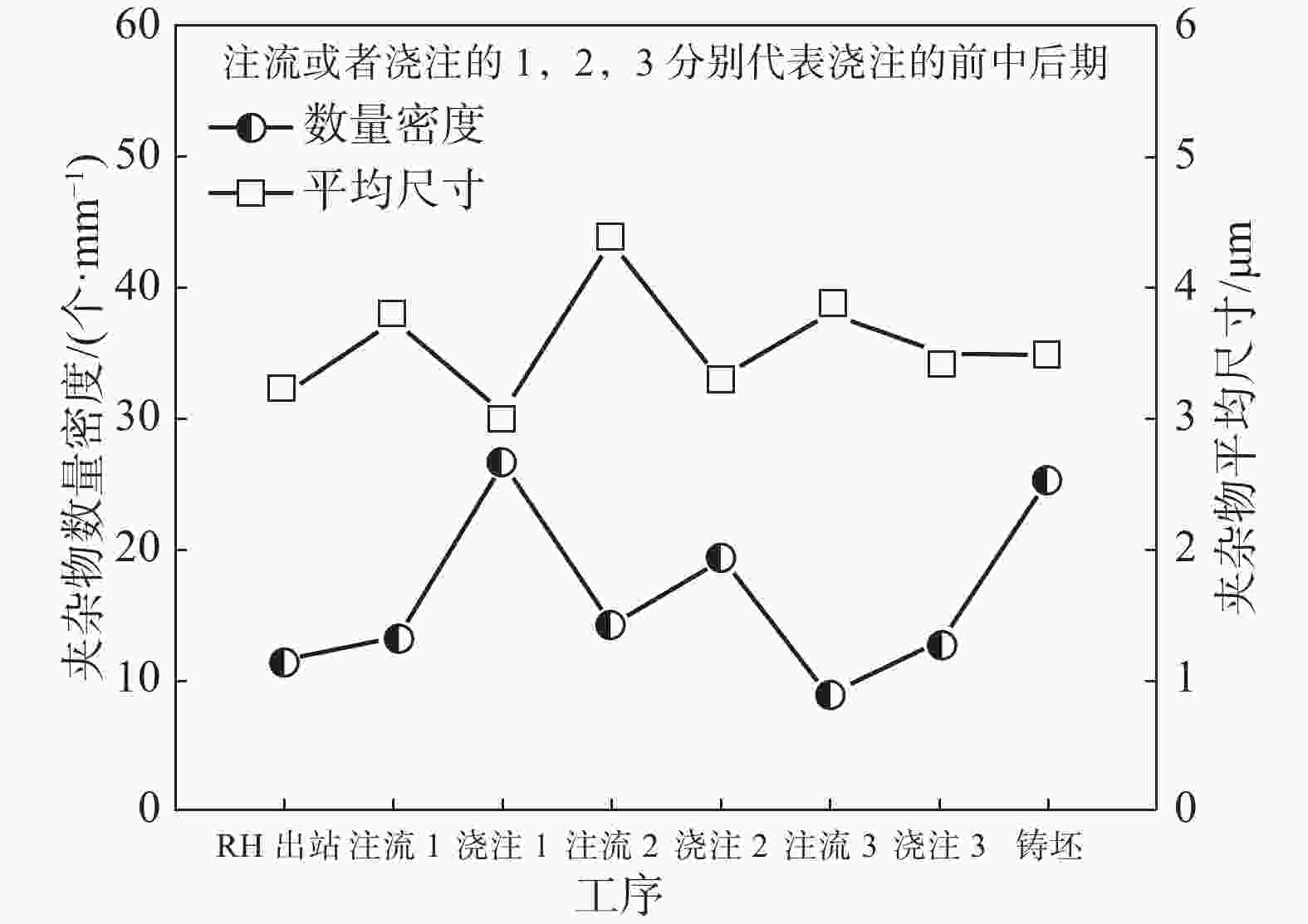
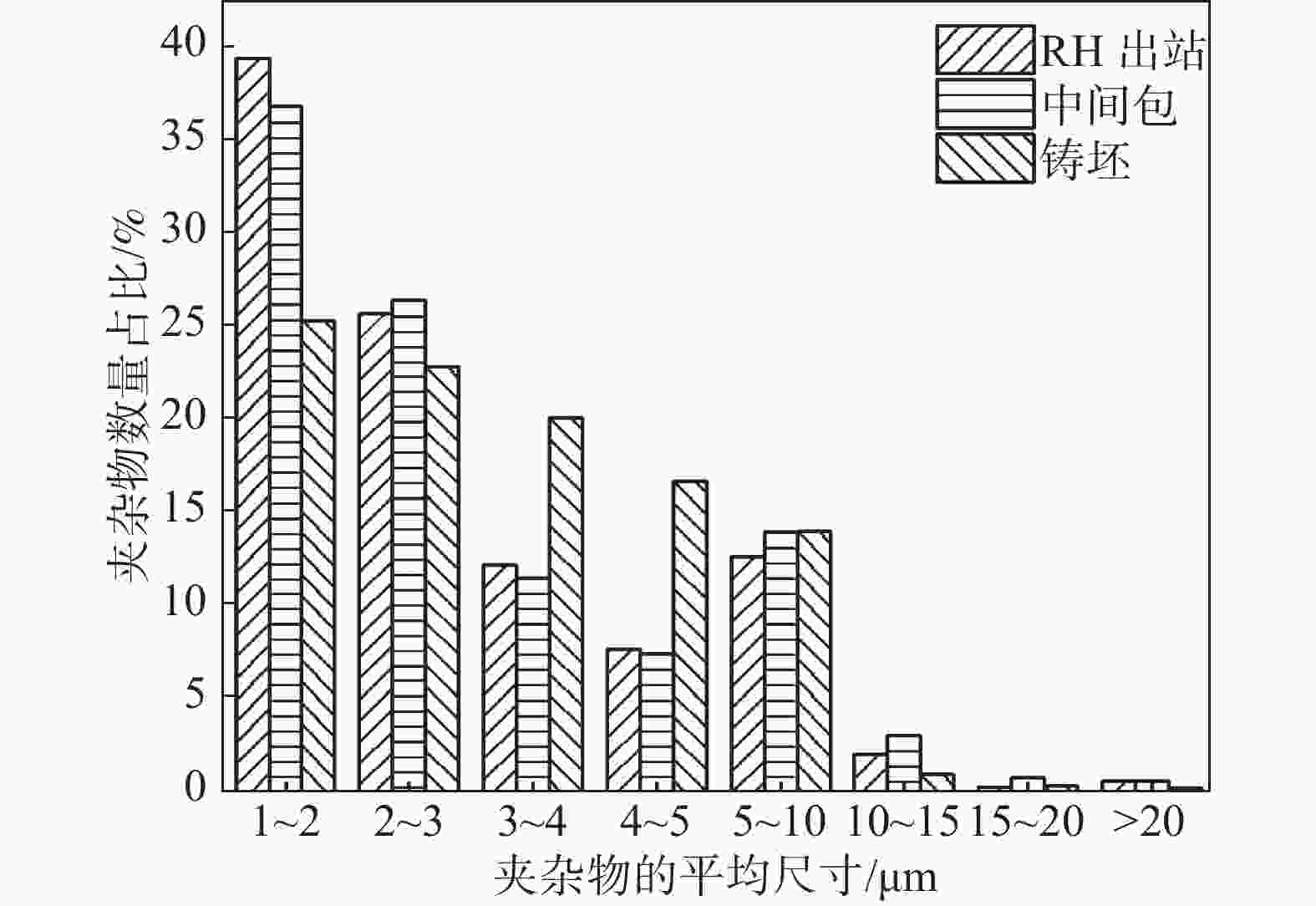
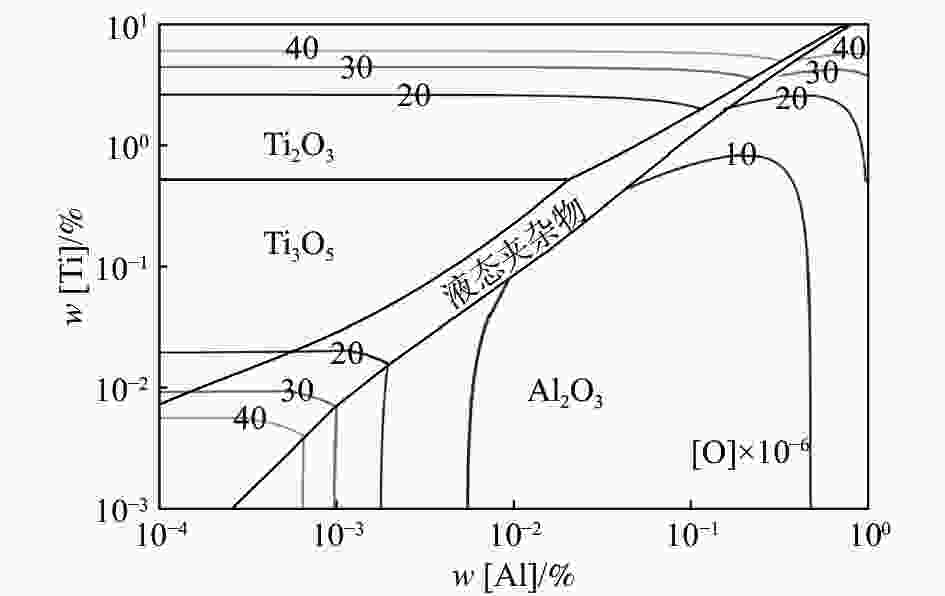
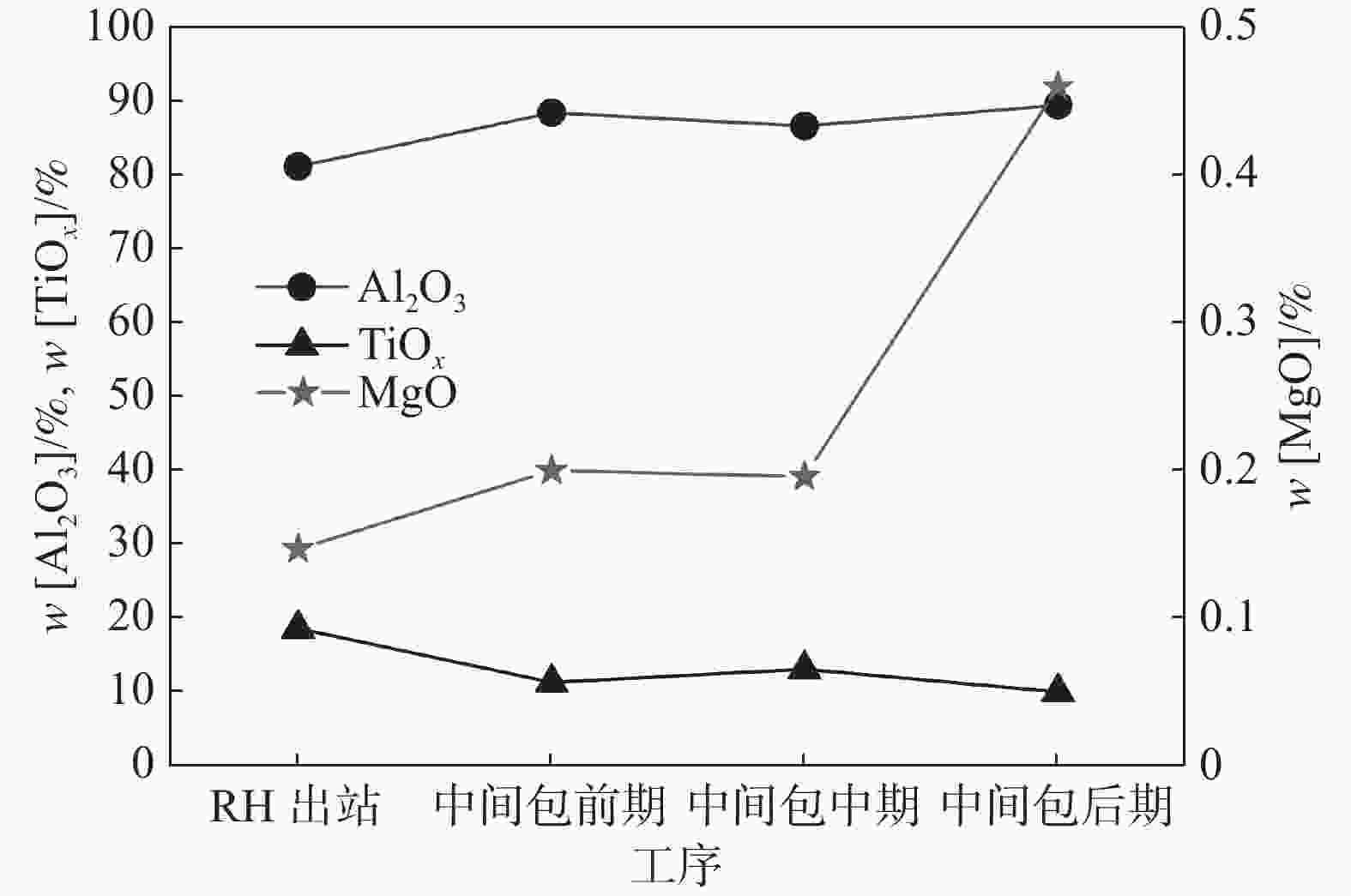
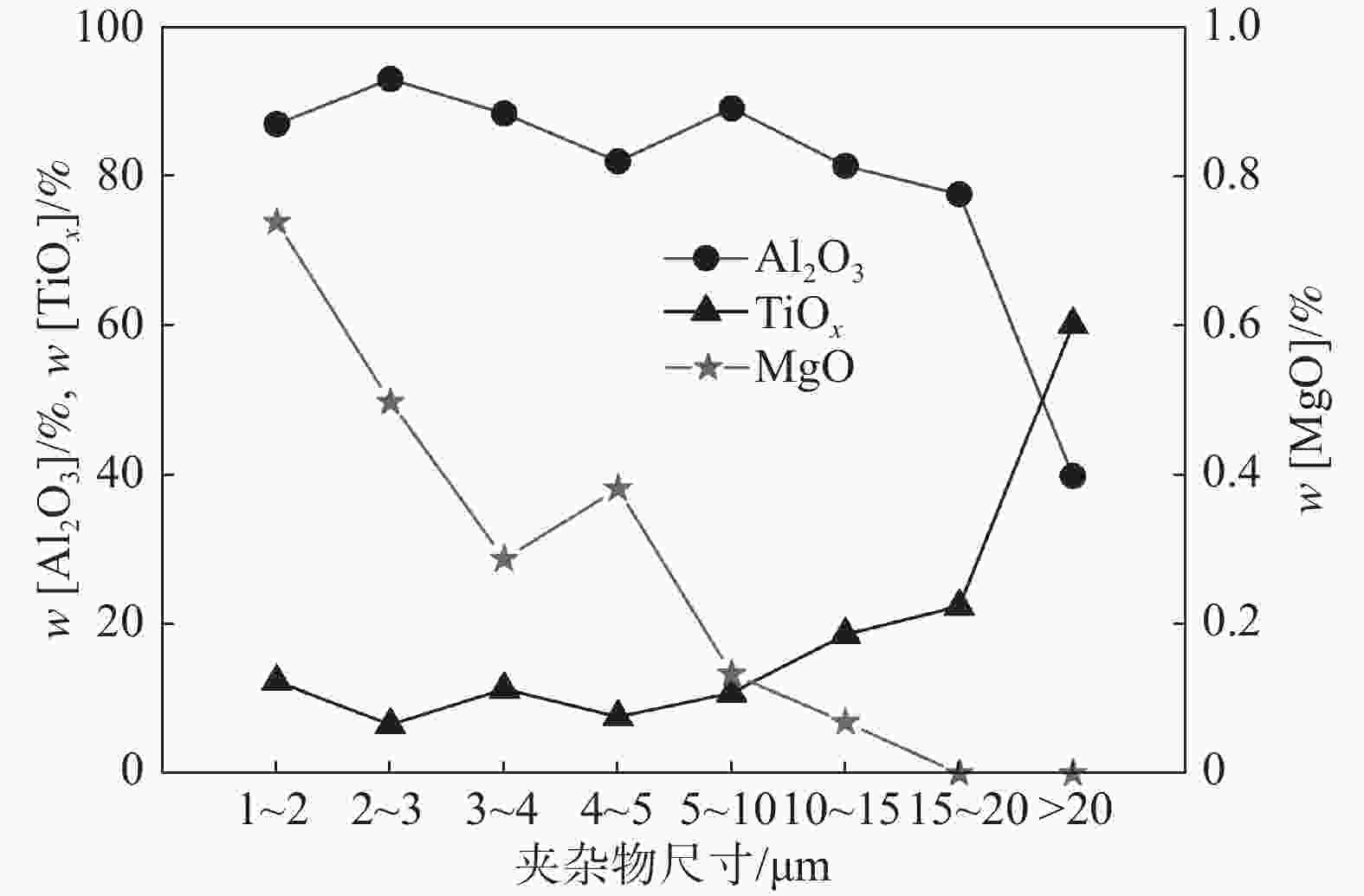
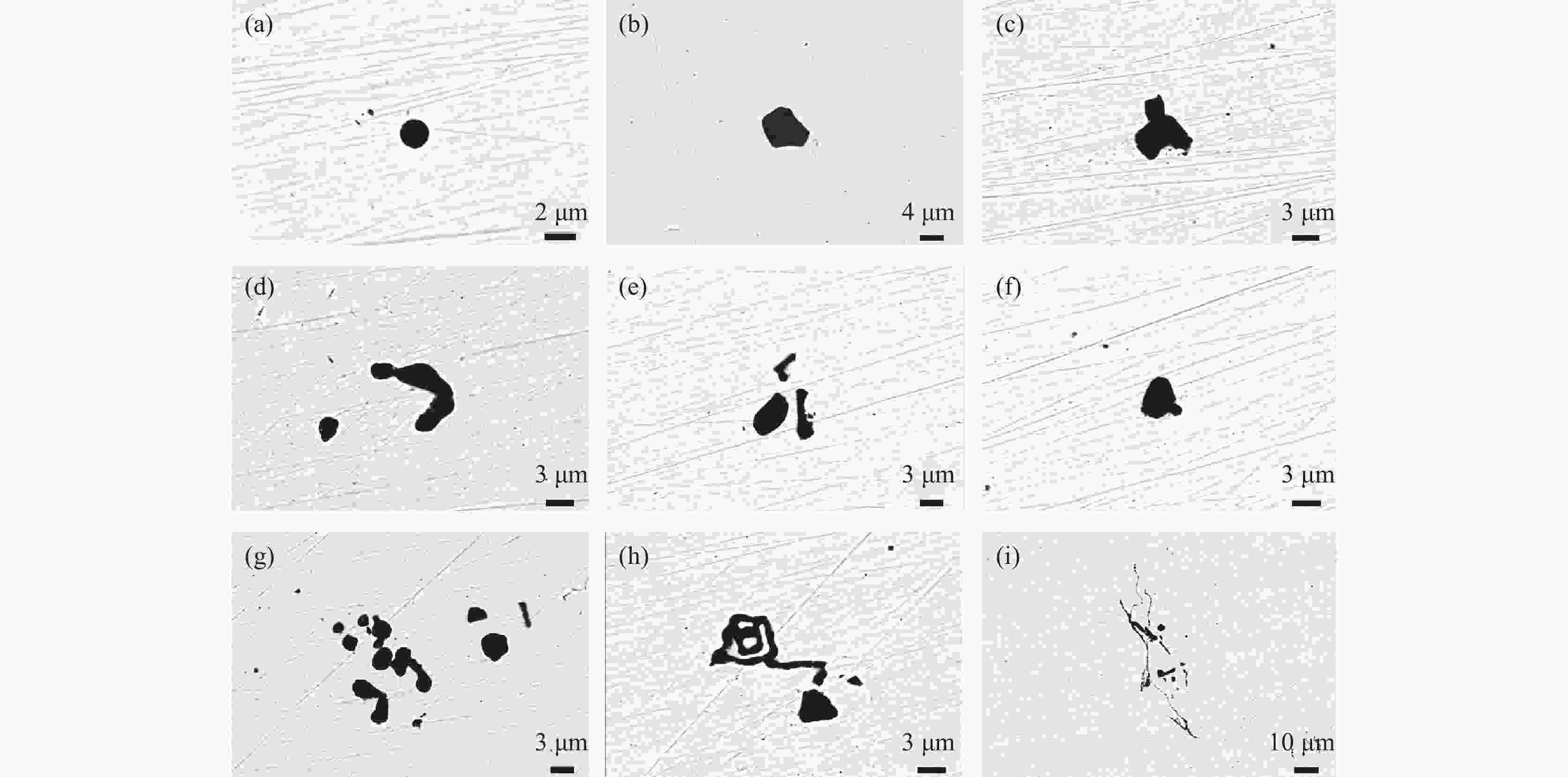
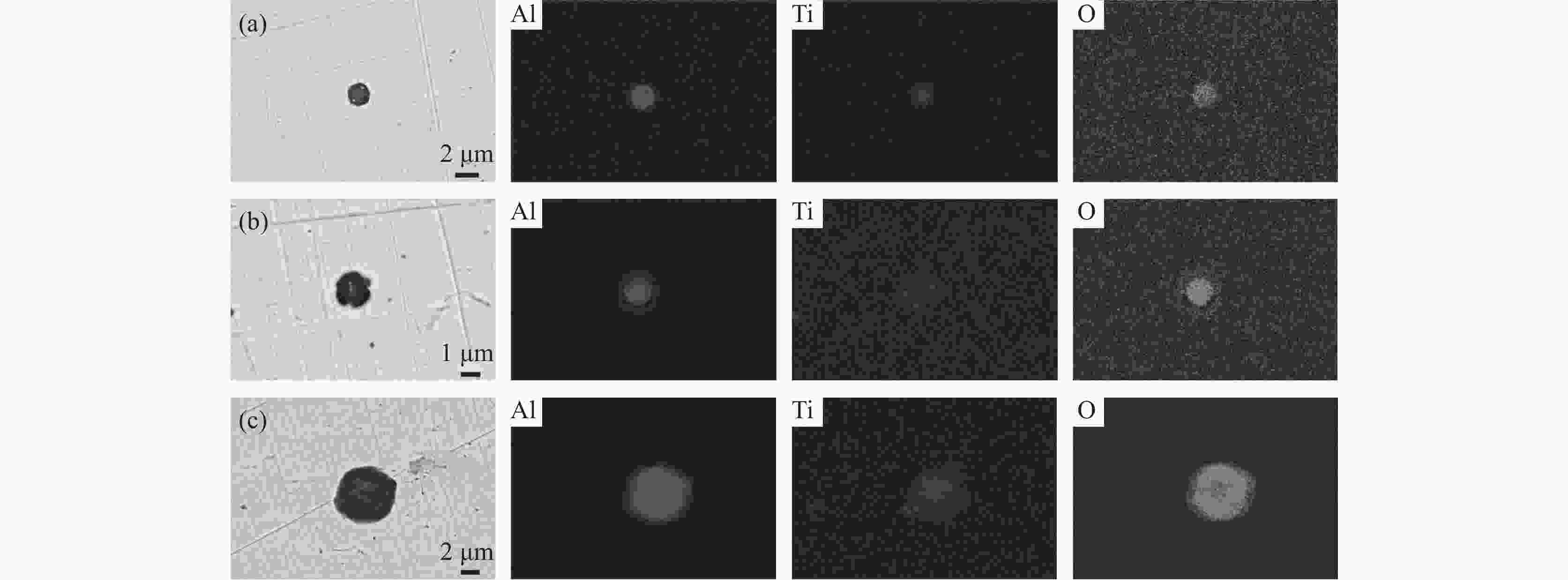
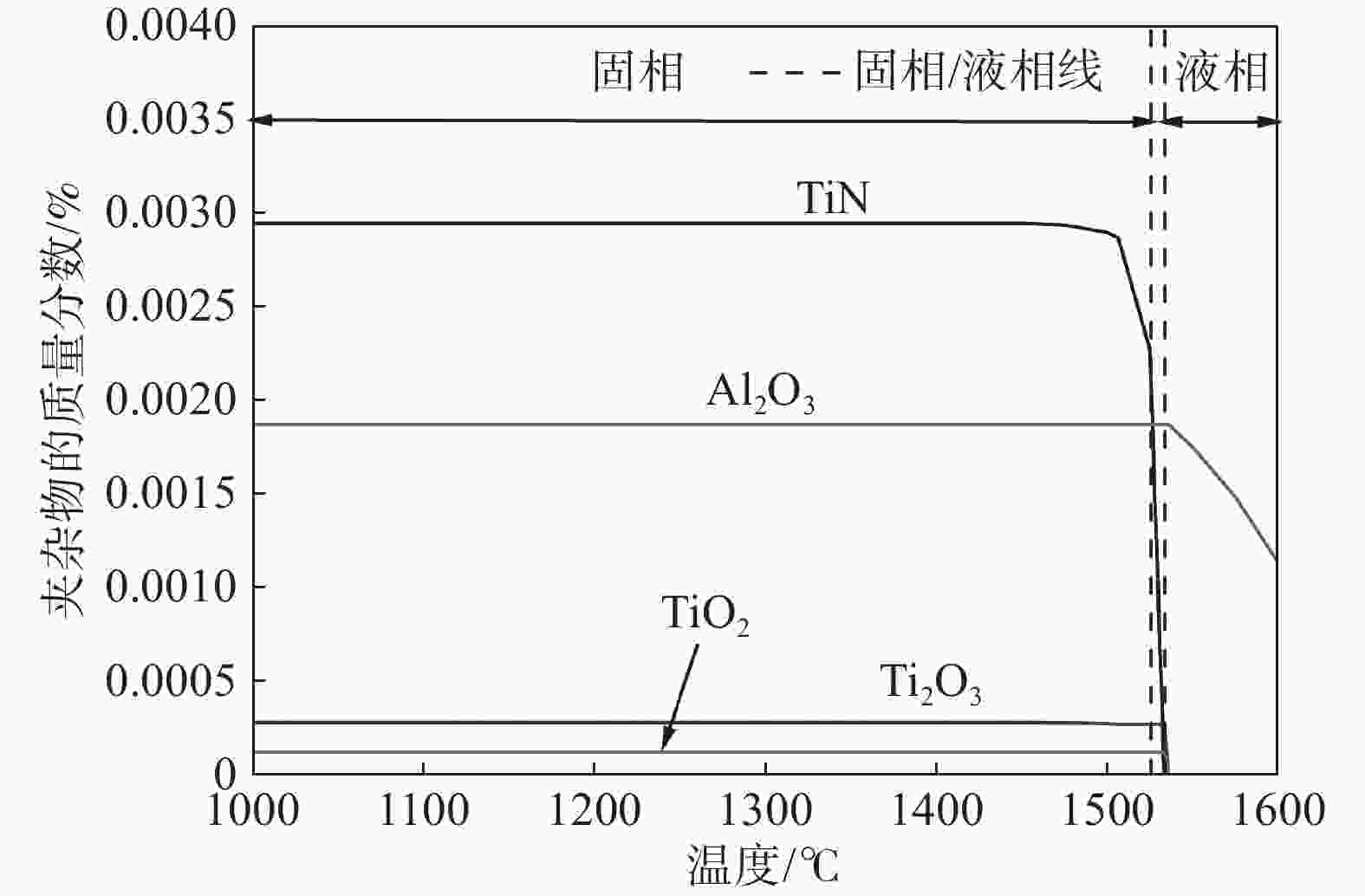
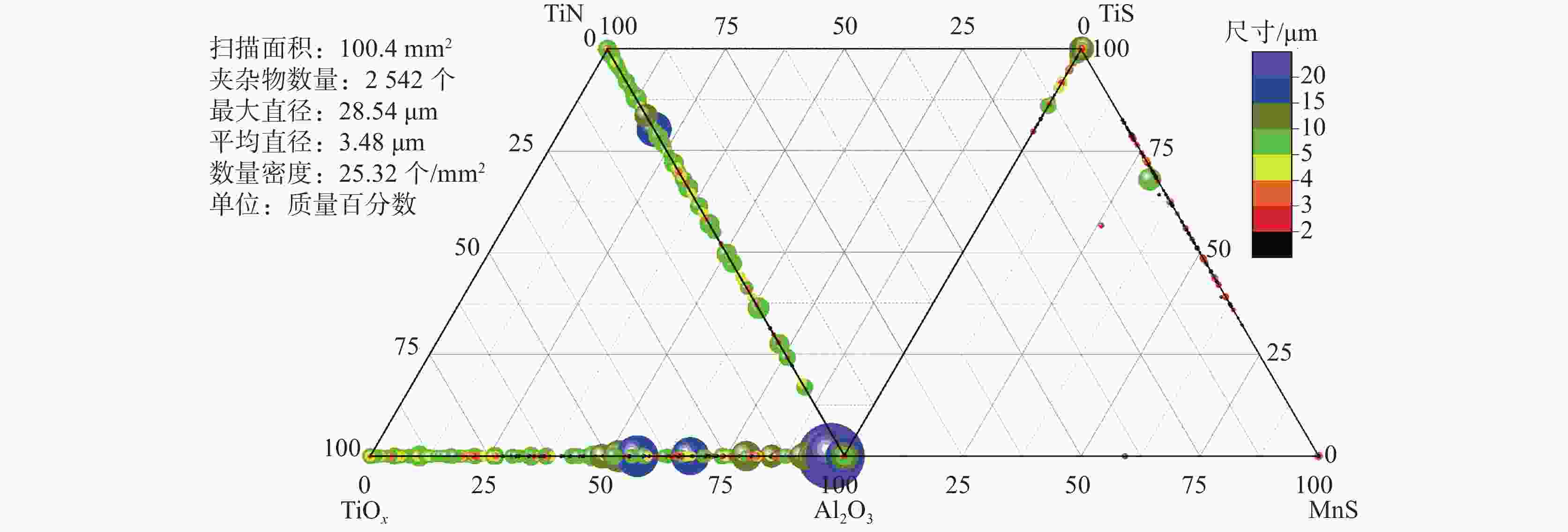
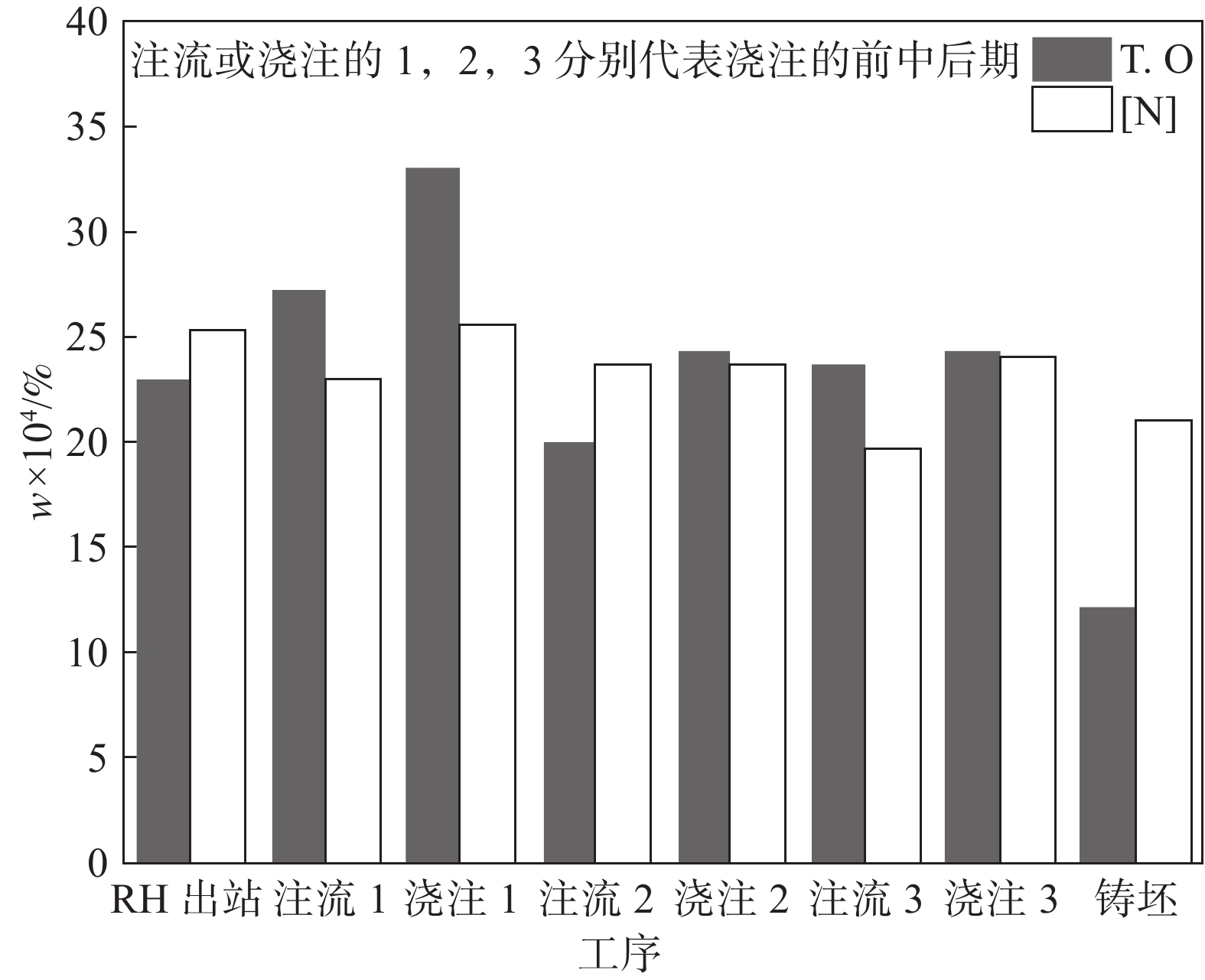
摘要: 针对某厂生产的IF钢连铸过程中间包钢液和铸坯取样,采取T.O、[N]含量分析和ASPEX扫描电镜-能谱仪等方法,并结合热力学计算分析了连铸过程钢中夹杂物的演变行为。结果表明,连铸过程钢中T.O含量整体呈现下降趋势,但中间包开浇阶段钢液受到覆盖剂或耐材的二次氧化,应适当调整覆盖剂成分或炉衬成分,铸坯中T.O含量为12×10−6,[N]含量为21×10−6,符合IF钢控制要求。夹杂物数量密度的变化趋势与T.O一致,铸坯中夹杂物数量密度增加是因为凝固冷却过程中有大量TiN析出。整个中间包过程注流区钢液中夹杂物的数量密度低于浇注区,但平均尺寸更大。随着浇注进行,中间包钢液夹杂物中MgO的含量逐渐升高,且与尺寸呈现负相关关系,大于10 μm的夹杂物集中分布在Al2O3含量高的区域。热力学计算结果表明1600 ℃时,钢液中稳定存在的夹杂物相只有Al2O3,然而试验结果中发现了较多的Al2O3-TiOx夹杂物,这是由于RH精炼过程加钛合金后,造成局部Ti浓度过高,为TiOx和Al2O3-TiOx的形成提供了条件。铸坯中存在TiS类夹杂物,包含纯TiS夹杂物和Al2O3-TiS及TiS-TiN的复合夹杂物,此类夹杂物的尺寸随着TiS质量分数的增大而减小。Abstract: The evolution of inclusions in steel of the continuous casting process of IF steel produced by a plant was studied by systematically sampling including molten steel and casting billet. The methods of analysis mainly include analysis of total oxygen and nitrogen content, ASPEX scanning electron microscope-spectrometer and thermodynamic calculations. The results show that the content of total oxygen in steel during continuous casting process presents a total decreasing trend. But there is a secondary oxidation of molten steel by covering agent or resistant material at the opening stage of tundish. The composition of covering agent or lining should be adjusted appropriately, so as to make the content of T.O and [N] in casting slab is 12×10−6 and 21×10−6, respectively, which meet the control requirements of IF steel. The trend of the number density of inclusions in steel during the continuous casting process is consistent with the trend of total oxygen content. The increase of the number density of inclusions in slab is subject to TiN precipitation during solidification and cooling. The number density of inclusions in the molten steel in the tundish injection area is lower than that in the pouring area during the entire tundish process, whose size is larger. With the pouring, the content of MgO of inclusions in the molten steel of tundish gradually increases, and shows a negative correlation with the size, and the inclusions larger than 10 μm are concentrated in the area with high Al2O3 content. Thermodynamic calculation results show that the stable inclusion phase in the molten steel at 1 600 °C is only Al2O3, but some Al2O3−TiOx inclusions are found in the experimental results, which is due to the addition of titanium alloys in the RH refining process causing the local Ti concentration to be too high, which provides conditions for the formation of TiOx and Al2O3−TiOx. There are TiS-containing inclusions in slab, including pure TiS inclusions and composite inclusions of Al2O3−TiS and TiS-TiN, and the size of such inclusions decreases with the increase of mass fraction of TiS.
-
Key words:
- IF steel /
- continuous casting /
- non-metallic inclusions /
- evolution /
- thermodynamic calculation
-
表 1 IF钢化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of IF steel
% 工序 C Si Mn P S Als T.Al T.Ti RH出站 0.001 0.0018 0.13 0.007 0.007 0.035 0.038 0.063 成品值 0.0018 0.002 0.13 0.007 0.007 0.026 0.027 0.056 表 2 连铸中间包钢液中不同类型夹杂物的比例
Table 2. Proportion of different types of inclusions in molten steel of continuous casting tundish
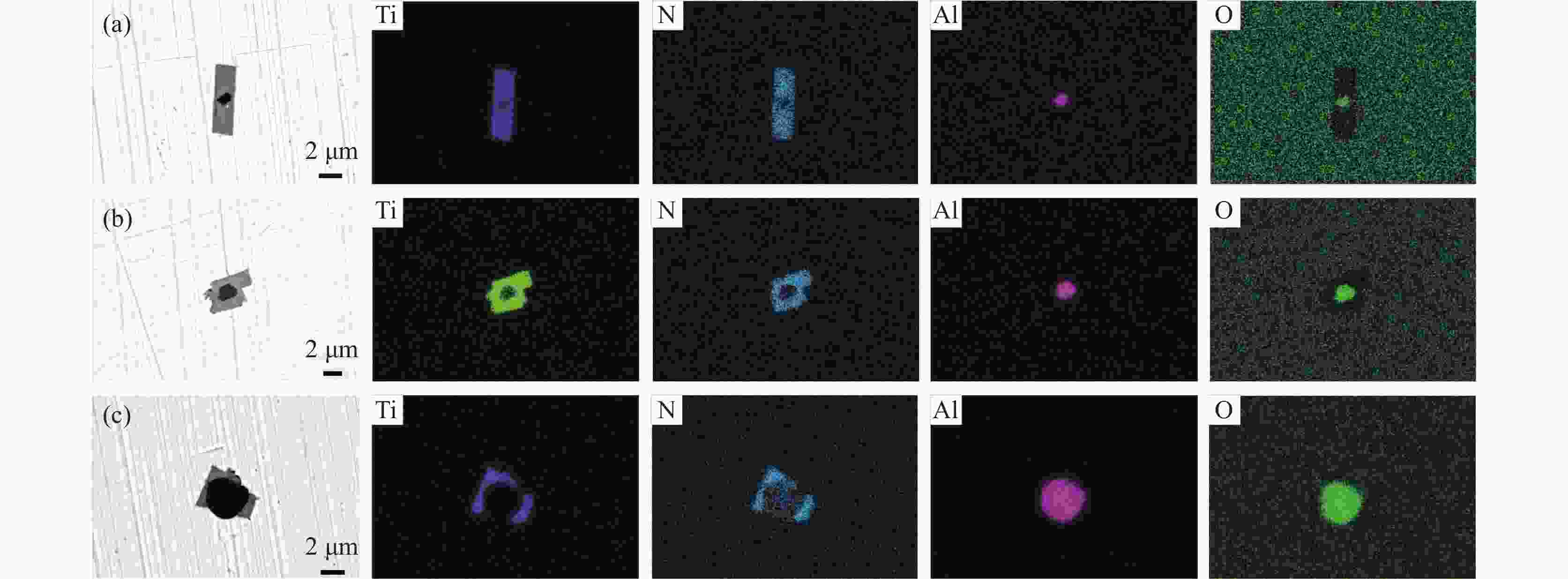
% 工序 Al2O3 Al2O3-TiOx 其他 RH出站 55.2 32.7 12.1 中间包前期注流区 67.3 24.4 8.3 中间包前期浇注区 75.5 17.9 6.6 中间包中期注流区 46.6 33.3 20.1 中间包中期浇注区 68.3 22.7 9 中间包后期注流区 65.6 23.6 10.8 中间包后期浇注区 72.2 16.4 11.4 表 3 铸坯中不同类型夹杂物的比例
Table 3. Proportion of different types of inclusions in slab
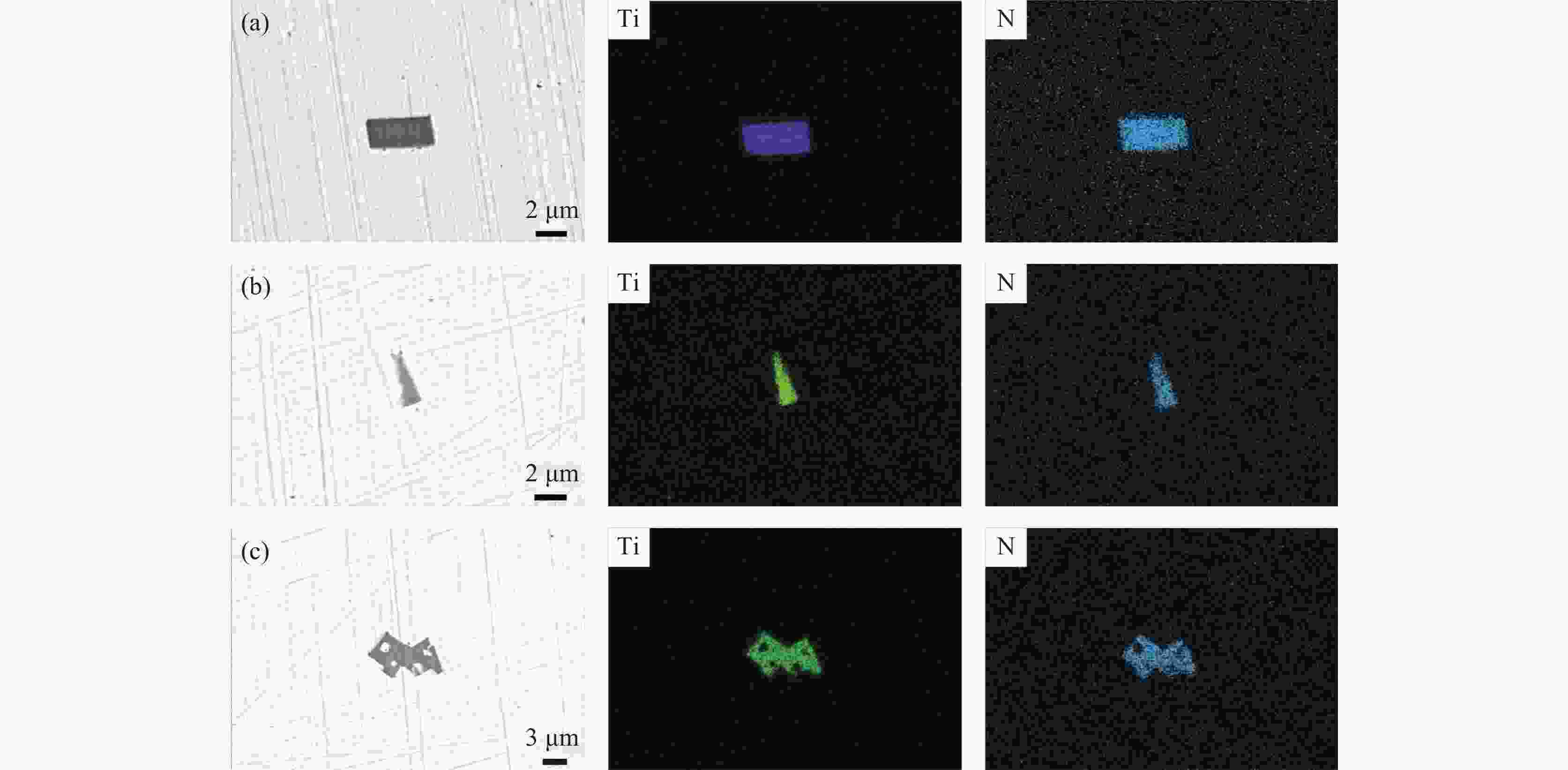
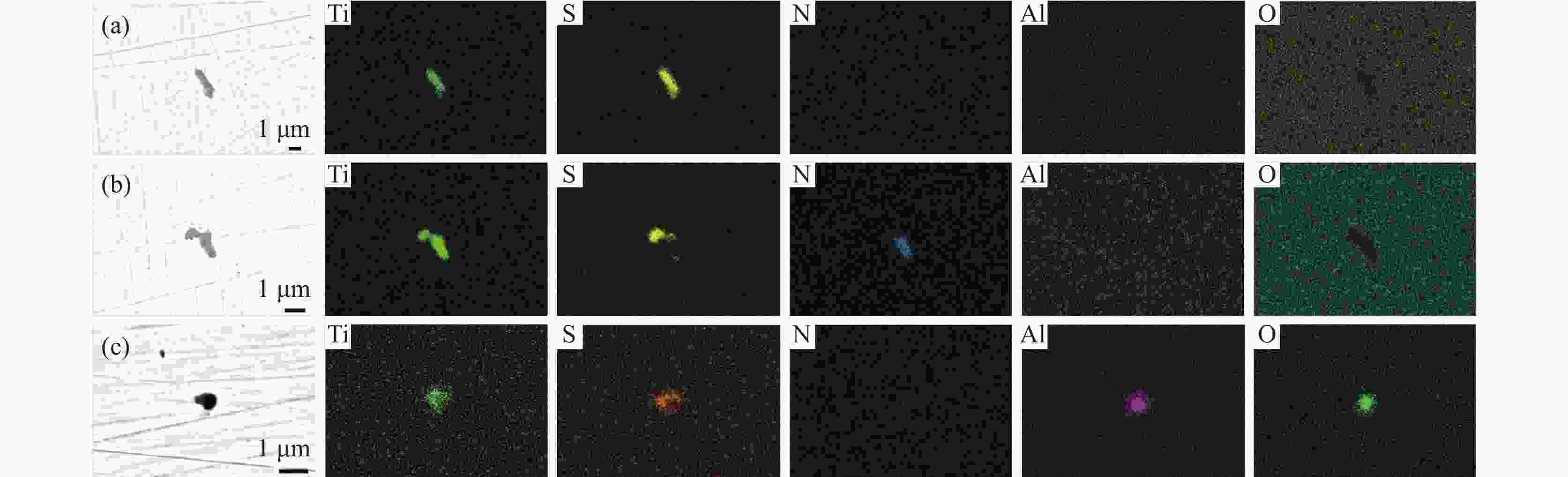
% Al2O3 Al2O3-TiOx TiN Al2O3-TiN 含TiS类 MnS 11.1 24.4 28.7 19.7 15.5 0.6 -
[1] Yang Wen, Wang Xinhua, Zhang Lifeng, et al. Cleanliness of low carbon aluminum-killed steels during secondary refining processes[J]. Steel Research International, 2013,84(5):473. doi: 10.1002/srin.201200213 [2] Deng Jianjun, Wang Rui, Hao Yang, et al. Cause and control of strip defects on the surface of IF steel cold-rolled plate[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(2):156−160. (邓建军, 王睿, 郝阳, 等. IF钢冷轧板表面条状缺陷成因及控制[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(2):156−160. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.02.027Deng Jianjun, Wang Rui, Hao Yang, et al. Cause and control of strip defects on the surface of IF steel cold-rolled plate[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium , 2017, 38(2): 156-160. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.02.027 [3] Yue Feng, Cui Heng, Bao Yanping, et al. Behavior of inclusions in Ti-IF steel[J]. Steelmaking, 2009,25(4):9−12. (岳峰, 崔衡, 包燕平, 等. Ti-IF钢中夹杂物的行为[J]. 炼钢, 2009,25(4):9−12.Yue Feng, Cui Heng, Bao Yanping, et al. Behavior of inclusions in Ti-IF Steel[J]. Steelmaking, 2009, 25(4): 9-12. [4] Wang Quan, Liu Jianhua, Liu Jianfei, et al. Distribution of inclusions in IF steel casting billet[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2013,34(4):62−67. (王全, 刘建华, 刘建飞, 等. IF钢铸坯中夹杂物的分布规律[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2013,34(4):62−67. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2013.04.012Wang Quan, Liu Jianhua, Liu Jianfei, et al. Distribution of inclusions in IF steel casting billet[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2013, 34(4): 62-67. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2013.04.012 [5] Huang Rikang, Zhang Lifeng, Jiang Renbo, et al. Evolution of non-metallic inclusions in ultra-low carbon aluminum deoxygenated steel continuous casting process[J]. Steelmaking, 2020,36(6):39−45,66. (黄日康, 张立峰, 姜仁波, 等. 超低碳铝脱氧钢连铸过程钢中非金属夹杂物的演变[J]. 炼钢, 2020,36(6):39−45,66.Huang Rikang, Zhang Lifeng, Jiang Renbo, et al. Evolution of non-metallic inclusions in ultra-low carbon aluminum deoxygenated steel continuous casting process[J]. Steelmaking, 2020, 36(6): 39-45, 66 [6] Liu Junshan, Ni Hongwei, Zhang Hua, et al. Ultra-low carbon steel inclusion control and research[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018,39(6):150−154,167. (刘俊山, 倪红卫, 张华, 等. 超低碳钢夹杂物控制与研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2018,39(6):150−154,167. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2018.06.024Liu Junshan, Ni Hongwei, Zhang Hua, et al. Ultra-low carbon steel inclusion control and research[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018, 39(6): 150-154, 167. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2018.06.024 [7] Deng Birong, Zhang Bo, Zhou Jianfeng, et al. Influence of 210 t RH refining parameters on cleanliness of IF steel and process optimization[J]. Special Steel, 2018,39(3):31−34. (邓必荣, 张波, 周剑丰, 等. 210 t RH精炼参数对IF钢洁净度的影响和工艺优化[J]. 特殊钢, 2018,39(3):31−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2018.03.009Deng Birong, Zhang Bo, Zhou Jianfeng, et al. Influence of 210 t RH refining parameters on cleanliness of IF steel and process optimization[J]. Special Steel, 2018, 39(3): 31-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2018.03.009 [8] Wang Yang, Cui Heng, Wang Zheng, et al. Effect of RH refining pure cycle time and sedation time on cleanliness of IF steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2017,29(8):649−653. (王洋, 崔衡, 王征, 等. RH精炼纯循环时间和镇静时间对IF钢洁净度影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2017,29(8):649−653.Wang Yang, Cui Heng, Wang Zheng, et al. Effect of RH refining pure cycle time and sedation time on cleanliness of IF steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2017, 29(8): 649-653. [9] Yang Wen, Zhang Ying, Zhang Lifeng, et al. Population evolution of oxide inclusions in Ti-stabilized ultra-low carbon steels after deoxidation[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research(International), 2015,22(12):1069−1077. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(15)30114-X [10] Zhang Lifeng, Thomas Brian G. State of the art in evaluation and control of steel cleanliness[J]. ISIJ International, 2003,43(3):282. [11] 蔡开科. 连铸坯质量控制[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2009.Cai Kaike. Quality control of continuous casting billet[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2009. [12] Katsuhiro Sasai, Yoshimasa Mizukami. Reoxidation behavior of molten steel in tundish[J]. ISIJ International, 2000,40(1):40. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.40.40 [13] Wang Min, Bao Yanping, Cui Heng, et al. The composition and morphology evolution of oxide inclusions in Ti-bearing ultra low-carbon steel melt refined in the RH process[J]. ISIJ International, 2010,50(11):1606. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.50.1606 [14] Wang Cong, Neerav Verma, Youjong Kwon, et al. A study on the transient inclusion evolution during reoxidation of a Fe–Al–Ti–O melt[J]. ISIJ International, 2011,51(3):375. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.51.375 [15] Yan Pengcheng, Marie-Aline Van Ende, Enno Zinngrebe, et al. Interaction between steel and distinct gunning materials in the tundish[J]. ISIJ International, 2014,54(11):2551. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.54.2551 [16] Ren Ying, Zhang Lifeng, Zhang Ying. Modeling reoxidation behavior of Al–Ti-containing steels by CaO–Al2O3–MgO–SiO2 slag[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2018,25(2):146. doi: 10.1007/s42243-018-0015-5 [17] Zhu Tanhua, Zhou Qiuyue, Ren Ying, et al. Inclusion evolution in IF steel during tundish reoxidation[J]. Iron and Steel, 2020,55(3):35−39,49. (朱坦华, 周秋月, 任英, 等. 二次氧化过程IF钢中间包中夹杂物演变行为[J]. 钢铁, 2020,55(3):35−39,49.Zhu Tanhua, Zhou Qiuyue, Ren Ying, et al. Evolution behavior of inclusions in if steel tundishes in secondary oxidation process[J]. Iron and Steel, 2020, 55(3): 35-39, 49. [18] Wang Min, Bao Yanping, Cui Heng, et al. Generation mechanism of Al2O3-TiN inclusion in IF steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2010,22(7):29−32,55. (王敏, 包燕平, 崔衡, 等. IF钢中Al2O3-TiN复合夹杂生成机理研究[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2010,22(7):29−32,55.Wang Min, Bao Yanping, Cui Heng, et al. Study on the formation mechanism of Al2O3-TiN composite inclusion in IF steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2010, 22(7): 29-32, 55. [19] 张立峰. 钢中非金属夹杂物: 工业实践[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2019.Zhang Lifeng. Non-metallic inclusions in steel: Industrial practice[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2019. [20] Yu Shuzhong, Wang Dejun, Liu Zhenglong, et al. Effects of containing calcined forsterite tundish materials on steel cleanliness[J]. Steelmaking, 2019,35(1):39−46. (郁书中, 王德军, 刘正龙, 等. 含烧结镁橄榄石中间包涂料对汽车板钢洁净度的影响[J]. 炼钢, 2019,35(1):39−46.Yu Shuzhong, Wang Dejun, Liu Zhenglong, et al. Effect of sintered magnesium-containing olivine tundish coating on cleanliness of automotive sheet steel[J]. Steelmaking, 2019, 35(1): 39-46. -





 下载:
下载: