Effect of tempering time on hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of martensitic steel
-
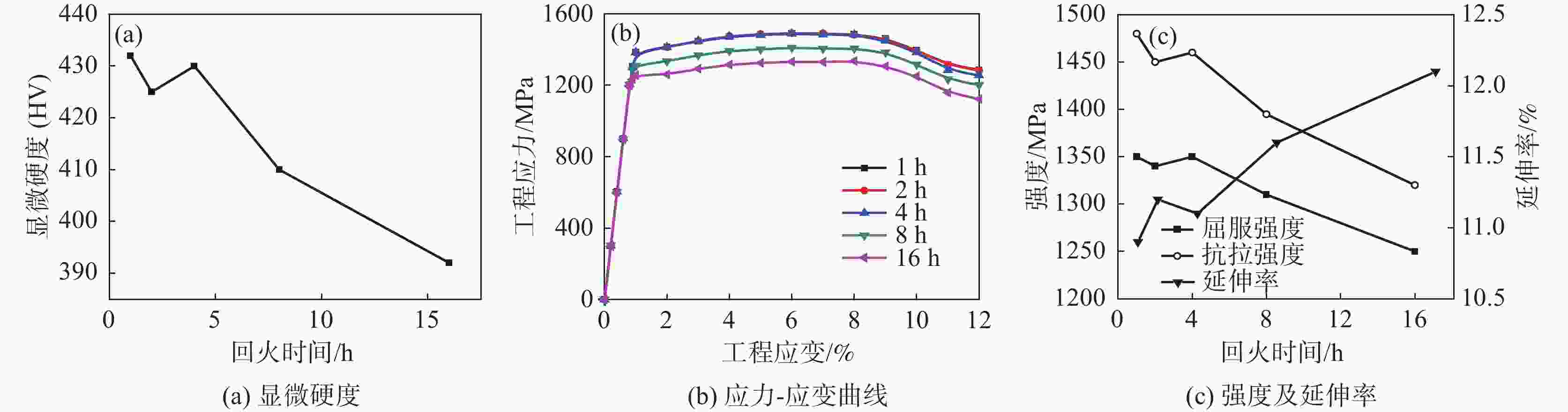
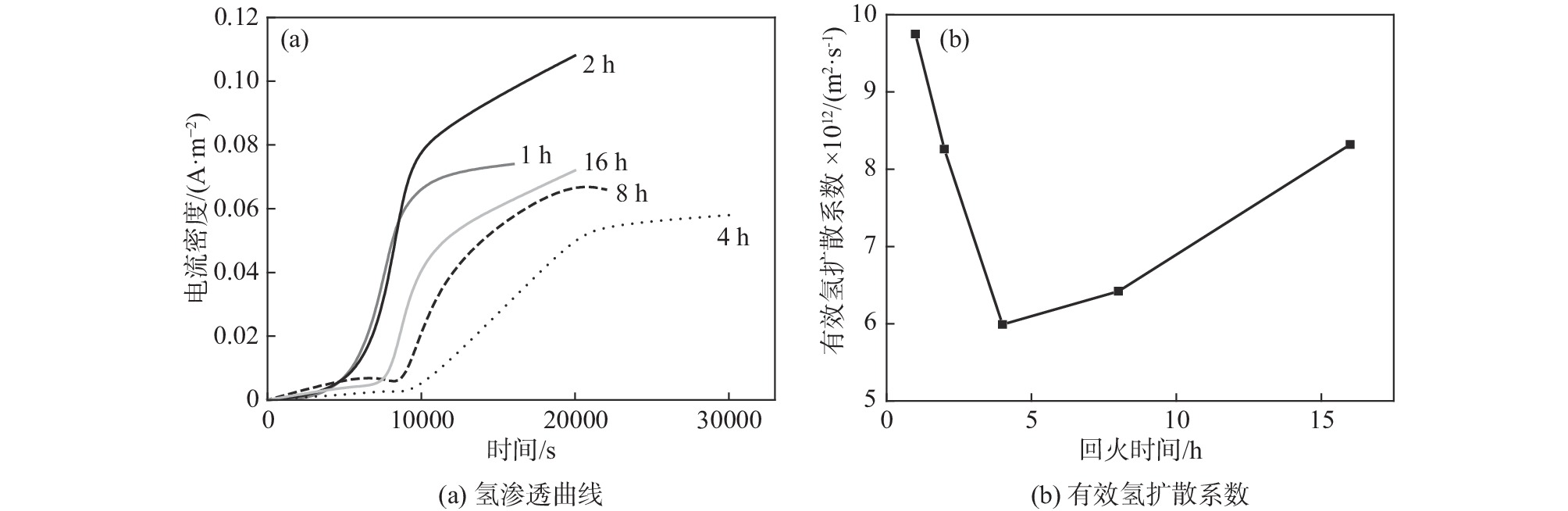
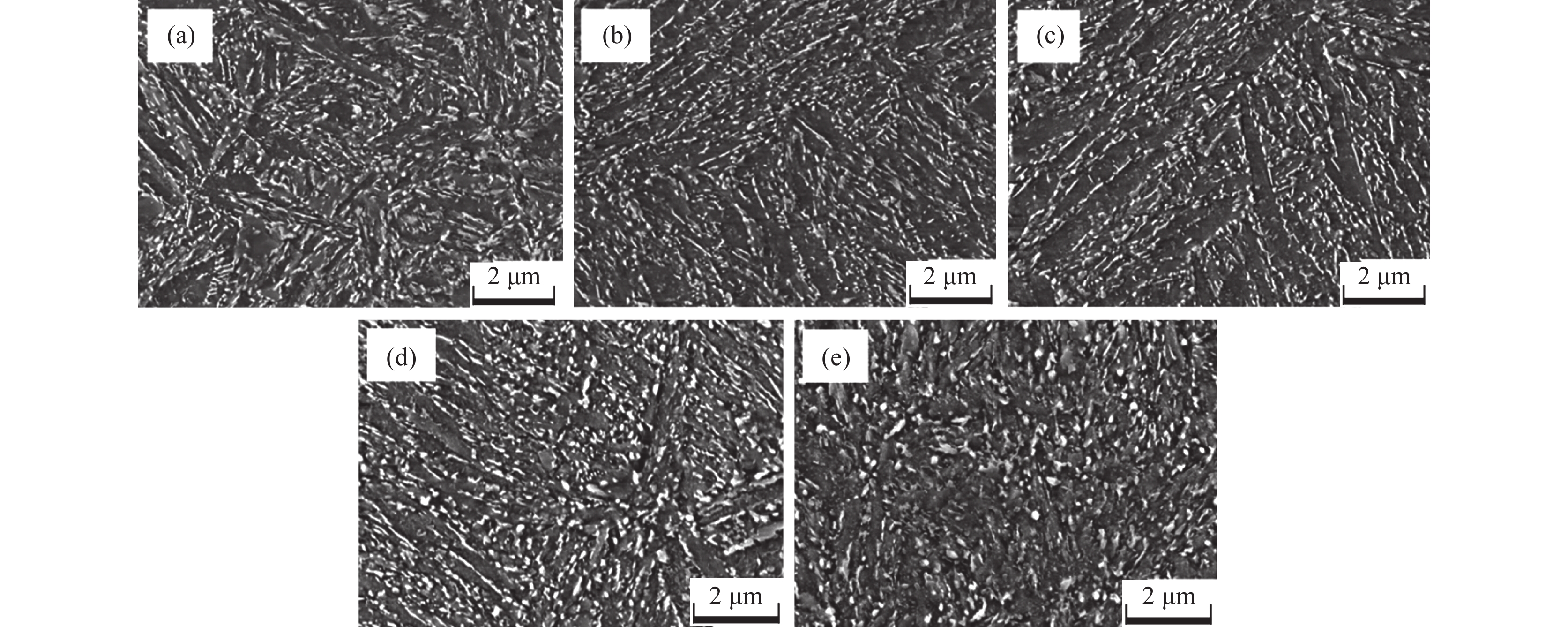
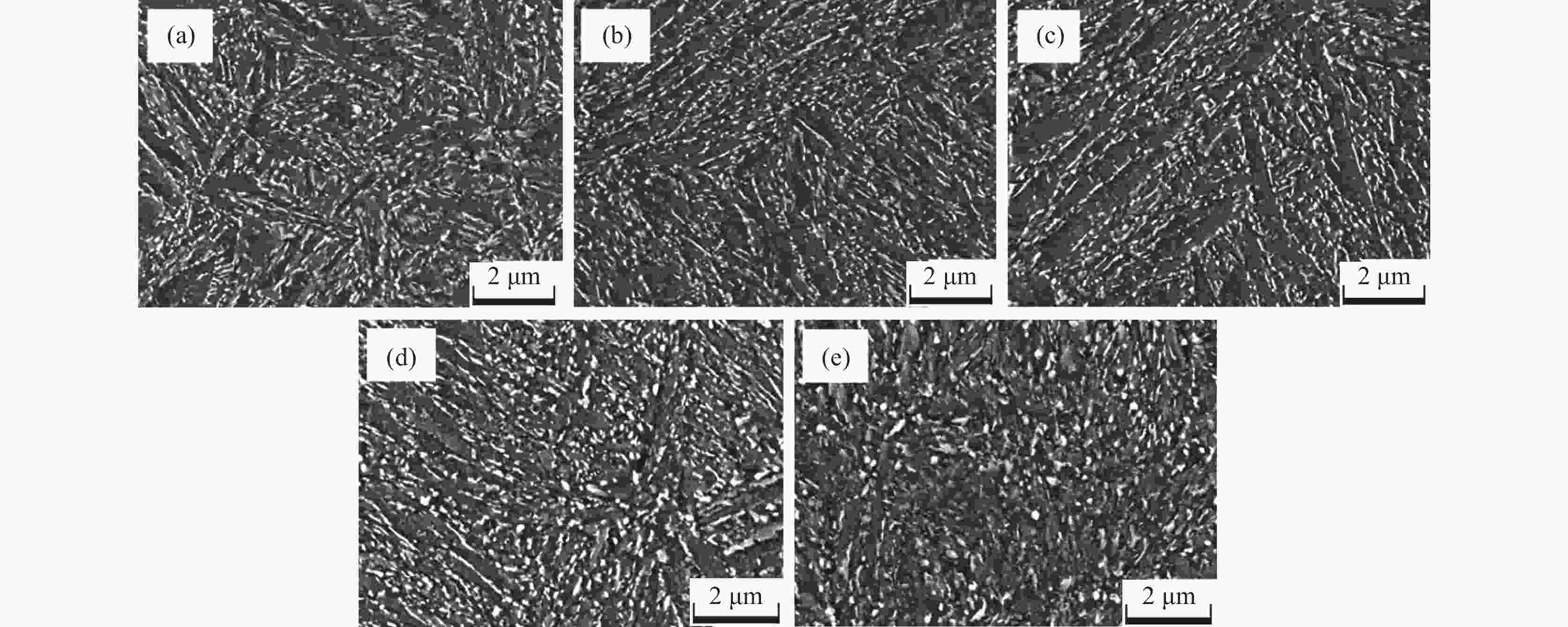
摘要: 采用慢应变速率拉伸及氢渗透试验研究了回火热处理时间对一种马氏体钢氢脆敏感性的影响。试验结果表明:随着回火时间的延长,试样的氢脆敏感性先降低后增加,当回火时间为4 h时,材料的氢脆敏感性指数达到最低值。其主要原因是当回火时间小于4 h时,大量碳化物的析出有效捕获了氢原子,使有效氢扩散系数及氢脆敏感性均降低;但当回火时间大于4 h时,碳化物粗化长大,其对氢原子的捕获作用减弱,导致有效氢扩散系数增加,氢脆敏感性增强。Abstract: The effect of annealing time on the hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of martensitic steel was studied by slow strain rate tensile and hydrogen permeation tests. The results show that the hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity decreases first and then increases with the extension of tempering time. When the tempering time is 4 h, the hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity index reaches the lowest value. The reason is that when the tempering time is less than 4 h, a large number of carbide precipitates can effectively capture hydrogen atoms, which reduces the effective hydrogen diffusion coefficient and hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity. However, when the tempering time is longer than 4 h, the carbide coarsens and grows up, which weakens the trapping effect on hydrogen atoms, increases the effective hydrogen diffusion coefficient and enhances the sensitivity to hydrogen embrittlement.
-
Key words:
- martensite steel /
- tempering /
- hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity
-
表 1 试验钢的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of test steel
% C Si Mn P S Cr V 0.48 0.51 0.73 0.002 0.001 1.04 0.31 -
[1] Wu Guangzong, Wang Maoqiu, Wang Chunfang, et al. Hydrogen diffusion behavior and hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity in tempered martensitic steel[J]. Journal of Material Heat Treatment, 2012,33(1):136−140. (武光宗, 王毛球, 王春芳, 等. 回火马氏体钢中氢的扩散行为及其氢脆敏感性[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2012,33(1):136−140.Wu Guangzong, Wang Maoqiu, Wang Chunfang, et al. Hydrogen diffusion behavior and hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity in tempered martensitic steel[J]. Journal of Material Heat Treatment, 2012, 33 (1): 136-140 [2] Chang Kaidi, Gu Jialin, Fang Hongsheng. Effect of heat treatment process on hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of new bainite / martensite dual phase high strength steel[J]. World Iron and Steel, 2002,2(4):23−27. (常开地, 顾家琳, 方鸿生. 热处理工艺对新型贝氏体/马氏体双相高强钢氢脆敏感性的影响[J]. 世界钢铁, 2002,2(4):23−27.Chang Kaidi, Gu Jialin, Fang Hongsheng. Effect of heat treatment process on hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of new bainite / martensite dual phase high strength steel[J]. World Iron and Steel, 2002, 2 (4): 23-27 [3] Zhong Zhenqian, Tian Zhiling, Yang Chun. Application of EBSD technology in the study of hydrogen embrittlement mechanism of high strength martensitic stainless steel[J]. Journal of Material Heat Treatment, 2015,36(2):77−83. (钟振前, 田志凌, 杨春. EBSD技术在研究高强马氏体不锈钢氢脆机理中的应用[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2015,36(2):77−83.Zhong Zhenqian, Tian Zhiling, Yang Chun. Application of EBSD technology in the study of hydrogen embrittlement mechanism of high strength martensitic stainless steel[J]. Journal of Material Heat Treatment, 2015, 36 (2): 77-83 [4] Chen Kang, Xia Bin, Xu Le, et al. Hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of 2000 MPa martensitic steel[J]. Journal of Material Heat Treatment, 2017,38(8):76−79. (谌康, 夏彬, 徐乐, 等. 2000 MPa级马氏体钢的氢脆敏感性[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2017,38(8):76−79.Chen Kang, Xia Bin, Xu Le, et al. Hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of 2000 MPa martensitic steel[J]. Journal of Material Heat Treatment, 2017, 38 (8): 76-79 [5] Li Yu, Li Wei, Jin Xuejun. Research progress of quenched carbon distribution tempered (QPT) steel[J]. Progress of Materials in China, 2019,37(7):631−640. (黎雨, 李伟, 金学军. 淬火-碳分配-回火(QPT)钢的研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展, 2019,37(7):631−640.Li Yu, Li Wei, Jin Xuejun. Research progress of quenched carbon distribution tempered (QPT) steel[J]. Progress of Materials in China, 2019, 37 (7): 631-640 [6] Liu Dan, Song Wenying, Shi Pengliang, et al. Hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of low carbon and low alloy steel treated by quenching composition tempering process[J]. Mechanical Engineering Materials, 2015,39(10):66−68. (刘丹, 宋文英, 石鹏亮, 等. 淬火-配分-回火工艺处理低碳低合金钢的氢脆敏感性[J]. 机械工程材料, 2015,39(10):66−68. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl201510015Liu Dan, Song Wenying, Shi Pengliang, et al. Hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of low carbon and low alloy steel treated by quenching composition tempering process[J]. Mechanical Engineering Materials, 2015, 39 (10): 66-68 doi: 10.11973/jxgccl201510015 [7] Wang J, Shao B, Shan D, et al. Effect of strain on solution energy of hydrogen in alpha-zirconium from first-principle calculations[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020,45(35):18001−18009. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.04.244 [8] Jin X, Xu L, Yu W, et al. The effect of undissolved and temper-induced (Ti, Mo)C precipitates on hydrogen embrittlement of quenched and tempered Cr-Mo steel[J]. Corrosion Science, 2020,166:108421. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2019.108421 [9] Zhao Xiaoli, Zhang Yongjian, Hui Weijun, et al. Hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of 0.1C-5Mn medium manganese steel under different treatment conditions[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2019,31(9):70−80. (赵晓丽, 张永健, 惠卫军, 等. 不同处理状态下0.1C-5Mn中锰钢的氢脆敏感性[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2019,31(9):70−80.Zhao Xiaoli, Zhang Yongjian, Hui Weijun, et al. Hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of 0.1 C-5 Mn medium manganese steel under different treatment conditions[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2019, 31 (9): 70-80 [10] Zhang Haixia, Cheng Xiaoying, Li Heng, et al. Effect of tempering temperature on microstructure and hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of new mooring chain steel[J]. Metal Heat Treatment, 2015,40(11):114−119. (张海霞, 程晓英, 李恒, 等. 回火温度对新型系泊链钢的组织与氢脆敏感性的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2015,40(11):114−119.Zhang Haixia, Cheng Xiaoying, Li Heng, et al. Effect of tempering temperature on microstructure and hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of new mooring chain steel[J]. Metal Heat Treatment, 2015, 40 (11): 114-119 -




 下载:
下载: