Research and development of low-cost light gauge L485M pipeline steel
-
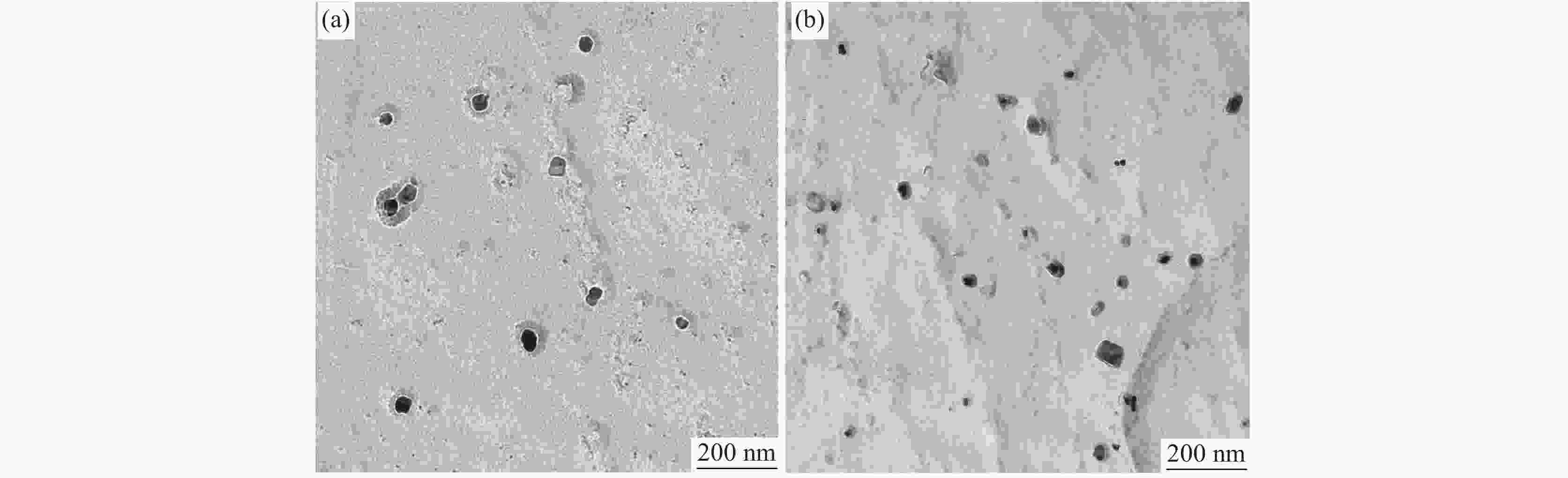
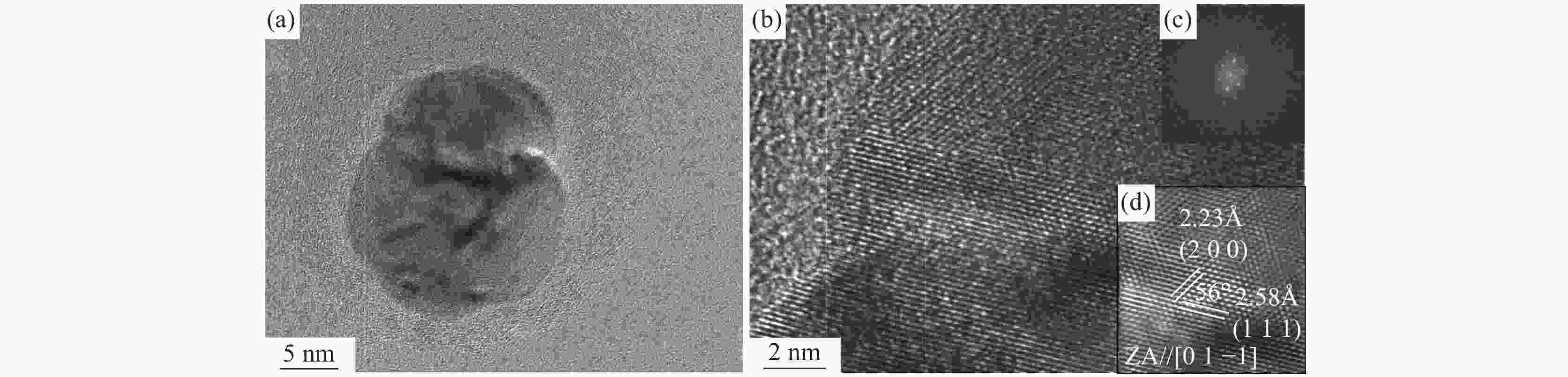
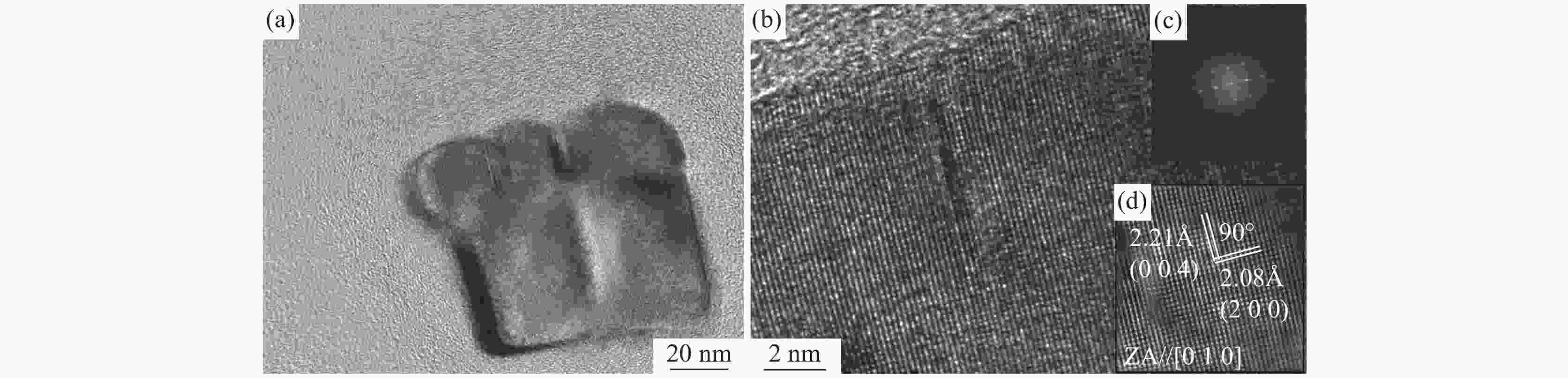
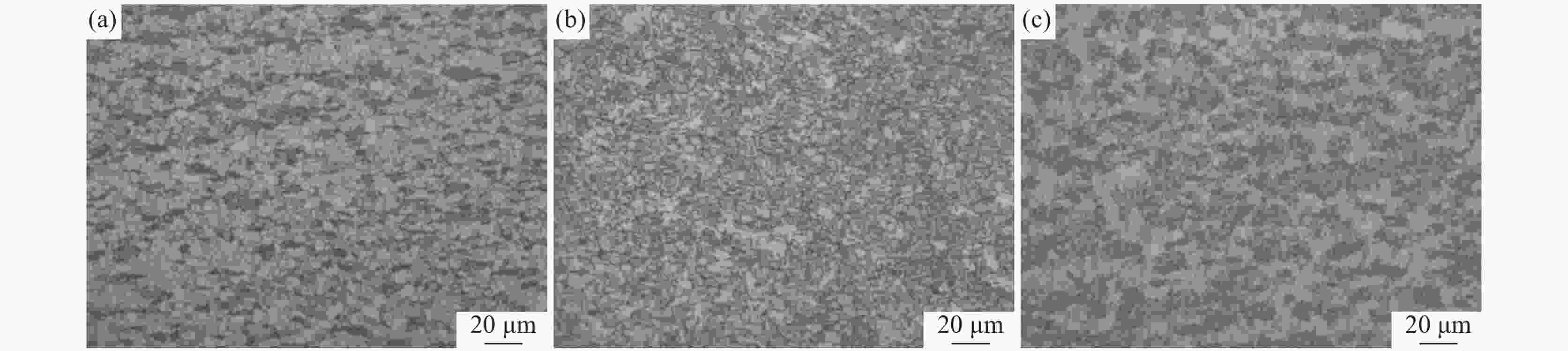
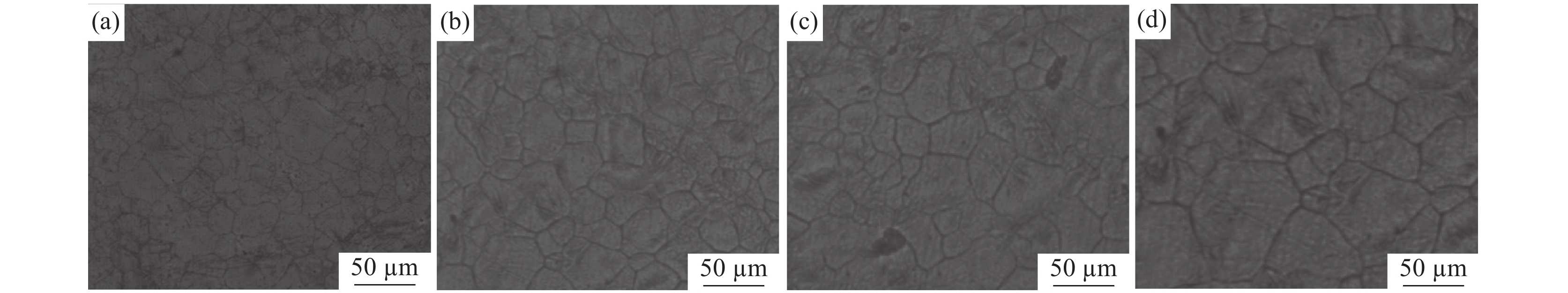
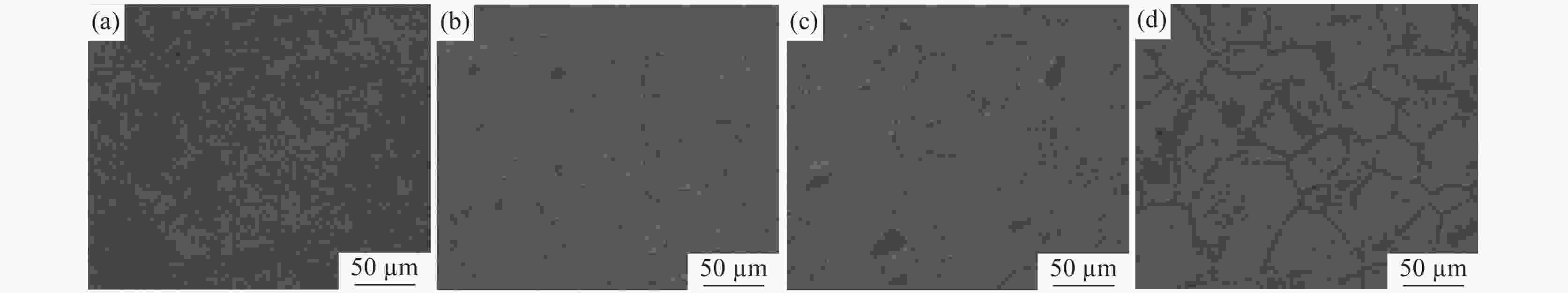
摘要: 研究了不同加热温度、轧制工艺和冷却速率在内的低成本L485M管线钢组织及性能变化。结果表明:随着加热温度升高,奥氏体晶粒尺寸逐渐长大,当加热温度≤1200 ℃时,奥氏体平均晶粒尺寸可控制在50 μm以内;通过增加中间坯厚度,使其精轧阶段累计压下量增加,可显著细化钢板心部组织,同时增加析出相密度;通过提高轧后钢板的冷却速率,既抑制了先共析铁素体的转变,也促进了针状铁素体和粒状贝氏体形成。当冷却速率为25 ℃/s时,可得到有利于试验钢性能的由针状铁素体和粒状贝氏体为主的复相组织,钢板的强韧性得到显著改善;生产的L485M级管线钢满足技术条件要求,可实现L485M级别管线钢降低成本生产。目前,鞍钢已可以实现无Mo低成本薄规格L485M管线钢稳定化批量生产。Abstract: Effects of heating temperature, rolling process, and cooling rates on microstructure variation and mechanical properties for low-cost L485M were studied. The results show that the austenite grains grow continuously with increasing temperatures. The average austenite grains can be controlled within 50 μm by maintaining the heating temperature below 1200 ℃. The grains can be refined by increasing the thickness of the intermediate slab to enhance the cumulative reduction rates and increase the number density of precipitates. Eventually, the cooling rate is improved, which inhibits pro-eutectoid ferrite transformation and promotes the formation of ultrafine granular bainite and acicular ferrite. In addition, the microstructure of investigated steel consists of acicular ferrite and granular bainite at the cooling rate of 25 ℃/s, which was beneficial to improving the strength and toughness of steel. The L485M grade pipeline steel satisfies the requirements of the technical agreements, which can provide a route to produce the low-cost L485M plates. A batch of L485M plates without Mo addition was steadily produced in Ansteel Company.
-
Key words:
- L485M pipeline steel /
- heating temperature /
- cooling rate /
- acicular ferrite
-
表 1 L485M管线钢的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of L485M pipeline steel
% C Si Mn P S Al Cr Nb Mo ≤0.07 ≤0.3 ≤1.7 0.008 0.002 0.032 0.2~0.35 0.03~0.05 ≤0.005 表 2 不同中间坯厚度L485M力学性能对比
Table 2. Comparison of mechanical properties obtained with different intermediate slab thickness of L485M
中间坯厚度/mm Rp0.2/MPa Rm/MPa akv2(−15 ℃)/J DWTT(−15 ℃)/% 60 503 588 213 88 70 518 612 245 92 技术协议 485~635 570~760 ≥150 ≥85 表 3 不同冷却速率下L485M力学性能对比
Table 3. Comparison of mechanical properties obtained with different cooling rate of L485M
冷却速率/(℃·s−1) Rp0.2/MPa Rm/MPa akv2(−15 ℃)/J DWTT(−15 ℃)/% 15 465 568 205 92 25 532 592 257 95 35 553 621 243 80 技术协议 485~635 570~760 ≥150 ≥85 -
[1] Zheng Lei, Fu Junyan. Recent development of high performance pipeline steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2006,41(10):1−10. (郑磊, 付俊岩. 高等级管线钢的发展现状[J]. 钢铁, 2006,41(10):1−10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2006.10.001Zheng Lei, Fu Junyan. Recent development of high performance pipeline steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2006, 41(10): 1-10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2006.10.001 [2] Li Shaopo, Ma Qingshen, Li Jiading, et al. Research on basic parameters of Nb-Ni series X70 pipe steel[J]. Steel Rolling, 2009,26(5):5−8. (李少坡, 麻庆申, 李家鼎, 等. Nb-Ni系X70管线钢基础参数研究[J]. 轧钢, 2009,26(5):5−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9996.2009.05.002Li Shaopo, Ma Qingshen, Li Jiading, et al. Research on basic parameters of Nb-Ni series X70 pipe steel[J]. Steel Rolling, 2009, 26(5): 5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9996.2009.05.002 [3] Kang M, Kim H, Lee S. Effect of dynamic strain hardening exponent on abnormal cleavage fracture occurring during drop weight tear test of API X70 and X80 linepile steels[J]. Metall. Mater. Trans A, 2014,45(2):68. [4] Shanmugam S, Misra R, Hartmann J, et al. Microstructure of high strength niobium-containing pipeline steel[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006,441(1−2):215−229. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.08.017 [5] Shanmugam S, Ramisetti N K, Misra R D K, et al. Microstructure and high strength–toughness combination of a new 700 MPa Nb microalloyed pipeline steel[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008,478(1-2):26−37. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2007.06.003 [6] Bott I, Souza L, Teixeira J, et al. High-strength steel development for pipelines: a Brazilian perspective[C]// Proceedings of the International Symposium on Microalloyed Steels for the Oil and Gas Industry, 2005, 36: 443−454. [7] Jacobs T R, Matlock D K, Findley K O, et al. The short and long term effects of elevated temperature on the mechanical properties of line pipe steels[C]// Proceedings of the 2016 11th International Pipeline Conference 3, V003 T05 A035. ASME, Alberta, Canada, 2016: 26-30.https://doi.org/10.1115/ IPC2016-64568. [8] Hu J, Du L X, Wang J J. Effect of cooling procedure on microstructures and mechanical properties of hot rolled Nb-Ti bainitic high strength steel[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012,554:79−85. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.06.018 [9] Wang Zhiyong, Li Shaopo, Li Qun, et al. Research on development of low-cost X80 pipeline steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2016,26(11):64−68. (王志勇, 李少坡, 李群, 等. 经济型X80管线钢的研制开发[J]. 中国冶金, 2016,26(11):64−68.Wang Zhiyong, Li Shaopo, Li Qun, et al. Research on development of low-cost X80 pipeline steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2016, 26(11): 64-68. [10] Jacobs T R. Elevated temperature mechanical properties of line pipe steels[D]. Fort Collins: Colorado School of Mines, 2018. -




 下载:
下载: