Feasibility analysis of high-titanium heavy slag as aggregate for asphalt mixture
-
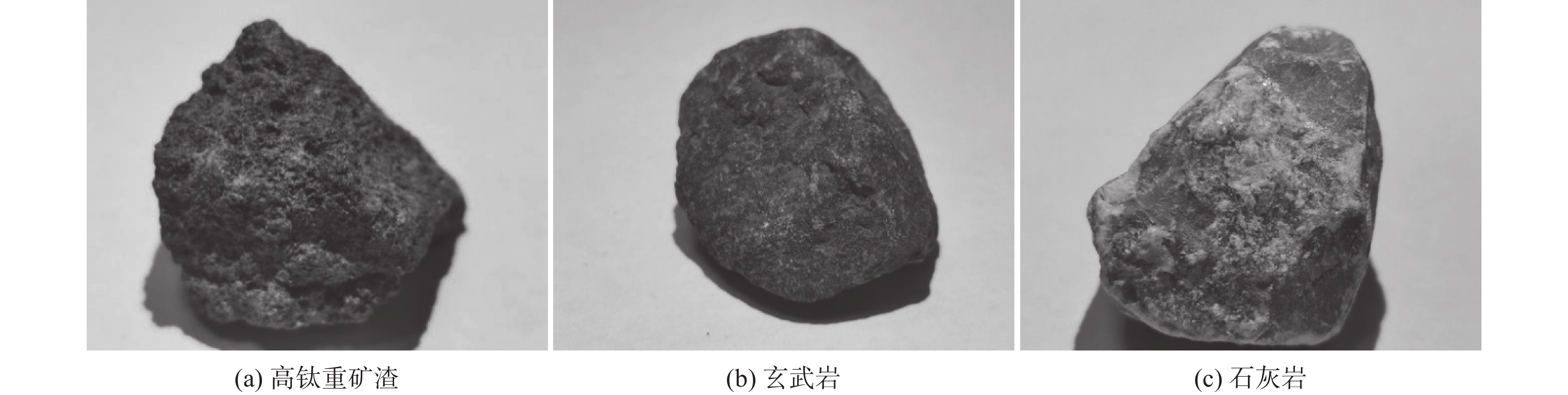
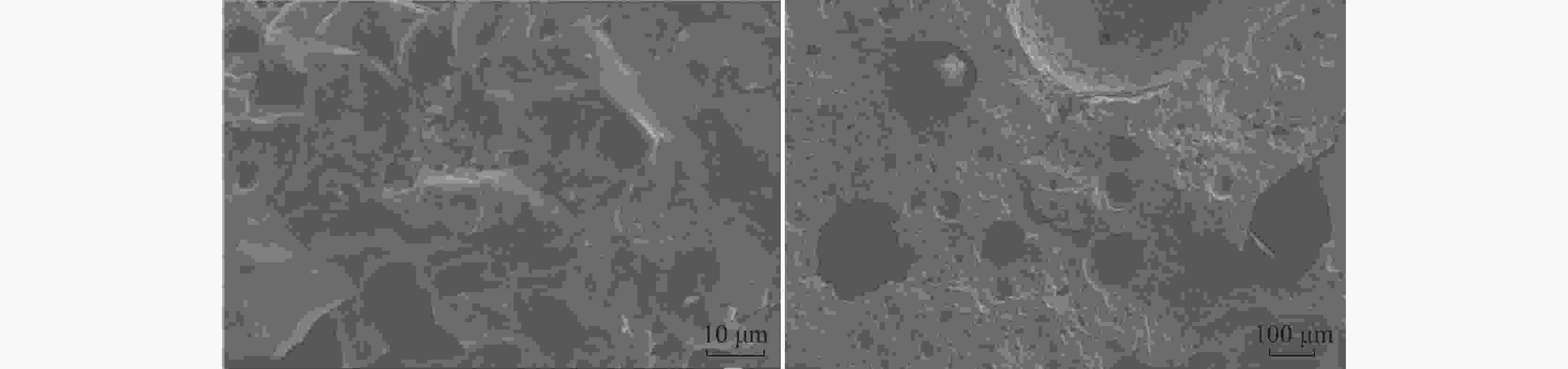
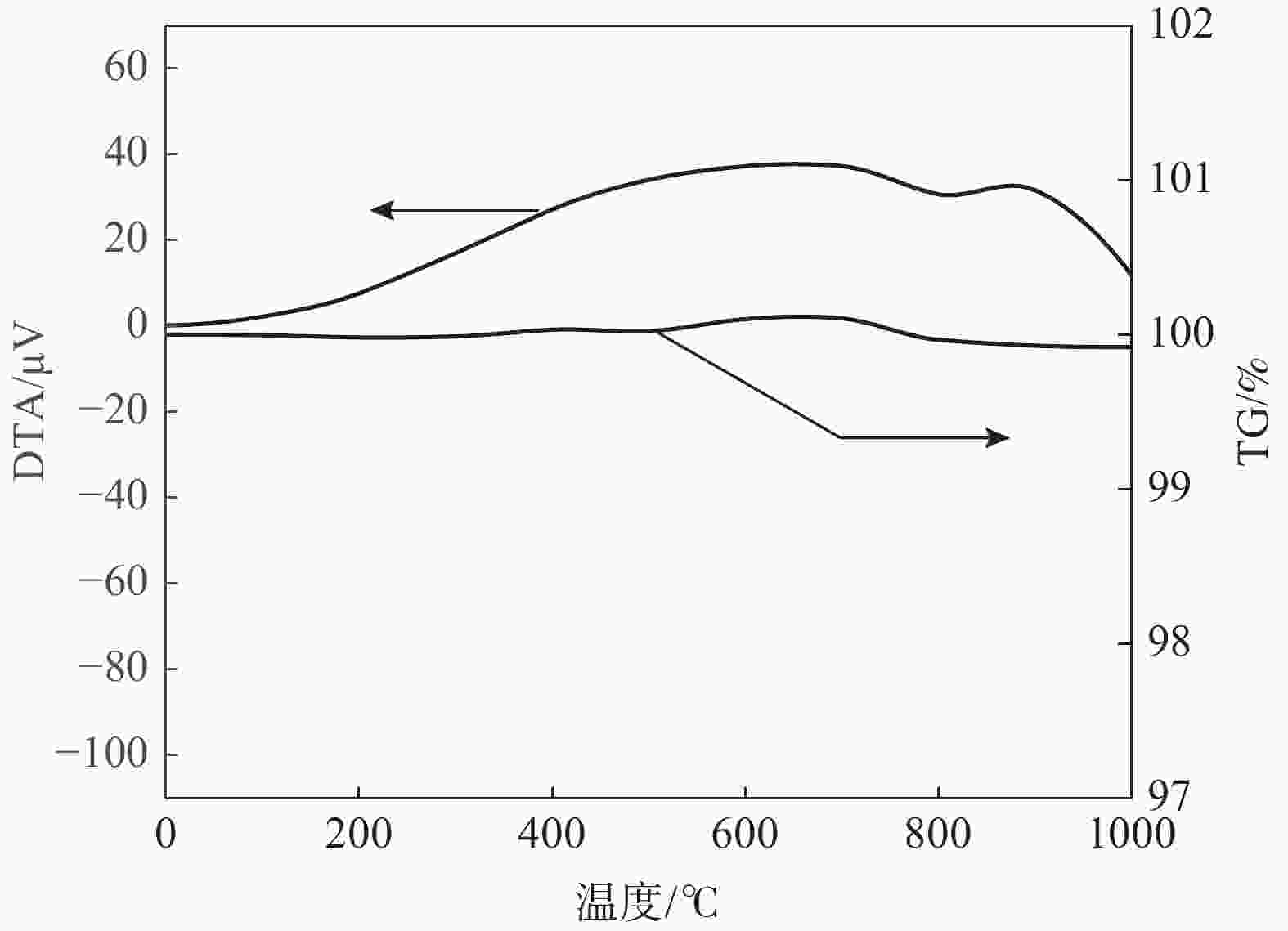
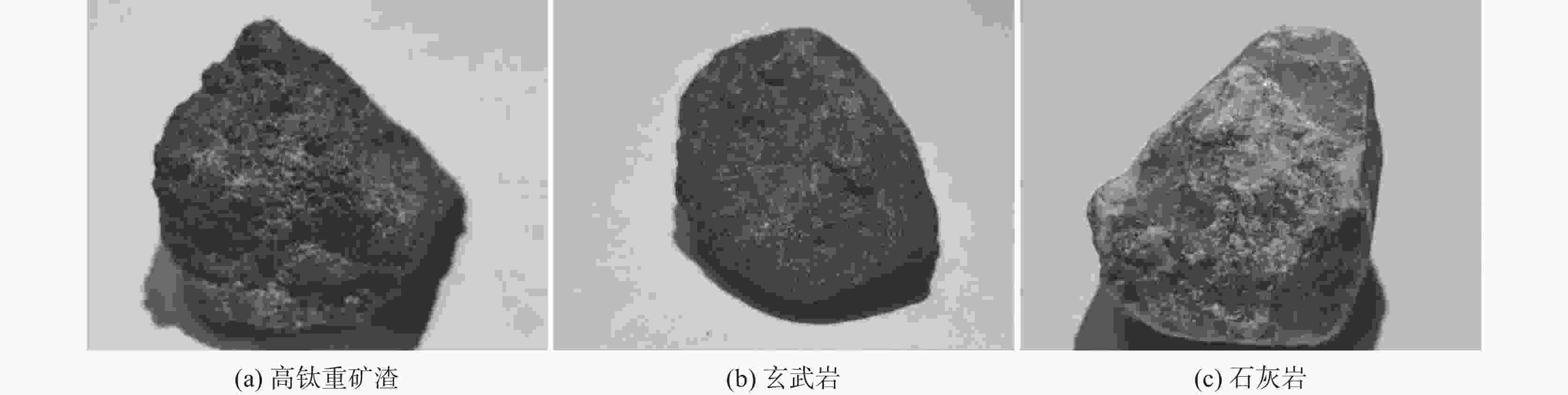
摘要: 以攀西地区高钛重矿渣为研究对象,通过理论及试验研究分析了其作为集料用于沥青混合料的可行性,并与目前沥青混合料常用的玄武岩等天然石料进行了对比分析。研究结果表明:高钛重矿渣表观形貌呈粗糙多孔状且为碱性集料,与沥青黏附性能优于天然石料,粘附性等级为5级;高钛重矿渣为五元渣系,属低钙富钛渣、低活性渣,体积稳定性及高温稳定性好;高钛重矿渣具有优异的颗粒形态特性且力学性能、耐久性能良好,但密度略低于天然石料且吸水率更高;高钛重矿渣作为沥青混合料集料的综合性能不低于天然石料,且具有明显的环境、经济效益。Abstract: Taking the high-titanium heavy slag in Panxi area as the research object, the feasibility of using it as aggregate for asphalt mixture was analyzed through theoretical and experimental research, also it was compared with the natural stone such as basalt commonly used in asphalt mixture at present. The results show that the surface morphology of high-titanium heavy slag is rough and porous, and it is alkaline aggregate. Its adhesion performance with asphalt is better than that of natural stone, and its adhesion grade is grade 5. High-titanium heavy slag is a five-element slag system, belonging to low calcium and titanium-rich slag and low active slag, with good volume stability and high-temperature stability. High-titanium heavy slag has excellent particle morphology, mechanical properties and durability, but its density is slightly lower than that of natural stone and the water absorption is higher. The comprehensive performance of high-titanium heavy slag as aggregate of asphalt mixture is no worse than natural stone, and it has obvious environmental and economic benefits.
-
Key words:
- high titanium heavy slag /
- asphalt mixture /
- apparent characteristics /
- stability /
- adhesivity
-
表 1 基质沥青性能参数
Table 1. Performance parameters of asphalt matrix
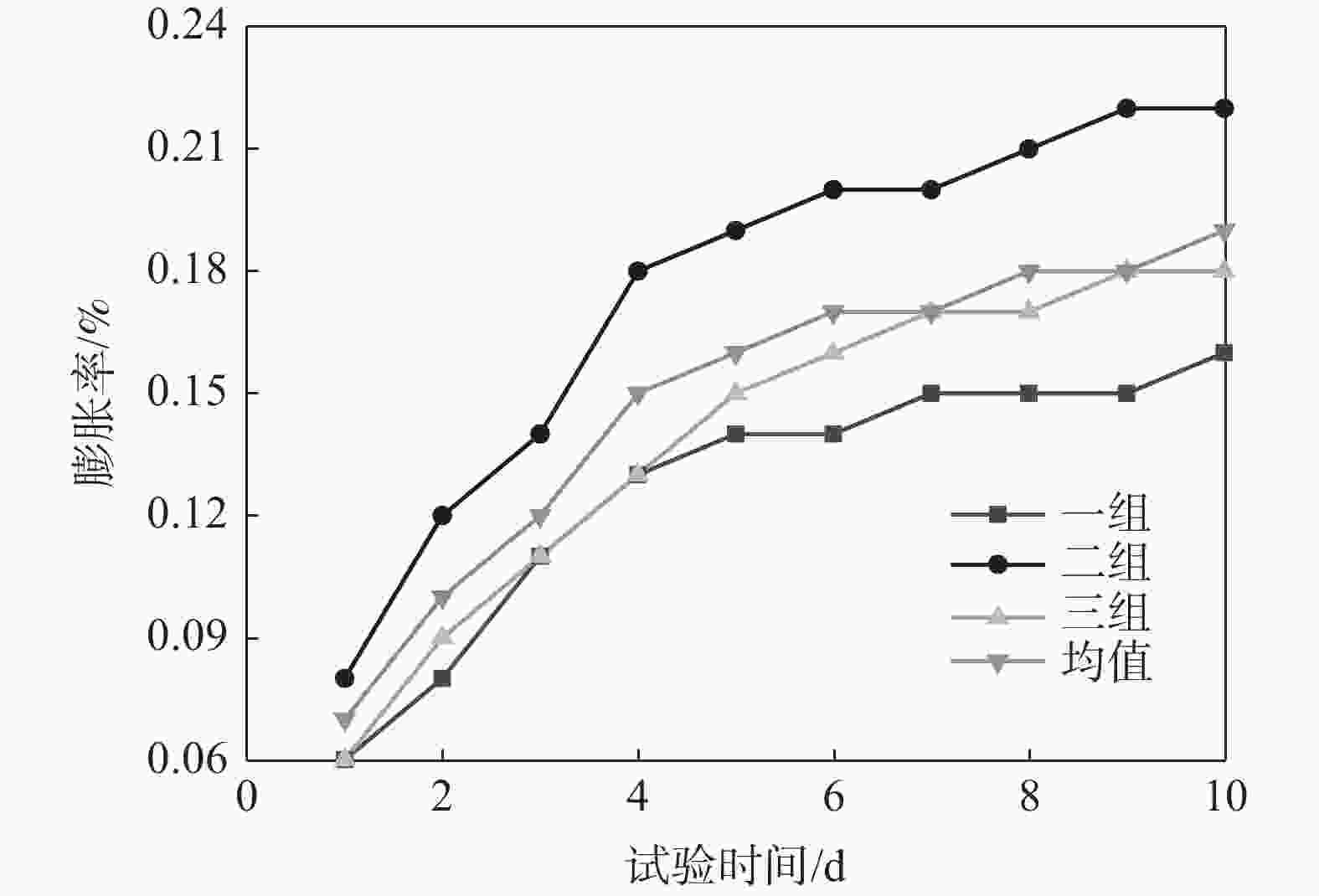
25℃针入度(0.1 mm计)/(°) 15 ℃延度/cm 软化点/℃ 闪点/℃ 60 ℃动力粘度/(Pa·s) 68 >150 48 350 189 表 2 膨胀性试验级配
Table 2. Grade of expansion test
尺寸/mm 筛余/% 尺寸/mm 筛余/% 16 5.5 1.18 4.5 13.2 20 0.6 3 9.5 23.5 0.3 2 4.75 30.5 0.15 2 2.36 5.5 0.075 3.5 表 3 普通高炉渣与高钛重矿渣主要组成成分
Table 3. Main components of common blast furnace slag and high-titanium heavy slag
% 矿渣类型 CaO SiO2 A12O3 MgO TiO2 普通高炉渣 38~46 26~42 7~20 4~13 高钛重矿渣 22~29 22~26 16~19 7~9 20~29 表 4 不同粒径骨料的密度和吸水率
Table 4. Density and water absorption of aggregates with different particle sizes
公称最大粒径/mm 表观相对密度 毛体积相对密度 吸水率/% 1# 2# 3# 1# 2# 3# 1# 2# 3# 16 2.66 2.80 2.74 2.55 2.57 2.70 2.89 0.62 0.32 13.2 2.68 2.84 2.75 2.54 2.58 2.72 3.41 0.84 0.37 9.5 2.63 2.81 2.77 2.47 2.58 2.73 4.22 1.19 0.41 4.75 2.61 2.80 2.77 2.42 2.56 2.73 4.93 1.40 0.44 表 5 不同集料的针片状含量、压碎值及磨耗值
Table 5. The needle-shape content, crushing value and wear value of different aggregates
集料类型 针片状含量/% 压碎值/% 磨耗值/% 4.75~9.5 mm 9.5~13.2 mm 13.2~16 mm 16~19 mm 高钛重矿渣 4.6 4.0 3.9 6.0 11.6 15.6 玄武岩 8.9 7.1 7.5 8.2 11.2 12.9 石灰岩 15.8 10.9 9.9 11.3 15.2 17.5 规范值 ≤18 ≤12 ≤12 ≤12 ≤26 ≤28 表 6 不同集料与沥青粘附性
Table 6. Adhesion of different aggregates to asphalt
水煮时间/min 粘附性等级/级 高钛重矿渣 玄武岩 石灰岩 3 5 5 5 5 5 4 3 10 3 3 2 15 2 2 1 20 1 1 1 -
[1] Chen Deming. Characteristics of titanium resources in Panxi area[J]. Panzhihua Sci-Tech & Information, 2009,(3):5−9. (陈德明. 攀西地区钛资源的特点及其利用途径[J]. 攀枝花科技与信息, 2009,(3):5−9.Chen Deming. Characteristics of titanium resources in Panxi area [J]. Panzhihua Sci-Tech & Information, 2009(3): 5-9. [2] 杜鹤桂. 高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996.Du Hegui. The principle of blast furnace smelting vanadium titanomagnetite[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996. [3] 周春林. 应用钒钛磁铁矿生产高品质钢铁材料关键技术问题的研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2013.Zhou Chunlin. Investigation on the key technological problems during manufacturing superior quality ferrous materials by vanadium-titanium bearing magnetite ore[D]. Shengyang: Northeastern University, 2013. [4] 甄玉兰. 攀枝花含钛高炉渣资源化利用新途径[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2016.Zhen Yulan. New ways of recycling titanium-bearing blast furnace slag in Panzhihua[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2016. [5] 白晨光. 含钛高炉渣的若干物理化学问题研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2003.Bai Chenguang. Study on some physical chemistry problems of blast furnace slag-bearing titania [D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2003. [6] 周志明. 高钛型高炉渣渣钛分离研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2004.Zhou Zhiming. Study on separating titania from furnace slag containing high TiO2[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2004. [7] Wang Hao, Wang Xiaojia, Gui Feng, et al. The status and prospect of blast furnace slag resource utilization[J]. Industrial Minerals & Processing, 2021,50(11):48−53. (王浩, 王晓佳, 桂峰, 等. 高炉矿渣资源化利用现状及展望[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2021,50(11):48−53.Wang Hao, Wang Xiaojia, Gui Feng, et al. The status and prospect of blast furnace slag resource utilization[J]. Industrial Minerals & Processing, 2021, 50(11): 48-53. [8] Fang Rongli, Jin Chengchang. The way of high value comprehensive utilization of titanium slag in Panzhihua Iron & Steel Co., Ltd. production of composite cement and less clinker cement by residue after titanium extraction[J]. Sichuan Environment, 1994,(2):39−42. (方荣利, 金成昌. 高价值综合利用攀钢钛矿渣的途径─利用提钛后残渣生产复合水泥与少熟料水泥[J]. 四川环境, 1994,(2):39−42.Fang Rongli, Jin Chengchang. The way of high value comprehensive utilization of titanium slag in Panzhihua Iron & Steel Co. , Ltd. production of composite cement and less clinker cement by residue after titanium extraction [J]. Sichuan Environment, 1994(2): 39-42. [9] 何思祺. 攀枝花高钛高炉渣有价组分提取分离原理与化学动力学研究[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2020.He Siqi. Study on principle and xhemical kinetics of valuable components extraction and separation from Panzhihua high titanium-vlast furnace slag [J]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2020. [10] Sun Changxin, Wang Binggang. Application of the blast furnace heavy slag in asphalt concrete pavement[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 1994,(2):9−14,26. (孙长新, 王秉纲. 高炉重矿渣在沥青混凝土路面中的应用研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 1994,(2):9−14,26.Sun Changxin, Wang Binggang. Application of the blast furnace heavy slag in asphalt concrete pavement[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 1994(2): 9-14, 26. [11] Qin lin, Li Jianghua, Ma Yaozong, et al. Study on the influence of blast furnace slag as the aggregate on low-temperature performance of asphalt road[J]. Western China Communications Science & Technology, 2018,(8):18−21. (覃琳, 李江华, 马耀宗, 等. 高炉炉渣作为骨料对沥青道路低温性能的影响研究[J]. 西部交通科技, 2018,(8):18−21.Tanlin, Li Jianghua, Ma Yaozong, et al. Study on the influence of blast furnace slag as the aggregate on low-temperature performance of asphalt road[J]. Western China Communications Science & Technology, 2018(8): 18-21. [12] Sun Jianguo, Chen Yujie, Wang Qiuyun, et al. Discussion on the application of blast furnace slag in asphalt concrete pavement surface[J]. Create Living, 2019,(5):128−131. (孙建国, 陈玉洁, 王秋云, 等. 浅谈高炉矿渣用于沥青混凝土路面面层的应用探索[J]. 居业, 2019,(5):128−131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4085.2019.05.087Sun Jianguo, Chen Yujie, Wang Qiuyun, et al. Discussion on the application of blast furnace slag in asphalt concrete pavement surface [J]. Create Living, 2019(5): 128-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4085.2019.05.087 [13] 柴潮. 季冻区复合改性多孔钢渣沥青混合料力学性能及耐久性研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2021.Chai Chao. Research on mechanical properties and durability of composite modified porous steel slag asphalt mixture in seasonal frozen region[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021. [14] 谭巍. 基于沥青路面抗滑特性的实验系统开发与石灰岩优选关键技术研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2017.Tan Wei. Study on experimental system development and key technology of limestone optimization based on anti-sliding characteristics of asphalt pavement[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2017. [15] 杨合. 含钛高炉渣再资源化的一个启发性观点[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2005.Yang He. A heuristie view about resource reovery of titania-bearing blast furnace slags [D]. Shengyang: Northeastern University, 2005. -





 下载:
下载: