Experimental study on treatment of the tailings containing manganese using composite agglomeration process
-
摘要: 针对一种含锰尾矿资源用于普通烧结工艺时存在料层透气性差和烧结矿产量、质量低等问题,基于复合造块工艺探索含锰尾矿资源的合理利用方式。考虑到高炉冶炼对炉渣碱度的要求,通过在基体料中配加熔剂调节复合烧结矿(简称复合矿)的碱度。通过实验室烧结杯试验,对复合料固定碳配比、球团料比例以及布料方式等影响因素进行系统研究。结果表明,采用复合造块工艺处理这种含锰尾矿资源是可行的。适宜的基体料固定碳配比为3.3%,最佳的球团比例为40%。冶金性能检测结果表明,复合矿还原度指数为72.49%,低于普通烧结矿3.27个百分点,低温还原粉化指数为79.53%,高于普通烧结矿3.49个百分点,熔滴性能明显优于普通烧结矿。复合矿显微结构中主要以磁铁矿和少量玻璃相构成的斑状结构为主,基体部分铁酸钙粘结相含量相比普通烧结矿明显减少,硅酸二钙生成量较多。Abstract: In order to address the issue of poor material permeability and low yield and quality of sinter when a kind of tailings containing manganese was used in the 100% concentrate sintering process, the rational utilization of tailings containing manganese was investigated by the composite agglomeration process. Considering the requirements of blast furnace ironmaking on raw material and slag basicity, the silica, dolomite and burnt lime were added to adjust the basicity of the composite sinter. Through the lab-scale sintering pot test, the influencing factors such as fixed carbon ratio of composite material, the ratio of pellet and the distribution mode were systematically studied. The results showed that it was feasible to utilize the tailings containing manganese by the composite agglomeration process. The appropriate fixed carbon ratio could be reduced to 3.3%, and the suitable pellet ratio was 40%. The reduction index (RI) was 72.49%, which was 3.27 percentage points lower than that of ordinary sinter. The low-temperature reduction-disintegration index (RDI+3.15 mm) of composite sinter was 79.53%, which was 3.49 percentage points higher than that of ordinary sinter. The melting and dropping property of the composite sinter was better than those of the ordinary sinter. The microstructure of the composite ore was mainly porphyritic structure composed of magnetite and a small amount of glass phase. The content of calcium ferrite binder phase in the matrix parts was significantly lower and the amount of dicalcium silicate was higher than that of ordinary sinter.
-
表 1 试验用原料化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of the raw materials
% 原料 TFe FeO CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 Mn LOI 含锰尾矿 67.46 27.20 0.12 0.89 0.05 0.80 2.92 −2.63 白云石 50.21 3.93 34.33 1.04 7.76 硅石 0.13 98.00 0.08 0.25 生石灰 75.23 5.82 1.93 1.34 12.57 焦粉灰成分 2.17 1.50 51.08 1.05 41.29 注:焦粉工业分析结果:固定碳 85.46%, 挥发分 1.07%, 灰分 13.37%。 表 2 试验用原料的粒度组成
Table 2. Size distribution of the raw materials
原料 粒度组成 /% 合计 >4 mm 4~2 mm 2~1 mm 1~0.5 mm 0.5~0.25 mm 0.25~0.125 mm 0.125~0.063 mm <0.063 mm 含锰尾矿 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 36.57 19.31 14.92 29.20 100 白云石 0.00 2.07 24.42 13.61 13.21 10.67 16.27 19.75 100 硅石 0.00 0.00 59.50 39.28 0.96 0.14 0.08 0.03 100 生石灰 1.39 7.14 11.71 5.16 5.36 8.13 22.62 38.49 100 焦粉 1.93 13.50 21.82 14.50 10.60 9.09 12.18 16.38 100 表 3 含锰尾矿复合造块试验研究方案
Table 3. Experiment scheme of tailings containing manganese composite agglomeration
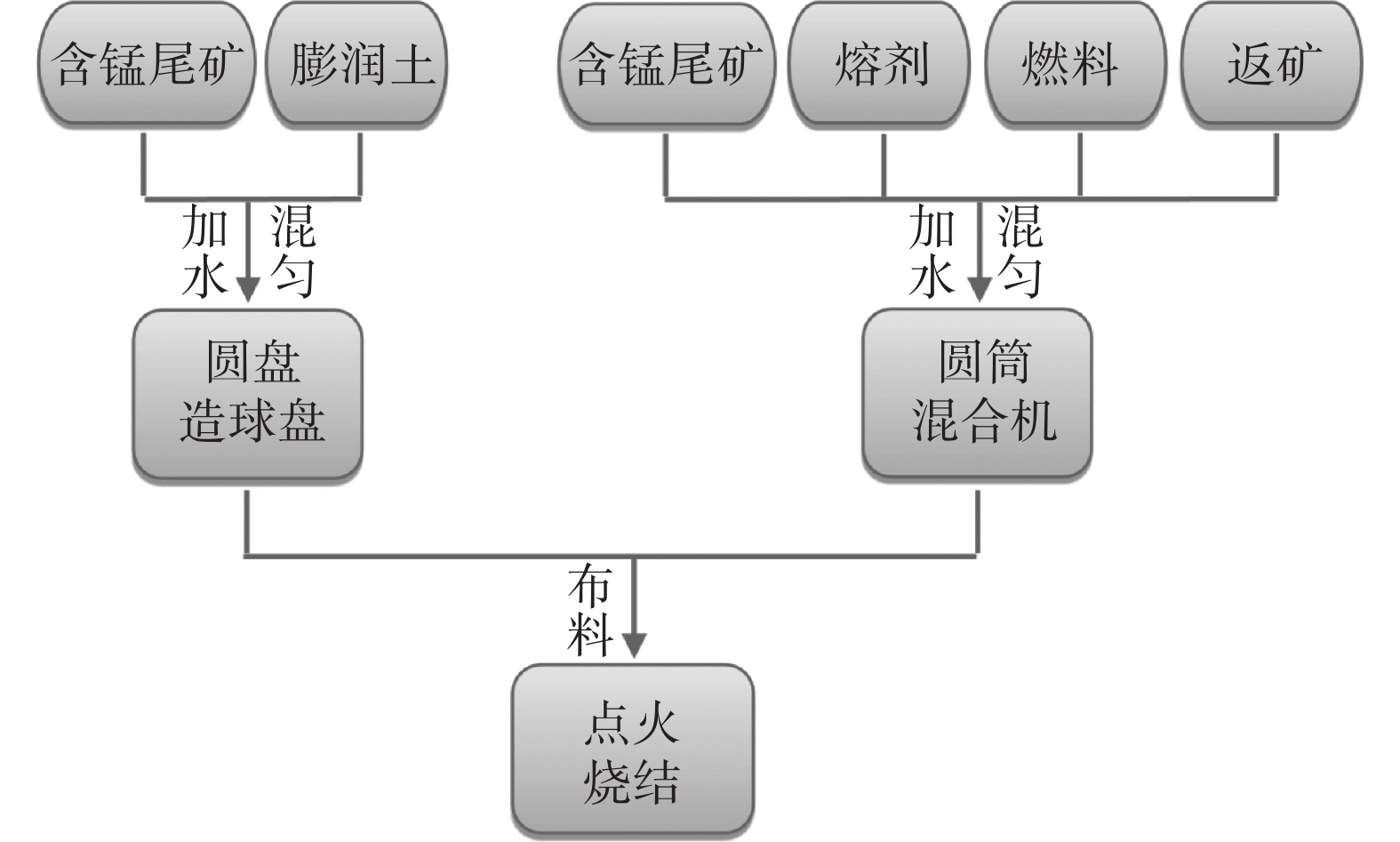
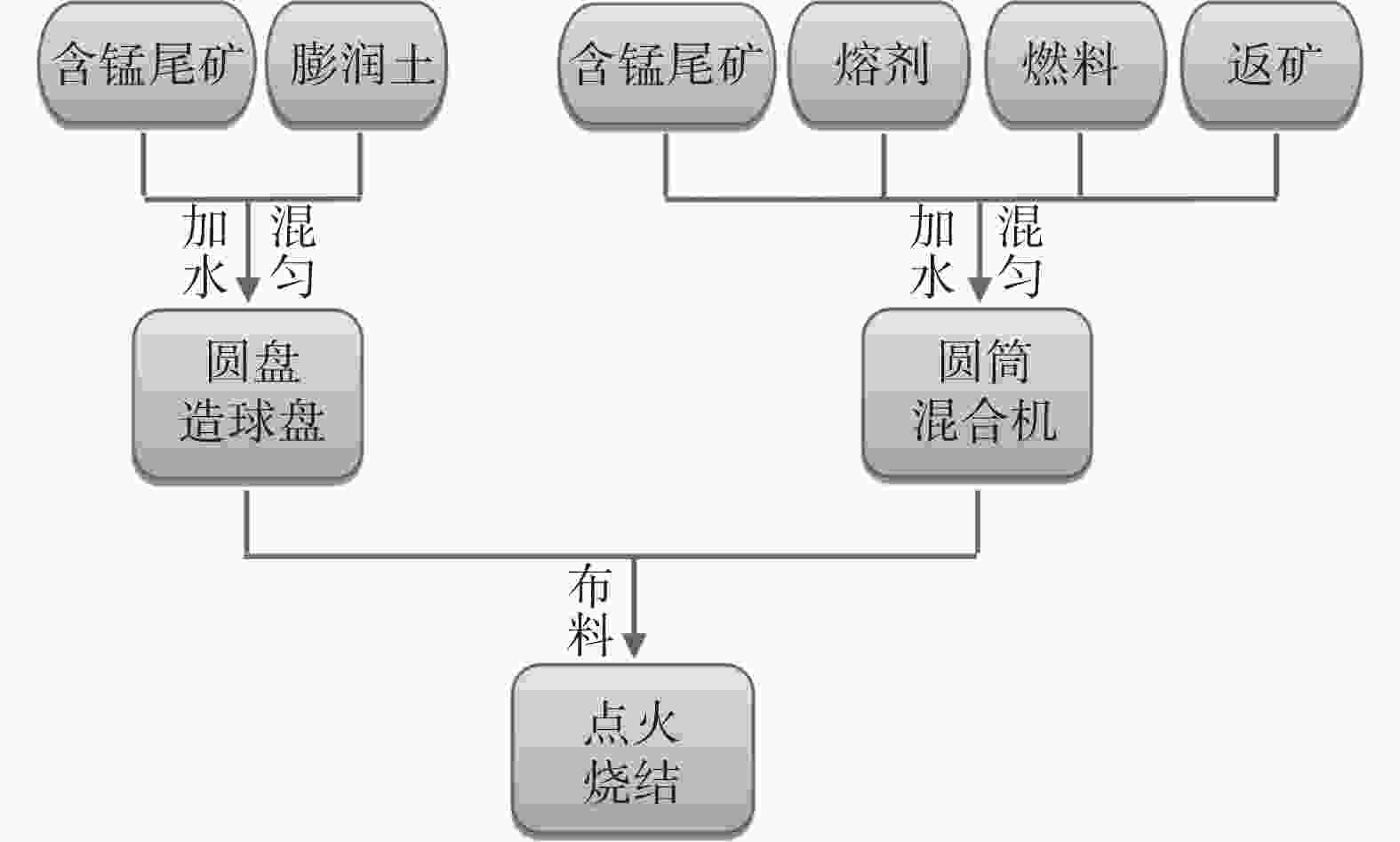
烧结工艺 方案 固定碳配比/% 球团比例/% 布料方式 普通烧结 0 3.8 0 常规装料 复合造块
第一阶段1 3.8 35 交替布料 2 3.6 35 交替布料 3 3.3 35 交替布料 4 3.0 35 交替布料 复合造块
第二阶段5 3.3 40 交替布料 6 3.3 45 交替布料 7 3.3 40 分批布料 8 3.3 40 混匀布料 9 3.3 40 偏析布料 表 4 含锰尾矿普通烧结工艺及复合造块工艺的烧结杯试验结果
Table 4. Sintering pot test results under regular sintering process and composite agglomeration process
方案 基体料水分
/%生球水分
/%垂烧速度/
(mm·min−1)成品率
/%利用系数/
[t·(m2·h)−1]返矿
平衡转鼓强度
/%固体燃耗
/(kg·t−1)0 11.30 10.97 52.63 0.52 2.35 61.33 89.27 1 8.28 11.08 18.22 82.61 1.50 0.91 64.80 55.46 2 8.76 11.10 15.30 82.44 1.24 0.89 63.13 52.84 3 8.72 11.07 17.55 80.33 1.41 1.03 62.72 50.04 4 8.36 11.14 21.88 77.16 1.72 1.16 61.14 46.45 5 8.56 11.15 18.03 81.68 1.50 0.97 61.96 48.21 6 8.62 11.19 12.37 79.63 1.00 1.04 63.60 49.71 7 9.16 11.06 11.35 82.66 0.96 0.94 58.33 47.44 8 9.16 11.06 23.78 75.54 1.82 1.25 56.67 52.39 9 8.12 11.28 16.29 80.74 1.43 1.02 60.63 48.87 表 5 成品烧结矿的化学成分
Table 5. Chemical compositions of the sinter products
烧结工艺 w/% R (倍) TFe FeO SiO2 CaO Al2O3 MgO K2O Na2O Mn S P 普通烧结 56.19 9.46 4.80 9.36 0.45 0.29 0.12 0.025 1.64 0.007 0.011 1.95 复合造块 59.63 15.59 3.94 5.51 1.30 1.22 0.14 0.037 2.76 0.009 0.014 1.40 表 6 成品烧结矿冶金性能测定试验结果
Table 6. Test results of metallurgical properties of the sinter products
工艺 低温还
原粉化
(RDI+3.15)/%还原度
(RI)/%T10%
/°CT40%
/°CΔT1
/°CTS
/°CTd
/°CΔT2
/°CΔPm
/kPaS
/(kPa·°C)普通烧结 76.04 75.76 1061.1 1213.0 151.9 1288.2 1467.5 179.3 10.76 864.6 复合造块 79.53 72.49 1011.6 1160.1 148.5 1270.8 1359.3 88.5 8.27 222.0 注:ΔT1 (软化温度区间)= T40%-T10%;ΔT2 (熔滴温度区间)= Td (滴落开始温度)-Ts (熔化开始温度)。 -
[1] Zhao Liqun, Wang Chunnv, Zhang Min, et al. Current exploration status and supply-demand situation of iron ore resources in China mainland[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2020,56(3):635−642. (赵立群, 王春女, 张敏, 等. 中国铁矿资源勘查开发现状及供需形势分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2020,56(3):635−642.Zhao Liqun, Wang Chunnü, Zhang Min, et al. Current exploration status and supply-demand situation of iron ore resources in China mainland [J]. Geology and Exploration, 2020, 56(3): 635-642. [2] Wu Qiujie, Lv Zhenfu, Cao Jincheng. Study on the current situation of development and utilization of large iron ore resource bases in China[J]. Modern Mining, 2020,36(8):113−115. (武秋杰, 吕振福, 曹进成. 我国铁矿大型资源基地开发利用现状研究[J]. 现代矿业, 2020,36(8):113−115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2020.08.034Wu Qiujie, Lv Zhenfu, Cao Jincheng. Study on the current situation of development and utilization of large iron ore resource bases in China [J]. Modern Mining, 2020, 36(8): 113-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2020.08.034 [3] Zhang Xiang. The present situation and countermeasures of iron ore resource safety in China[J]. Fujian Metallurgy, 2021,50(3):56−58. (张翔. 浅谈我国铁矿资源安全的现状和对策[J]. 福建冶金, 2021,50(3):56−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7665.2021.03.015Zhang Xiang. The present situation and countermeasures of iron ore resource safety in China [J]. Fujian Metallurgy, 2021, 50(3): 56-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7665.2021.03.015 [4] Teng Fei, Zeng Zhiyan, Guo Peimin. Experimental study on pellets performance of a kind of manganese-containing iron concentrate[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2021,46(5):47−53. (滕飞, 曾志彦, 郭培民. 一种含锰铁精矿球团性能试验研究[J]. 烧结球团, 2021,46(5):47−53.Teng Fei, Zeng Zhiyan, Guo Peimin. Experimental study on pellets performance of a kind of manganese-containing iron concentrate [J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2021, 46(5): 47-53. [5] 姜涛, 李光辉, 张元波, 等. 铁矿粉复合造块法[C]//2010年全国炼铁生产技术会议暨炼铁年会论文集. 北京: 中国金属学会, 2010: 181-186.Jiang Tao, Li Guanghui, Zhang Yuanbo, et al. Composite agglomeration process [C]//Proceedings of 2010 National Ironmaking Production Technology Conference and Annual Ironmaking Conference. Beijing: The Chinese Society for Metals, 2010: 181-186. [6] Chen Ge, Wang Ruijun, Shen Maosen. Application of superfine iron ore concentrate in composite agglomeration process[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2011,31(3):100−103. (陈革, 王瑞军, 沈茂森. 超细精矿在复合造块工艺中的应用[J]. 矿业工程, 2011,31(3):100−103.Chen Ge, Wang Ruijun, Shen Maosen. Application of superfine iron ore concentrate in composite agglomeration process [J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2011, 31(3): 100-103. [7] Rao Jiating, Hu Peng, Qin Xingguo, et al. Parameters optimization of composite sintering titanium magnetite concentrate[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(3):83−87. (饶家庭, 胡鹏, 秦兴国, 等. 钒钛磁铁精矿复合烧结参数优化研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(3):83−87. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.03.015Rao Jiating, Hu Peng, Qin Xingguo , et al. Parameters optimization of composite sintering titanium magnetite concentrate [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017, 38(3): 83-87. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.03.015 [8] Zhang Zhanlei, Yu Heng, Song Zhifang, et al. Experimental study on composite agglomeration of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrates[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2014,39(4):1−5. (张展雷, 于恒, 宋志芳, 等. 钒钛磁铁精矿复合造块试验研究[J]. 烧结球团, 2014,39(4):1−5.Zhang Zhanlei, Yu Heng, Song Zhifang, et al. Experimental study on composite agglomeration of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrates [J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2014, 39(4): 1-5. [9] Wan Xinyu, Lv Qing, Zhang Shuhui, et al. Researches on vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrates by composite agglomeration process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014,35(3):63−68. (万新宇, 吕庆, 张淑会, 等. 难烧钒钛磁铁精粉的复合造块研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2014,35(3):63−68. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2014.03.014Wan Xinyu, Lv Qing, Zhang Shuhui , et al. Researches on vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrates by composite agglomeration process [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014, 35(3): 63-68. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2014.03.014 [10] Zhang Ronghua, Liu Bingbing, Zhang Yuanbo, et al. Research on preparation of low-medium basicity BF burden from high-MgO content iron ore concentrates by composite agglomeration process[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2017,42(6):27−33. (张荣华, 刘兵兵, 张元波, 等. 高镁精矿复合造块法制备中低碱度炉料研究[J]. 烧结球团, 2017,42(6):27−33.Zhang Ronghua, Liu Bingbing, Zhang Yuanbo, et al. Research on preparation of low-medium basicity BF burden from high-MgO content iron ore concentrates by composite agglomeration process [J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2017, 42(6): 27-33. [11] Zhang Yuanbo, Du Minghui, Li Guanghui, et al. New advances on application of composite agglomeration process in hard-to-treat iron-bearing mineral resources[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2016,41(4):39−44. (张元波, 杜明辉, 李光辉, 等. 复合造块法在难处理含铁资源中的应用新进展[J]. 烧结球团, 2016,41(4):39−44.Zhang Yuanbo, Du Minghui, Li Guanghui , et al. New advances on application of composite agglomeration process in hard-to-treat iron-bearing mineral resources [J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2016, 41(4): 39-44. [12] 马丁·戈德斯, 瑞纳德·谢尼奥, 奥斯卡·林格阿迪, 等. 现代高炉炼铁(4版)[M]. 沙永志译. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 2021: 84-86, 145-149.Maarten Geerdes, Renard Chaigneau, Oscar Lingiardi, et al. Modern blast furnace ironmaking (Fourth edition)[M]. Sha Yongzhi's Translation. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press, 2021: 84-86, 145-149 [13] 姜涛. 烧结球团生产技术手册[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2014: 875.Jiang Tao. Technical manual of sintering pellet production[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2014: 875. -




 下载:
下载: