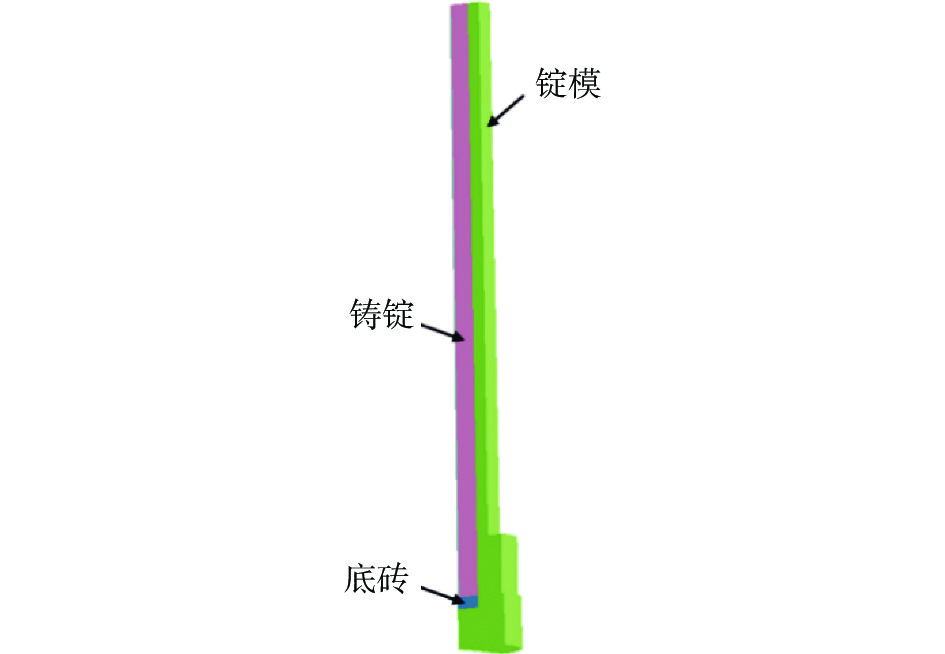
Numerical simulation on pouring process of nickel base superalloy induction ingot
-
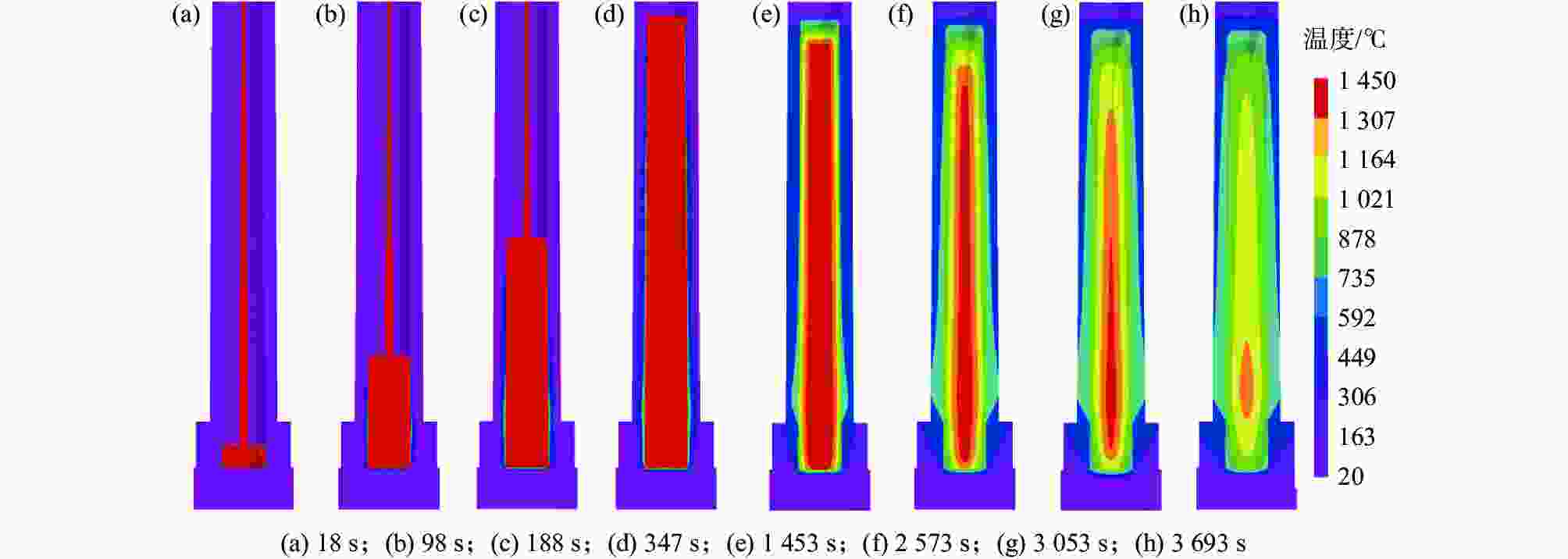
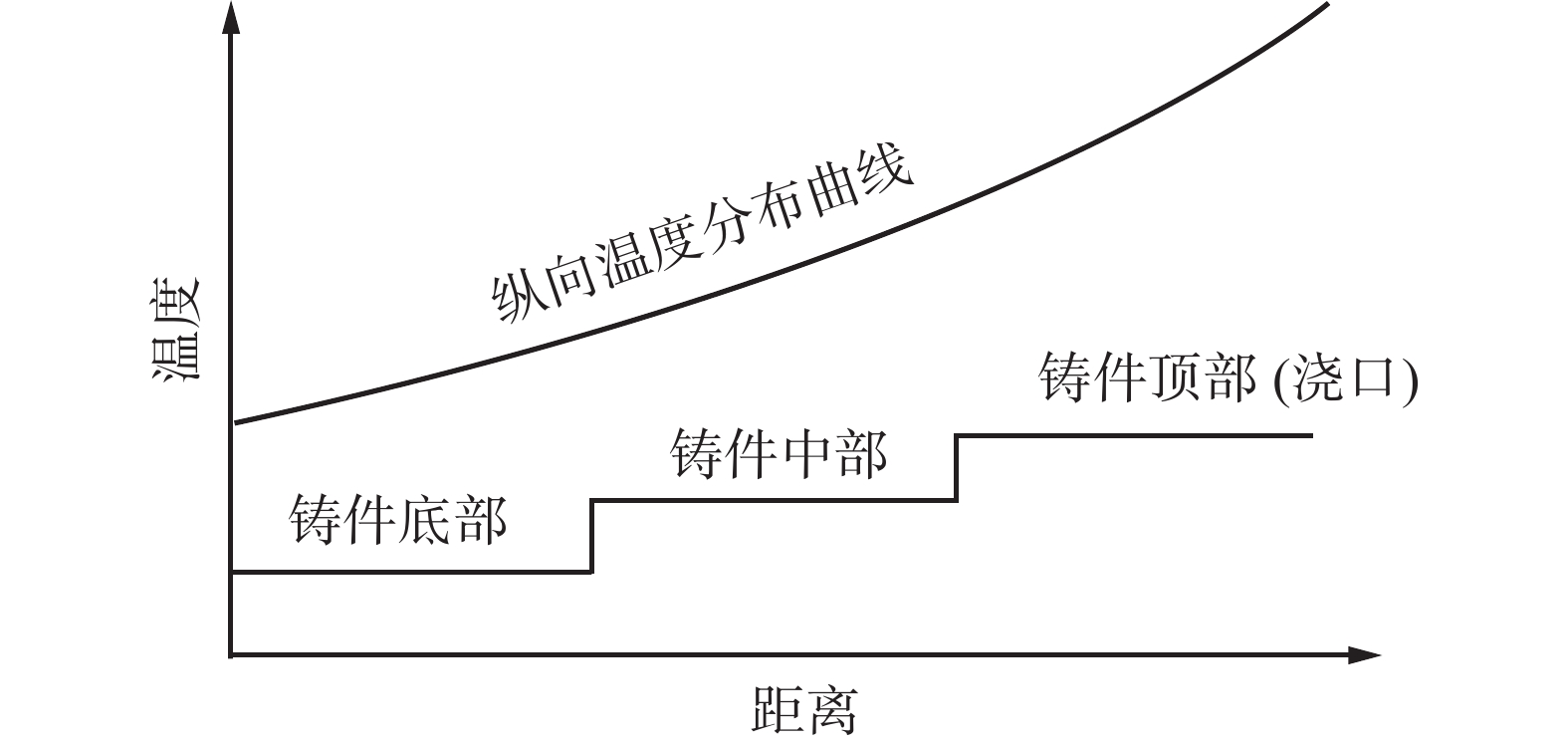
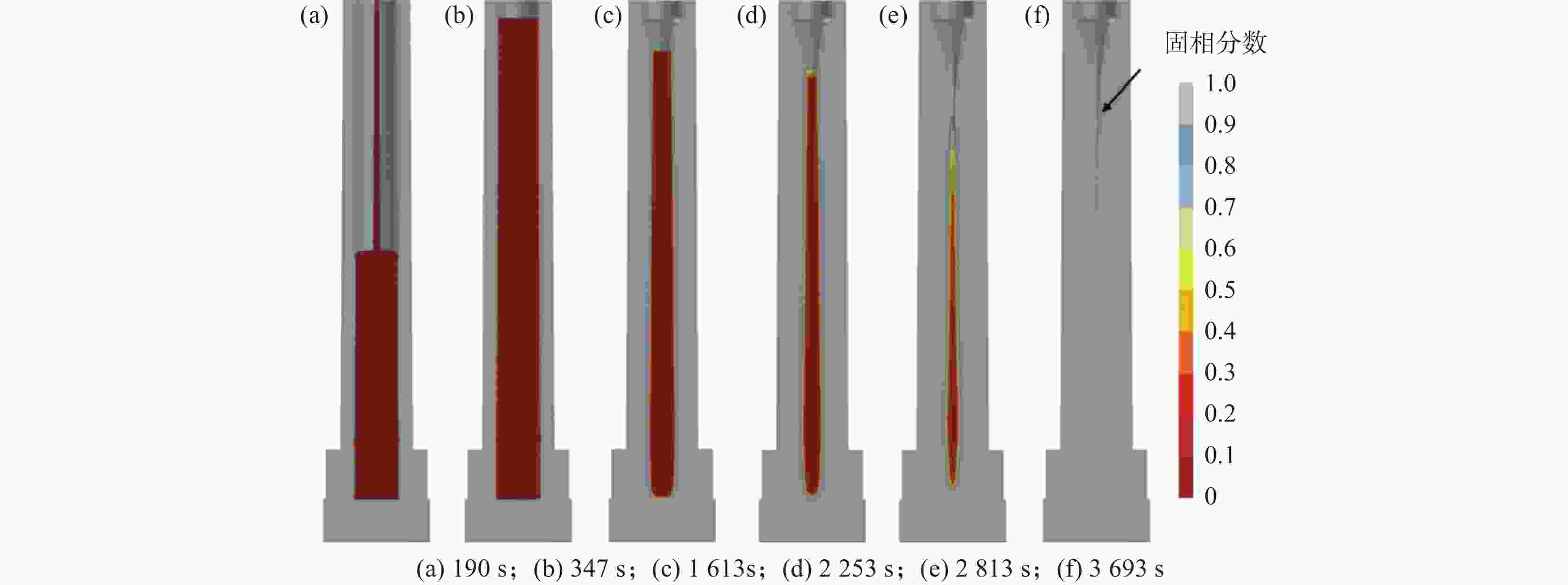
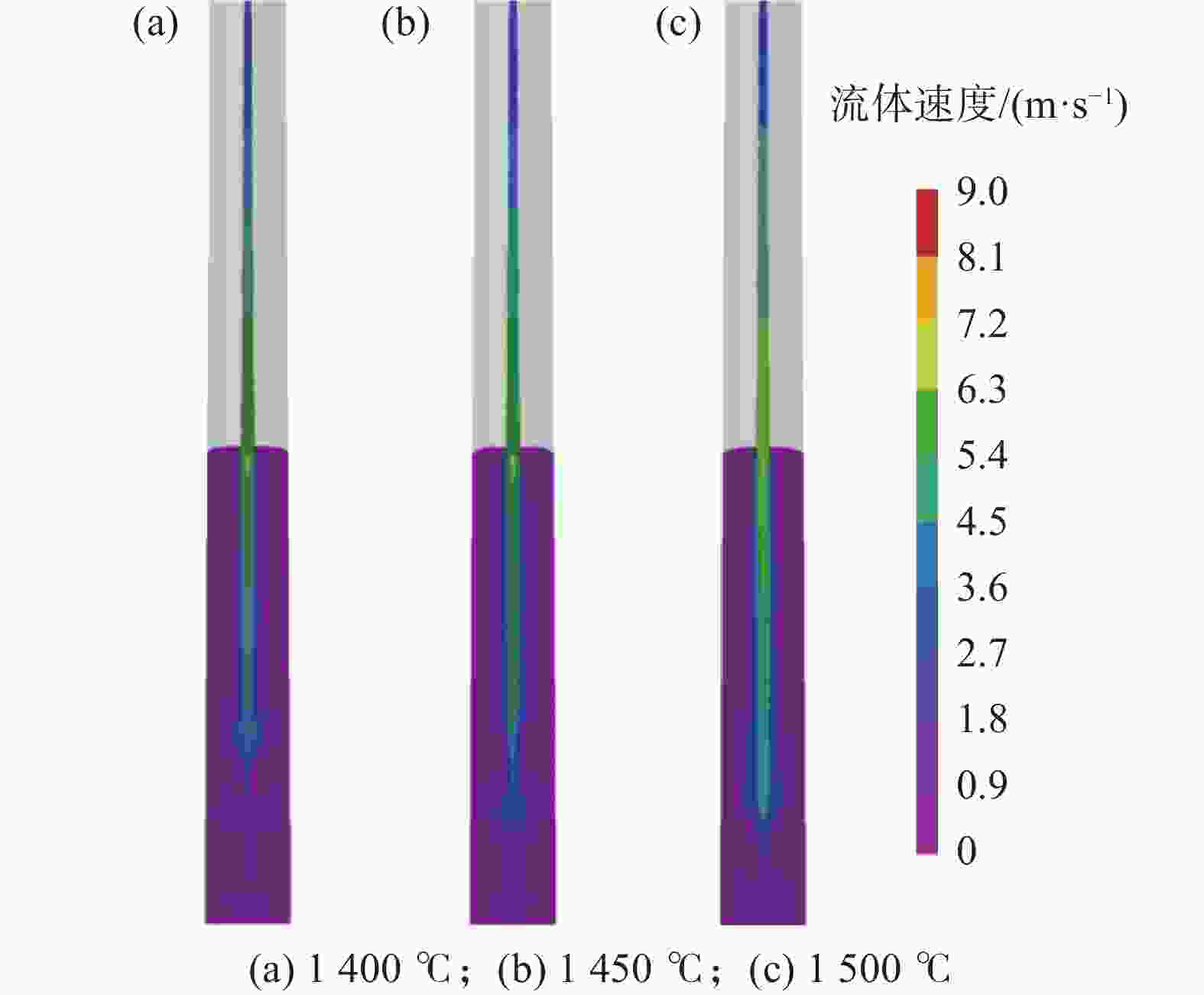
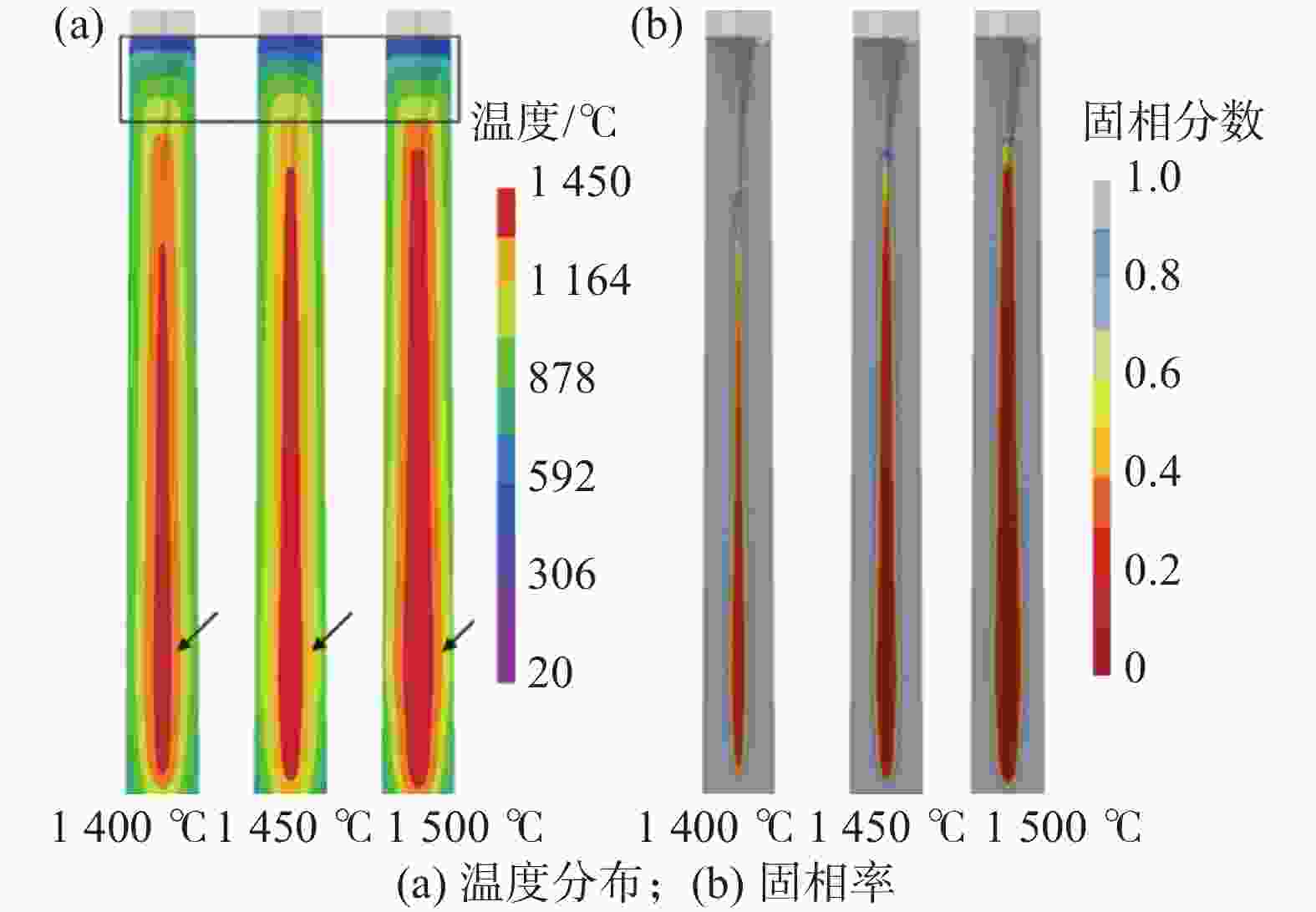
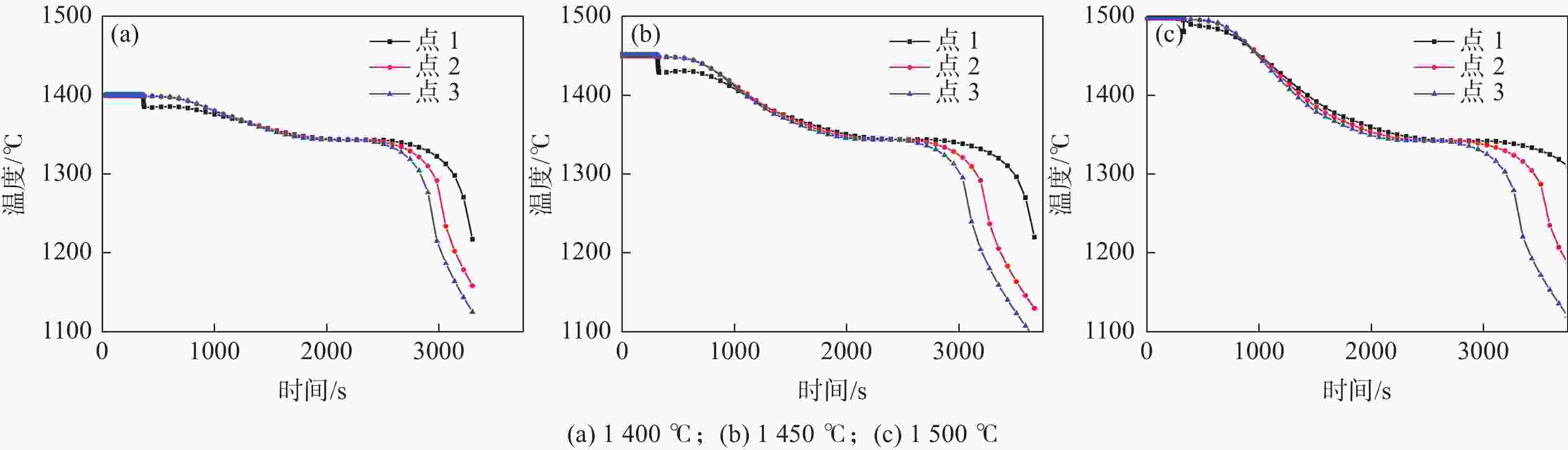
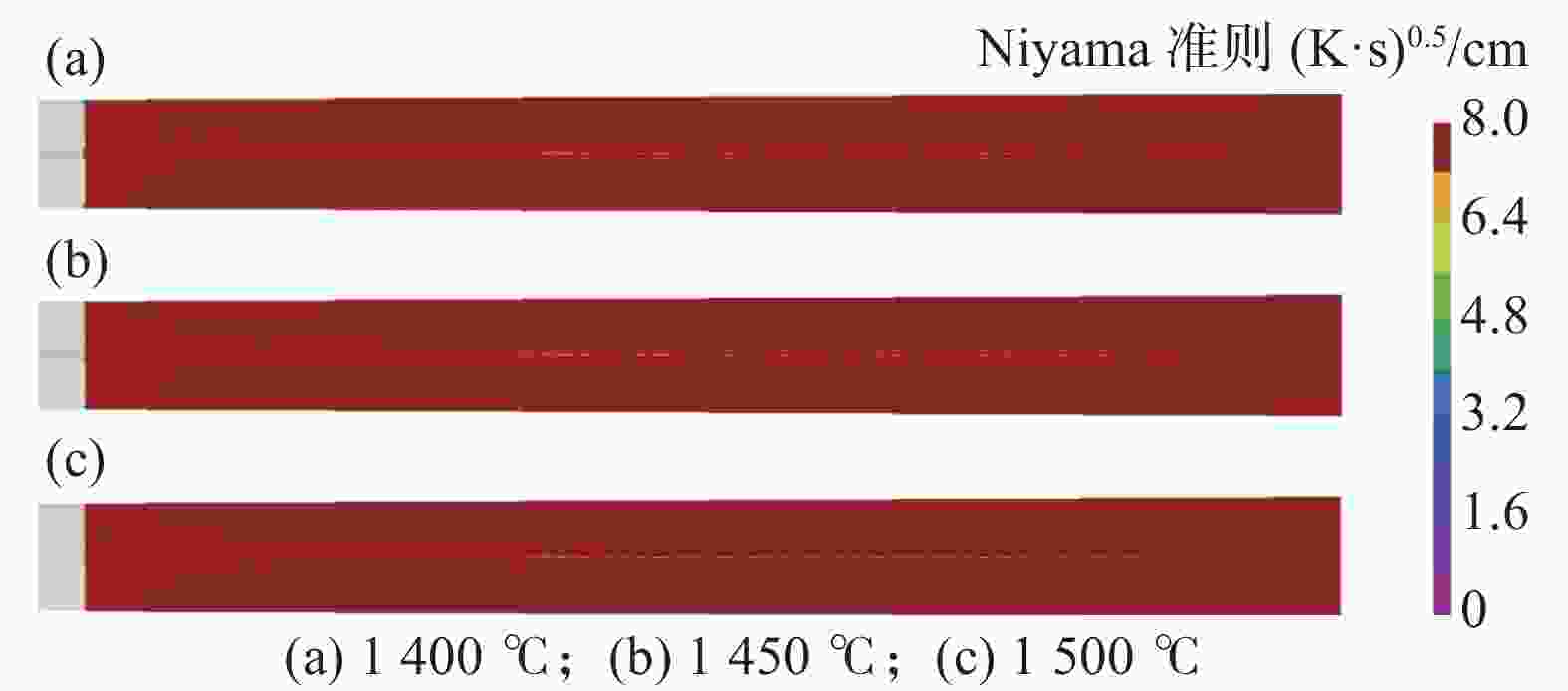
摘要: 利用ProCAST软件对镍基高温合金感应锭的浇注过程进行了数值模拟研究,分析了铸锭充型与凝固过程温度场、固相率等的变化特征及其对铸锭缩孔的影响,探讨了铸锭缩孔缩松随浇注温度的变化规律。结果表明,镍基高温合金感应锭凝固过程中,在铸锭纵向方向上,铸锭上部合金温度低,下部合金温度高,铸锭未实现从底部到顶部(浇口)的顺序凝固,铸锭端部的“V”形一次缩孔较深。在充型阶段,浇注温度的变化对合金流动的最大速度及合金液面波动的影响较小;在凝固阶段,降低浇注温度减小了铸锭下部的高温区域,能在一定程度上减小铸锭端部的一次缩孔深度,但由于其未能使铸锭在纵向方向上实现顺序凝固,因此降低浇注温度并不能显著减小铸锭端部的一次缩孔深度。另外,浇注温度的变化对铸锭内部缩松的影响较小。Abstract: In this paper, the numerical simulation on pouring process of nickel base superalloy induction ingot had been carried out by using ProCAST software. The change characteristics of temperature field and solid fraction during the filling and solidification process of ingot and their influence on ingot shrinkage porosity had been studied. Moreover, the change rule of ingot shrinkage porosity with pouring temperature had been investigated in detail. The results show that the temperature of the upper ingot is lower than that of the lower ingot along the longitudinal direction of ingot during solidification process, and sequential solidification does not occur in the ingot, thus the V-shaped primary shrinkage porosity of the ingot is deep. In the filling stage, the change of pouring temperature has little effect on the maximum flow speed and level fluctuation of alloy. In the solidification stage, lowering pouring temperature can reduce the high-temperature area at the lower part of the ingot and the primary shrinkage depth at the end of the ingot to a certain extent. Nevertheless, changing pouring temperature can not make the ingot achieve sequential solidification in the longitudinal direction, consequently, lowering the pouring temperature can not significantly reduce the primary shrinkage porosity at the end of the ingot. Moreover, the change of pouring temperature has little effect on the small shrinkage porosity in the ingot.
-
Key words:
- nickel base superalloy /
- ingot casting /
- numerical simulation /
- pouring temperature /
- shrinkage porosity
-
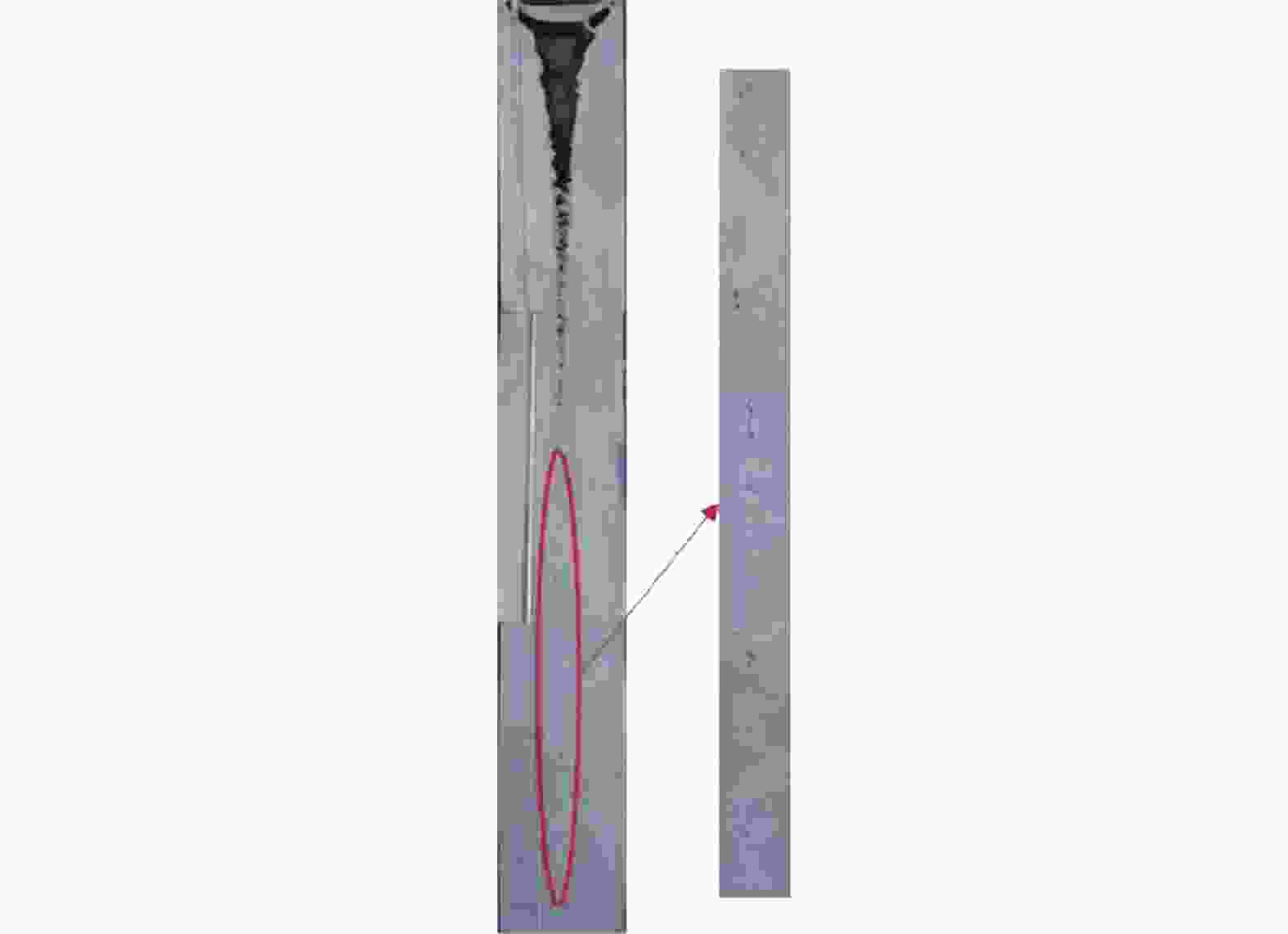
图 6 镍基高温合金感应锭的缩孔缩松[12]
Figure 6. The shrinkage porosity of nickel base superalloy induction ingot
表 1 镍合金的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of nickel alloys
% Al C Cr Fe Mo Nb Ti Ni 0.5 0.02 18.3 18.9 3 5 0.97 余量 表 2 模拟采用的主要工艺参数
Table 2. The main process parameters used in the simulation
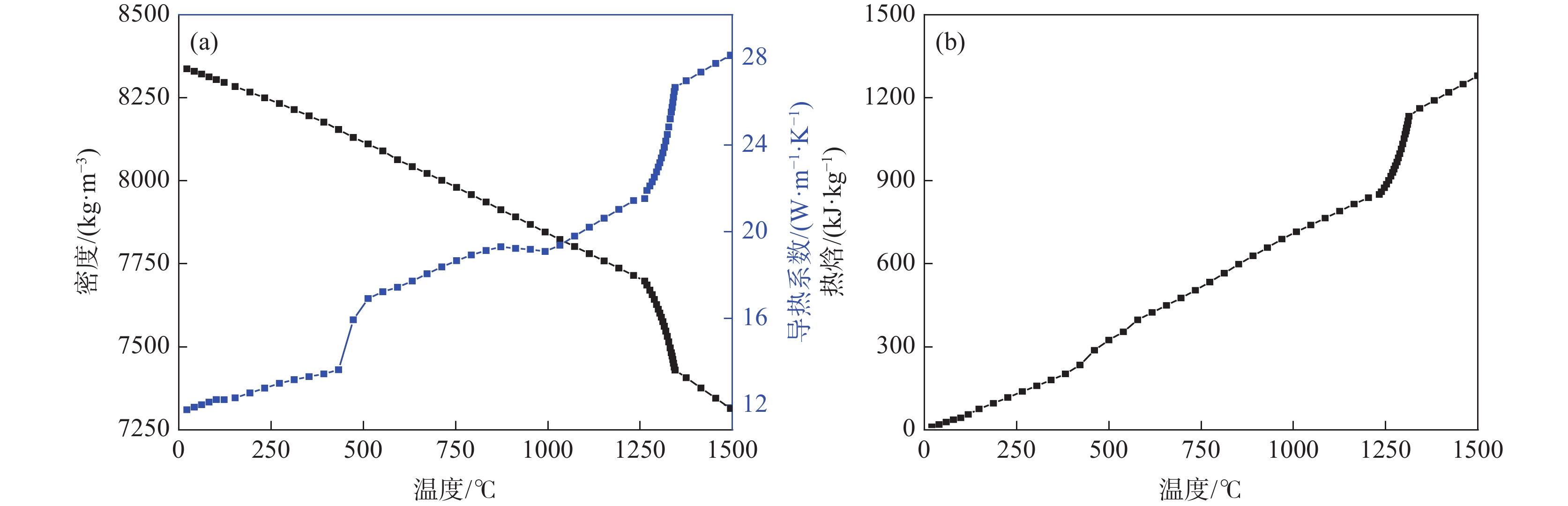
浇注温度/℃ 入口直径/mm 入口速度/(kg·s−1) 1400, 1450, 1500 27 1.96 -
[1] 郭建亭. 高温合金材料学(高温合金材料与工程应用) [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010.Guo Jianting. Materials science and engineering for superalloy (Superalloy materials and engineering applications)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010. [2] Geng L, Na Y S, Park N K. Oxidation behavior of alloy 718 at a high temperature[J]. Materials & Design, 2007,28(3):978−981. [3] Jiang Shichuan, Zhang Jian, He Yunhua, et al. Microstructure evolution and processing maps of GH4169 during deformation[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021,42(2):161−166. (蒋世川, 张健, 何云华, 等. GH4169 合金高温变形显微组织演变及热加工图[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2021,42(2):161−166.Jiang Shichuan, Zhang Jian, He Yunhua, et al. Microstructure evolution and processing maps of GH4169 during deformation [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021, 42(02): 161-166. [4] 段生朝. 电渣重熔大型IN718镍基合金铸锭合金元素氧化控制的基础研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2020.Duan Shengchao. Fundamental study on the controlling loss of alloying elements of large IN718 electroslag remelting ingots[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2020. [5] Mitchell A. Recent developments in specialty melting processes[J]. Materials Technology, 1994,9(9-10):201−206. doi: 10.1080/10667857.1994.11785070 [6] 石骁. 电渣重熔大型IN718镍基合金铸锭凝固和偏析行为基础研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2019.Shi Xiao. Fundamental study on the solidification and segregation behavior of large-sized as-cast IN718 electroslag remelting ingots[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2019. [7] 凌云. 多力场作用下铸件凝固过程基于动态压强的缩孔预测方法及应用[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017.Ling Yun. A dynamic pressure-based method to predict casting shrinkage cavities during solidification process under multi-force fields and its application[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science & Technology, 2017. [8] Hardin R A, Beckermann C. Effect of porosity on deformation, damage, and fracture of cast steel[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2013,44(12):5316−5332. doi: 10.1007/s11661-013-1669-z [9] Liu Keli, Wang Junsheng, Guo Yuelin, et al. Research progress on numerical simulation and control methods of hole defects in nickel base single crystal superalloy[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2020,63(16):75−85. (刘可立, 王俊升, 郭跃岭, 等. 镍基单晶高温合金孔洞缺陷数值模拟与控制方法研究进展[J]. 航空制造技术, 2020,63(16):75−85.Liu Like, Wang Junsheng, Guo Yuelin, et al. Research progress on numerical simulation and control methods of hole defects in nickel base single crystal superalloy[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2020, 63(16): 75-85. [10] Li Chao, Liu Jia, Yu Ang, et al. Study of vacuum induction melting process for superalloy[J]. Vacuum, 2016,53(2):37−41. (李超, 刘佳, 于昂, 等. 铸造高温合金真空感应熔炼过程的研究[J]. 真空, 2016,53(2):37−41.Li Chao, Liu Jia, Yu Ang, et al. Study of vacuum induction melting process for superalloy[J]. Vacuum, 2016, 53(02): 37-41. [11] Cheng Jianqiang, Hu Xianjun, Gu Hua, et al. Application of exothermic insulated riser in superalloy vacuum casting[J]. Foundry Technology, 2016,37(1):110−113. (成建强, 胡显军, 顾晔, 等. 发热保温冒口在高温合金真空浇注中的应用[J]. 铸造技术, 2016,37(1):110−113.Cheng Jianqiang, Hu Xianjun, Gu Hua, et al. Application of exothermic insulated riser in superalloy vacuum casting[J]. Foundry Technology, 2016, 37(01): 110-113. [12] 王建武, 徐志强, 杨树峰. 热顶设计对镍基高温合金铸锭收缩孔隙的影响[J/OL]. 中国冶金: 1-9[2022-04-24]Wang Jianwu, Xu Zhiqiang, Yang Shufeng, et al. Effect of hot top design on the shrinkage porosity of nickel-based superalloy ingots[J/OL]. China Metallurgy, 1-9[2022-04-24]. [13] Zhou Jianxin. Current status and development trend of casting numerical simulation technology[J]. Foundry, 2012,61(10):1105−1115. (周建新. 铸造计算机模拟仿真技术现状及发展趋势[J]. 铸造, 2012,61(10):1105−1115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4977.2012.10.001Zhou Jianxin. Current status and development trend of casting numerical simulation technology[J]. Foundry, 2012, 61(10): 1105-1115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4977.2012.10.001 [14] Khalajzadeh V, Beckermann C. Simulation of shrinkage porosity formation during alloy solidification[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2020,51(5):2239−2254. doi: 10.1007/s11661-020-05699-z [15] 陈峥. 大铸锭凝固过程的模拟研究[D]. 上海: 上海大学, 2019.Chen Zheng. Simulation research on the heavy ingot solidification process[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University, 2019. [16] Zhang Minhua, Qu Yinhu, Liang Tao. Simulation of filling and solidification processes of faucet cover by procast[J]. Foundry Technology, 2015,36(4):1055−1062. (张敏华, 屈银虎, 梁涛. ProCAST 在水龙头罩铸造模拟过程中的应用[J]. 铸造技术, 2015,36(4):1055−1062.Zhang Minhua, Qu Yinhu, Liang Tao, Simulation of filling and solidification processes of faucet cover by procast[J]. Foundry Technology, 2015, 36(04): 1055-1062 [17] 李庆春. 铸件形成理论基础[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1982.Li Qingchun. Theoretical basis of casting formation[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1982. [18] 郭建亭. 髙温合金材料学(应用基础理论) [M]. 北京, 科学出版社, 2008.Guo Jianting. Materials science and engineering for superalloy (application basic theory)[M]. Beijing, Science Press, 2008. [19] Wang Jiaqi, Fu Paixian, Liu Hongwei, et al. Shrinkage porosity criteria and optimized design of a 100-ton 30Cr2Ni4MoV forging ingot[J]. Materials and Design, 2012,35:446−456. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2011.09.056 [20] Carlson K D, Beckermann C. Prediction of shrinkage pore volume fraction using a dimensionless Niyama criterion[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2009,40(1):163−175. doi: 10.1007/s11661-008-9715-y [21] Riedler M, Michelic S. Bernhard C. Formation of shrinkage porosity during solidification of steel: Numerical simulation and experimental validation[C]//IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. IOP Publishing, 2016, 143(1): 012035. -




 下载:
下载: