Study on microstructure and properties of TiC-based high manganese steel bonded cemented carbide prepared by spark plasma sintering
-
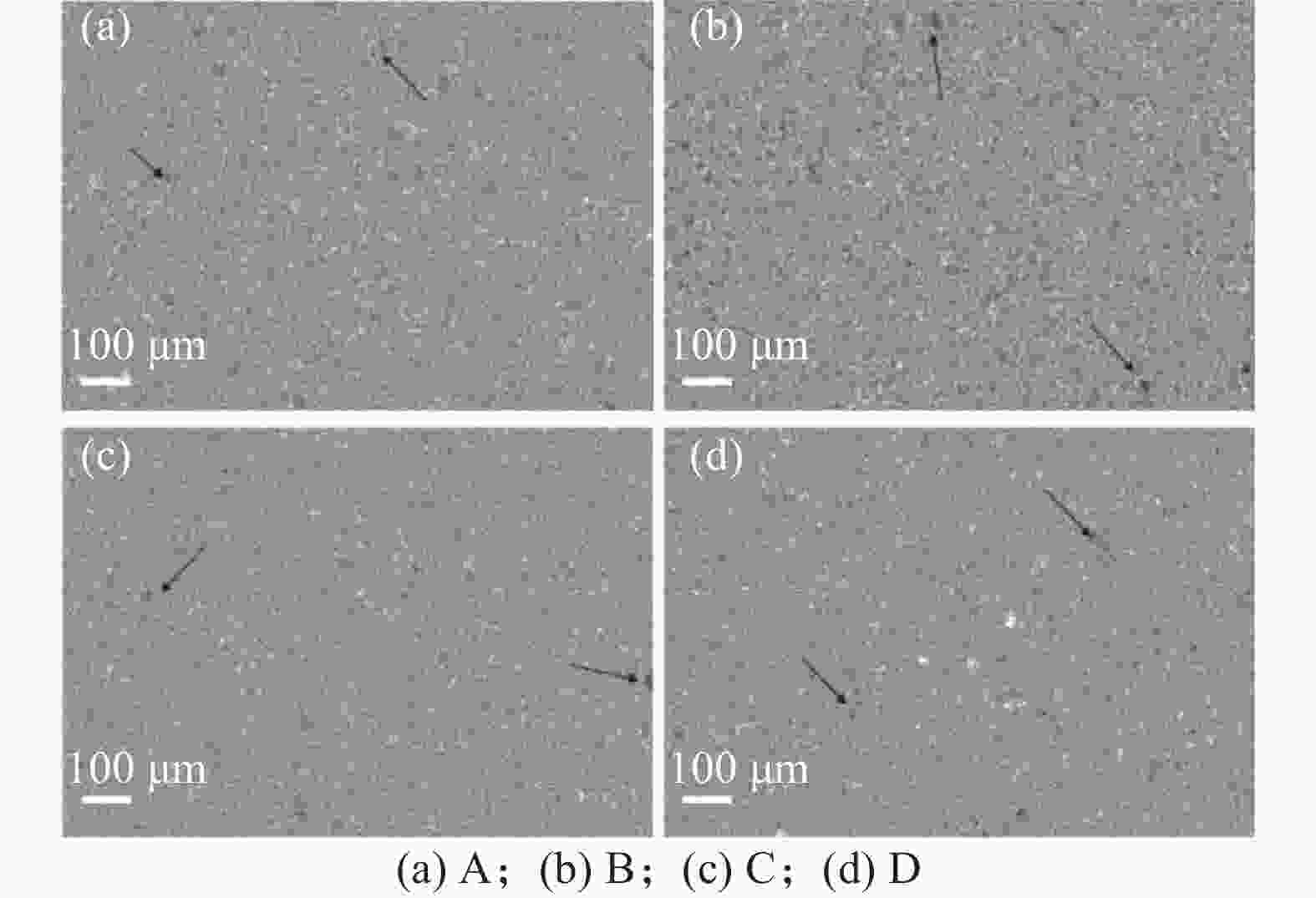
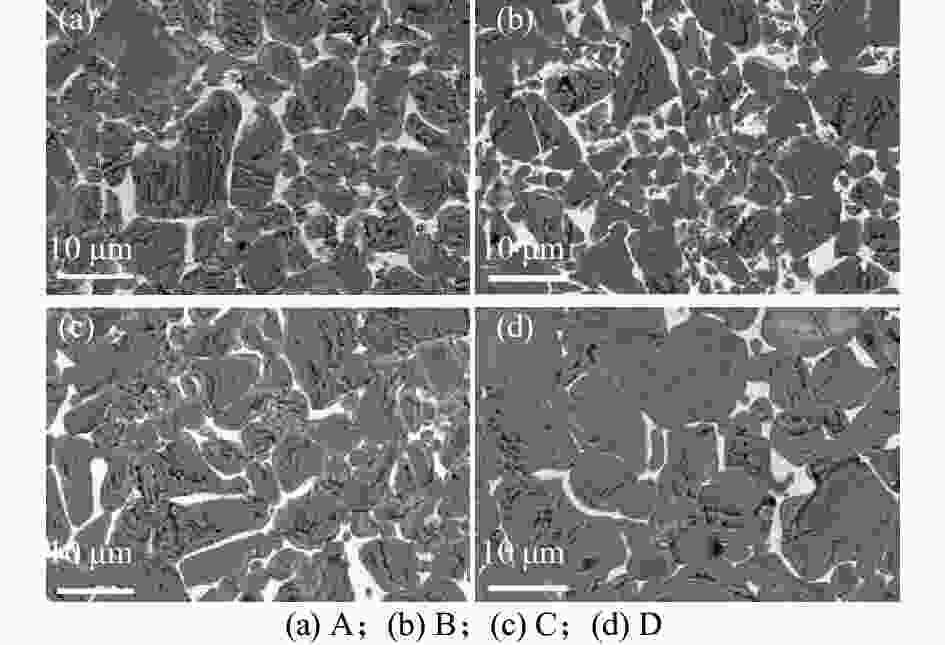
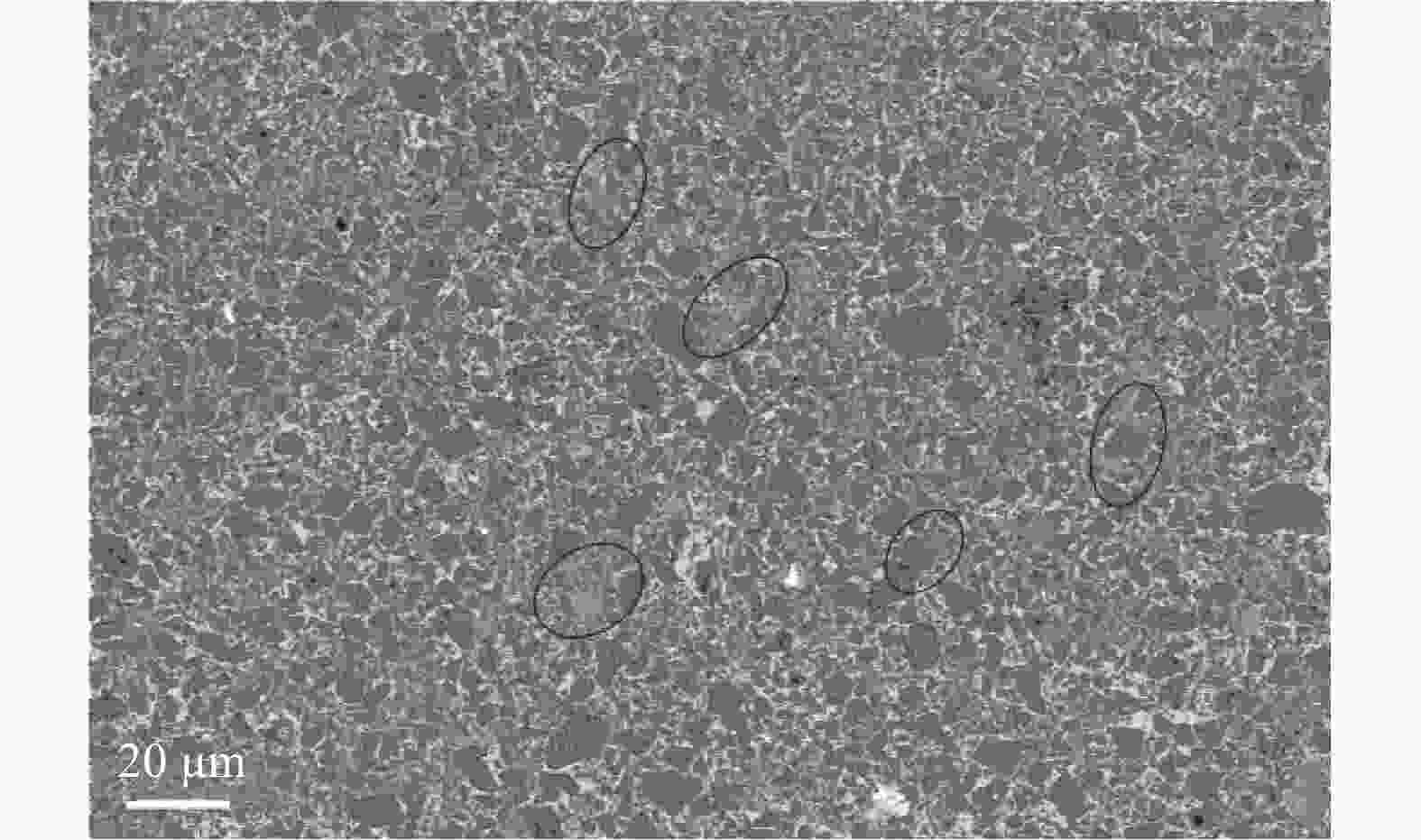
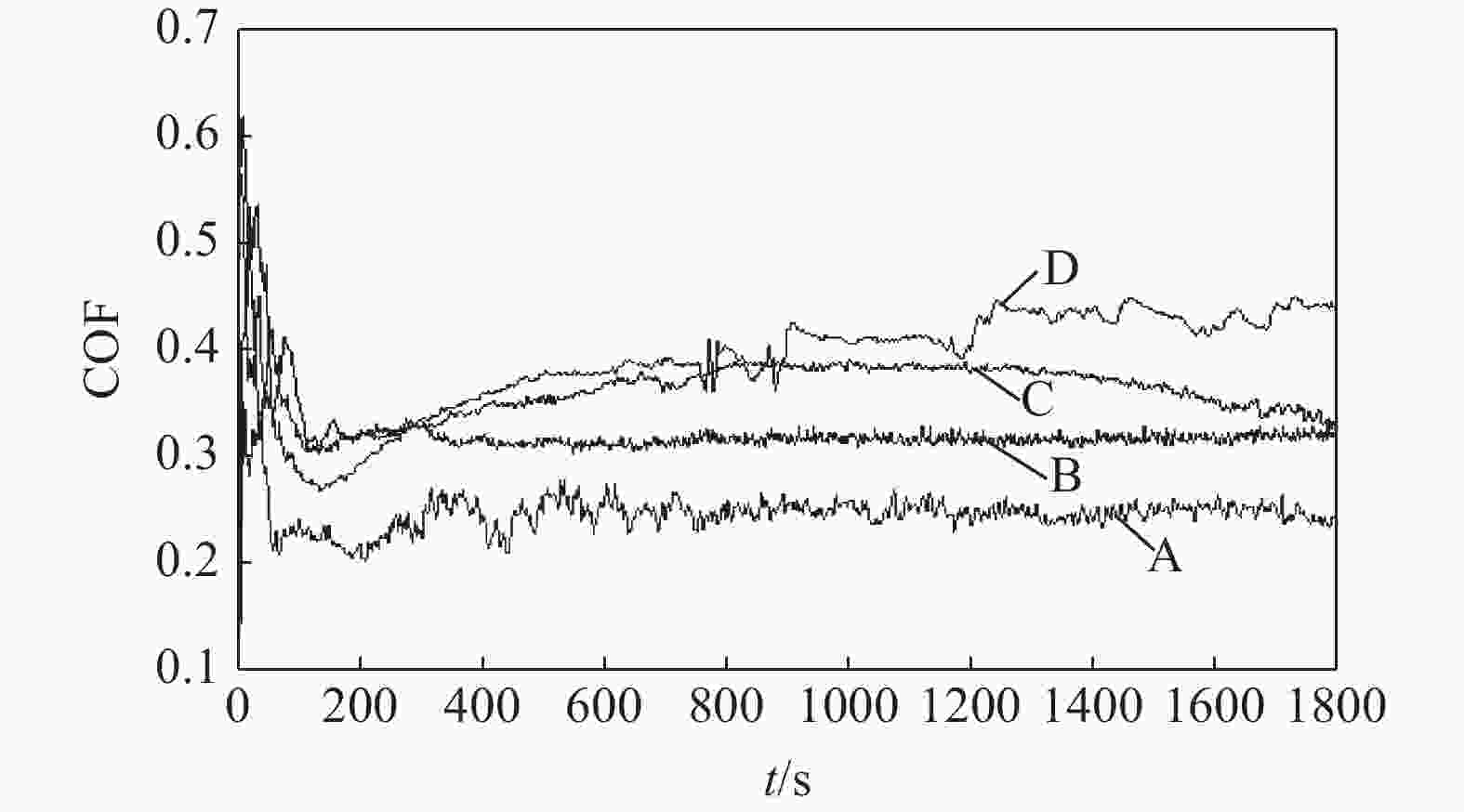
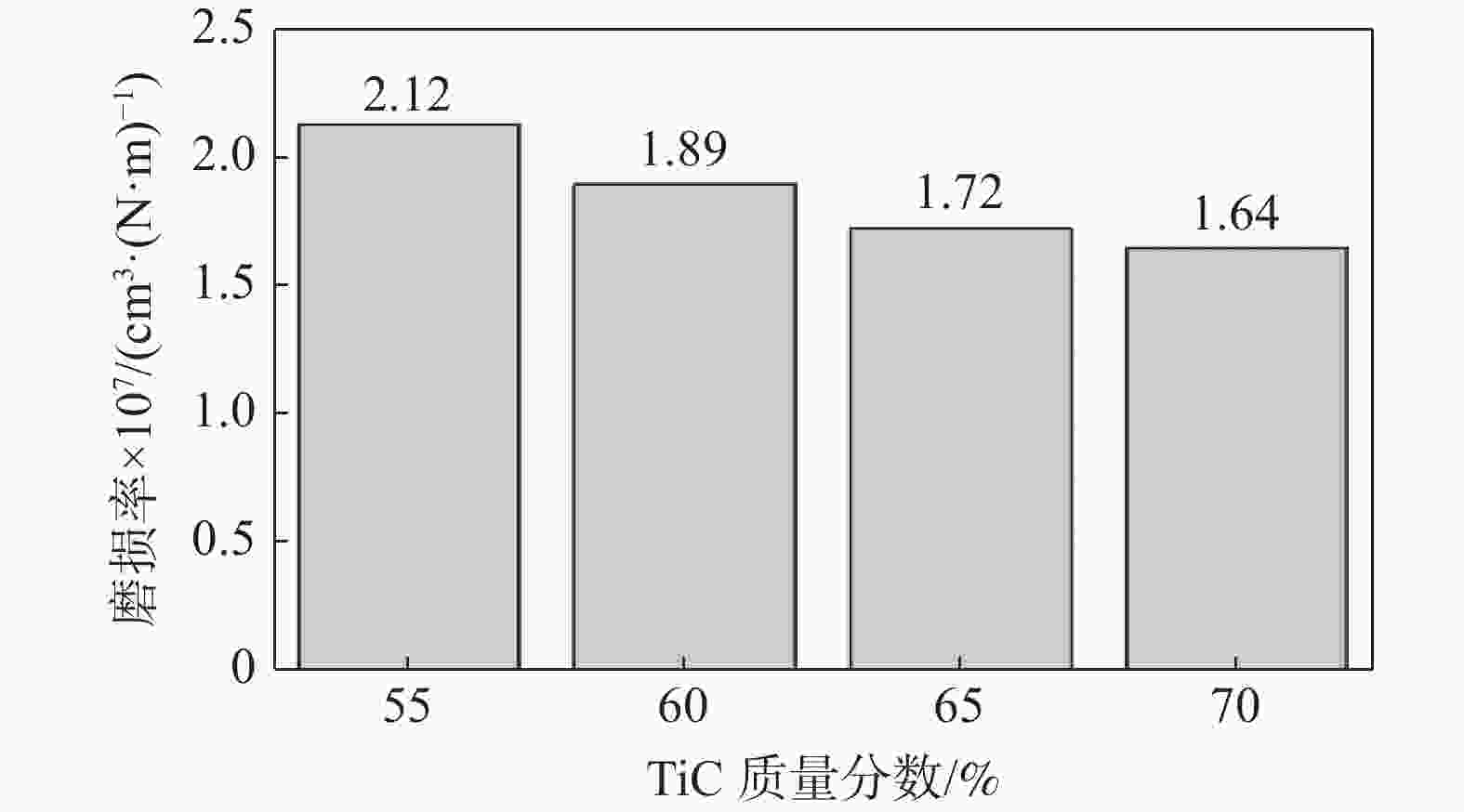
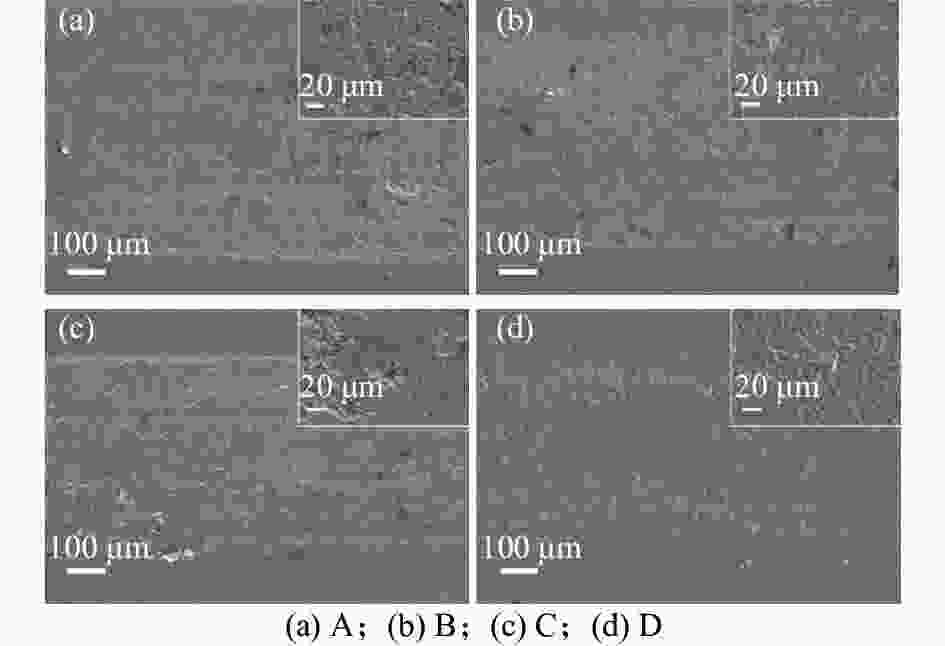
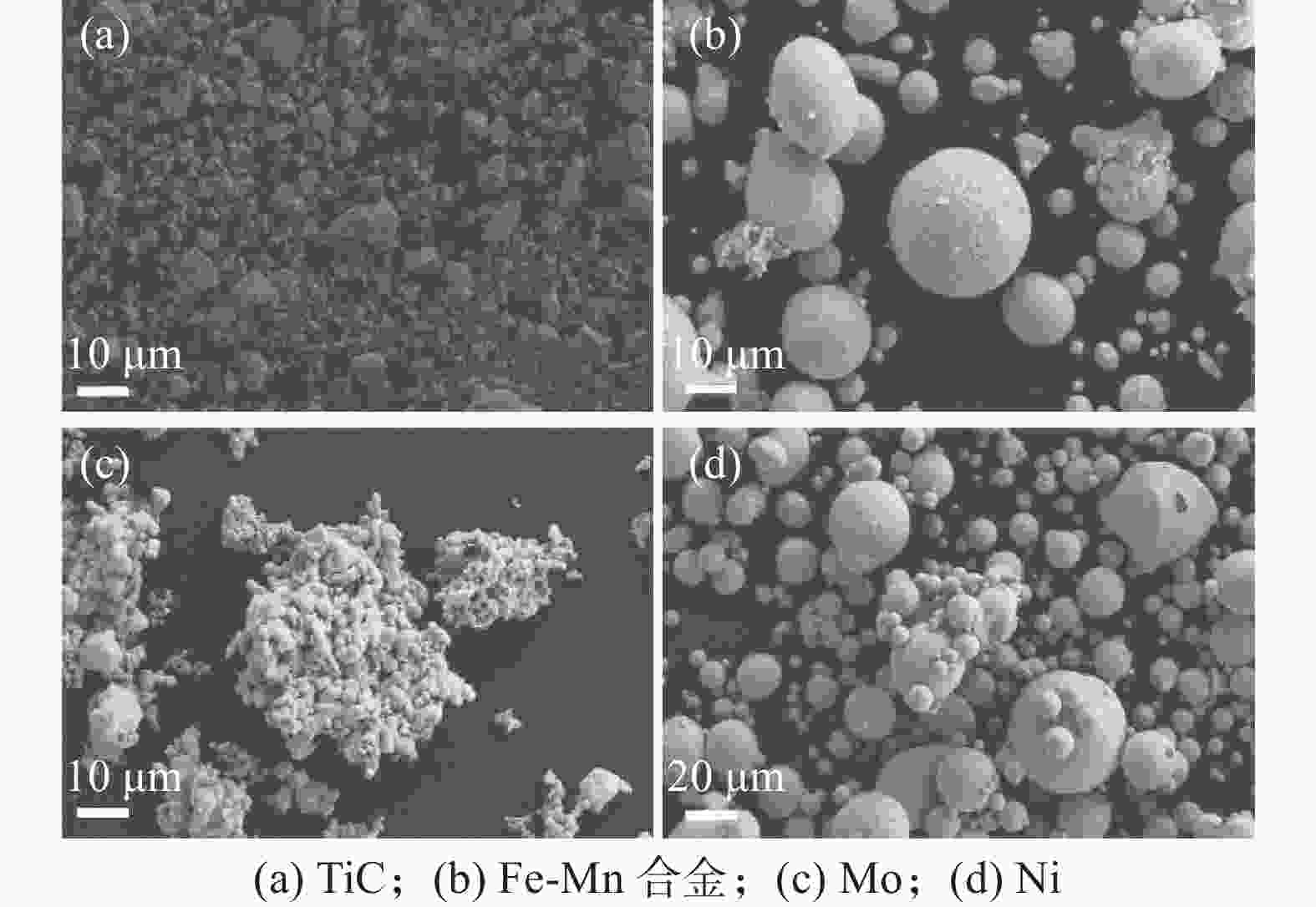
摘要: 采用放电等离子烧结技术(SPS)制备含有不同TiC质量分数的硬质合金,揭示材料的显微结构对其硬度和磨损行为的影响机理,探索高TiC质量分数硬质合金作为耐磨材料的可能性。结果表明:SPS烧结可以得到组织致密的样品,TiC质量分数为55%的硬质合金孔隙率为0.07%,随着TiC质量分数的增加,硬质合金的孔隙率也随之上升,当TiC质量分数为70%时,孔隙率为0.21%。在烧结过程中,Mo在TiC颗粒周围参与形成复杂的核壳结构,Ni分布于金属粘结相中。大尺寸TiC颗粒保持原始形貌,小尺寸TiC颗粒逐渐球化,并出现颗粒富集区。硬质合金的硬度随TiC质量分数的增加而增加,TiC质量分数70%的硬质合金的显微硬度(HV)相较于TiC质量分数55%的增加559。通过摩擦磨损试验发现,TiC颗粒受到应力出现破碎与剥落,TiC质量分数55%硬质合金的磨损率最高,耐磨性最差。TiC质量分数70%硬质合金的磨损率最低,耐磨性最好。Abstract: Cemented carbides with different TiC mass fractions were prepared by spark plasma sintering (SPS) to reveal the influence mechanism of microstructure on hardness and wear behavior, and to explore the possibility of cemented carbides with high TiC mass fraction as wear-resistant materials. The results show that the sample with compact microstructure can be obtained by SPS sintering. The porosity of cemented carbide with 55% TiC mass fraction is 0.07%, and the porosity of cemented carbide increases with the increase of TiC mass fraction. In the sintering process, Mo participates in the formation of complex core-shell structure around TiC particles, and Ni distributes in the metal bonded phase. The large size TiC particles keeps their original morphology, while the small size TiC particles spheroidizes gradually and the particle enrichment area appears. The hardness of cemented carbide increases with the increase of TiC mass fraction. The microhardness (HV) of cemented carbide with 70% TiC mass fraction is 559 higher than that with 55% TiC mass fraction. The friction and wear tests show that the TiC particles are broken and spalling under stress, and the cemented carbide with 55% TiC mass fraction has the highest wear rate and the worst wear resistance. The cemented carbide with 70% TiC mass fraction has the lowest wear rate and the best wear resistance.
-
Key words:
- cermet /
- TiC /
- high manganese steel /
- spark plasma sintering /
- microhardness /
- friction and wear
-
表 1 金属基TiC陶瓷的成分配比
Table 1. Composition ratio of metal-based TiC ceramics
% 编号 TiC Ni Mo Fe-Mn A 55 2 2 余量 B 60 2 2 余量 C 65 2 2 余量 D 70 2 2 余量 表 2 硬质合金B核壳结构EDS原子比能谱
Table 2. EDS atomic specific energy spectrum of cermet B core-shell structure
% C Ti Cr Mn Fe Ni Mo 总量 谱图3 52.10 40.19 0.85 4.62 2.23 100.00 谱图2 45.70 7.78 0.38 5.50 37.55 3.09 100.00 谱图1 54.51 45.26 0.22 100.00 -
[1] Lu Qingzhong, Zhang Furun, Yu Lixin. The condition and trend of Ti(C, N) cermet[J]. Journal of Wuhan Institute of Science and Technology, 2002,(5):42−46. (陆庆忠, 张福润, 余立新. Ti(C, N)基硬质合金的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 武汉科技学院学报, 2002,(5):42−46. [2] Prava Dalai R, Das S, Das K. Development of TiC reinforced austenitic manganese steel[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2014,53(3):317−325. doi: 10.1179/1879139514Y.0000000140 [3] Ning Jiapei, Zheng Kaihong, Wang Juan, et al. Microstructure and abrasive wear properties of TiC-reinforced hadfield steel matrix composites[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2020,49(7):2407−2416. (宁嘉沛, 郑开宏, 王娟, 等. TiC增强高锰钢基复合材料的组织与磨料磨损性能[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2020,49(7):2407−2416. [4] 熊拥军, 李溪滨, 刘如铁, 等. 新型TiC钢结硬质合金致密化技术[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 40(6): 1563-1567.Xiong Yongjun, Li Xibin, Liu Rutie, et al. Densification processing of a new steel bonded titanium carbide[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2009, 40(6): 1563-1567. [5] Zhang M, Yang Q, Xiong W, et al. Effect of vacuum-sintering temperature on magnetic and mechanical properties of TiC-TiN-Ni-Mo-C cermets[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2018,49(8):3550−3555. doi: 10.1007/s11661-018-4659-3 [6] Zheng Y, Wang S, You M, et al. Fabrication of nanocomposite Ti(C, N)-based cermet by spark plasma sintering[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2005,92(1):64−70. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2004.12.031 [7] Han C, Kong M. Fabrication and properties of TiC-based cermet with intra/intergranular microstructure[J]. Materials & Design, 2009,30(4):1205−1208. [8] Zhou S, Zhao W, Xiong W. Microstructure and properties of the cermets based on Ti(C, N)[J]. Int. J. Refract Met. Hard Mater., 2009,27:26−32. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2008.01.011 [9] Xiong J, Guo Z X, Shen B L, et al. The effect of WC, Mo2C, TaC content on the microstructure and properties of ultra-fine TiC 0.7 N 0.3 cermet[J]. Mater. Design., 2007,28(5):1689−1694. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2006.03.005 [10] Stewart T L, Plucknett K P. The effects of Mo2C additions on the microstructure and sliding wear of TiC0.3N0.7-Ni3Al cermets[J]. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2015,50:227−239. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2015.01.013 [11] Liu C, Lin N, He Y H. Influence of Mo2C and TaC additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti(C, N)-based cermets[J]. Ceram. Int., 2016,42(2):3569−3574. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.10.168 [12] Wan W C, Xiong J, Li Y H, et al. Erosion-corrosion behavior of Ti(C, N)-based cermets containing different secondary carbides[J]. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2017,66:180−187. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2017.03.018 [13] Shin S G, Lee J H. Effect of carbide additions on grain growth in TiC-Ni cermets[J]. Met. Mater. Int., 2006,12(1):57−62. doi: 10.1007/BF03027524 [14] Li Y, Hu J, Wang H, et al. Study of TiC/Ni3Al composites by laser ignited self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (LISHS)[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008,140(1-3):621−625. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2007.11.034 -




 下载:
下载: